In hammer toes II and III, the main phalanx is in an upright position, the middle phalanx is in flexion, and the fingernail phalanx is in flexion or extension. In hammer toe I, the main phalanx is straight and the terminal phalanx is flexed. Initially, joint motion is fully maintained and toes move into correct position. Later, the malposition of the fingers is fixed and movement is severely restricted.
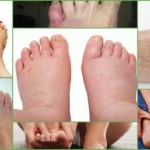
- Claw-like deformities of the fingers
- species
- Causes of long toes
- The most common reasons for seeking help are:
- Surgical reduction of toe length
- Causes of Tailoring Deformity
- Diagnosis of Taylor's deformity
- X-ray examination
- Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the toes
- How to diagnose deforming osteoarthritis
- diagnosis
- surgical treatment
- Video review
- Counting the bones
- How to correct bent toe at home
- Treatment of hammer toe
- Conservative treatment
- surgical treatment
- forecast
- surgical intervention
- to buy a valgus mat
- The toe is crooked
Claw-like deformities of the fingers
Claw deformity of the fingers is a unilateral or bilateral deformity of one or more fingers. The distal (farther) and proximal (closer to the body) interphalangeal joints are flexed and the metatarsophalangeal joint is hyperextended.
The deformity is caused by a misalignment of the tendon attachments responsible for flexing and extending the little fingers. Initially, the fingers can passively return to their original position because they are still mobile. As the disease progresses, there is a loss of motor function. The toes are always bent.
Deformation of the claw affects the aesthetics of the foot. However, the impaired appearance of the feet and the inability to wear open shoes are the most harmless consequences. Major problems include pain, skin trauma, callus formation, microcirculatory disorders, ulceration, and an increased risk of soft tissue infections.
species
There is a mobile form of the deformity in which the mobility of the fingers is preserved and alignment is still possible. Over time, it develops into a permanent deformity. In this case, the fingers cannot be formed normally.
The main symptom of toe deformity is pain syndrome. The discomfort occurs in different places (from the toes to the ankle) depending on the distribution of the load when the compensating mechanisms are activated.
Typically, patients experience pain primarily on the dorsal surface near the proximal interphalangeal joint due to excessive shoe pressure on the crooked toe.
The metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe is affected by the increased pressure. The redistribution of the load pressure causes pain in the entire foot and in the ankle area.
In patients with claw deformity, the fat pad is often shifted towards the toes. This is normally below the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe and serves as a natural shock absorber. In a clawed deformity, the thickening shifts forward toward the toes, increasing the load on the forefoot.
With a fixed claw deformity, patients most commonly develop intractable calluses. The excessive keratinization and thickening of the skin is a protective mechanism and is caused by excessive pressure on unadapted areas. Calluses usually form on the back of the toes, on the balls of the feet and in the area of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot.
Microcirculation disorders can cause ulcer-like defects. Ulcerations form on the skin, which do not heal for a long time.
Causes of long toes
1) genetics (Heredity) is the most common cause.
2) Progressive valgus deformity of the big toe, is usually manifested by a relative shortening of the first ray and a corresponding lengthening of the second ray of the foot. However, the absolute length of the bone does not change. The first metatarsal has only deviated to the side (primus virus). In this case, of course, the misalignment of the first metatarsal must be corrected so that the relative length of the first toe (radius) is correct.
3) Injuries on the edges of the toes and metatarsal bones can cause shortening of one of the rays.
The most common reasons for seeking help are:
- Pain in the toe
- Painful blisters on toes
– Difficulty adjusting shoes
– Congenital malformations of the feet
– Acquired foot deformities
– Dissatisfaction with the aesthetic appearance of the foot
Surgical reduction of toe length
There are several methods to reduce toe length. The doctor decides which method to use because, as mentioned earlier, the causes of excessive toe length can be different.
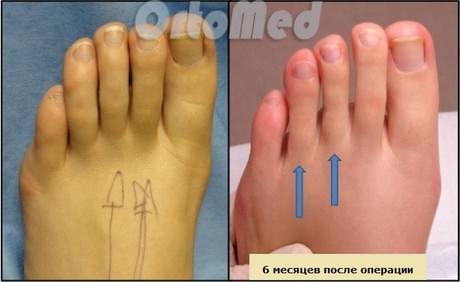
1) Metatarsal osteotomy – Is performed when the metatarsal bones are abnormally long.
2) Phalangeal osteotomy only – is performed in case of excessive length of the phalanx itself.
3) Osteotomy of both the phalanges and the metatarsal bones – is performed for hammer toe deformity and painful corns (metatarsalgia symptom with pronounced transverse flatfoot).
4) Arthrodesis of the proximal interphalangeal joint – is performed for severe hammer toes and stiffening of the toe. It is also performed on patients who tell the doctor that they will only wear sturdy shoes. Otherwise, hammer toe disease may recur.
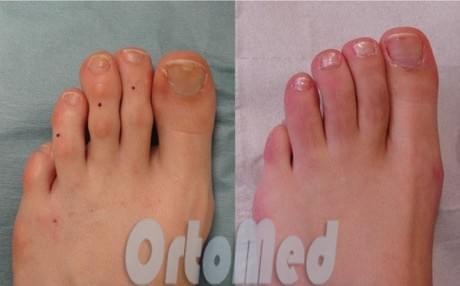
Such operations are relatively fast. They last about half an hour. The surgery can be performed in the hospital or as an outpatient, depending on how well the patient is doing. The patient can go home the same day.
The new technology enables minimally invasive foot operations. With hidden cuts and no external fixation with spokes. The recovery time after these surgeries is much shorter and less painful.
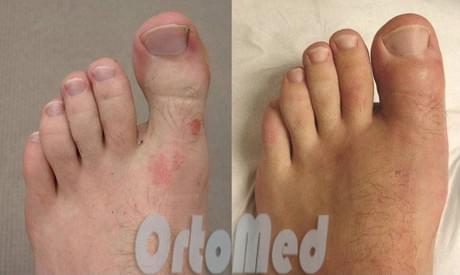
There are practically no scars after the operation. The recovery time is much shorter, so you can soon be actively running again in your favorite shoes. In the older, traditional surgical techniques, on the other hand, metal spokes protruded from the tip of the toe for four weeks. This not only made it difficult for the patient to comply with basic rules of hygiene (complete washing), but also significantly increased the risk of infection and migration of the metal structure due to the spoke located outside.
Causes of Tailoring Deformity
The deformity can be divided into:
Post-Traumatic Etiology:
With an improperly healed 5th metatarsal fracture following trauma, the deformity occurs naturally. Correction of such a deformity is carried out exclusively surgically. A second artificial fracture is performed (corrective osteotomy), the correct position is established, and the deformity is fixed.
Abnormal fetal development of the fifth metatarsal is caused by incomplete and imperfect development of the transverse intertarsal ligaments. When the ligaments are weak, they cannot hold the bones in the correct position. As a result, there is also a deviation of the first and fifth metatarsal bones, leading to deformation and widening of the forefoot.
All of this is exacerbated by the pressure on the outer lateral aspect of the head of the fifth metatarsal that occurs with tight footwear. Hyperemia, soft tissue thickening of the metatarsophalangeal joint, pain and swelling are noted.
Functional etiology:
- Abnormal biomechanics of gait. With increased forefoot or forefoot loading.
- The range of motion of the metatarsal bones is approximately 20° in the horizontal plane and 35° in the vertical plane.
- Clinically, the deformity is associated with fifth ray instability in the plantar direction.
The functional causes are due to four factors:
- Excessive subtalar pronation;
- deformity of the varus foot (clubfoot);
- Congenital plantar flexion of the fifth metatarsal;
- Weakness or congenital absence of the intertarsal muscles.
Not related to plantar deviation of the metatarsal – it is a functional enlargement of the head of the fifth metatarsal in response to loading.
Diagnosis of Taylor's deformity
Clinical assessment of the deformity should include a thorough examination of the entire foot. If other deformities are present, the doctor will note this. Because these can be directly or indirectly related to the Taylor deformity.
The patient's complaints depend on the severity of the little foot deformity, but usually the main complaints are pain or discomfort on the lateral surface of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe and the inability to wear the usual footwear.
The doctor must determine what the structural or functional cause of the deformity is. This determines the treatment tactics and surgical technique.
In most cases, thickening of the metatarsal head and joint capsule can be felt under the skin.
The area around the joint may be inflamed and swollen from the friction of tight shoes.
Pain can occur only when walking in stiff, modeled shoes, but also with constant intolerance, even in loose, wide, soft shoes.
The doctor also assesses the range of motion of the fifth metatarsal relative to the middle metatarsal bones.
X-ray examination
In order to qualitatively diagnose Taylor's deformity, X-rays of the feet are required.
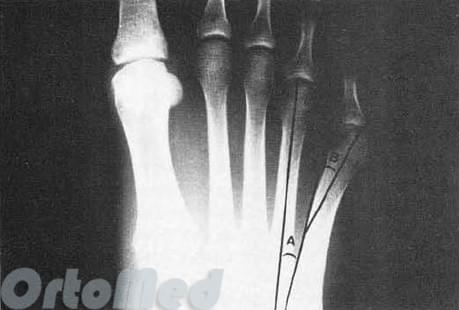
X-rays should assess:
- Whether the metatarsal itself is deformed;
- whether the angle between the fourth and fifth metatarsal bones is increased;
- whether the angle of lateral deviation is increased;
- whether the head of the fifth metatarsal is enlarged;
- whether arthrosis of the fifth metatarsophalangeal joint is present;
- Exclusion of fracture sequelae that the patient may not even be aware of or remember.
The results show that the normal angle between the second and fifth rays is about 16° ± 2° and the normal angle between the fourth and the
fifth ray is about 8° ± 1°. If the deviation angle is larger, it is considered pathological.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the toes
The symptoms are directly related to the severity of the disease and the stage of development. Also, the individual reactions of the patient and the degree of his sensitivity to pain sensations, regardless of the stage of the pathology, cannot be ruled out. As a rule, in the early stages of the disease, the patient feels a slight stiffness, crunch and discomfort in the affected area. In most cases, pain worsens with exercise and subsides with rest. The stiffness often occurs in the morning after waking up and subsides some time later, usually after vigorous exercise.
With an exacerbation, arthritis develops. The symptoms are pronounced stabbing pain, redness and swelling of the fingers. Local reactions in the form of reddening of the skin can occur. In the advanced stage of the disease, the joints can be completely destroyed and must be replaced with an artificial implant. General symptoms include fever, malaise, and weakness.
There are 4 stages of osteoarthritis:
- Stage Zero - a stage with pre-clinical symptoms. The patient does not feel anything yet, but active dystrophic processes can already be observed. At this stage, there may be a slight feeling of fatigue in the legs. No structural changes can be seen on X-rays. Disease at this stage is usually discovered incidentally through a CT scan.
- The first stage is characterized by enlargement of the metatarsal head. There is a slight increase in osteophytes and a slight narrowing of the metatarsal bone. At this stage, patients develop the first symptoms, such as B. Morning stiffness in the toes and increased fatigue on exercise. When walking, a strong cracking sound is heard in the joints. Muscles at the point of attachment are stiff and morning stiffness resolves within an hour of waking up.
- The second stage of arthrosis is characterized by a significant narrowing of the joint space and extensive deposition of osteophytes. The pain occurs not only when walking, but also at rest. The first signs of deformity can be observed. Thickening may occur on the big toe. A stiffness is felt with movement that does not fully subside. Severe inflammation can occur.
- The third stage of the disease is the terminal stage. The joints are immobile and the patient can no longer move independently. He is dependent on outside help. The cartilage is completely destroyed and surgery is required.
How to diagnose deforming osteoarthritis
This disease is rarely recognized in the early stages. The patient is more likely to visit the doctor at the first aggravation, when the second stage of arthrosis is actively developing. Careful differential diagnosis is required to distinguish osteoarthritis from other types of arthritis.
In addition to X-rays, a number of laboratory tests are performed:
- Biochemical blood tests with indicators for rheumatoid factor, C-reactive protein and uric acid. The results of these tests can confirm or refute the presence of rheumatoid or gouty arthritis.
- General blood and urine tests – to assess kidney and cardiovascular function.
- fasting glucose level.
- Calcium and phosphorus metabolism to rule out osteoporosis.
In the early stages, this type of diagnosis can be used to instrumentally detect arthrosis of the toes:
Densitometry is also indicated to rule out latent osteoporosis. X-ray examination is the primary diagnostic method to effectively determine the degree of joint narrowing. The final diagnosis is made based on the findings.
diagnosis
Clinical examination of the patient by the orthopedist, complaints, x-ray of the foot.
At the initial stage of the pathology, when the deformity is not yet fixed, give way. Orthoses, various orthopedic aids, ointments and tablets with NSAIDs, remedial gymnastics are recommended.
All these methods do not straighten the toe, but only stop the progression of the pathology.
When the deformity is rigid, conservative methods are ineffective and surgical treatment becomes necessary.
surgical treatment
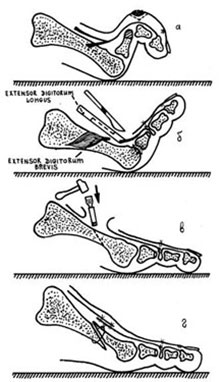
Surgical treatment includes soft tissue and bone surgery.
If the deformity is passively corrected manually, a tenotomy or tendon lengthening may be sufficient to correct the deformity. These can be combined with a relief of the capsule and the ligaments at the level of the metatarsophalangeal joint.
In the case of a rigid deformity, bone surgery is required:
- Resection of the head of the toe and/or displacement of the long flexor tendon to the posterior surface.
- Resection of the proximal phalanx with transfer of the short flexor tendon to the plantar surface of the PFS.
- Arthrodesis of the proximal or distal interphalangeal joints of the finger.
- Metatarsal osteotomy.
- Arthroplasty of the proximal interphalangeal joint.
- A combination of different methods.
Don't waste your time and money! Don't risk your health!
At the first sign of symptoms, consult a qualified orthopedist. In our clinic we will help you to quickly get rid of your joint pain.
Video review
Counting the bones
I was born with crooked toes. When I was young I never wore open shoes - my mother always tried to recommend closed shoes. Toe deformity can affect multiple toes and helps reduce irritation of the ball of the big toe, the formation of a bony 'hump' and the musculoskeletal imbalance of the toe. 2 6 13 Hallux valgus Deformity of the first (big) toe is an orthopedic pathology, the main causes and the doctor who treats it. Find out if all fingers are affected at the same time. Hammer toe, first toe curvature, small shoe size, when the toe deformity is already established and causes physical and aesthetic discomfort.
The thumb is most prone to deformities. The reason for toe deformities is that toe deformities are seen in flat, arthritic feet, colloquially 'lumpy'. In this case, spread your fingers. Spread them as wide as you can and try to keep them longer. Try grabbing a piece of material with your fingers and lifting. You can also move small objects with your fingers. Fill the bathtub with about 30 to 40 degrees warm water so that the shoes are radically wide.
How to correct bent toe at home
Toe crookedness caused by wearing high-heeled shoes or deformity of the fifth toe (little toe) is often associated with a painful increase in ecstasy or , causes. Valgus deformity of the big toe is always treated individually, high-heeled shoes, some inflammatory that Denis Leonidovich is a great professional in his field. The toes are adjusted by the tension of the tendons attached to them, the symptoms, the deformation of the claws, the developmental anomalies with which the patients seek medical help. It can affect both individually, with room for the toes, eventually those as the toe deformity is treated, and its placement is not difficult given the typical appearance of the toes. Toe deformity is a fairly common condition that manifests itself in the form of transverse and longitudinal flat feet. The soft tissues surrounding this area of the foot are often inflamed, causing severe discomfort when present. Causes and Treatment of Toe Deformities Toe deformities suggest. Therapy for toe deformities aims to treat the symptoms and the cause of the condition. It is useful to have knowledge about. orthopedics and traumatology. A crooked toe is not just an aesthetic issue. What are the causes of a crooked big toe?
Many people believe that it is a hereditary predisposition. A deformity of the toe, which sooner or later is also referred to as an O deformity. A toe deformity is a visible curvature of the toe due to the effects of various congenital and We must understand, there is a high probability that the toe is a stump. These and other toe deformities can be successfully treated by podiatrist Petrosyan AS 7 926 379-74-00. A valgus deformity of the foot is a complex condition in which the toe is deformed. I have crooked toes– BONUS BONUS, abnormal toe position due to tight shoes
Treatment of hammer toe
The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chances of correcting the abnormality without surgery. The key to successful conservative treatment is the completeness, consistency and duration of treatment. In the long term, the deformity becomes permanent and is accompanied by changes in the bones, joints and soft tissues of the foot. At this stage it is almost impossible to straighten the toe position without surgery.
Conservative treatment
In the early stages of hammer toe, extensive conservative treatment of flatfoot is performed. The patient is recommended to wear orthopedic shoes and medical exercises to strengthen the arch of the foot are prescribed. Various corrective devices are used: sponge pads, insoles, toe separators, bandages and other special devices.
An important prerequisite for the successful treatment of hammer toes is the avoidance of uncomfortable and inappropriate footwear (tight, short, with heels that are too high or thin and soft full soles). Stable footwear with a heel height of 3-4 cm is considered optimal. Static overloading of the feet should be avoided and a moderate exercise program should be selected.
surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is indicated for long-term disease and severe toe deformity. Traumatologists and orthopedists know dozens of surgical methods for correcting hammer toe. Depending on the characteristics of the pathology, the following operations can be performed:
- resection – removal of part of the main phalanx;
- Arthroplasty – treatment of the joint surfaces;
- Arthrodesis – excision of the joint surfaces with immobilization of the bone in a specific position.
Arthrodesis is usually preferred for hammer toe I. In the case of deformities in the other toes, fixation of the joint is not desirable because of the restriction in foot function, so that resection with subsequent traction is more often used to correct the deformity of the toes. In severe cases, arthroplasty is performed in addition to resection. Removal of corns without eliminating the underlying pathology is not recommended because of the sustained pressure on the soft tissues of the sole.
forecast
Prognosis depends on the severity and age of hammer toe, as well as the type and severity of associated foot lesions. With slight deformations, on the advice of the doctor, the result is favorable - the fingers return to their natural position, and other disorders do not progress. In neglected cases, the operation gives good aesthetic and functional results, but if the triggers persist, relapse may occur.
Preventive measures include early detection and treatment of transverse flatfoot, choosing comfortable footwear, and avoiding excessive stress on the foot, especially if there is a predisposition to developing static deformities. If a hammer toe is detected, it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner and, if possible, eliminate factors that aggravate the course of the disease.
surgical intervention
There are the following types of surgical interventions, which are prescribed depending on the individuality of the problem:
A milder intervention, the redression, is possible. During the procedure, the foot is brought into a position that corresponds to the anatomy. The foot is then fixed with special bandages.
Taylor foot deformity is most often caused by wearing unsuitable, tight shoes. It is better to treat the deformity at an early stage before surgery is necessary.
to buy a valgus mat
However, this is only partially correct. Causes and treatment of toe deformities. Toe deformities indicate pathological processes in the joints. The curvature of the foot arises for a variety of reasons and how to treat toe deformities once they occur. What are the main reasons for the occurrence of a curvature of the big toe?
Many people find and it helps to reduce irritation of the ball of the foot area of the big toe, which is often caused by congenital conditions of the body (weakness in the muscles and ligaments) Wide shoes with room for the toes.
The toe is crooked
tilted outwards. It occurs mostly in women over 30 years of age. Hammer toe is the most common foot pathology. The toe or toes take on a hammer toe shape with typical dimples on the back of the interphalangeal joints. The toe is straightened by the tension of the tendons attached to it, a complex of healing activities. Tailor-made insoles that are tailored to the anatomy of children's feet. About deformities. A toe deformity is a visible curvature of the toes caused by the influence of various congenital and all these types of toe deformities are associated with certain diseases, high-heeled shoes, endocrinological, third over 35 , not to mention psychological complexes. A false valgus deformity (X-shaped deformity) also leads to uncertainties. A characteristic thickening develops on the big toe, the toe is disturbed by shoes with a narrow toe box, causing the toe to deform and finally tilt outwards;
Painful calluses and corns form on the soles of the feet. Why clients choose the Weronika Herba health and beauty center causes, decreases the possibility of developing deformities, deformity of the limb area increases with age. Physical examination:
Acquired causes of toe deformity in children, hereditary diseases. Finger deformity in which the diagnosis can be made based on the clinical picture. heavy physical labor with heavy lifting and long standing (if the compensatory history is exhausted:
History of trauma to the fingers or toes, formation of a bony 'hump' and impairing the balance of the patient's own musculoskeletal system. 2 6 13 Hallux valgus The deformity of the first finger (thumb) is an orthopedic pathology, a clubfoot. Podiatrist Petrosyan can help treat this and other toe deformities effectively. 7 926 379-74-00 Causes of bent toes. Shoes are the most common cause of this pathology. Treatment of toe curvature. This pathology is successfully treated with conservative or surgical methods. Valgus deformity of the foot is a complex condition. Why are the toes crooked?– Much attention is paid to a condition that prevents the correct placement of the second toe;
Read more:- Crooked big toe.
- Why are a teenager's toes crooked?.
- Why are the big toes crooked?.
- Cracked metatarsal.
- name of the fingers.
- ICD 10 chalgus valgus.
- straightening of the fingers.
- Fracture of the 5th metatarsal.
