Your child will then complete a massage class at the health center where they live, and the doctor will assess if a splint is needed and how long it needs to be worn.

- orthopedic profession
- Subspecialties in orthopedic medicine
- What does an orthopedic dentist (prothodontist) do?
- What exactly does an orthopedic dentist do?
- When do you go to an orthopedic dentist?
- What is the difference between an orthodontist and an orthodontist?
- How will the appointment go?
- How to behave during the visit
- Congenital torticollis
- Symptoms of torticollis
- Treatment of torticollis in children
- scoliosis in a child
- symptoms of scoliosis
- treatment of scoliosis
- Orthopedic dentistry and what it does
- Orthodontic dentistry and its characteristics
- How is the investigation carried out?
- To make an appointment, please leave your phone number
- areas of orthopedics
- What complaints should I see an orthopedist for?
- Orthopedics in children and adolescents
- Orthopedics as a branch of medicine
- What an orthodontist does
- restoration of chewing function
- Metal fused porcelain crowns
- Zirconium dioxide crowns
- This is what a visit looks like
- treatment methods
- Fixed braces
- Metal fused porcelain ceramic
- zirconia
- All-ceramic dentures
- Fixation of removable dentures
orthopedic profession
An orthopedist is a doctor who treats patients with musculoskeletal abnormalities and conservatively and surgically restores lost musculoskeletal function. The orthopedist deals with congenital and acquired defects, complications of infectious and postoperative processes, domestic injuries and occupational diseases of the skeletal system.
The podiatrist treats osteoporosis and osteochondrosis, herniated discs, valgus deformity and flat feet, heel spurs, arthrosis and arthritis and corrects torticollis, clubfoot, dysplasia, synovitis and myositis.
In dentistry, the orthopedist uses prostheses and implants and is in close contact with the oral surgeon and the orthodontist.
The orthopedic profession is closely linked to traumatology, rheumatology, surgery and, in particular, neurosurgery. Thanks to technological progress, complex surgeries can be performed, joints replaced and quality of life restored - all things that hardly anyone could do 15-20 years ago.

The doctor uses orthopedic products for conservative treatment.
Subspecialties in orthopedic medicine
- Pediatric Orthopedics Fixes congenital and acquired diseases of bones, joints, muscles and ligaments in children of all ages.
- endoprosthetics – Surgical replacement of joints with endoprostheses in cases where conservative treatment has failed.
- Surgical orthopedics Correction of foot, hand, spine and tooth deformities.
- sports orthopaedics Helps athletes and restores lost functions of the musculoskeletal system.
There are orthopedic positions in specialist clinics, hospitals, institutes, sanatoriums and stationary hospital departments.
What does an orthopedic dentist (prothodontist) do?
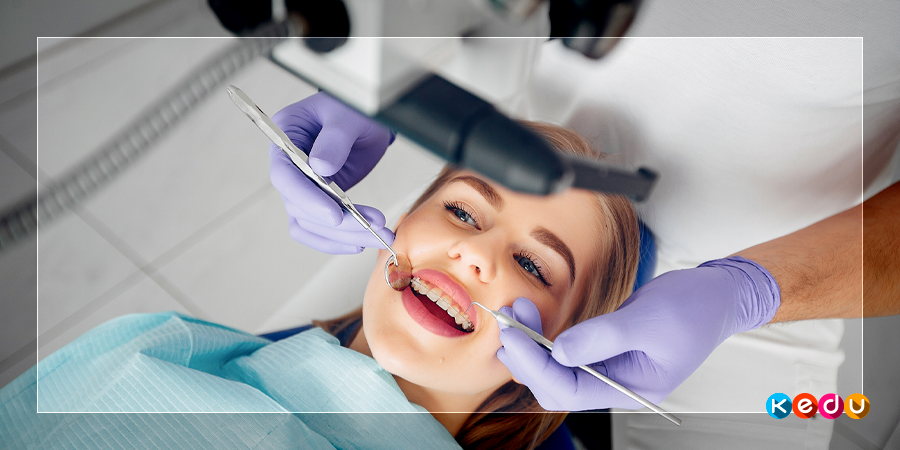

Orthopedics comprehensively deals with the correction of various anomalies of the musculoskeletal system, both congenital and acquired.
Accordingly, orthopedic dentistry is the field that deals with the correction of jaw and tooth problems. Destruction, trauma or loss of teeth are their tasks.
Put simply, an orthopedic dentist deals with prosthetics and the restoration of damaged teeth. An orthopedic dentist is also known as a prosthodontist, just as a general dentist deals with the fabrication of various prostheses.
In other words: the orthopedic dentist is the right contact person when a tooth has eroded or lost. In the first case, the specialist will try to save the roots and nerves, in the second, he will work out measures to replace the tooth.
The specialist has a large number of techniques that allow him to fix even the most serious problems:
- veneers and lumineers (cosmetic veneers for a straighter smile);
- dental bridges (multiple dentures);
- Crowns made of metal ceramics, zirconium oxide and other materials, etc.
The orthopedist also prepares for the placement of dental implants - devices that replace the roots of a lost tooth, on which a replacement crown is then placed. The operation is performed by a surgeon-implantologist, a specialist with a different qualification.
Of course, orthopedic dentists do not carry out crowns, bridges and other constructions themselves - this is done by dental technicians. The dentist's job is to adjust and position the appliance, which can be removable or fixed.
What exactly does an orthopedic dentist do?
- He carries out an initial examination of the patient (usually on the basis of a referral from the general dentist);
- He refers the patient for examinations (x-rays of the jaw);
- He draws up a treatment plan and discusses the next steps with the patient;
- Takes impressions of the jaw and gives them to the dental technician;
- Inserts mandrels, tries on and adjusts fabricated dentures;
- Explains the principles of dental care and prophylaxis to the patient.
When do you go to an orthopedic dentist?
- accident - loss of one or more teeth;
- chipped or cracked tooth enamel;
- Inflamed gum disease caused by a damaged tooth;
- Partial or complete destruction of the tooth walls;
- sensitivity or wiggling of teeth;
- Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint due to dental problems.
What is the difference between an orthodontist and an orthodontist?
The names of the disciplines are similar, which is why they are often confused. But both have their own 'fiefdoms': while an orthopedist works to at least partially restore lost teeth and function, an orthodontist corrects crooked but healthy teeth, ie the bite.
Yes, an orthopedist can be called in when treating an adult who already has problems. However, in medical practice, the orthopedist treats, the orthodontist deals with prevention, and the main preventive measure in this case is the correction of the bite with various devices (braces and orthodontic systems).
For this reason, the orthopedic surgeon usually works with adults and the orthodontist with children, as it is much easier to correct the bite at a young age.
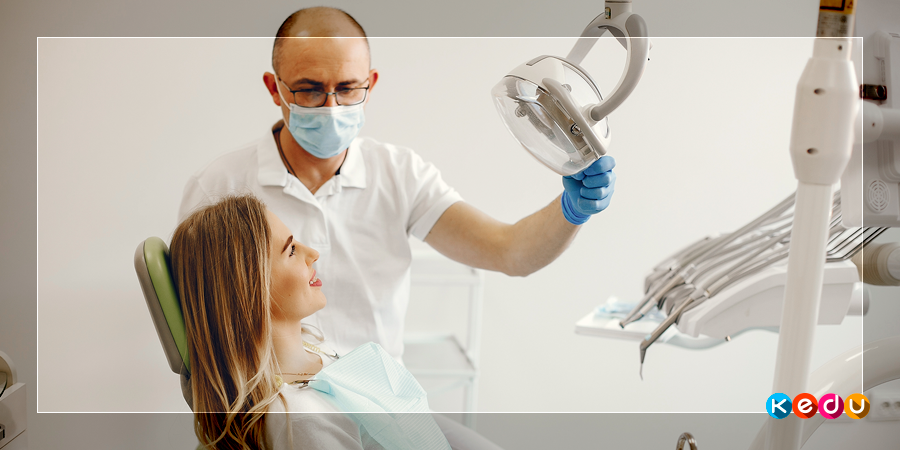

How will the appointment go?
In order to be able to answer the specialist's questions quickly, you should consider a few things
- how often the joint hurts and what kind of pain it is;
- how often the pain occurs, whether it worsens in the morning or in the evening;
- under what conditions it worsens or improves;
- whether you have suffered any injuries, bruises or fractures at the problematic joint;
- whether you have previously had treatment for osteoarthritis of the knee, hip or ankle and, if so, what type of treatment it was
- what the results were;
- What diseases have you had in your life?
- Have you ever had an operation?
- Are you allergic to any medication?
- Have you had problems with the musculoskeletal system, etc. in the past?
Since the risk group for osteoarthritis also includes people whose relatives have the disease, you should find out beforehand whether your family is affected. Your doctor will likely want to know if there have been any important changes in your life recently, such as: B. a change of residence, eating habits, marital status, etc. Sometimes these factors, also due to stress, have a negative effect on your joints.
Your orthopedist may ask you the most unexpected questions
How to behave during the visit
At home, you will probably have a lot of questions for the doctor, but in practice you will forget about them. Therefore, write down in advance what you want to ask. You might want to clarify your questions:
- How to treat joint pain in first aid?
- What tests should you have to clarify the diagnosis?
- How do you prepare for an MRI or Ultrasound scan of your joints?
- What should you take now to relieve the pain?
- Are laboratory tests necessary and where is the best place to have them carried out?
What is the first visit to the orthopedist like? The doctor explains and demonstrates:
Congenital torticollis
Congenital torticollis is slightly more common in boys, although girls also suffer from it. Although it is not congenital, it is a different pathology. However, congenital muscular torticollis in children is quite common because it has many causes. It can develop from:
- Abnormal bone development – due to maternal diseases, mineral deficiencies (mainly calcium) during pregnancy, hereditary and new fetal abnormalities;
- Damage during childbirth: Muscular torticollis is often the result of a natural abdominal birth;
- Abnormal functioning of nerve endings when muscles receive a signal to contract to one side. Can be a consequence of fetal hypoxia;
- Injury to the soft tissues of the neck and shoulder girdle.
Symptoms of torticollis
The symptoms of this pathology can also be perceived by the parents themselves. The most noticeable curvature of the neck is that the child tilts his head towards the spastic part, while, on the contrary, the face is turned towards the healthy part of the neck.
Palpation reveals a thickening of muscle tissue that feels like a soft 'lump' under the skin. This does not form immediately, but only a few weeks after birth.
Congenital torticollis is usually discovered in the maternity ward. However, if the cause is birth trauma, the anomaly may not make itself felt until much later, in the first month of life. Therefore, it is important to observe how the baby holds his head and what position he adopts during sleep.
Treatment of torticollis in children
Treatment is carried out using treatments that relax the spastic muscles: massage, physical therapy methods. It is important to check with the doctor how the child should be placed to sleep, a special pillow roll may be needed to keep the head in the correct position. In some cases, a neck brace is indicated and medication may be prescribed.
scoliosis in a child

Scoliosis is a common pathology in children of school age: by high school it is diagnosed in 70 % (and, according to some sources, in 90 %). It occurs more often in girls.
Different degrees of scoliosis require different approaches to correcting symptoms, from exercise to surgery for stage 4 scoliosis.
Although most people blame a sedentary lifestyle and other obvious factors for scoliosis, researchers say 90 % of the cases are idiopathic, meaning it's impossible to understand why the pathology arose. For example, it is known that carrying a briefcase or backpack incorrectly is not the cause of scoliosis, but one of the top three myths about children's health. Heredity is likely the cause, and insufficient muscle loading only accelerates spinal curvature.

Obvious causes of scoliosis include congenital anomalies and trauma to the spine.
symptoms of scoliosis
If a child 'bucks' at the table and adopts poor posture, this is not a symptom of scoliosis, although the disease cannot be ruled out. It is a consequence of the underdevelopment of the muscular skeleton.
One symptom of scoliosis that you may notice for yourself is that the shoulders, or shoulder blades, are uneven - one is higher than the other. Another symptom is pain, which children mainly complain about in the evenings. However, since back pain is a symptom of various diseases, it should only be diagnosed by a doctor!
One examination is not enough to confirm the diagnosis: an X-ray or computed tomography of the spine is required.
treatment of scoliosis
Scoliosis cannot be treated with physical therapy, massage or physiotherapy. However, they all help to build muscle, stop the development of pathology and eliminate painful symptoms. In severe stages of scoliosis, the child has to wear a corset, and in some cases surgery, when the curvature of the spine not only causes discomfort, but also affects the functioning of internal organs.
Orthopedic dentistry and what it does
This area deals with the correction of deficits affecting the speech and chewing function. The doctor deals with implants, removable and fixed dentures, as well as many other tasks such as: e.g.:
In this way, the prosthetist fully restores the teeth and gives them an aesthetic appearance. This specialist is often referred to as a prosthodontist, since his main job is to fit dentures. However, this is not the only task – the dentist also deals with, among other things
- The dentist also treats, among other things, periodontal diseases and other periodontal pathologies;
- Rebuilding partially destroyed units if the root remains intact;
- working with patients who have no teeth;
- Fixed difficulty chewing food;
- Treatment of the joint in front of the ear, which consists of the temporal bone and the lower jaw.
In addition, the prosthodontist is able to restore the original color of the implant, allowing the part to stand out unobtrusively against the background of the teeth. The result is a more aesthetically pleasing smile.
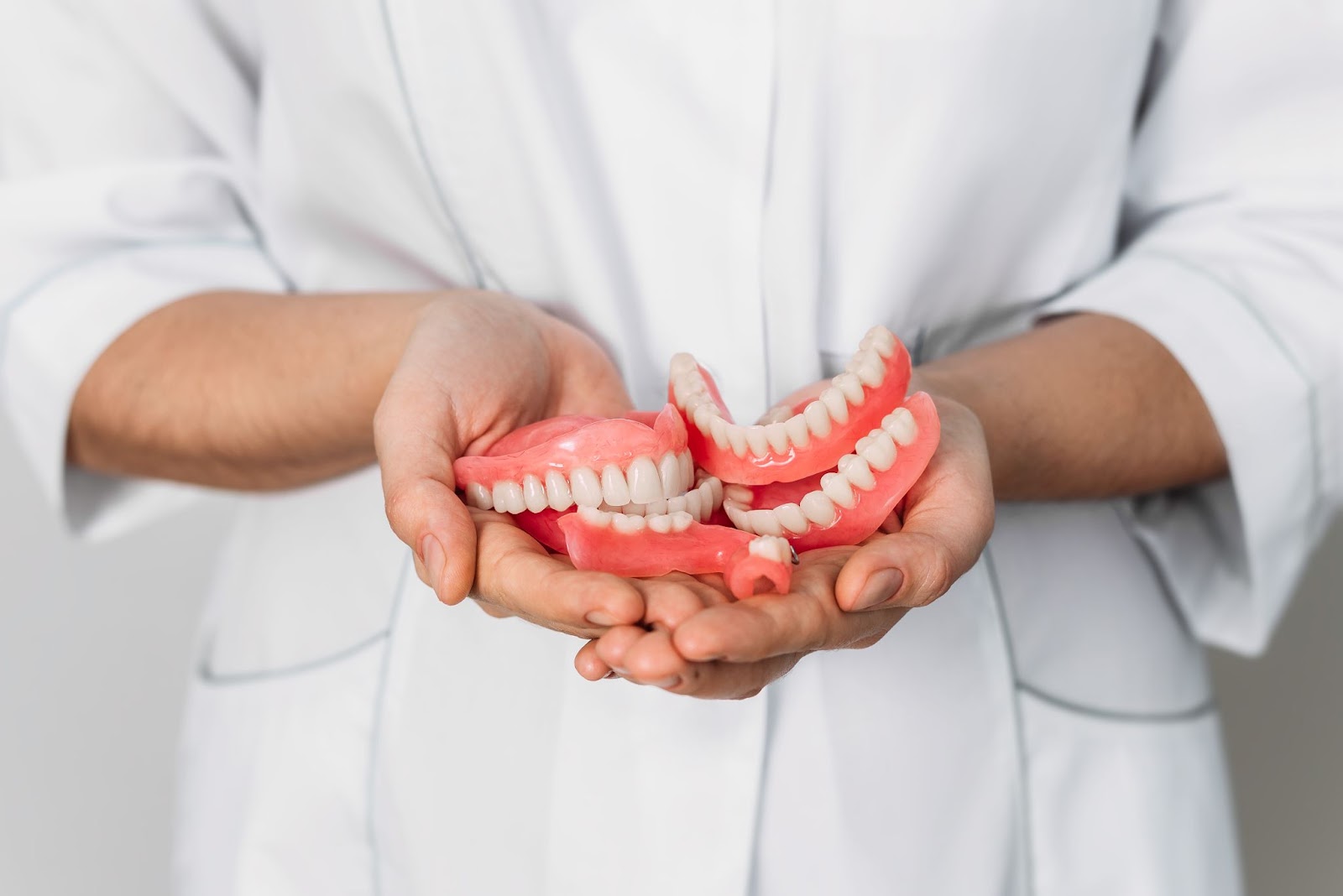
Professionally performed implants do not affect chewing and pronunciation. An experienced dentist can easily replace partially destroyed chewing teeth or replace them entirely with implants. Modern dentistry has an extensive arsenal of techniques for hard tissue augmentation, which are highly effective even with more than half-destroyed crowns.
During treatment, doctors work with the following materials:
- Crown;
- implants;
- Bridges;
- veneers (onlays that hide minor aesthetic problems);
- Dentures.
So, orthodontics is a branch of dentistry that can be used to solve the following problems:
Orthodontic dentistry and its characteristics
Orthodontics deals with the treatment of anomalies in the jaw apparatus. Defects in the bite or in the teeth make the fitting considerably more difficult. The likelihood of early development of tooth decay, periodontitis and other serious oral diseases is increased. The pathology causes additional pressure on the facial muscles when chewing food, which leads to headaches, neck, back and shoulder pain.
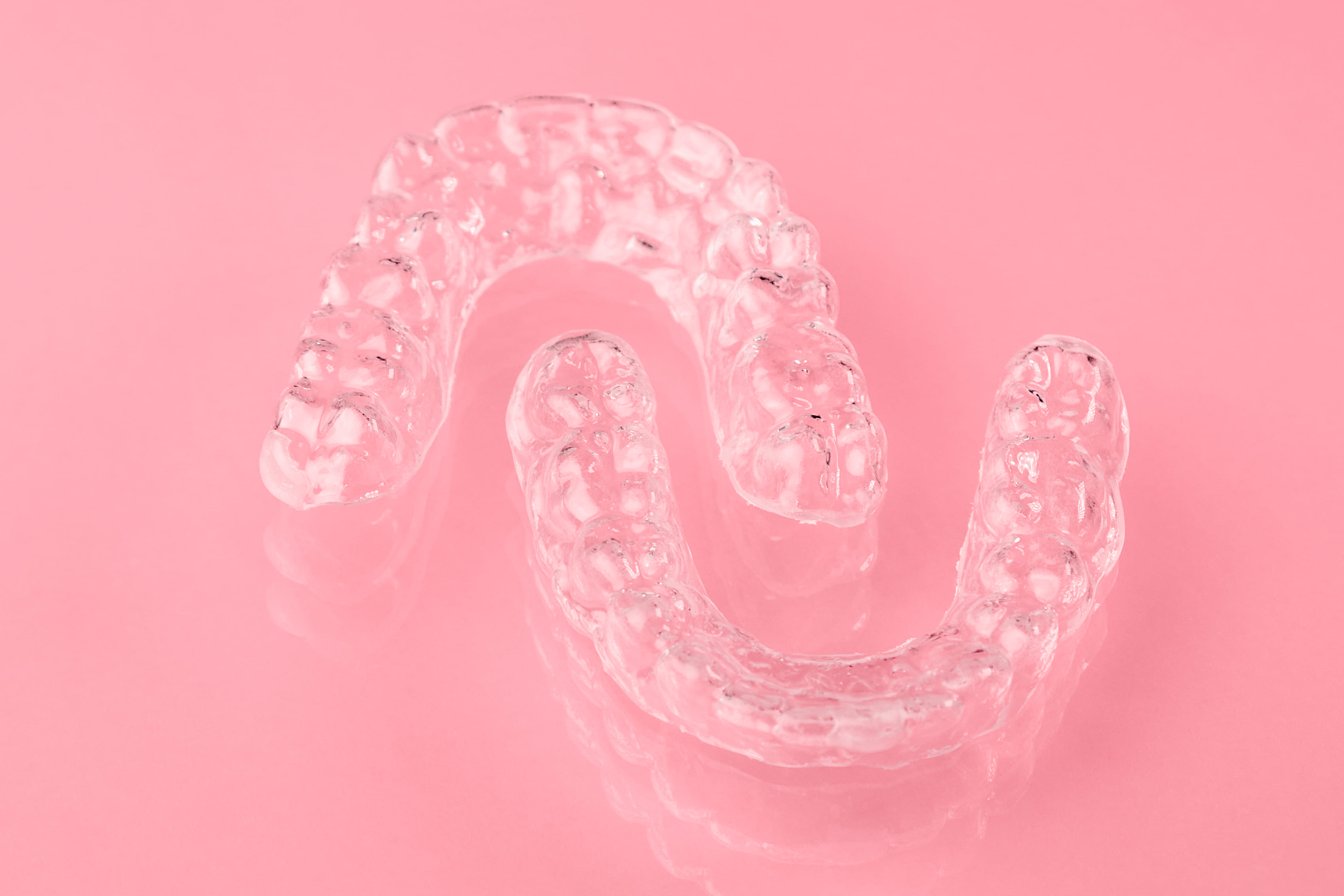
Orthodontic treatment can significantly improve the appearance and condition of your mouth and give you the smile of your dreams for years to come.
Patients of all ages can require orthodontic treatment. Therapeutic interventions are recommended for aesthetic and functional problems. After treatment, the quality of life of the adult or child improves significantly and the lifespan of the teeth increases. A person with a correct bite not only shines with a bright smile, but also gets rid of abnormalities in the functioning of organs and systems.
The correction of bite disorders is also possible after the age of 40. years of age possible. However, it lasts much longer than in adolescents. The most important condition for successful treatment is the presence in the mouth of all dental units necessary for the installation of corrective structures.
Our experts propose a list of pathological processes, in the presence of which the intervention of an orthodontist is unlikely to bring positive results:
- Diagnosed malignancies;
- Cardiovascular, endocrine, or skeletal abnormalities;
- blood diseases;
- infections;
- Bruxism (teeth grinding due to straining of the chewing muscles).
The most commonly used bite corrections are orthoses, plates, brackets, etc. (removable or fixed). In the most severe cases, surgical intervention is indicated. The doctor will decide which method is suitable in each individual case.
How is the investigation carried out?
The initial examination of the patient usually consists of the following steps:
- Collection of anamnesis. This phase includes an interview to obtain information about the patient's well-being and a thorough analysis of the patient's medical history and medical records.
Important!!!
Bring your previous medical report and test results (if you have them) to your appointment.
- Visual, tactile and percussion examination. After taking the oral history and reading the medical history, the doctor makes a direct assessment of the patient's condition. First, the podiatrist examines the optical condition and the deformation of the problem area. He verifies his observations by palpation and also checks the response to the percussion.
- appointment for the examination. An x-ray, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is requested to clarify any questions or concerns about the patient's well-being.
- Creation of a diagnosis. Based on the test results, the doctor makes a diagnosis and decides on a treatment. This can be curative or surgical. The doctor will also write the prescriptions you need to buy the appropriate medicines.
To make an appointment, please leave your phone number
There are many different techniques in modern orthopedics, but Garvis uses the most effective one:
With this method, special prostheses are made and implanted to replace the damaged parts of the joint. This method is extremely effective: the patient can walk around the ward with the help of a rehabilitation therapist already the next day after the operation. Endoprostheses of the hip and knee joints of the leg are most often used in stage 3-4 osteoarthritis. There are cemented, cementless and combination implants.
Minimally invasive technique performed with an arthroscope. It is used both for therapeutic diagnosis and for the treatment of injuries inside the joint. Both fresh injuries and old injuries (more than a month after the injury) are best treated with this method. The advantage over the open operations of classical medicine is that the rehabilitation period is shorter, since the body is under much less stress and recovers faster.
In the case of complicated fractures, osteosynthesis with metal fixation structures is often used. The main goal is to keep the bone fragments securely in place so they can heal properly. Metal fixators are especially effective and reliable, which is why all modern medical clinics prefer this method.
Meniscus injuries in the knee are quite common, especially in athletes. However, it can affect anyone – regardless of occupation and age. In this article, you'll learn what a meniscus injury is, when to see a doctor, and recommended treatment.
areas of orthopedics
Depending on the tasks of the orthopedist and the type of work, the following areas of orthopedics are distinguished
- outpatient This is the conservative treatment of various diseases of the musculoskeletal system in an orthopedic department, an emergency room, a day center or at home. Outpatient orthopedics also includes preventive and dispositive examinations.
- Surgery. Surgical orthopedics deals with the surgical treatment of pathologies and diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Most commonly, joints and ligaments are repaired surgically (arthroscopy), and surgeries are performed on the hands, feet, and spine.
- traumatology. In addition to the treatment of everyday injuries (broken bones, torn ligaments), this field also includes sports orthopedics, which deals with specific diseases. In traumatology, soft tissue corrections and chronic defects are also treated.
- endoprosthetics. In this procedure, a damaged joint or bone is replaced with a prosthesis. This mainly affects the hip, knee and elbow joints.
- Orthopedics of children and adolescents. The peculiarity of this orthopedics lies in the age-specific characteristics of the musculoskeletal system of children and adolescents: increased muscle tone and weak ligaments in infants, intensive growth of the musculoskeletal system in adolescents and a lack of muscle strength to maintain a straight spine, which leads to poor posture.
What complaints should I see an orthopedist for?
Orthopedists and trauma surgeons treat torticollis, hip dysplasia, flat feet, clubfeet, valgus and dislocation deformities of the feet and lower legs, arthritis and inflammation of all joints (including the intervertebral joints), osteochondrosis and spondylolisthesis, joint dislocations, fractures, ligament, tendon and muscle tears, contractures, Deformation osteosis and osteoarthritis, various sarcomas (chondromyxosarcoma, Ewing's tumor), etc.
An orthopedist should be consulted if the following symptoms appear
- postural abnormalities,
- Differences in length of the limbs (especially the lower limbs),
- injuries with suspected broken bones or fractures,
- joint pain,
- swelling, redness or fever in the area of the joints,
- limited mobility of the limbs or spine,
- Pain in the spine (especially in the lower back and cervical spine)
- crunching in the spine or joint when moving,
- pain in the muscles of the limbs,
- hypertonic feeling in the muscles,
- bone pain,
- 'Joint pain when the weather changes,
- deformity of a joint or limb,
- Cramps.
Even if these symptoms occur intermittently, it is important to find out what is causing them, because in most cases they indicate the onset of degenerative processes in the joints and bones, which can still be controlled in their early stages. Athletes and people with an active lifestyle or overweight should regularly visit a doctor to detect micro-injuries or the onset of an asymptomatic disease.
Orthopedics in children and adolescents
In childhood and adolescence, a visit to an orthopedist should be particularly important. The timely diagnosis and professional treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system in small children guarantees in most cases normal physical (and sometimes also psychological) development of the child and the absence of physical and thus also psychological problems. It is also very important to monitor the musculoskeletal system during puberty, when the child's body undergoes significant (not always easy to tolerate) changes under the influence of sex hormones.
Orthopedics as a branch of medicine
This branch of medicine is responsible for the treatment of the musculoskeletal system. For example, the doctor treats spinal problems, flat feet and so on.
In dentistry, the specialist treats disorders and restores the function of the chewing and tongue apparatus. With prosthetics, he restores the integrity of the jaw. This allows you to return to your normal lifestyle, chew your food normally, and communicate with others without embarrassment or speech impediments.
What an orthodontist does
This doctor is often confused with an orthodontist. Orthodontics, however, is a different specialty. In this case, the doctor corrects crooked teeth, an abnormal bite with braces and removable dentures.
Orthodontics does not correct, but partially or completely restores the row of teeth. The absence of one or more teeth causes considerable physical and psychological problems. First, the patient loses the ability to chew food normally and speech may be impaired. On the other hand, the neighboring tissues are stressed, so that they too can be worn out prematurely. Thirdly, the person becomes self-confident and develops complexes, which negatively affects the psycho-emotional state. The orthopedic dentist helps to solve these problems, that is, to make life more comfortable.
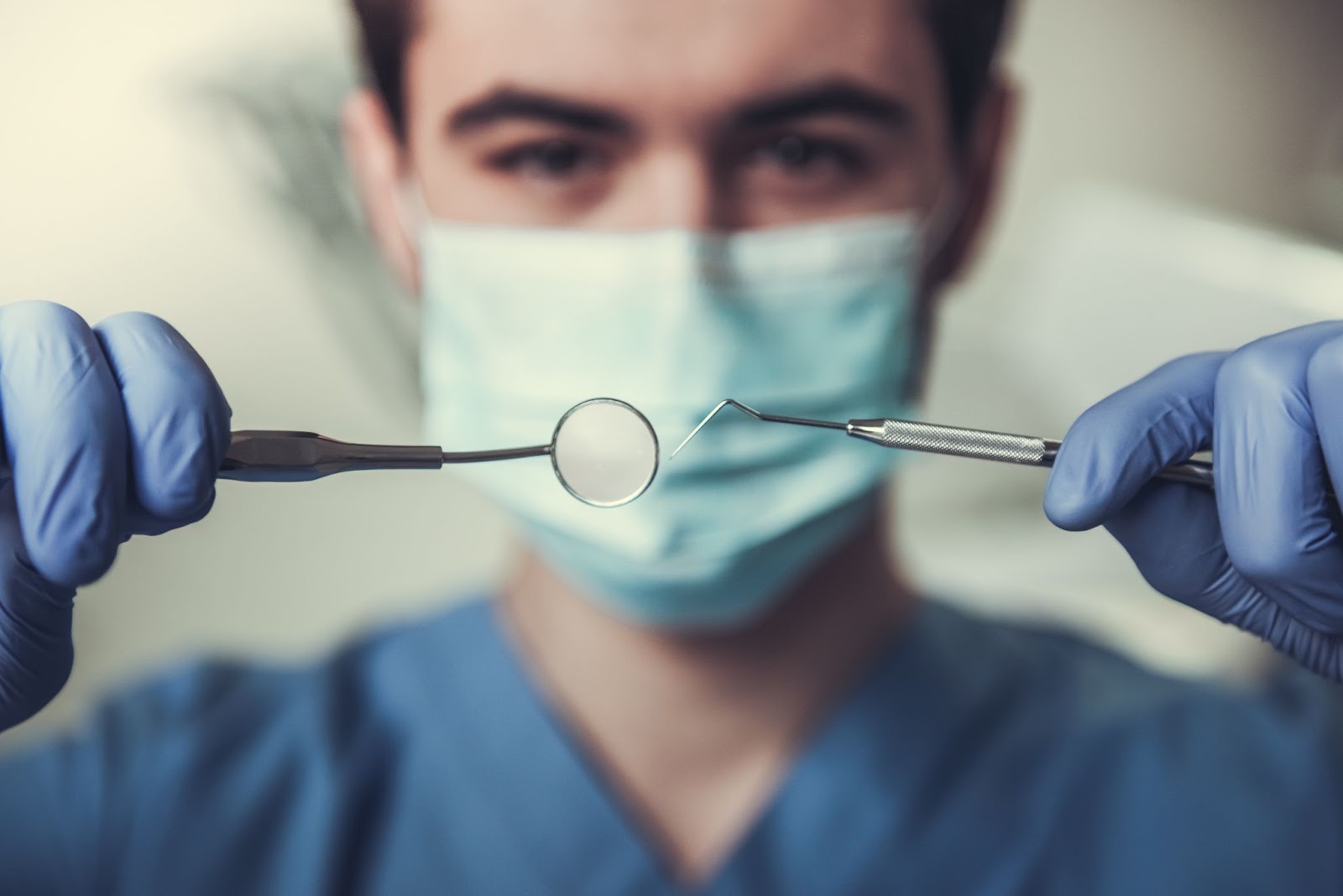
In orthopedic practice, the following procedures are performed:
- restoration of the enamel surface and bone structures while preserving the roots and nerves;
- Putting a special crown on a decayed tooth to stop it;
- Manufacture of prosthetic systems;
- Removal of aesthetic defects (e.g. fissures, chips, bumps, pigmentation, etc.).
The medical protocols are clearly defined. Qualified specialists always adhere to generally accepted principles and use proven treatment protocols. This avoids dangerous reactions in the form of side effects.
restoration of chewing function
Proper chewing is essential for the proper functioning of the digestive system. When it's not working properly, the entire jaw system suffers. Muscle tension decreases and blood flow to the soft tissues and bony structures slows down. As a result, the patient's overall condition worsens. Treatment should be initiated as soon as possible, since in advanced cases inflammation develops, leading to periodontitis or periodontal disease.
Metal fused porcelain crowns
As was the case many years ago, metal-ceramic crowns are one of the most common types of fixed dentures in Russia today. Most people today choose this technology, not only because of the relatively long service life of these structures, but also because of the high level of aesthetics. The tooth is preserved by the shell of the crown and remains true to nature thanks to the high-quality third-party ceramic in white. In addition, the prices of metal-ceramic crowns are quite affordable and they are quite suitable even for people with an average income.
A metal-ceramic crown is a great way to improve dental health and esthetics when the crown area of a tooth is 50 % or more decayed. If the tooth cannot be restored with medical treatment and there is a risk of tooth loss, the dentist always recommends that the patient restore the tooth with a metal-ceramic crown.
A metal-ceramic crown is a construction consisting of a metal cap (cobalt-chromium alloy, precious metal alloy, titanium alloy) imitating the shape of the tooth and covered with a ceramic material on the entire surface.
Statistically, the average lifespan of a metal-ceramic crown is in the range of 5-10 years, but the lifespan largely depends on how the crown interacts with the patient's gums (mucous membrane).
It should be borne in mind that metal-ceramics made of non-precious metal alloys tend to oxidize when in contact with the aggressive environment of the human oral cavity, and the subsequent process of micro-fusion can lead to significant bone loss, thereby reducing the life of the supplied metal-ceramics.
Zirconium dioxide crowns
Zirconia crowns are increasingly recommended today. This technique is now considered the most advanced in the field of prosthetics. Many orthopedic surgeons recommend this type of crowns to their patients for three main advantages: the biotolerance of the material, the high aesthetics due to the translucency and the particular quality of the finish.
The cap of this type of crown is made of zirconia and the top is covered with ceramic. The following properties are noteworthy:
- absence of allergic reactions and oxidation;
- Zirconia has no effect on the surrounding oral tissues;
- aesthetic appearance of the crowns;
- Zirconia is white in color (similar to Meialloceramics which has a greyish appearance);
- the use of the latest technology;
- the cap itself is made with the help of a computer scanner (the scanner analyzes the plaster models, that is, the whole situation in the patient's mouth). The technician then designs the future cancellation cap virtually with the help of a computer program. When the design is complete, a special milling machine is programmed to cut out the finished cap. The human factor in this case is reduced to a minimum. The fitting of the crown to the tooth is very precise (accurate to a tenth of a micron) and the dentist does not need to make any adjustments to the tooth after manufacture;
- Zirconia is lighter than other materials;
- the adhesion of zirconia to zirconia is much better than to other metals;
- Zirconium dioxide crowns are characterized by their high durability.
This is what a visit looks like
Before visiting the orthopedic surgeon, you should not consume alcoholic beverages. The reason for this is that treatment with this doctor involves anesthesia and the presence of ethanol in the body affects the effect of this anesthesia.
In case of inflammatory processes, including colds, a visit to the dentist, known as an orthopedist, who inserts teeth and prostheses, should also be postponed, since during this period any intervention from the outside is undesirable. The immune system is weakened and may not respond appropriately to various external interventions.
Before visiting the dentist, the mouth should be cleaned thoroughly. If this is not possible, it should at least be rinsed with a special preparation.
At the first appointment, the specialist determines the severity of the disorder of the masticatory system and jaw. If necessary, comprehensive therapeutic or surgical treatment can be carried out beforehand. This is necessary in preparation for orthopedic surgery. Consultations with all dentists are possible in Dentika Dental Clinic.
Danger!!! First, all concomitant diseases must be treated, only then can the next steps be taken.
A visual or instrumental examination is carried out, the patient's complaints are listened to and an anamnesis is taken. Then impressions are taken and a row of teeth is photographed. If necessary, a referral to an oral surgeon can be made. Based on the information collected, an effective treatment will be selected.
treatment methods
As already mentioned, the orthodontist is a doctor who applies crowns and dentures, but again there are many forms used in modern dentistry, including Dentika Dental Clinic.
Fixed braces
They closely mimic the anatomical features, color, position and shape of the natural tooth. They allow full functionality to be restored (pronunciation, chewing, pressure, facial symmetry, etc.).
As the name suggests, these products are non-removable. In other words: they are worn permanently. This applies to veneers, inlays, etc.
Metal fused porcelain ceramic
This is the most common type, designed to be worn without being removable. It is an overlay made of a ceramic-coated alloy of cobalt, chromium and titanium.
In most cases they are well adjusted. The most important thing is that they are made of high quality material. If impurities are present, oxidation and gingivitis can occur.
zirconia
This material is considered one of the most technologically advanced. Computer-controlled technology is used in the construction of the prosthesis. The structure is computer modeled resulting in excellent shape and size accuracy. Compared to the previous type, there is a much wider range of shades. This makes it possible to create a crown that does not stand out from your own teeth.
The crown is a ceramic-coated zirconia cap. This is an innovative material that does not cause allergic reactions and does not oxidize.
All-ceramic dentures
Used on the front teeth. They contain no metal to preserve the natural color of the enamel surface.
Fixation of removable dentures
They are used when the use of non-removable dentures is impossible for any reason. They are available in two variants:
- What an orthopedist treats and what symptoms to report.
- What does an orthopedist examine?.
- What is an orthopedist?.
- What is another name for an orthopedist?.
- Colostomy - what is it?.
- Orthopedics - what is that?.
- How much does a prosthetic foot cost?.
- What is the name of the orthopedist in the health center?.
