Custom made insoles are the ideal solution for people already struggling with knee osteoarthritis. The springy insoles should be made of abrasion-resistant, breathable material according to your personal measurements and considering the defects of your foot. This is the only way they can cushion the shock load when walking.

- Osteoarthritis of the knee: causes, symptoms and treatment
- Why does arthrosis occur?
- Physical therapy for osteoarthritis
- effectiveness of exercise therapy
- Causes of deforming arthritis
- Symptoms of gonarthrosis
- Osteoarthritis pain: what to do, what mistakes you can make
- 'Minimalist Shoe'
- 5 rules for footwear for osteoarthritis
- The short conclusion
- Description
- What to do at the first sign of joint disease?
- What to eat when you have arthritis
- Function and structure of the kneecap
- knee pad
- closed type
- open type
- rail type
- Treatment in the Health Energy Clinic
- Benefits of the clinic
Osteoarthritis of the knee: causes, symptoms and treatment
Osteoarthritis of the knee is a reduction in cartilage performance due to deformation and destruction of the cartilage. Other terms are also used to describe this condition – including. osteoarthritis of the knee i deforming osteoarthritis. Currently, there are several methods of treating this disease: the specific option is tailored to the individual patient.
Osteoarthritis of the knee usually develops gradually. It mostly occurs in women and older people who are overweight or have venous abnormalities. The disease can occur in one or both knees at the same time.
The most important stages in the development of knee osteoarthritis:
- initial stage . The joint's ability to absorb shock decreases as the cartilages rub against each other and the roughness of the joint increases. Occasionally, fracture formation is also observed.
- second . At this stage, the bone begins to be covered with growths (osteophytes). Curvatures remain on the inside of the joint capsule and the limbs become stiff. As a result, the knee joint gradually loses its function. Due to a reduction in the thickness of the intercondylar pad, the distance between the tibia and femur decreases.
- Third. If nothing is done, the pain in the knee area will become permanent due to irreversible cartilage damage. At this stage, the patient is no longer able to move normally.
The first signs of osteoarthritis in the knee are reason enough to see a specialist. Otherwise there is a real risk of disability.

Why does arthrosis occur?
The main causes for the development of osteoarthritis in the knee are.
- inherited predisposition;
- Temporary immobilisation of the knee joint as a result of trauma;
- surgical removal of the meniscus;
- strong physical exertion, constant hypothermia;
- Obesity, overweight problems
- malfunction of the ligaments (weakening of the ligaments);
- other joint diseases (arthritis, tumors, various inflammatory diseases)
- metabolic disorders, lack of calcium in the body;
- flat feet (the shift in the center of gravity increases the pressure on the joint);
- Stress, general fatigue and lack of sleep.
Physical therapy for osteoarthritis
The main goals of physical therapy are to eliminate all symptoms of osteoarthritis and to prevent the osteoarthritis from spreading to the healthy structures of the knee joint. Regular exercise is an excellent prevention against relapse. She avoids taking systemic medications that have adverse effects on the liver, kidneys, and digestive tract.
Physical therapy is indicated for people at risk of developing osteoarthritis. People who have previously suffered a knee injury, are on their feet most of the day, are overweight, wear high heels, or have a sedentary lifestyle.
Stages of osteoarthritis in the hip and knee. At stages 1 and 2, gymnastics is effective, at stages 3 and 4 it is no longer effective. In this state, the cartilage tissue has almost completely disappeared and cannot be regenerated.
effectiveness of exercise therapy
The movement therapy must be carried out regularly. Therapeutically, 15-30 minutes of daily exercise is more effective than 2-3 hours of exercise per week. This is due to the gradual adaptation of the muscles to the arising loads.
When exercising, pay attention to the sensations that arise. A slight discomfort in the muscles is acceptable. However, if you feel pain in the muscles, you should stop training and rest. For exercises that make you feel better, the stiffness will go away and you can do them in multiple sets.
Use the exercises wisely and you will definitely get results.
Causes of deforming arthritis
Researchers believe that loss of type II collagen (about 50 % of cartilage mass), flat feet and dysplasia of the knee joint are responsible for the early wear and tear of cartilage tissue. Cartilage loss is caused by an age-related decrease in collagen production. In most cases, however, these changes can be delayed with an appropriate lifestyle. For many older people, the joint discomfort is minor. For some people in their 50s, the severe pain associated with osteoarthritis has reached a critical point and is limiting their ability to work.
There are no vessels in the cartilaginous tissue; the substances required for nutrition come from the synovial fluid. If there is not enough water, the volume of synovial fluid decreases. The cartilage loses its elasticity, cracks appear, increased friction in the joint capsule, pain and a characteristic crunching sound. In order to support the cartilage tissue and alleviate the course of the disease, you should drink at least 2 liters of water per day.
In order to maintain freedom of movement, you should relieve your joints from the age of 40. Wear shoes with shock-absorbing soles, alternate prolonged static loads with sitting or walking, and wear knee braces for heavy loads.
The cartilage tissue receives less oxygen and nutrients and the muscles lose strength. Helpful for relieving the pain associated with knee osteoarthritis and stimulating the supply of nutrients to the periarticular tissue: swimming, hiking, skiing, Nordic walking, cycling.
Excess weight 4 times increases the likelihood of osteoarthritis, meniscus tears and cartilage micro-injuries. Slow down the pace of destructive processes and contribute to weight loss: limited salt intake, vegetables and greens, filling meals, dairy products, lean cheeses, lean meats.
Symptoms of gonarthrosis
The severity and duration of the symptoms, the external changes in the knee joint and the intensity of the pain arising from the inflammation of the joint depend on the stage of the destructive process.
The cartilage changes are small, their surface becomes dry and microtraumas occur. Osteophytes (bony outgrowths) can be seen on x-rays. Pain occurs after exercise, climbing stairs or in wet weather. The kneecap is not deformed and the morning stiffness disappears after a few movements.
Osteoarthritis pain: what to do, what mistakes you can make
If you feel the onset of pain or a crunching sensation, you should consult your family doctor, rheumatologist or orthopaedist. Symptoms of gonarthrosis can be confused with arthritis (inflammatory process), gout (salt deposit). Each pathology is treated differently. Only the doctor can distinguish between these diseases after an X-ray and an ultrasound scan of the knee.
- In osteoarthritis, NSAIDs are prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation. The new generation drugs are less toxic and stimulate the production of intercellular cartilage.
- Corticosteroid injections are used for synovitis.
- Hyaluronic acid injections stimulate cartilage repair, reduce pain and improve mobility of the knee joint. After an intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid, the pain disappeared for about six months.
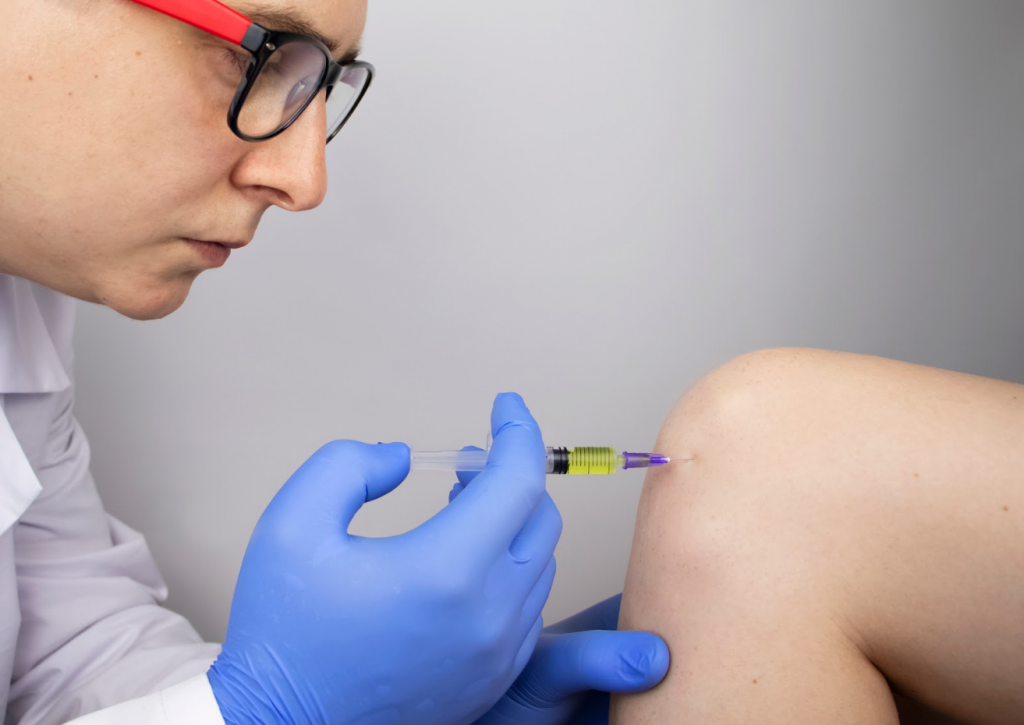
- Anti-enzyme drugs inhibit the production of cartilage-destroying enzymes.
- Chondroprotectors slow down the degenerative process and stimulate the regeneration of cartilage tissue.
- Physiotherapy eliminates contractures, strengthens weak muscles, relieves pain and improves joint mobility.
- Shock wave therapy eliminates osteophytes. Pain decreases and range of motion increases.
- Myostimulation reduces venous congestion and pain and improves metabolism.
- Ultraphonophoresis enhances the effect of hormonal, anti-inflammatory drugs (hydrocortisone, dimethicone).
- Plasmolifting is used to regenerate cartilage tissue. When plasma is injected into the joints, synovial fluid production improves, micro-injuries heal and pain is relieved.
- Kinesio taping – elastic bands relieve tension and pain, improve blood circulation.
- Endoprosthetics are indicated for stage 3 and 4 osteoarthritis. The life expectancy of the endoprosthesis is 15 years.
'Minimalist Shoe'
There are also some models on the market: very thin sneakers with a very flexible sole. These simulate walking barefoot: they have no ankle or ankle support. They are now recommended by progressive orthopedists as the best option for treating joint fluid deficiency and osteoarthritis.
The best way to stop osteoarthritis of the lower limbs from progressing is to go barefoot.
5 rules for footwear for osteoarthritis
- The shoes must be the right size for you - length, width and fullness of the foot. They must be neither too loose nor too tight, otherwise you risk putting extra strain on your feet.
- The distance between the toes of the shoes or sneakers and your biggest toe should be at least 1 cm.
- Instead of laces and buckles that are uncomfortable to put on, opt for a solution with elastic inserts.
- Pay attention to soft material: heavy leather models have a negative effect on joint function.
- Avoid unstable flip-flops and overly fashionable shoes with narrow toes or heels: all of these put additional strain on the musculoskeletal system.
An experienced trauma therapist will answer your most burning questions about footwear choices:
The short conclusion
Well-fitting footwear for arthrosis in combination with orthoses alleviates the symptoms. The cushioning of the movement relieves the spine and improves the general well-being of the patient. In the prevention of cartilage deformation, the choice of sports and modeling shoes should be strict. Quality materials and comfort should be the priority. Blisters and corns should not form when worn.
To reduce the stress on your ankles, choose shoes with a soft, flexible sole. When walking, it absorbs the impact that occurs when the heel touches the ground and is transmitted to all joints of the foot. Heels should be low and always wide. This makes the shoe more stable and reduces the risk of twisting your foot. These are usually not noticed, but can seriously injure the already worn cartilage. High heels are absolutely contraindicated for arthrosis in the knees, hips or spine.
- Pain relievers, especially nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These relieve the pain quickly. However, they have a number of side effects and, first of all, they have a negative effect on articular cartilage, accelerating its destruction. Therefore, they are used at short intervals and only when necessary.
- chondroprotectors. These drugs slow down the destruction of articular cartilage and increase its strength and elasticity. Chondroprotectors should be used in courses of 3-6 months, followed by a long break.
Description
These are the first insoles in Russia indicated for knee joint pain.
They reduce the progression of osteoarthritis in the inner part of the knee joints. The special 4-layer frame has an increase of 3 mm to 5 mm on the outside (under the metatarsophalangeal joints 3, 4, 5). It transfers the load to the less affected (outer) part of the knee and relieves the inner part of the foot when walking. The insoles change the position of the foot and improve gait mechanics, resulting in less stress on the knee joints.
The main purpose of these insoles is to relieve persistent pain and slow joint destruction. They can be used to treat osteoarthritis and also for prevention.
What to do at the first sign of joint disease?
Most of the tips above apply to people with perfectly healthy joints, but what about those experiencing pain, stiffness and limited mobility? In this case, you should do something different, trying to reduce the load on the painful area and not overload the joint. Regular exercise should be avoided, as should other activities that put stress on the affected area - knitting, sewing, gardening, and lifting weights. Talk to your doctor about the possibility of doing special exercises.
In addition, your doctor may recommend purchasing orthotics or a cane. The former help relieve pressure on the legs and spine, while the latter reduce stress on the leg joints. For some people it makes sense to wear a special orthosis that stabilizes the joint and fixes it in the correct position. Such measures will help slow the progression of the disease, but this, too, should be discussed with a specialist doctor. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and chondroprotectors prescribed by the doctor help to stop the destruction of the mobile joints in the skeleton.
What to eat when you have arthritis
With arthritis, it is important that the body produces enough prostaglandins and antibodies. Therefore, in the case of arthrosis or knee arthrosis, foods with vitamins A, B, C and E as well as essential fatty acids should be included in the diet. These include eggs, fish, dairy, fruits and vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and sprouted wheat.
Eat lean meat, but avoid fried, salty, or sweet foods. Eat small portions and drink up to 2 liters of clean water per day. It is also important to wear low-heeled shoes, avoid sitting 'leg to leg' for long periods of time, strengthen and relieve knees, and dress appropriately for the weather. This is the only way the body can reduce inflammation quickly and prevent the development of arthrosis or other complications!
Function and structure of the kneecap

Knee pads for osteoarthritis are orthopedic aids that support the knee joint and ligaments in the correct anatomical position, delaying the onset of discomfort and making walking easier.
According to medical research, the main causes of osteoarthritis are trauma and improper mechanical loading of the knee. Excessive loading leads to degenerative-dystrophic changes and premature destruction of the tissue structures of the joint, so that it requires additional support and support.
Knee pads for arthrosis are an excellent alternative to basic therapy. They are partially equipped with fixators that transfer the load to a support mechanism and evenly distribute it to all parts of the knee (cartilage, meniscus, ligaments) and normalize the correct position of the joint. Thanks to the tight fit, they reduce pain.
Wearing the product is beneficial:
The knee socks have an undeniable advantage over elastic bandages: there is no need to re-bandage the bandage with a calculation of the acceptable tension. The product can be worn from 2 to 8 hours a day, depending on the model. It is recommended to wear them before vigorous physical activity.
knee pad
There are several types of knee pads. Each model has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. The main difference is in the method of attachment.
closed type
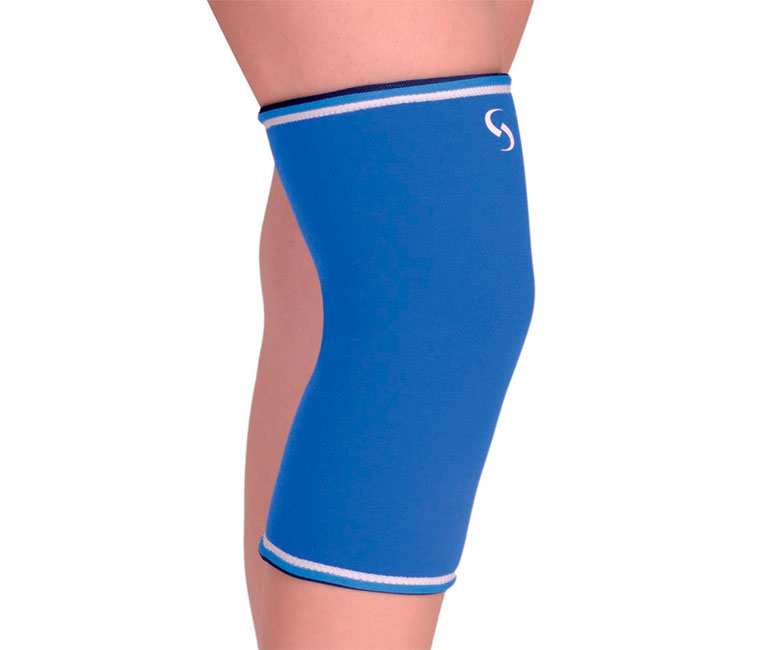
This type offers semi-rigid or soft support. It covers a large area of the leg and offers a good fit and a warming effect. The knee pads are usually made of elastic material, sometimes with additional insulation. They are suitable for non-localized knee pain.
- Complete all-around immobilisation;
- helps to overcome the pain in the knee;
- improves blood circulation and acts like a micromassage;
- comfortable to wear.
open type
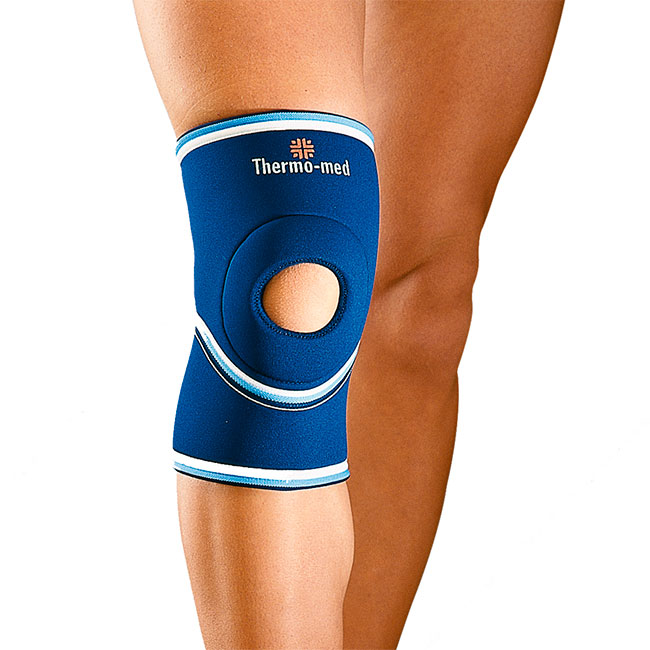
Usually provides a soft fixation of the device. The design includes special ribs to alleviate the stress. The bandage has indentations in the kneecap area. The knee bandage is suitable for non-severe pain or occasional discomfort under the kneecap.
rail type
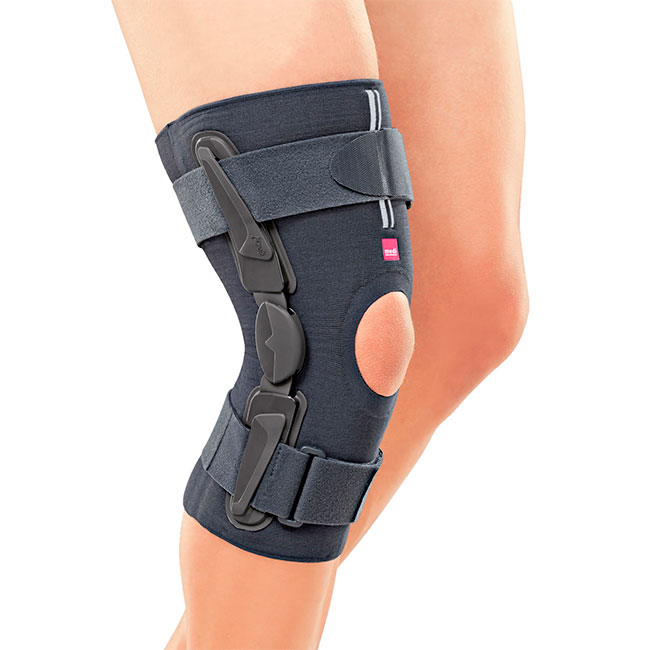
The product can be semi-rigid or rigid. In the area of lateral flexion there are rigid metal feet embedded in elastic fabric. The joints of these kneecaps are free to move (no restriction of forward/backward movement) and polycentric (restriction of movement in all directions). There are straps to regulate the snug fit. This type is considered quite universal, since it is prescribed for all forms of arthrosis.
Treatment in the Health Energy Clinic
If your knee starts to grind or whine suspiciously after exercising, you should see an orthopedist as soon as possible. Health Energy Clinic offers patients the most desirable and effective treatments for the early stages of osteoarthritis:
- modern drug therapies for cartilage development and pain relief;
- Intra-articular injection of drugs for rapid pain relief;
- physiotherapeutic techniques;
- Therapeutic exercises under the guidance of an experienced trainer;
- professional massage;
- PRP therapy;
- Injection of artificial synovial fluid to promote mobility.
All treatment and prevention methods are selected individually based on the findings.
Benefits of the clinic
The Health Energy Clinic has state-of-the-art equipment for diagnosing and treating a variety of diseases. We offer every customer:
- comprehensive screening programs to detect various diseases;
- effective laboratory diagnostic and instrumental methods;
- modern disease management that includes not only medication but also physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage and nutritional advice;
- Consultations with highly qualified specialists;
- flawless execution of medical interventions;
- pleasant conditions and maximum comfort in the clinic;
- reasonable prices for all services.
Your health is your greatest asset. We will help you restore and strengthen them. Take the first step towards optimal well-being, make an appointment with The Energy of Health!
Read more:- Ellipsoid in knee osteoarthritis.
- How to wear a knee brace for osteoarthritis.
- Insoles for knee osteoarthritis.
- Correct wearing of an ankle bandage.
- Rupture of the medial collateral ligament.
- recurrence of joints.
- What kind of doctor treats the joints.
- patellofemoral fold.
