A pediatric orthopedist will be able to tell you exactly why your child has splay feet. The following causes are usually responsible for this:
- O and X foot curvature
- Types of shin deformities:
- Types of leg curvatures
- Methods for determining the type of curvature
- Correction of incorrect curvature
- surgical intervention
- massage
- Straightening on the trainer
- mechanism of development
- Up to what age is a curvature normal?
- How does the pathology arise?
- symptoms
- Free foot correction: special offers on our website
- Promotions:
- Ratings and Comments (54)
- Blog (Foot Correction)
- Therapeutic gymnastics.
- Physiotherapy methods
- Possible causes of X-shaped feet
- Symptoms and diagnosis of leg curvature
- Variants of anomaly in a child
- What diseases cause X-shaped deformities?
- Massage for valgus in children
- Massage of x-shaped feet in children
- Also read:
O and X foot curvature

A lower leg curvature is caused by malformed bones and joints and/or soft tissues - muscles, subcutaneous fatty tissue. In our article we will look at curvatures that are related to the development of bones and joints, how they manifest themselves and how they can be corrected.
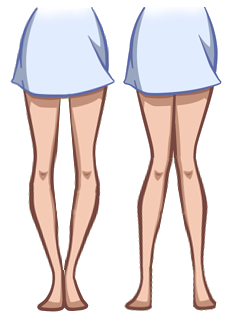
Types of shin deformities:
- O-shaped or varus. When the feet are close together, there is a space between the knees and the shape of the legs resembles the letter O.
- X-shaped or valgus. The knees are not close together, and the shape of the lower limbs resembles the letter X.
Unfortunately, the type of curvature is not always apparent from the shape of the lower limbs. Fat deposits on the thighs and knee joints obscure the external signs of deformity. The exact diagnosis is made only after the doctor examines the patient.
To determine the nature of the deformity, the orthopedist conducts an external examination, a clinical examination and the evaluation of X-rays of the lower limbs, including the knee joints, or orders a panoramic X-ray of the legs. Only then does the specialist make a judgment – a diagnosis – and choose the best correction method.
Types of leg curvatures
Variations in which the femur and shinbone have an arch shape. The cause of this disorder is usually a hereditary predisposition or a disease caused by a vitamin and mineral deficiency. To correct the situation, consultation with an orthopedist is required.
With incorrect curvature of the leg, the bone has a regular shape. The cause of the problem lies in abnormal development of muscle tissue. The knees and ankle touch, creating a curvature of the ankle. This condition can be corrected with a series of exercises.
This defect has the appearance of an oval because the condition begins at the hips and extends to the ankle joint. The knee joints do not come into contact with each other.
A defect in which the knees are together and the ankles do not come together. The legs look like the letter X.
Methods for determining the type of curvature
To determine the shape of the limbs and detect any anomalies, do the following
- Stand upright in front of a mirror and bend your leg:
- If the knee is displaced inward, this indicates an O-shaped deformity;
- If the kneecap is displaced outwards, this indicates an X-curve;
- Place your hands on your hips (feet shoulder-width apart) and do a squat:
- In a type O deformity – the legs are spread;
- Type X – the limbs are connected to each other;
- Normal form – flexion parallel to the feet.
To fully confirm or rule out the diagnosis, x-rays must be taken. The condition of the bones determines the nature and solution to the problem.
Correction of incorrect curvature
This deformation is not harmful to health and only has an aesthetic aspect. To correct this condition, it is necessary to exercise, lose excess weight and build muscle tissue. With proper practice, the cosmetic changes will gradually disappear. The exercises can be done at home or in gyms.
A true curvature is due to a bone defect in the leg and is sometimes difficult to correct with physical therapy.
surgical intervention
There are two types of operations:
A. Attaching an Ilizarov brace to the tibia.
The procedure is relatively quick and becomes noticeable after just 2 months. The operation can be performed from the age of 14. year of life. After the braces are removed, you should not bear any weight for several weeks. The technique is traditional and is used in most cases.
B. Plastic surgery – crossplasty.
Also read: Topography of the hip triangle
The procedure takes place under general anesthesia in the hospital. Rehabilitation lasts 2 months, the disadvantage is the displacement of the implant and distortion of the shape of the leg. Sports activities are prohibited.
massage
Massage sessions are important from birth to 3 years of age. Treatment only helps correct bowed legs in early childhood.
In adults, chiropractic treatments and lumbar spine exposures are used when the core of the defect is in the sacrum. It is not possible to completely eliminate the deformity because the formed bone tissue is difficult to deform.
Straightening on the trainer
mechanism of development
By the age of 2-3 years, the O-shape of the legs should have disappeared. At this age, a slight curvature of the lower limbs may remain. In the initial phase of varus curvature, the outer condyle of the femur is enlarged and the inner condyle is reduced in size. The gap between the joints changes. It narrows from the inside and enlarges from the outside. This puts pressure on the meniscus, stretches the ligaments on the outside of the joint, and causes the heels to tilt inward.

Over time, the disease progresses and the body develops a compensatory response in which the feet become deformed. In severe stages, the shinbone shifts inward and the femur shifts outward. This leads to loss of flexion in the knees, impaired gait and fatigue in the child. Due to the abnormal center of gravity, the load is incorrectly distributed, and the child's posture and curvature of the spine are disturbed.
Up to what age is a curvature normal?
A healthy child can have O-shaped legs in the first year of life. Until the ligaments and muscles that support the skeleton of the lower limbs have sufficiently strengthened. As a rule, the feet of a 1-year-old child are characterized by a slight curvature, which is a variant of the norm, as if the child had a club foot. By the age of 3 or 4, this should resolve and no treatment is needed.
If the problem persists after this age, a visit to the pediatrician and orthopedist is necessary. The pathology should be examined to avoid leg fatigue, pain and heaviness when walking. As a result, the child's ability to walk is limited, the skeleton is deformed, and excessive weight gain occurs. Parents should consult a doctor in the following cases:
Only an orthopedist can accurately say whether O-shaped feet are pathological.
How does the pathology arise?
When causative factors act on the child's body, the metabolic processes in the tissues of the lower limbs are disrupted. This causes the bones to gradually lose strength and the ligaments to become more easily stretchable.
The pathology is aggravated if the child learns to walk early - under the weight of the body, the legs gradually begin to bend, resulting in deformity. In the initial stages, the child experiences discomfort due to changes in his gait, which contributes to the aggravation of the curvature. If correction is not started in time, the condition will gradually progress, such as: B. X-shaped feet in children.
symptoms
X-shaped feet in children in neglected cases can be immediately recognized by the special shape of the limbs. Clinicians also distinguish pseudodeformities, in which the bone structure is not disturbed, but the shape of the muscles and subcutaneous tissue causes curvature. In the initial stages, symptoms are mild, but as the child begins to walk independently, some signs are immediately noticeable. This includes:
- Quick fatigue when walking – this shape of the legs is unnatural, the muscles have to work harder to contract than normal. All this leads to fatigue in the child, even during normal walking;
- Unstable gait – The disease gradually leads to overloading of the ligaments and instability of the knee joints. As a result, gait becomes more unsteady and unstable under the weight of the child's own body. In severe cases, subluxation of the knees and hips may occur;
- Curvature of the lower limbs – with age, as the child grows and the limbs straighten, the deformity becomes clearly visible;
- Cramps – with curvatures and gait abnormalities, hypertension and muscle fatigue occur, leading to cramps;
- Pain in the legs – occurs several years after the onset of the disease, when a permanent curvature develops, forcing the child to change his gait and physical activity.
Important!!!
If no correction is made, over time the child will develop foot deformity and curvature of the spine.
Over time, the normal gait is disrupted - the child begins to twist the foot so that the load is on the outer edge of the foot. While under normal conditions the load is distributed evenly across the entire foot, in this condition the support line shifts to the side. All this leads to bone deformities and the development of flat feet. Gradually, the ankles twist, and the redistribution of axial load leads to a posture disorder, which manifests itself as scoliosis or kyphosis of the spine.
Free foot correction: special offers on our website
Are you worried about how to get rid of a foot curvature, but even more so about the high cost of such a procedure? Is it possible to correct foot curvature free of charge? Our answer: Yes! Orthopedic operations to correct foot curvature in clinics in Moscow and St. Petersburg are now available to everyone.
Our project is specifically designed for people who dream of improving their appearance. Your task is to follow the suggestions and actively participate in the life of our resource. Register now, don't hesitate to ask questions and give advice to other users: your rating depends on how friendly and interesting you are. The higher it is, the more chances you have to win!
Promotions:
Ratings and Comments (54)
Only registered users can post comments. Please log in.
Natalia 11:05 Oct 18, 2020 Wow? Wonderful, I didn't know about such operations ❤️
Annaast 23:06 April 14, 2017 There are even promotions for such operations?
I had my curvature corrected a few years ago. The rehabilitation period is difficult, but worth it. I am very satisfied with the result! 1
Seema 12:01 13 Dec 2016 Hello everyone. I'm new here)))I dream of taking part in this operation, there. I have O-shaped legs, a complex since childhood, everyone around looks, can't go to the beach normally and can't wear skirts, and I would love to wear skirts as a woman ((((.
MarinaMalina 22:55 April 23, 2016 I have a friend who had surgery and had to wear Elizarov braces for 3 months. But the operation was paid for by the government).
Sayhopee 11:08 Jan 2 2021 How did the state pay for this?
Olga 00:41 Jan 30, 2016 I think it's a serious operation
Tyusha 13:49 Jan 3, 2016 Hello everyone. I dream of taking part in this operation because I have O-shaped legs, complex since childhood, would also increase the height by a few centimeters. Am willing to attend every meeting. If this operation is not expected in the coming year, please advise me on the price and suggest a good doctor. Thank you.
Summers 00:24 August 14, 2015 The second video is great, very positive girls)) I remembered after the operation, I also ran, jumped, also injured that no one gave way on the subway))))
Alina 19:26 November 20, 2014 Is it possible to apply if you do not have a curvature, but just need to lengthen your legs?
zuma 19:12 April 21, 2014 Hello, I'm new here :)) can you tell me if there are any stocks for this procedure?
Inspiration 17:20 6 December 2013 yes it's a good procedure) I had it done + extension
Blog (Foot Correction)
- Valgus deformation of the toe? My Opiration Author Post Farida Oct 23, 2021
- A year after my surgery.
 Flight normal.??? Author post Natalia??? 24 Jan 2020.
Flight normal.??? Author post Natalia??? 24 Jan 2020. - 7 months after my surgery at Makinian Levon Gagikovich.
 Emotions, impressions, feelings. Written by Natalia??? on August 6, 2019.
Emotions, impressions, feelings. Written by Natalia??? on August 6, 2019. - Surgical treatment of valgus toe misalignment – 'toe bones'. Author Entry Nina? on July 22, 2019.
- One month after surgery to correct a forefoot deformity.
 Recovery author of the entry Natalia??? March 24, 2019.
Recovery author of the entry Natalia??? March 24, 2019. - How I examined myself for the operation.
 Interesting information. Written by Natalia??? January 22, 2019.
Interesting information. Written by Natalia??? January 22, 2019. - Day 2.3 after surgery with Levon Gagikovic
 Conditions at home, rehabilitation. Written by Natalia??? January 20, 2019.
Conditions at home, rehabilitation. Written by Natalia??? January 20, 2019. - My forefoot deformity correction surgery by Dr. LG Makinian at the Galaxy Clinic.
 Part 2. Written by Natalia??? January 18, 2019.
Part 2. Written by Natalia??? January 18, 2019. - My forefoot deformity correction surgery by Dr. LG Makinian at Galaxy Clinic.
 Part 2. Written by Natalia??? on January 18, 2019.
Part 2. Written by Natalia??? on January 18, 2019. - My operation with the orthopedist and traumatologist Dr. Makinian Levon Gagikovic at the Galaxy Clinic
 Part one Natalia??? on January 18, 2019.
Part one Natalia??? on January 18, 2019.
Therapeutic gymnastics.
The gymnastic exercises are carried out after the massages. They are carried out under the guidance of a specialist. Once the child has mastered the correct movements, parents can do the exercises themselves at home. To correct the shape of the legs, exercises are chosen that increase muscle tone on the inside of the thigh and shin and reduce it on the outside.
The experts recommend the following as basic exercises:
- The lotus pose, which relaxes the outer thigh muscles. If the child cannot sit in this position, simply bring the feet together and bend and separate the knees;
- 'Bicycle', performed in the supine position. The child puts the legs up, keeping the lower back on the surface, and moves them in a series of movements that mimic cycling;
- Walk with the weight of your body on the outside of your foot. With each step, the child rolls to the side and rocks from side to side;
- heel and toe walking;
- Walking on a flat line, curb, or other object places the feet in close positioning and strains the muscles on the inside of the legs.
The doctor selects exercises for therapeutic training. Otherwise, the condition can lead to flat feet and other complications.
Physiotherapy is a supplement to therapy. Children with leg curvature should do this daily. Heavy exercises that cause muscle pain should be avoided. This poses the risk of the child being abandoned or having negative consequences for the musculoskeletal system.
Physiotherapy methods
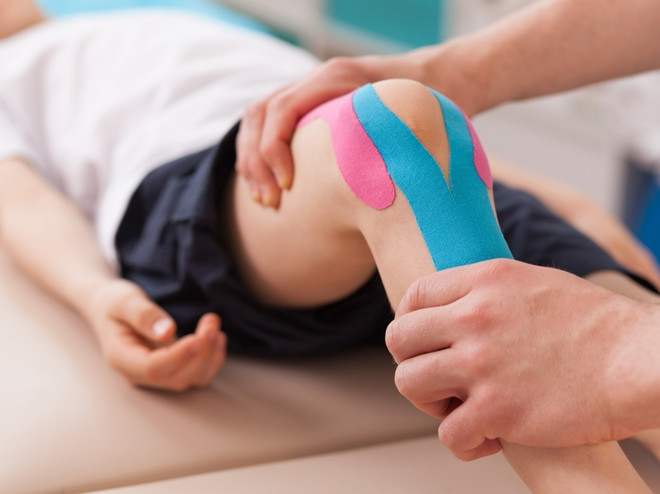
Exposure of the knee joint tissue to magnetic and electromagnetic fields helps prevent disease progression. Physiotherapy improves blood circulation and prevents the development of inflammatory changes in the knee. Electrical stimulation of the muscle groups on the inside of the thigh and shin increases their tension and aligns the bone structures in the knee joint.
In addition to the above methods, taping and nutritional supplementation with foods rich in calcium, phosphorus, protein and vitamins are used to correct leg curvature. During treatment, children must limit walking and other physical activities.
If the knee joint is severely deformed, an operation is performed. The goal of the operation is to restore normal bone alignment by removing the deformed tissue.
The X-shaped curvature in childhood has a favorable prognosis. Adequate early conservative treatment restores the shape of the knee joint and prevents progression of the pathology. If parents do not seek medical attention or self-medicate in time, the child is more likely to develop arthritis, non-infectious arthritis, flat feet and other orthopedic diseases.
Possible causes of X-shaped feet
X-shaped feet can be physiological or pathological. The first case concerns children between the ages of 3 and 5 years. During this period of lower limb development, approximately 85 % of children have a mild X-shaped leg deformity. By school age, this deformity should have completely disappeared naturally through the building and strengthening of the muscular skeleton.
In adults, this deviation can be between 5° and 8°; in women after birth, a valgus deviation of up to 10° - 12° can persist for up to 3-4 years. Greater angles of inclination are considered abnormal and lead to a misalignment of the tibial condyles in the joint capsule. This has a detrimental effect on the meniscus and the cartilage-synovial layer.
In patients with valgus torsion, knee joint deformities can develop as early as 20 to 25 years of age. Until the age of 35, this leads to persistent, chronic pain and the development of grade 3 gonarthrosis. Therefore, the condition of the lower limbs should be carefully monitored.
For active prevention, all risk factors and potential causes for the development of leg deformity X must be eliminated. Below we will mention only the main types of negative influences that can provoke this pathology:
- Congenital anomalies in the development of the bones and cartilages of the lower limbs (as a rule, the first signs of this appear in the first year of the child's life);
- Early positioning of the child when the muscular and ligamentous apparatus is weak, the condyles of the tibia and femur are displaced, and the foot is misaligned;
- Widening of the foot when standing and walking;
- Inappropriate footwear for constant wear and sports activities (this problem often occurs among teenagers who do not want to wear comfortable shoes for fashion reasons);
- Excessive body weight, since each additional kilogram places a significant load on all the bones of the lower limbs, they gradually slip and thus a compensatory load distribution occurs;
- Asthenic physique with poorly developed tendons and ligaments;
- Dystrophy and muscular atrophy of the lower limbs (can be caused by a sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work, or impaired innervation and blood supply);
- metabolic diseases such as angiopathy and diabetic nephropathy;
- Alcohol consumption and smoking also cause toxic and vasomotor damage to the muscles of the lower limbs and progressive deformity of the legs;
- Peculiarities of the female pelvis can cause misalignment of the legs; in girls, this pathology begins to manifest itself at early school age;
- Calcium and phosphorus deficiencies, which can be caused by nutritional disorders, bowel dysfunction, or vitamin D deficiency;
- kidney disease, in which there is an increased excretion of calcium and phosphorus salts;
- Rickets before the age of 3 years
- poor heredity (if the parents suffer from valgus deformities of the lower limbs, there is a high probability that the child will be affected by the same condition)
- Anomalies in the ossification process of the outer border of the femoral or tibial condyle;
- valgus deformity (primary or secondary) of the femoral neck;
- Traumatic consequences (usually intra-articular fractures, tears of the ligament and tendon apparatus of the knee joint with subsequent scar deformation);
- Tumors of the musculoskeletal system in the area of the knee or ankle joint.
Symptoms and diagnosis of leg curvature
X-shaped legs are often visible to the naked eye. However, in the initial stages, it is worth paying close attention to the specific symptoms of knock knees, which can manifest themselves as follows
- increased fatigue of the lower leg muscles during usual physical activity;
- Pain in the legs that occurs after standing for a long time
- cramps in the calf muscles;
- impairment of gait, feeling of instability;
- Loss of muscle tone in the legs.
An X-shaped curvature of the legs is visible to the naked eye if the degree of deviation is significant. However, to make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to visit an orthopedist. The doctor will conduct a comprehensive examination, during which not only the extent of the deformity will be determined, but also its possible cause.
Anatomical changes in the knee joints and spine lead to secondary clinical symptoms. Tension of the medial collateral ligaments leads to instability of the joint in lateral projection. Hyperextension can result in fractures and fractures of the tibial and femoral condyles. This then leads to deformative thickenings in the form of bone protrusions and nodules.
Flat feet are another characteristic feature of X-shaped foot deformities in children and adults. Severe flat feet causes persistent foot pain, contractures of the arch muscles, etc.
When walking, the trunk leans to one side or the other, which leads to the development of scoliosis, destruction and twisting of the pelvic bones, and deformation of the hip joints. With unilateral deformation of the limbs, significant swelling is observed.
Diagnosis begins with a comprehensive examination by an orthopedist. He determines the degree of deformity and the possible negative consequences of this pathology. This is followed by an X-ray examination in several projections. With their help, the degree of deformity and the presence of secondary pathological changes can be determined.
Variants of anomaly in a child
A leg curvature in a child is a deviation from the conventionally defined line inwards or outwards. In addition to a clear cosmetic defect, various curvatures of the limbs significantly affect the normal functioning of the child's limbs and body.
There are two main types of curvature:
- Valgus or so-called 'X-shaped' leg deformities, in which the child's knees bend inwards;
- Varus, also known as 'O-shaped' leg deformities. The child has too large a gap between the shin and knee.
What diseases cause X-shaped deformities?

Valgus or X-shaped lower leg deformities are more common on both sides. It is characterized by the center of the lower leg shifting inward, causing the knees to bend and the legs to begin to resemble the letter X'. This happens some time after the child begins to actively walk. Sometimes these deformities are the result of a hereditary or congenital disease, but most often they are acquired in the first years of life. The curvature of the legs is associated with diseases of the bone tissue itself - this is called osteogenesis imperfecta (abnormal development of the bone structure), a metabolic disorder. It can also be caused by metabolic diseases and mineral disorders - calcium and magnesium in rickets, endocrine pathology (parathyroid disorders), osteomyelitis and some others. As a rule, these diseases are diagnosed in the first two years of life. Very rarely, the disorders develop during the period of intensive growth in adolescents, with significant vitamin and calcium deficiencies in the diet, lack of walks and fresh air.
In addition, leg curvature is sometimes a consequence of problems in the hip and knee joints - with arthrosis. Some children have problems because of the overzealousness of their parents in trying to get up and walk toddlers whose skeletons and ligaments are not ready for the strain.
Massage for valgus in children
The first thing parents should pay attention to is the child's gait and any complaints the child may have about tiredness or leg pain. Determine the presence of X-shaped leg deformity Place the child on a firm surface, back to back, legs together and facing straight ahead (do not turn the body). Pay attention to the child's lower legs. Normally the knee joints should touch and the inner ankles should meet. With an X-shaped knee joint misalignment (valgus), the inner ankles do not touch and the knee joints touch each other.
The distance between the inner ankles when the knees touch while standing is considered pathological:
What should I do? How dangerous is this condition? Will it go away on its own? Parents usually ask themselves these questions.
The answers are fine. The X-shaped deformity can and should be treated, and this is the most effective treatment. is a massage for X-shaped deformities the lower limbs as well Exercises for X-shaped deformities. Treatment must be comprehensive, with massage, gymnastics, and in severe cases, special footwear and positioning therapy.
The massage should start with the back, as all nerve endings in the muscles originate from the spinal cord. The lumbosacral area of the back is massaged thoroughly. The legs are massaged diffusely, that is, a stimulating massage on the inside of the upper and lower leg muscles and a relaxing massage on the outside of the same areas. Stimulation of the inner thigh and lower leg muscles aims to encourage the child to place the leg closer to the midline when walking, rather than to the side, as may occur in children who are beginning to walk, which contributes to development one X-shaped deformity (valgus) Lower limbs. The knee joints themselves are also massaged, carefully working on the outer edges of the thigh bones to stimulate the growth of these parts of the knee joint.
Massage of x-shaped feet in children
The danger of this deformity is that the elastic function of the lower limbs is disturbed, which leads to wear and tear on the articular surfaces of not only the legs, but also the spine, abnormal distribution of weight among the various parts of the musculoskeletal system, and, as a result, poor Posture, scoliosis and very often to one X-shaped curvature The X-shaped curvature of the knee joints is often associated with flat feet.
Uncorrected and progressive lateral deviations in the knee area contribute to the development of deforming arthritis, so more active methods of correcting them are advisable. Children of preschool and school age suffer from pain, tire quickly and are unable to play sports or dance due to severe knee joint deformity.
The massage therapists at Happy Baby Massage Center can help your child grow up healthy.
Also read:
If you found this article interesting, please share it on social media, maybe someone else will find it useful. Moms always have a lot of questions, let us help them find the answers!
Read more:- Orthopedist who treats children and with what.
- Paid pediatric orthopedist.
- How to correct a clubfoot in a child.
- A child begins to have clubfoot between the ages of 1 and 5.
- What does an orthopedist examine?.
- How a child's feet grow at the age of one.
- What does the pediatric orthopedist treat?.
- How do you correct clubfoot in an adult?.
