If a tendon ruptures, it will be treated by a trauma surgeon because the only treatment is surgery to stitch up the damaged fibers. In cases where the trophic changes are irreversible, an amputation operation is also performed by a specialist.

- traumatology
- Specialties in trauma care
- What is the difference between a traumatologist and an orthopedist?
- The responsibilities of a traumatologist include:
- When should you see a trauma surgeon?
- Stages of consultation
- When should you see a trauma surgeon?
- What a trauma surgeon treats
- fractures
- What does the trauma surgeon do during the visit?
- Which diagnostic methods are used?
- What examinations can a trauma surgeon prescribe?
- roentgen
- angiography
- Ultrasonic
- Consultation with a trauma surgeon
- What falls within the scope of responsibility
- When should you see a trauma surgeon?
- Who is a trauma surgeon and what does he do?
- What examinations must be carried out by a trauma surgeon?
- What are traumatology and orthopedics?
- What tasks does traumatology and orthopedics solve?
- Joint plasma lifting.
- Therapeutic and surgical treatment
traumatology
A traumatologist is a doctor who deals with conservative and surgical treatment of degenerative and traumatic bone deformations, rehabilitation of patients after operations and prevention of arthritis, arthrosis and injuries.
The traumatologist deals with osteosynthesis, endoprosthetics, transplantation, immobilization of injured limbs and damaged joints, relieves pain syndromes, stops bleeding caused by trauma and prevents secondary infections. The doctor also fights traumatic shock and contusion syndrome (compression syndrome).
- Joint diseases and injuries.
- Osteoporosis.
- Curvature of the spine, feet.
- flat feet.
- Inflammation of the bones.
- New growths of bone structures.
- Pathological fractures.
- Ruptures and dislocations.
- Sprains and bruises.
The work of the trauma surgeon requires close collaboration with surgeons, orthopedists, transplantologists, radiologists and immunologists.
Sedentary work, urban environments, poor nutrition and lack of exercise lead to an increase in musculoskeletal disorders, which makes the profession of trauma surgeon popular and in demand.

Specialties in trauma care
- Pediatric trauma surgeons – help children under 18 years old.
- Sports injury specialists
- Traumatologists who amputate limbs.
- Prosthetists – replace the missing limb with special prostheses (electric, pneumatic, hydraulic and combined) or treat movement disorders with robotic exoskeletons.
- Trauma oncologists or osteo-oncologists – operate on benign and malignant bone tumors.
- Vertebrologists – deal with spinal problems.
- Traumatologists – operate on the hand.
- Arthroscopists – deal with the endoscopic correction of joint injuries.
- Burn specialists – deal with the treatment of burns.
- Military traumatologists – treat musculoskeletal injuries and their complications and sequelae, as well as injury prevention in the military.
Traumatologists work in trauma clinics, multi-purpose clinics, polyclinics, scientific research institutes, diagnostic and rehabilitation centers and specialized sanatoriums.
What is the difference between a traumatologist and an orthopedist?
Traumatologists and orthopedists are often confused, but they are two different specialties.
If you have problems with the musculoskeletal system, the specialist is an orthopedist. This can also include disorders in the form of dislocations.
A trauma surgeon treats fractures of varying degrees of severity. Sometimes an orthopedist and a traumatologist work together, since it is not possible to place a patient under the care of only one specialist.
Over time, a related profession has emerged - orthopedic traumatologist. A specialist in orthopedics and trauma surgery diagnoses, treats and rehabilitates patients with complex joint and limb fractures.
The responsibilities of a traumatologist include:
- the admission and diagnosis of patients;
- Creation of the treatment and rehabilitation plan;
- Carrying out the necessary treatments (casting, injections, etc.);
- Working with medical records.
Many patients have very serious injuries that are difficult to rehabilitate. Every case is different and requires a well-thought-out treatment plan.
To be successful, a trauma surgeon must have an encyclopedic knowledge of fractures, human anatomy and physiology.
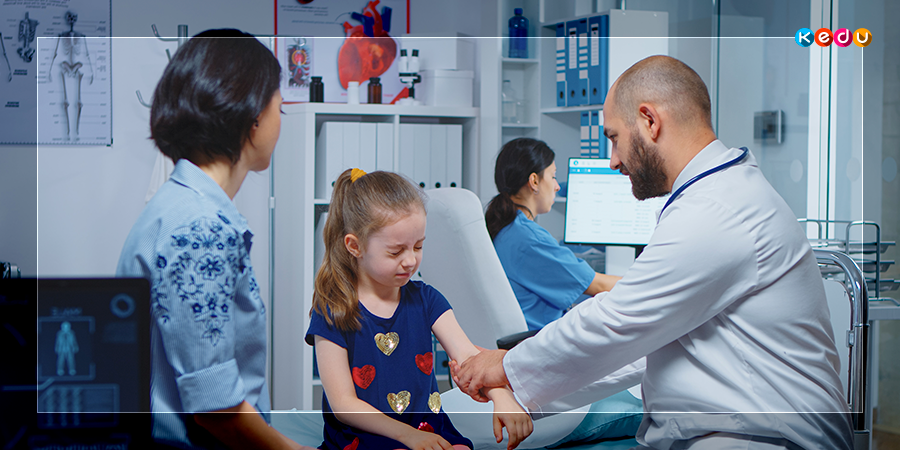

When should you see a trauma surgeon?
Consultation with a trauma surgeon is necessary for people who:
- has suffered an injury to the musculoskeletal system as a result of a traffic accident, domestic or commercial activity or sporting activity;
- A bone fracture has occurred or is suspected;
- sprains, abrasions, bruises or bruises have occurred;
- There is recent trauma that caused a hematoma or skin breakdown;
- There is severe pain in the injured area;
- severe pain in the limb when leaning on it;
- the joints are swollen and enlarged;
- There is pain in the limbs and joints;
- Deformities of the spine, chest or limbs are observed;
- Burns or wounds are present;
- Pain occurs when breathing deeply;
- Nausea and dizziness occur after a head injury;
- Joints and limbs are restricted in their movement.
A trauma surgeon is also called in for animal bites, ticks and other insects.
Stages of consultation
Patients who can move independently visit the trauma surgeon in the outpatient clinic. Patients who are unable to make an appointment themselves may be seen at home by a trauma surgeon or may be taken to a trauma clinic or hospital department with serious injuries.
The initial consultation with a trauma surgeon includes:
- Examination of the patient's complaints and explanation of the anamnesis (how long the complaints have existed, what causes the pain, etc.);
- a family history, as the fracture may be the result of certain hereditary diseases;
- Examination, which consists of palpating the injured area and checking the functionality of the injured limb;
- Arrangement of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
When should you see a trauma surgeon?
As a rule, you only see this doctor in extreme cases, when the pain becomes unbearable or when a limb is completely immobile. In fact, injuries are not always obvious, and the consequences of a minor injury can lead to unfortunate results.
It is important to see a trauma surgeon immediately in the following situations:
- Injuries caused by external influences that result in severe pain and restricted movement in the affected area.
- Severe pain and limited mobility in various places after unsuccessful strength training.
- Traffic accidents. The effects of these types of injuries may take some time to become noticeable.
- Occurrence of wounds with extensive damage.
- Burns and chilblains.
- Swelling and redness around the joint, palpable deformation of the joint, impairment of its mobility.
- Chest pain when taking a deep breath (this may indicate a rib fracture).
- Falls in older people, which are accompanied by severe pain, dizziness, nausea and restricted mobility.
The World Health Organization estimates that 37.3 million falls occur worldwide each year that have serious consequences and require medical attention.
What a trauma surgeon treats
A trauma surgeon is familiar with the function of the human musculoskeletal system and how it is affected by traumatic factors. This allows him to successfully diagnose and treat a variety of conditions related to injuries of various types.
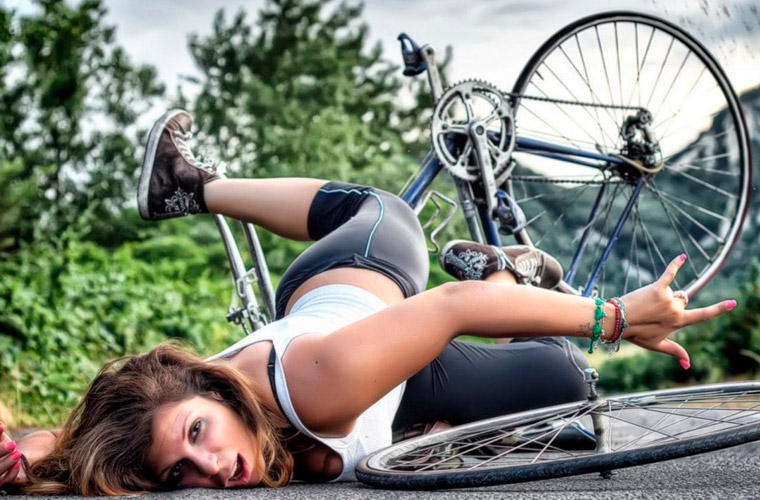

fractures
A fracture is defined as a disruption in the continuity of a bone resulting from an impact that exceeds the strength of the bone (each bone has a different tolerance limit).
Fractures are common: Many people suffer at least one fracture in their lives. It can be caused by an unfortunate fall, collision, traffic accident, natural disaster, etc. – This type of fracture is called a traumatic fracture and is characterized by the fact that it occurs in healthy, physiologically intact tissue.
A fracture can even occur with an awkward movement or twist. These fractures are more common in older people and are associated with loss of bone strength due to the development of a pathological process.
A distinction is made between closed fractures (without injury to the skin and mucous membranes) and open fractures (with injury to the skin and mucous membranes).
- Deformity of the injured limb.
- Crunching of bones that may be heard or felt by the doctor.
- Abnormal mobility in the injured area.
- Visually visible bone splinters in the wound (in the case of an open fracture).
- Pain at the site of injury that increases when attempting to move.
- Swelling at the injured area, bruising. These usually appear some time after the injury and then worsen.
- Impaired motor function: inability to move or stand up.
What does the trauma surgeon do during the visit?
The visit to a trauma surgeon begins with an examination and listening to the patient's complaints; The doctor examines the bones and joints, detects swelling and bruising and checks the mobility of the limbs. The affected person should describe the course of the disease in detail - when the first symptoms appeared and, if there was an injury, the time at which it occurred. Taking a medical history is an important part of correct further diagnosis and treatment.
- Assessment of the person's state of consciousness, general condition, physique, appearance and skin integrity;
- Assessment of gait posture – limping, duck gait, cock gait;
- The doctor asks the person to perform a few simple movements to check the presence or absence of a crunch in the joints, assess their mobility and detect changes in the nature of the pain syndrome;
- Palpate the injured area.
During the visit, the doctor should note the presence of symptoms such as: E.g. grinding in the joints, clearly check.
When visiting a trauma center, the doctor will provide first aid by correcting the dislocation, applying a cast, or otherwise immobilizing the injured limb.
At a scheduled consultation, when a patient comes with the consequences of an injury or a chronic bone or joint disease, the doctor during the examination detects positive or negative dynamics and evaluates the effectiveness of medications and physiotherapy.
For bite wounds, skin lesions, rabies and tetanus prophylaxis, a referral to the clinic is mandatory.
Which diagnostic methods are used?
Laboratory diagnostic methods are rarely used in traumatology - before the operation, in the presence of infectious processes, clinical and biochemical blood tests, coagulation tests, Rh factor and group, tests for syphilis, brucellosis, tuberculosis are carried out. In case of necrosis, a bacteriological examination of the wound contents is carried out to determine the type of pathogenic microorganisms and their sensitivity to antibiotics.
Most important types of examinations:
The most important examination for diagnosis is the X-ray, which can help detect bruises, fractures or other types of injuries
- X-RAY – is a cost-effective method of diagnosing orthopedic problems, with mandatory exposures in multiple projections, even if the front is clearly visible. The examination makes it possible to detect displacements, the presence of bone fragments and the condition of the surrounding tissues.
- angiography – is performed to assess the condition of blood vessels and blood flow. The images are taken after injection of a contrast medium; Areas with poor circulation appear dark.
- ULTRA SOUND – Diagnosis when dislocation, meniscus damage, dysplasia, joint capsular fluid and bone masses are suspected.
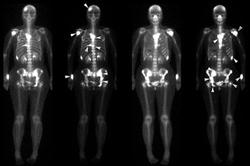
- scintigraphy – Scintigraphy of the skeletal system is carried out after intravenous administration of radioactive material in doses that are safe for humans. This method makes it possible to detect all changes in bone and cartilage tissue and to assess the degree and progression of pathological processes. The diagnosis is made in cases of osteoarthritis, degenerative joint diseases, infectious diseases of the bones and joints, severe trauma, tumors and metastases in bone tissue.
- MRI – is the most informative diagnostic method in orthopedics and is used for microtraumas, tumors and metastases in bone tissue, congenital and acquired joint pathologies and contractures.
What examinations can a trauma surgeon prescribe?
Like any other doctor, the trauma surgeon uses various tests and examinations in his practice. Most often these involve additional diagnostic methods, less often laboratory tests.
roentgen
The simplest and most commonly used diagnostic method in traumatology. In the vast majority of cases, an X-ray examination is mandatory. Even if the fracture is visible, the examination is performed to assess the extent of the injury - the presence of fragments, the length of the fracture, and the condition of the surrounding tissue. When conducting an X-ray examination, it is important to remember the basic principles of this procedure.
- Radiographs are always taken in two projections - lateral and anteroposterior;
- The injury site must always be in the center of the X-ray;
- When examining skeletal bones, the radiograph should also include adjacent joints.
angiography
A method that can be used to examine and assess the movement of blood through blood vessels using contrast media. The data about the blood supply gives the doctor information about the condition of the soft tissues, the periosteum and the bone. Without this data, it is not possible to predict the recovery and consequences of bone fractures.
The method takes place in two steps. The first is the administration of a contrast agent (e.g.Mayodil, urographer). The second step is the actual imaging. In the darkened image, the blood vessels look like light, winding stripes. Narrowed areas where blood flow has stopped appear darker. This method is particularly informative for congenital anomalies of the musculoskeletal system.
Ultrasonic
Ultrasound is also a relatively simple and inexpensive examination method. It also has the advantage of being mobile. There are now portable devices (portable) Ultrasound machines are available that can be used in trauma units near the accident.
Consultation with a trauma surgeon
Injuries cannot be completely prevented, but a few simple rules can help reduce the risk of serious complications from falls or bruises.
Injury prevention:
- Regularly eat foods high in calcium – hard cheese, sardines, basil, nuts, flax seeds, cabbage, beans;
- Do not forget to use safe protective equipment when carrying out dangerous work and extreme sports;
- exercise regularly, but no more than 10 % per week;
- Pay attention to your posture and control your weight;
- sleep on orthopedic mattresses;
- Wear comfortable sports and leisure footwear;
- In the initial phase of your sporting activity, train only with a trainer in the gym:
- Practice falling correctly and safely on special courses.

Eat more foods containing calcium to strengthen your bones
Caffeinated drinks deplete calcium from bones, so all coffee drinkers should eat more foods or take vitamin complexes to replenish this.
Bones and joints are subjected to enormous stress every day, which leads to their rapid deterioration, they become brittle, and even a small bruise can cause serious complications. After an injury, you should not self-medicate, but rather seek the advice of a trauma surgeon - correct diagnosis and timely treatment will avoid serious illnesses, disabilities and operations.

What falls within the scope of responsibility
A trauma surgeon treats the following conditions
- osteoarthritis;
- arthrosis
- Arthrosis;
- Osteoporosis;
- flat feet;
- bone tumors;
- curvatures of the spine;
- foot deformities;
- kyphosis
- lordosis;
- Arthrosis.
In addition to pathological processes, the doctor in this specialty also deals with the consequences of such injuries:
For any seemingly minor injury, you should see a trauma surgeon.
When should you see a trauma surgeon?
You should seek medical attention if you have sustained an injury
- Injury;
- Crunching in the joint when performing movements;
- restriction of mobility of the joint;
- Swelling of the skin of the joint, increase in size or swelling
- instability of the joint;
- Visible deformation;
- Local increase in temperature, redness of the skin.
It should be noted that in some musculoskeletal pathologies, symptoms of general intoxication may appear in the clinical picture, which may indicate the onset of an infectious process in the joint. If this is the case, the trauma surgeon can examine and treat together with a doctor in the relevant field.
Who is a trauma surgeon and what does he do?
A trauma surgeon is a doctor who treats trauma and post-traumatic syndromes. In addition, the trauma surgeon is often responsible for the treatment of flat feet, spinal curvatures and foot anomalies.
As a rule, a trauma surgeon specializes in the treatment of injuries, be they bone, muscle, joint or tendon ligament injuries. Recently, the number of injuries caused by extreme sports has increased significantly.
What examinations must be carried out by a trauma surgeon?
The trauma surgeon at the polyclinic will usually use the following diagnostic methods:
Unfortunately, injuries are an inevitable side effect of human existence. It is crucial that first aid is provided in a timely and appropriate manner - with this in mind, below is guidance on the main types of fractures:
1). Fractures of the wrist and hand – the fracture should be fixed by applying a splint from the base of the finger to the top of the forearm. If the pain is severe, an analgesic may be given.
2). Forearm fractures - before going to the trauma ward, it is advisable to immobilize the arm with a wooden splint from the lower third of the shoulder to the metatarsophalangeal joints. The arm should be bent at the elbow at a right angle. If pain is severe, analgesics should be taken.
3). Rib fractures – depending on the severity of the fracture, an elevated position, analgesics and oxygen are recommended. If hospitalization is delayed, intercostal novocaine blockade is indicated. In the case of multiple fractures, the patient must be admitted to the local trauma hospital.
4). Spinal fractures – the patient must not be placed in an upright or sitting position and the head must not be tilted. The patient should be placed gently on a stretcher on his back with a roller under his head. Admission to the local emergency room is mandatory.
5). Fractures of the lower leg bones – splinting of the lower leg is required first: The splint is applied from the upper third of the thigh to the ends of the fingers. If pain is severe, anesthesia is indicated. The patient must be transported on a stretcher to the nearest trauma unit.
In general, it should be emphasized that all broken bones must be treated by a professional trauma surgeon.
What are traumatology and orthopedics?
Both are branches of medicine that deal with the function and disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Although everyone has dealt with an injury at some point, not everyone knows what traumatology studies, what it involves, and what it treats
traumatology and orthopedics is a combination of two areas of knowledge.
It deals with the causes of movement disorders and the healing of injuries as well as the treatment of diseases that lead to mobility problems, muscle and joint pain, as well as methods of prevention.
Both disciplines emerged a long time ago, in the 19th century. Initially they were part of surgery, later they became an independent department in medical faculties.
- Diagnosis and search for new treatment options for various diseases that affect motor functions.
- Differentiation of diseases with similar symptoms that may cause similar complications.
The discipline requires knowledge of human physiology as well as sports and exercise therapy, massage and physiotherapy.
One of the field's most important tasks is the development of new conservative treatments to avoid surgery.
Mild treatments allow recovery from injuries or illnesses without surgery. The search for minimal, benign surgical interventions also continues. Currently, endoprosthetics is actively used. It involves replacing the damaged joint with a prosthesis made of safe materials through a small incision. The likelihood of complications and high blood loss is minimal.
Another important area is limb transplantation – the reattachment of a lost limb or part of a limb.
B Moscow There are many centers and institutions dealing with traumatology. It is important to choose the right specialist and make sure they are qualified.
What tasks does traumatology and orthopedics solve?
The specialty solves a number of tasks. One of these is treating existing conditions that cause pain or mobility problems. The tasks of traumatology and orthopedics also include the differential diagnosis of pathologies, the search for methods of intensive recovery from injuries, etc.
Joint plasma lifting.
We offer you an advanced method of treating arthritis, spondyloarthritis, spinal hernia.
The 'Plasmolifting TM' method eliminates pain, swelling and inflammation. Already after the first treatment, the anti-inflammatory process is activated, the regeneration (restoration) of all joint structures: cartilage, bone tissue, synovial fluid, ligamentous apparatus. At the end of treatment, many patients are able to significantly reduce the dosage of painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications or stop taking them.
The TM Plasmolifting method offers a real chance to rebuild the joints and avoid endoprosthesis surgery. Take advantage of the Yu Clinic offer and give yourself freedom of movement without pain!
These effects can be caused by both mechanical external influences and various diseases.
Orthopedic traumatology combines the examination and treatment of all of these diseases.
As far as we are concerned, Orthopedic traumatologist in DolgoprudnyIf you are experiencing muscle and joint pain, bone fractures, bruises, strokes and other injuries, stiffness and other symptoms, you should seek help. During a consultation you can determine whether treatment is necessary and which methods are most suitable.
Therapeutic and surgical treatment
Podiatrists usually try to avoid surgery and opt for conservative, medical and alternative treatments. However, in severe cases that cannot be treated this way, surgery is necessary.
Various diagnostic methods are used in traumatology
The examination methods include laboratory diagnostics.
The examination methods in traumatology make it possible to make a differential diagnosis and select the most appropriate and effective treatment methods.
Read more:- Consultation of an orthopedic traumatologist.
- Free online consultation with an orthopedic trauma surgeon.
- Traumatology orthopedist which doctor.
- How to make an appointment with a traumatologist.
- tibia and fibula.
- Traumatologist what he treats.
- Moscow orthopedist.
- Fracture of the lateral condyle.
