A hernia can also be diagnosed through a geniography. The examination is considered positive if the hernial sac 'bulges' against the normal abdominal contour after administration of a contrast agent.

- Why does my head hurt after training?
- 1) Pain that occurs in response to intense exertion.
- 2. Pain associated with chronic illnesses
- Why does the head hurt after exercise?
- Pain during exercise
- Pain caused by a muscle being strained under strain
- Pain – burning during exercise
- joint pain
- Muscle pain after exercise
- Why do muscles hurt the next day?
- Is it harmful?
- Muscle soreness after training: good or bad?
- How can I relieve muscle pain?
- Is it worth putting up with muscle pain?
- Crepitation (microdamage to muscle tissue)
- Other news
- Did you not find what you were looking for?
- The most common causes of back pain
- Treatment
- diagnostic procedures
- X-ray examination
- Investigation
- Conservative treatment
- What accompanying symptoms can accompany the pain?
- Which doctors you should see
- Treatment of muscle pain
Why does my head hurt after training?
This unpleasant symptom can occur after both endurance training and strength training. And sometimes even after a yoga class. How does this happen? And what should you do if you get a headache after a workout?
Doctors distinguish two types of post-exercise headaches.
1) Pain that occurs in response to intense exertion.
These are the so-called primary headaches, which can occur even in completely healthy people.
'Primary headaches are usually harmless, have nothing to do with any illness and can be treated simply by taking medication or changing exercise intensity,' explains Fedor Mikhnevich, a sports medicine doctor. – comments Fedor Mikhnevich, general practitioner at the GMS clinic.
This headache often resembles a throbbing headache that occurs during or after an intense workout. It is usually bilateral - for example a 'throbbing' feeling in the temples after an intense run.
'Most often, this symptom occurs after intense running, cardio or plyometric exercises (these are exercises that can simultaneously increase muscle strength and overall endurance and burn maximum fat)' explains Greg Zheja. – says Gregory Zheja, doctor of physiotherapy and sports medicine at the SportMedica clinic.
2. Pain associated with chronic illnesses
'They are caused by health problems: related to the brain (bleeding, tumor) or external to the brain (e.g. arterial heart disease). Secondary headaches may require urgent medical attention' – notes Fedor Mikhnevich.
Secondary headaches can feel similar to primary headaches, but are often accompanied by other symptoms: vomiting, loss of consciousness, double vision, and excessive tension in the neck muscles.
Read more:'Primary headaches can occur within five minutes of starting exercise but do not last very long. Secondary headaches will plague you for at least a day, sometimes even several days, after exercise'. – comments Fedor Mikhnevich.
Why does the head hurt after exercise?
Primary headaches after exercise can occur for a variety of reasons. Let's look at the most important of them.
'There are several possible causes: increased pressure in the body due to the absorption of a load (can occur in conjunction with a reaction to increased air pressure), vasospasm (along with the blood vessels of the brain), various restrictions in the mobility of the cervical spine (compression of the canals and bundles of the nervous system). Headaches have little to do with the type of training itself, as they can occur with a variety of types of training - cardio, strength and even functional training, says Ruslan Panov, a methodology expert at the X-Fit network in Russia.
Pain during exercise
Pain caused by a muscle being strained under strain
This happens when a muscle is stretched under a weight load. For example, the stretched glutes and the back of the thigh during the Romanian pull-up. It is a diffuse pain throughout the muscle, as if it was being pulled away from the bone (figuratively speaking). A moderate sensation is normal. In addition, it is recognized that the controlled stretching of the muscle under load is one of the additional stimuli for muscle growth. Therefore, there is even a separate type of training based on 'negative', in which the stretching phase of the muscle is intentionally prolonged under load.
Pain – burning during exercise
A strong burning sensation occurs when the muscle is stressed for a long period of time, i.e. 12 or more repetitions. Somewhere in the middle of the exercise the burning sensation occurs and then increases with each repetition until it becomes so unbearable that it is impossible to continue.
The muscle cells are no longer supplied with oxygen and become acidic due to the breakdown products of glucose, the main fuel for muscle activity. This chemical poisoning is also one of the incentives for muscle growth, so training for stitches is effective (even if they are not very pleasant).
joint pain
Another type of pain during exercise is a sharp, needle-like pain in the joint that increases rapidly with each repetition. Many people train to combat the pain by using bandages, braces, bandages, warm-up ointments, and painkillers. However, the pain is a signal that it is unsafe to continue movement.
Joint pain (and likely subsequent injuries as a result) can be the result of poor technique, potentially dangerous or simply unnatural exercises for the joints, incomplete recovery of not only muscles but also connective tissue between training sessions, poor warm-up before training, poor posture and incorrect joint alignment.
Muscle pain after exercise
Everyone waits until morning to check how well their training went. Many people think that the harder it is to run after 'leg day', the better for building muscle. There is a direct connection between this and this. And when pain = growth, creping becomes the ultimate goal of training. But there is no direct connection, and pain is not a prerequisite for muscle growth and in some cases even hinders it.
Why do muscles hurt the next day?
Muscle soreness usually occurs 6-24 hours after training and subsides within a few days. It can be very strong or barely noticeable. Most often, crepitus occurs when you have put more strain on your muscles than usual: you have increased your work weights or started training again after a break.
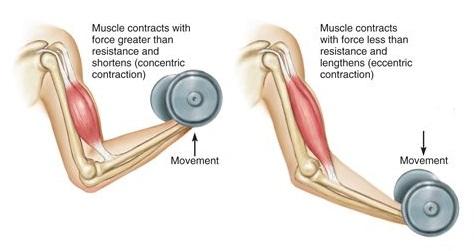
The pain most often occurs after exercises that heavily emphasize the eccentric phase (stretching of the muscle under strain).
For example, when you lift a barbell onto your biceps, the muscle contracts and becomes shorter. As you lower the dumbbell, the weight of the dumbbell stretches the muscle. During this phase, called the eccentric phase, micro-damage to the muscle fibers occurs.
It is now recognized that delayed pain is the result of inflammation following microdamage to the muscle and the body's immune response.
Sometimes you still hear that the muscles hurt 'in the morning' because of the lactic acid, but this is eliminated from the body within an hour after training.
Is it harmful?
There is the concept of the inverted U-curve, which shows the dose dependence of the effect. Too little is bad and ineffective, too much is also bad, and anything in between is best.
Muscle soreness after training: good or bad?
Muscle soreness cannot be used as a criterion for assessing the effectiveness of a workout. If there is no pain, it does not mean that muscle growth has stopped. Therefore, you should not concentrate on the pain. It is better to evaluate the actual results that you can see in the mirror.
To avoid pain syndrome, you should:
- follow your training technique;
- increase the load gradually and change regularly;
- start with warm-up exercises to prepare your muscles and joints for further stress;
- at the end of training, perform stretching and relaxation exercises to stimulate blood circulation and accelerate the removal of damaged cells;
- Drink at least 2 liters of water per day - it thins the blood and increases the flow of nerve impulses.
Things that can help with post-workout pain include:
- Healthy diet – the diet should contain enough protein;
- Massage – stimulates blood circulation and promotes the flow of nutrients and blood to affected areas;
- compression knitting;
- warming ointments;
- visits to a bath or sauna;
- take a warm bath;
- contrast showers;
- To swim;
- taking sports supplements;
- 2-4 days of rest - so that the tissue can recover.
How can I relieve muscle pain?
Professional trainers recommend several ways to relieve muscle soreness.
- After training, you can go to the sauna or steam room: many fitness clubs today have steam rooms (e.g. the Premium Fitness Club La salute (The premium fitness club La Salute, for example, offers its guests not only saunas, but also unique Roman baths). The heat has a soothing effect on your muscles and helps you relax. If this is not possible, a warm (but not hot!) bath with sea salt is a good idea.
- Massages with essential oils, e.g. B. Rosemary, can help relieve the pain. The most important thing is not to overdo it: the pressure should be moderate,
- For very severe muscle pain, pain-relieving ointments and creams that you can buy at the pharmacy can help.
But muscle pain can not only be treated, but also prevented. Don't neglect warming up before exercise and stretching afterward. A healthy diet can also play an important role: try to eat more nuts and legumes. On the other hand, avoid sweets and meat as much as possible. Muscle pain can be made worse by stress, so try to come to training calm and in a good mood. And of course, you should train under the guidance of an experienced trainer who can help you find the optimal level of exertion.
Is it worth putting up with muscle pain?
Some sports and fitness enthusiasts find muscle pain pleasant: for them, it is a sign that they have performed well. If the pain is not very unpleasant, it can be tolerated. Only take action if the discomfort makes you feel uncomfortable all over your body. By the way, if you don't feel any muscle pain at all after a workout, it could mean that you're not exercising well. The strain is probably too weak and too unfamiliar for your body.
If your muscles hurt, it means that they have not yet recovered from the previous stress. Don't put them under any additional stress just yet. However, you don't have to give up going to the gym: you can simply train a different muscle group or reduce the load. Ask your trainer to do a series of exercises that will improve blood circulation. This allows your muscles to recover faster.
Crepitation (microdamage to muscle tissue)
The pain occurs within the first 24 hours after exercise and lasts about 5-7 days. The most common cause of microtrauma is eccentric movements when lowering the device and relaxing the tense muscle.
When does creping occur?
- For beginners who are just starting training and have an untrained body
- When you have taken a break from training.
- After a new exercise with a different muscle combination
- When you increase the duration, frequency or intensity of your workouts.
What helps relieve pain?
- massage
- physical therapy
- Light training (with 50 % of usual load)
- Warm-up exercises (stretching exercises)
- A diet rich in protein products.
Training under the guidance of an LFC trainer or doctor can make physical activity safer and more beneficial for you.
Other news
Did you not find what you were looking for?
The materials and prices on this website are for informational and educational purposes only and do not constitute a public offer within the meaning of Article 437 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. They should not be relied on as medical advice by visitors to this website. The diagnosis and the choice of treatment is left to the doctor alone! The company is not responsible for any negative consequences that may result from the use of the information.
By concluding this Agreement and leaving data on kit-clinic.ru (hereinafter referred to as the 'Site') by filling out the form fields, the User
- Confirms that all data he/she provides belongs to him/her personally;
- confirms and acknowledges that he has carefully read the agreement and the conditions for the processing of his personal data that he indicated in the form fields, the text of the agreement and the conditions for the processing of the personal data are clear to him;
- consents to the processing by the contracting party of the personal data provided as part of the information for the purpose of entering into a contract between itself and the contracting party and the subsequent performance of that contract;
- agrees to the conditions for processing personal data.
The owner of the kit-clinic.ru website is LLC Beka-Invest
INN 7735598132, OTR 5137746131518
Legal address: Russia, 125466, Moscow, Yurovskaya Street, 93, bld. 1
Postal address: 93, Yurovskaya Street, bld. 1, Moscow, 125466, RussiaThe user consents to the processing of his personal data in order to carry out the activities provided for in paragraph 3. 3 ч. 1, Art. 3 of the Federal Law of July 27, 2006 N 152-FZ “On Personal Data”, and confirms that in giving this consent he/she acts freely, voluntarily and in his/her own interests.
The user's consent to the processing of personal data is specific, informed and consensual.
The most common causes of back pain
Unfortunately, many people suffer from pain caused by serious back problems - exercise only makes the disease worse. The most common causes of back pain during exertion are probably the following.
Myositis. A chronic or acute inflammation of muscle fibers that often occurs in people who do not exercise and lead a sedentary lifestyle.
If, in addition to the pain, you notice a severe limitation in your range of motion and a deterioration in your general condition, you should visit a health center in your area as soon as possible to receive a diagnosis and a treatment plan.
Treatment
To reduce the intensity of lower back pain after sports, two recommendations should be followed: eliminating the cause and using pain ointments. If this doesn't help, you should see a doctor.
As a topical treatment, it is recommended to treat the lower back area with Dolgit, Finalgon, Butadione and other ointments and gels with the same effect.
The list of funds is very extensive, but they do not differ in effectiveness. The price difference is due to the popularity of the brands and the success of the manufacturers' advertising campaigns. Inflammatory processes in the nerve fibers are treated with non-steroidal drugs.
There are many ointments for back pain. They all have different compositions and active ingredients. Some have a cooling effect, others have an immediate warming effect and it takes a long time for the pain-relieving effect to take effect. To choose the right ointment, we recommend that you read the detailed article on our website.
diagnostic procedures
Without a correct diagnosis and identification of the cause of pain, it is impossible to effectively localize or eliminate it.
X-ray examination
There are several traditional methods for diagnosing the condition of the spine in certain pathologies. In the initial phase of the examination, x-rays are taken in standard positions of the spine. The doctor can detect abnormalities in the physiology of the vertebrae or parts of the spine, detect bone degeneration in a timely manner and identify unnatural changes in the intervertebral discs. In some cases, the diagnosis is made of metastatic spinal lesions.
Investigation
The physical examination of the patient with sports hernia/athletic pubic bone disease begins with palpation of possible injury sites. In athletes, pain in the lower abdomen, in the adductor area and pain on palpation in the area of the pubic symphysis are characteristic. When examining the patient, painful sensations may be noted at or just above the pubic symphysis, near the insertion point of the rectus abdominis muscle or the adductors of the thigh. The rectus abdominis, oblique abdominis and transversal abdominis as well as the tendon insertions should also be palpated. The Valsalva test with sneezing or coughing can help reproduce the symptoms.
Sensory disturbances and dysesthesias in the lower abdomen, groin, anterior thigh, and genital area may occur when the iliac-femoral nerve, iliopsoas nerve, and femoral nerve are compressed.
Limitation of hip rotation, flexion, and adduction may indicate hip impingement syndrome. Various tests, particularly the anterior impingement syndrome test, which indicates pain during flexion, extension, and internal rotation of the hip, may also indicate an abnormality in the hip joint. The patient may have weakness of the adductor and flexor muscles of the hip joint during movement. A gait analysis can help detect abnormalities in pelvic movement and axial deviations of the lower limbs.
Examination of patients with pubalgia may include four pain provocation tests: unilateral adductor test, compression test, bilateral adductor tests, and resisted squats.
For the unilateral adductor test, the patient must lie on his back (hips extended and flexed to 80 degrees). The test is considered positive if the patient feels a deep, stabbing pain in the groin on the opposite side when attempting to bring the legs together and overcome resistance.
Conservative treatment
In general, conservative treatment of pubic inflammation should last at least three months, after which surgery may be considered. During the season, athletes may need to take a four-week rest break. Pharmacological treatment includes taking NSAIDs and oral steroids (with gradual dose reduction). Injections of selective corticosteroids or platelet-rich plasma directly into the insertion site of the rectus abdominis or adductor longus muscles are also performed. After the rest period, the patient can exercise again.
If the patient still experiences pain after physical therapy, exploratory surgery and surgical repair is indicated.
There are many types of operations, so it is difficult to compare their results. Most techniques produce convincing results that are reflected in the literature. Surgical principles include strengthening the posterior wall of the inguinal canal and strengthening the rectus abdominis muscle or associated tendon. Another type of surgical treatment is laparoscopy. This technique uses an endoscope to reconstruct damaged tissue behind the pubic bone and/or behind the inguinal canal.
According to Paajanen et al. Laparoscopic surgery for pubic inflammation in athletes is more effective than conservative treatment. After surgery, pain decreases within a month, and 90 % of the operated athletes return fully to their training program after 3 months.
For pain and dysfunction of the adductors, a tenotomy is recommended. Hip surgery may also be considered if the athlete has abnormalities in this area. It is believed that full recovery and return to sport is possible within 6-8 weeks if only pubic bone inflammation is present. If the patient was operated on for femoroacetabular impingement in addition to pubic bone irritation, recovery takes 4 months.
What accompanying symptoms can accompany the pain?
Amateur runners often not only experience lower back pain, but also accompanying symptoms if they are not trained properly. They all signal inflammatory processes in the body and impaired blood circulation.
The most common injuries in runners
There are also cases when during training the Transverse processes of the lumbar spine the lumbar spine tears and begins to press on nerve endings. However, this is an isolated case that just shows that you don't know the sport of running or your own body at all.
Headaches occur when there is poor blood exchange in the arms and neck. This most often happens when the shoulders don't move and are quite high during the run. To avoid this, simply keep them relaxed by moving them freely. And if you feel discomfort in your shoulders, try wringing and shaking your arms.
An increase in general body temperature indicates that an active inflammatory process is taking place in one of the body systems. It can be in the lower back, but also a muscle strain or a ligament injury.
Pain in the thoracic and cervical spine is usually caused by flat feet and poor posture. You need running shoe inserts, good cushioning in your running shoes and proper back posture - you should be looking straight ahead, not at the sidewalk, your head should be tilted up and your shoulders should remain straight.
Which doctors you should see
Before you start exercising, you should consult your family doctor and your cardiologist. Your doctor will analyze your symptoms, carry out an external examination and refer you for further tests with laboratory blood or urine samples.
If health problems are identified, the type of exercise should be reviewed based on the doctor's recommendations and an appropriate type and program of exercises and various special exercises should be selected.
In most cases, muscle pain goes away on its own after exercise. Muscle pain after exercise very rarely requires medical attention, but occasionally there are situations where you need to see a doctor. For example, if you have acute muscle pain that lasts for a long period of time after strength training. A doctor's consultation and analysis of laboratory results will help select an effective exercise program for the patient to avoid muscle soreness after exercise.
Various symptoms in which a doctor should be consulted immediately
- Muscle soreness a week after exercise and swelling of the upper and lower limbs.
- The color of the urine has taken on an unnaturally dark shade.
- The dull pain became more intense and the muscles became numb.
- Persistent muscle pain in patients with diabetes and kidney disease may be a sign of worsening of the condition.
- Oxygen accumulates in the cells, long processes and reactions lead to myoglobin poisoning of the kidneys, which can severely damage the kidneys or even stop them altogether.
Treatment of muscle pain
If your muscles start to hurt only when the amount of lactate produced after exercise increases, follow these rules to reduce lactate levels:
- Move correctly
Start your workout by warming up your muscles and end it by relaxing to normalize circulation after exercise. Warming up restores blood flow to the muscles after exercise, while warming up before running oxygenates not only the blood, but also muscle tissue, which leads to a reduction in lactate levels.- take breaks
Take rest breaks between physical activities to allow your body to flush lactic acid from your muscles. Light physical activity is recommended, and walks in the fresh air are also helpful. Loading should be increased gradually to reduce the risk of re-injury. A specialist should be consulted.- Dry warmth
If muscle pain persists for more than two days after exercise, warming the muscle with a warm heating pad or towel soaked in warm water can stimulate blood flow and relieve pain.- Stretch
Stretching allows the affected muscles to be slightly stretched and helps them recover more quickly.- Countertreatment
After training, it is advisable to warm up the muscles in water at 40 degrees for fifteen minutes to dilate blood vessels and promote blood flow to muscle tissue. Important: Treatment is not recommended for people suffering from diabetes or cardiovascular disease.- Drinking regime
If your body doesn't drink enough fluids, your muscles will hurt more after exercise. You can determine your fluid needs by multiplying your body weight by thirty milliliters of water. The result is the amount of fluid you need per day.- Balanced nutrition
To reduce unpleasant muscle pain, you should eat more foods with unsaturated fatty acids, as these can only be absorbed by the body through food, as well as so-called protein-rich foods. Excessive consumption of foods containing sugar and salt only contributes to swelling and stagnation.- More sleep
Since inflammatory processes in the body are increased by lack of sleep, it is necessary to rest well and for a long time after sporting activities so that the muscle tissue is refreshed during this time and can work actively again. During sleep, the central nervous system is renewed and the hormone melatonin is released. A good pillow and mattress will help you sleep better. Sleep in complete silence for eight hours every night. If you rest during the day and sleep early in the morning, your body cannot relax enough and therefore needs more time to recover.- Get a massage
A massage relaxes the body by relieving muscle tension, promoting blood circulation and improving mobility. If your muscles are sore after exercise, massage them using a relaxation massage technique with gentle pressure to help them recover. A Swedish massage or an acupressure massage that targets painful points is best. It relaxes the nerves and vessels trapped in the muscles, restores blood circulation and thus accelerates the metabolic processes in which harmful substances are released from the body.
- Why do feet hurt after running?.
- The long fibula muscle hurts.
- muscles in the legs.
- Muscles congest when running.
- Rudder bones hurt after running.
- running hurts.
- Why the legs hurt below the knees after running.
- Lamb Muscle Soreness.