While standing or sitting in a chair, roll first one foot and then the other foot with a round object such as a ball, roller, or exercise bar. While rocking your foot, press the sole of the object firmly into the ground from toe to heel. This exercise increases the flexibility of the foot by stretching the plantar fascia.
- Longitudinal and transverse flatfoot: treatment and symptoms
- How do flat feet occur?
- Symptoms of Flat Feet
- What's wrong with flat feet?
- reports of treatment
- What is a flat foot?
- Top 10 list of effective flatfoot exercises for adults by KP
- Walking on an uneven surface
- Three support positions
- calf stretch
- Yoga for the toes
- Pain is the main symptom of transverse flatfoot
- Methods for correcting transverse flatfoot. Exercises for the foot muscles
- Reinforcement of the arch of the foot
- Exercises for the foot muscles
- Transverse flatfoot surgery
- Combined treatment
- The main part of therapeutic training for flat feet.
- Additional physiotherapy exercises (balance cushion exercises).
- Physical therapy: important points
- Exercises for flat feet
- Complex 1: from the lying position
- Set 2: Sitting on a mat
- Can flat feet be treated with orthoses?
- manufacture of insoles
- Therapeutic exercises for flat feet
- Exercises for transverse flatfoot in adolescents
- THE IMPACT OF FLATFEET ON HUMAN HEALTH. PREVENTION AND CORRECTION
Longitudinal and transverse flatfoot: treatment and symptoms
With longitudinal and transverse flatfoot, the foot is deformed and the arch of the foot becomes flat. The condition causes severe pain in the feet after prolonged walking. Women are four times more likely to suffer from flat feet than men. If left untreated, the disease leads to complications such as spinal curvature, arthritis and osteoarthritis.
How do flat feet occur?
The human foot is a complex structure. The bones of the foot are connected to each other by joints, ligaments and tendons. The foot has two arches: a transverse and a longitudinal arch. The transverse arch is at the base of the toes and the longitudinal arch is at the inner edge of the foot.
Our feet have a unique property - they are elastic. As a result, they reduce the load on the spine when running and walking. When the muscles and ligaments in the foot weaken, it becomes flat and no longer has a cushioning function. This leads to the development of flat feet.
The type of foot deformity is classified as transverse, longitudinal, or combined flatfoot.
Symptoms of Flat Feet
At the Prolonged flat feet The feet tire more quickly after walking or standing, the foot hurts when pressed and swells in the evening. Over time, the longitudinal arch disappears, and the pain in the feet becomes strong and constant; they are also felt in the shins and ankles. The patient has difficulty finding comfortable shoes and buys shoes one size larger. Lower back pain may also occur.
Transverse flatfoot It can be accompanied by pain and a feeling of heaviness in the feet at the end of the day. As the disease progresses, the foot widens and the transverse arch disappears. The skin in the forefoot area hardens and the toes are pressed in.
What's wrong with flat feet?
Flat feet do not relieve the spine and joints when walking and running. This causes the spine to wear and deform faster to protect the brain from impact. Scoliosis, osteochondrosis, intervertebral fractures and radiculitis can occur.
reports of treatment
I would like to thank Dr. Thanks to Koreshkov Marina Kimovna who works professionally and is very helpful and attentive as if he could see right through you! I had a herniated disc in my neck and my shoulder was very weak. Marina Kimovna offered me the right treatment. Already after the first treatment I felt much better. Nice clinic and caring staff. I would like to thank everyone who was involved in my treatment. I HIGHLY RECOMMEND THIS CLINIC.
My flat feet are progressing rapidly. To avoid complications, you should see your doctor if you have pain in your foot. The doctor at Master's Health in St. Petersburg will examine your foot and, through a comprehensive examination, will make an accurate diagnosis. Our specialists use the following diagnostic methods:




What is a flat foot?
With a flat foot, the normal arch of the foot is low or absent on the inside. This makes the foot appear flat and the sole of the foot touches all or most of the ground. The supporting functions of the foot - cushioning and balance - are impaired by the misalignment of the foot.
A flat foot cannot support the body in the correct position and absorb shock when walking and running. While harmless at first glance, flat feet often lead to disorders of the joints, spine and internal organs 3 .
The most characteristic symptoms of flat feet:
- Changes in foot shape: flat feet, bunions on the big toe, too wide foot;
- valgus foot;
- changes in posture and gait;
- Pain in feet, knees and hips 1 .
The most common cause of flat feet is muscle weakness. Less commonly, foot deformities are caused by congenital malformations, nervous system disorders, trauma, or excessive fatigue from prolonged standing. Most children by age 5 have physiological flat feet, which decrease with age and normal foot development 2.

There are 2 main types of flat feet: flexible (movable) and rigid (rigid). In flexible flatfoot, the foot retains the ability to arch but flattens when standing. The flexible flat foot is much more common and in many cases can be corrected, including with therapeutic exercises.
With a rigid flatfoot, the foot cannot form an arch. This is usually a result of the way the bones in the foot are formed. This condition is rare and is unlikely to change with exercise 1 .
A distinction is also made between longitudinal and transverse flatfoot. In longitudinal flatfoot, the foot touches the ground with almost its entire surface and therefore increases in length. In transverse flatfoot, the foot is shorter and wider because the metatarsal bones fan out 1 .
Top 10 list of effective flatfoot exercises for adults by KP
our expert, Physiotherapy and sports medicine doctor, osteopath Yulia Tolmacheva has compiled 10 effective flatfoot exercises for adults. You can do these therapeutic exercises at home anytime. No special equipment is required for training; You can perform it with items that you always have on hand.
Walking on an uneven surface
This exercise requires minimal effort: just walk barefoot. Uneven surfaces at home can be designed using special mats that imitate pebbles, cones, tree roots or spikes. Lay out the mat where you walk most often, for example in front of the kitchen. The irritation of the foot on the uneven surface triggers a protective reflex and contracts the foot muscles.
Three support positions
Starting position: sitting or standing, feet in line, knees pointing forward. Place your feet so that you can feel the three points of support: middle of the heel, base of the little toe, base of the big toe. The balance between these points gives stability to the foot. Maintain this balance for as long as possible.
calf stretch
Stand facing a wall and support yourself with both hands on the wall. Stand the leg to be stretched back with your knee straight and toes pointing forward.
Keep the back leg straight and press the heel firmly to the floor. Lean forward slightly until you feel a stretch in the calf of the back leg. Hold this stretch for 30-60 seconds. Repeat this 4 times for each leg.
For the stretch to be effective, you must not allow your foot to roll inward. This exercise increases ankle flexibility and helps the foot stay in the correct position.
Yoga for the toes
Lift the big toe up and at the same time press the other four toes on the floor. Hold the foot in this position for 5 seconds. Push the big toe down while simultaneously lifting the other four toes. Hold this position for 5 seconds. Repeat the exercise 10 times for each foot.
Pain is the main symptom of transverse flatfoot
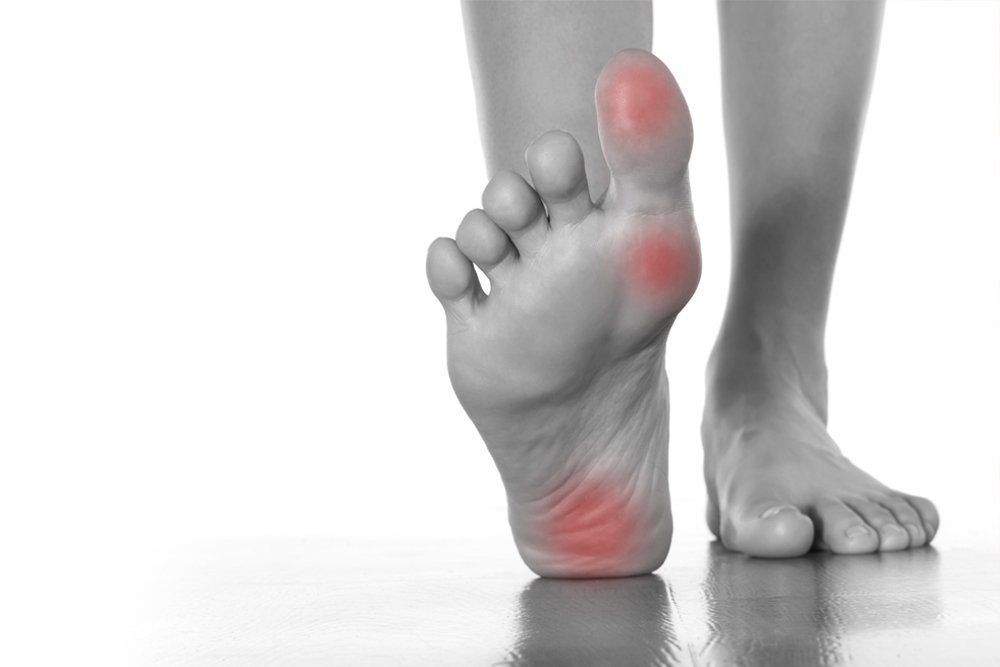
In the early stages, transverse flatfoot may not affect the patient's life in any way. However, if there is no adequate treatment, the pathological processes will cause a number of unpleasant symptoms. Initially, the patient feels a feeling of heaviness in the foot, which occurs after standing or walking for a long time and is triggered by physical exertion. Over time, these symptoms become more and more obvious. Sometimes patients point out the exact location of the pain - the area where the first and second toe meet.
As the disease progresses, the symptoms begin to appear constantly, regardless of exertion or time of day. There is noticeable swelling of the fingers and toes, sometimes extending to the knuckles. The severity of this symptom can vary, sometimes the swelling is barely noticeable. The thickening of the arch of the foot causes severe pain in the calf muscles, which become rock hard. The patient develops corns, that is, hard and dry calluses on the foot. They appear in the places that are most stressed. They mainly appear on the heels, the outside of the feet, the toes and the balls of the feet. As flatfoot progresses, the foot becomes wider and wider, so that the patient can no longer wear conventional shoes because they become uncomfortable and too tight. Attempting to walk in conventional shoes causes a great deal of discomfort and pain.
The classic symptom of transverse flatfoot is the presence of a valgus deformity of the big toe. This condition is also known as 'valgus' or 'bunions' of the foot.
Methods for correcting transverse flatfoot. Exercises for the foot muscles

To date, transverse flatfoot has been diagnosed in patients at a relatively young age. In the early stages, the disease can be treated with conservative therapy methods.
The doctor recommends that patients take measures to correct the arch of the foot, perform daily muscle exercises and use devices to correct the deformity. Physiotherapeutic techniques are also very effective. If the desired result is not achieved or the problem is very pronounced, then surgery is required.
Reinforcement of the arch of the foot
In preventing and correcting transverse flatfoot, it is very important to walk barefoot as often as possible, preferably on different types of surfaces - dirt, grass, rocks and sand. Such walks will help strengthen muscles.
Exercises for the foot muscles
An uncomplicated transverse flat foot can be corrected by systematically performing special muscle exercises:
- While sitting on a chair, slowly bend and straighten the toes;
- Pick up small items off the floor, e.g. B. a pen or a battery;
- spread a small piece of fabric on the floor and squeeze only with your toes; then carefully spread the fabric with your toes as well;
- step on tiptoe and walk around, then walk around the outside of the foot while bending the toes;
- flex and then straighten the foot;
- Squeezing a rubber ball in the foot has a good effect;
- Also moving your feet on the floor in different directions is good;
- Rolling a stick or roller on the floor while tightening the foot muscles.
Transverse flatfoot surgery
In the case of a transverse flatfoot, doctors perform the following corrective procedures On the forefoot. They usually perform an osteotomy (chevron or scarf) of the first metatarsal. If necessary, they supplement this with plastic surgery of the muscles, ligaments and tendons. The operation can correct not only a transverse but also a valgus deformity of the foot.
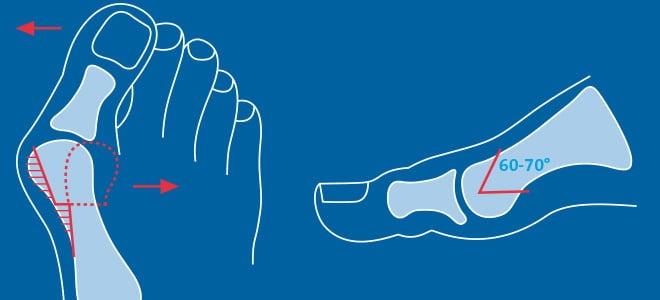
Doctors often find patients with exostoses (bone outgrowths) and hammer toe deformities of fingers II-V. The former are removed using the Schede method, the latter are corrected by resection or osteotomy. Multiple surgical procedures can therefore be performed simultaneously in patients with transverse flatfoot. This procedure can improve the quality of the correction of existing defects.
Combined treatment
The transverse-longitudinal flatfoot is the most severe form of the disease. Both arches of the foot are deformed at the same time and the foot becomes completely flat. This pathology is difficult to treat.
The goals of combined flatfoot surgery are.
- The restoration of the arch of the foot;
- Safe, permanent bone immobilization;
- Correction of deformity of the first toe;
- elimination of exostoses;
- Correction of the malposition of the hammer toe.
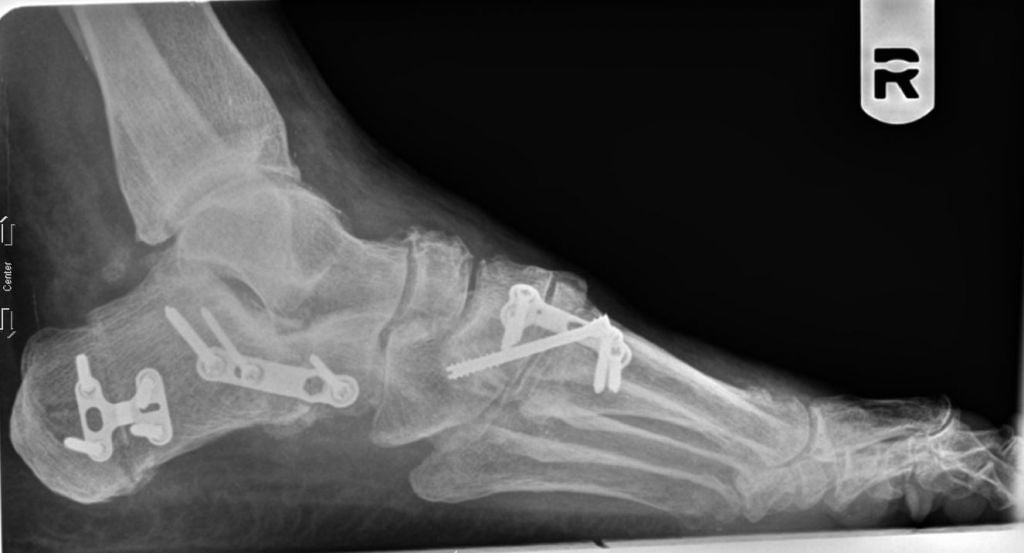
Operations for longitudinal and transverse deformities.
In the case of longitudinal transverse flatfoot, several interventions are carried out at the same time. For example, a patient may have Schede surgery, a Scarf osteotomy, and arthrodesis of some metatarsal joints performed at the same time. Doctors usually try to do everything in a single operation.
The recovery time after such operations is longer than in other cases. Fortunately, the patients do not need a cast or crutches. In the worst case, they have to go with fixation pins, which are removed along with the threads after 2 weeks.
Severe longitudinal flatfoot requires posterior tibial tendonoplasty and marginal subcutaneous tenotomy of the Achilles tendon. After the operation, the patient is placed in a plaster cast and can only walk on crutches.
The main part of therapeutic training for flat feet.
- Alternating extension and flexion of the toes until contact with the surface (Exercise 4)
- Roll a tennis ball over the sole of your foot. perform movements alternately with one foot and then the other (exercise 5);
- grasping and carrying small objects with toes and feet (Exercise 6);
- Moving the foot on a flat surface by alternately flexing and extending the toes (Exercise 7);
- Toes together on sole of foot - maximum flexion and extension in knee and ankle joints (Exercise 8);
- One sole of one foot on the inside of the opposite shin (Exercise 9);
- sitting, legs bent at the knees, heels pressed firmly to the floor, using toe movements to lift the mat from the fabric (Exercise 10);
- sitting, bend and stretch your feet together and alternately (exercise 11);
With increasing strengthening of the musculoskeletal system, one can proceed to a group of additional exercises.
Additional physiotherapy exercises (balance cushion exercises).
Exercises with the balance cushion strengthen the muscles of the lower leg and the arch of the foot, train the vestibular system and improve the sense of balance.
- Stand on the balance cushion and raise yourself on tiptoe 10-15 times (Exercise 13);
- stand with one leg on the balancing cushion and keep your balance for 1-2 minutes, repeat with the other leg (exercise 14)
- climb up and down the step on which the balancing cushion lies, 10-15 times (Exercise 15);
- sit on a chair, put a pillow under your feet, stand up 10-15 times, trying not to support yourself with your hands (exercise 16).
Regular physiotherapy for flat feet and wearing comfortable shoes with orthopedic insoles will help avoid deformities in the early stages of foot formation. In combination with general strengthening exercises, it promotes the formation of a correct posture. In advanced cases, therapeutic exercises can help stop the development of flat feet, eliminate pain in the muscles and joints of the legs, and improve the entire musculoskeletal system.
Physical therapy: important points
Therapeutic exercises for flat feet serve the conservative treatment of the orthopedic condition. It is suitable for people under the age of 14 because changing the shape of the foot in adults without surgery is difficult due to the complete ossification of the metatarsals and other bony structures.
Regularly performing a series of exercises for flat feet can halt the progression of the disease and reduce the severity of pain with movement. The training has a positive effect on muscle tone and increases the flexibility of the ligaments, so the cushioning function of the foot is partially restored. The main goals of physical therapy for flat feet include:
- elimination of the main symptoms of the disease;
- Strengthening of the muscles and ligaments of the foot;
- prevention of further deformation of the metatarsal;
- Restoring the balance and spring function of the foot.
Before starting the exercises, a podiatrist should be consulted to find out what exercises should be done for flat feet in adults and how often.
The effectiveness of the exercises depends on how regularly they are performed. Podiatrists recommend exercising for 15 minutes or at least 20-25 minutes a day if you have obvious bone deformities. According to practical observations, flatfoot exercises are most effective in flattening the longitudinal arch of the foot. Most exercises are designed to strengthen the foot and lower leg muscles, the elasticity of which determines the shape of the tarsal and metatarsal, as well as the heel and talus bones.
Also Read: Can You Walk With Flat Feet?
Exercises for flat feet
Gymnastics is a method of physiotherapy that will bring positive results only if it is practiced systematically and over a long period of time. In the treatment of flat feet, with regular gymnastics, the desired therapeutic effect can be achieved within 2-3 years. At the same time, self-massage to improve blood circulation in the limbs is recommended, as is the use of orthopedic shoes or insoles.
Complex 1: from the lying position
The first exercises for flat feet can only be done in the supine position. This prevents injuries and overtraining of the muscles. For regular exercise, buy an exercise mat or thin mattress.
- Sitting on the floor, lift your right leg off the floor and bend it at the knee;
- Slowly draw your toes toward you while turning your feet inward;
- Lift your heels off the floor and try to touch the floor with your toes;
- Touch one foot to the surface of the other foot, then return to the starting position.
The above exercises can be used for both lateral and longitudinal flat feet. They are a great way to warm up muscles and prevent weight training injuries.
Set 2: Sitting on a mat
To counteract the flattening of the metatarsal bones and increase the arch of the foot, it is advisable to perform the exercises while seated:
- Bend your knees and then alternately bend the toes of your feet;
- With your muscles relaxed, pull your toes toward you and then away from you;
- Lift your limbs off the ground and bring them closer together so your feet are touching;
- Kneel with your toes touching the floor and your heels together and apart.
Can flat feet be treated with orthoses?
The initial stage of flat feet, without accompanying foot deformities and without arthrosis, can be treated with orthotics or orthotic shoes. Orthoses should only be made individually. They are worn at least 5 to 6 hours a day. Treatment lasts 2 to 4 years and longer. The desired results are achieved in 60 % of the patients. For the rest, the situation is improving, but the disease is not completely cured.
- Perfect adaptation to the sole of the foot;
- No areas of increased pressure on the foot that can lead to structural changes in the soft tissue structures over time;
- Creating the conditions for training the arch muscles when walking.
Custom orthotics affect muscle tone, joint alignment, and tendon tension. They also influence proprioceptive sensitivity and contribute to better control of body dynamics. Good insoles not only alleviate symptoms and correct foot deformities, but also improve posture and form a correct gait.
manufacture of insoles
The basic elements for the manufacture of insoles against flat feet:

making insoles
When planning IUDs, a distinction is made between mechanical and computer-aided methods. Although the mechanical method was historically the first, the computerized method is now being used more and more in modern clinics.
With the mechanical method, an impression of the foot is taken. An orthosis is then made on this basis. However, this method has one fundamental drawback - it does not take into account the load on the foot when walking. The impression is taken in a static body position. During walking, the congested areas shift, and this varies from person to person. The incision is corrected subjectively, based on the patient's feeling and not on objective measurements.
The computerized method is more accurate. Pedobarography is performed using a special device. A number of parameters are evaluated: the location of the patient's center of gravity, the direction of the gait and the patient's gait. There are 5 zones with the greatest load on the sole of the foot:
- toes;
- Metatarsal bones (metatarsophalangeal joints, rolling axis of the foot);
- medial area (medial);
- medial lateral area;
- the heel area, which provides axial support.
Based on the results obtained, the structure of the integral load diagrams is evaluated. The insole model is prepared for production. After the production, the orthosis is adjusted to the patient not according to his feeling, but on the basis of the pedobarography and photoplantometry data.
The use of custom-made orthoses leads to positive treatment results in 85 percent of patients after 1.5 years. Muscle pain and fatigue when walking are reduced or disappear. The measurements show an increase in the height of the arch of the foot. Further treatment can be done with other insoles. The examination is repeated, the insoles are made according to the changed foot configuration. A person can recover from their flat feet within a few years, after which there is no need for additional insoles.
Therapeutic exercises for flat feet
LFK (therapeutic exercises) help to combat flat feet. LFK improves blood circulation in the lower limbs, strengthens the muscles of the legs, back, abdomen and chest, increases musculoskeletal strength and flexibility, and helps form the correct arch alignment. The physiotherapy courses are carried out after consultation with an orthopedic surgeon to determine the correct alignment of the foot. Physical therapy for flat feet begins with a warm-up session. After warming up, foot exercises and general strengthening exercises are started. The LFC exercises should be carried out daily, because only then can one assume that the method is effective.
- lower leg and thigh exercises;
- strengthening of the metatarsal bones;
- exercises to strengthen the ligaments on the heel bones;
- exercises to strengthen the muscles of the feet; plantar aponeurosis;
- Strengthening of the ankle.
The thickening of the arch of the foot with associated deformities leads to poor blood supply to the lower limbs. Changes in foot shape lead to inflammation of the plantar aponeurosis and the development of abnormalities in the skeletal, nervous and vascular systems. The effectiveness of physical therapy is increased when the patient walks barefoot on gravel or sand, or uses exercise equipment such as exercise sticks, rib boards, or small spiked balls to correct flat feet. It is advisable to start the LFC exercises for flat feet lying down or sitting. The standing position increases the load on the foot and prevents fixing the correct alignment of the foot.
- In a lying position. The arms are stretched out along the body, the legs are 20-25 cm apart. Slowly bend and spread your toes. repeat 10 times;
- Remain in the same position. Rotate the feet towards each other in a circular motion;
- Same position. Bend your knees. Grab the spiked ball with your toes and straighten your legs, raise and lower again. Repeat the exercise several times;
- Position - sitting on a chair. knees together, feet slightly apart;
- Rotate the inside of the foot up and push the outside of the foot toward the floor. repeat 10 times;
- Sitting on a chair. Feet together, hands on knees. crossing feet; Lift inside of foot, push outside of foot down.
Exercises for transverse flatfoot in adolescents
A juvenile transverse flatfoot occurs when the metatarsal bones separate, causing the forefoot to become flat and wide. One of the toes begins to protrude above the others, and three of the five toes have a hammer-like appearance. This form of flatfoot is difficult to treat. In patients with a longitudinal-transverse flatfoot, the load distribution between the ligaments and the sole aponeurosis is disturbed. Early stages of flat feet are corrected in the hospital and at home, severe stages of flat feet require special treatment with surgery, apparatus, operation, pharmacotherapy and massage.
In addition to conservative and surgical treatment, physical therapy is used to restore foot shape and consolidate the effects after foot shape recovery. Physical therapy of longitudinal and transverse flatfoot is combined with massage, special orthopedic insoles and orthoses, and depending on the cause of the flatfoot, drug and physiotherapeutic treatments are recommended. Surgical treatment is recommended for third degree flat feet. The postoperative rehabilitation is lengthy and difficult, the patient wears a special plaster splint for about four weeks, the foot bones are immobilized with titanium screws. After surgical treatment, a rehabilitation teacher draws up a training plan and after a certain time selects physiotherapeutic exercises.
The College of Fitness invites you to book a place in any program for Summer and Fall with an additional discount of 5%!
New course! fitness tests
There is a new and unique course 'Fitness Tests. body screening!
The holiday stream 'Sporturlaub. How to spend a weekend with your body'.
Have you already thought about how you want to spend your New Year's rest? If not, join our stream! The College of Fitness faculty have put together the best New Year's resolutions for you.

THE IMPACT OF FLATFEET ON HUMAN HEALTH. PREVENTION AND CORRECTION
Scientific and practical article by the speaker II International fitness congress 'TRIUMF' Valeria Baranova
The influence of the foot on the whole body
A healthy foot with an arched structure is an excellent aid to human movement. The way the foot performs its cushioning function affects the health of the leg joints, the spine (including the spinal cord), the condition of all internal organs and the brain.
Frankly, many people are surprised: the spine and knees hurt. But what does that have to do with the foot?
Axial loading disorder of the knee inevitably occurs when the arch of the foot is flattened. And a flattening of the arch of the foot is caused by a weakening of the foot muscles.
When the arches of the feet are deformed, the person steps on all the bones of the foot with all their might, and the foot muscles are disconnected from the cushioning process, causing the knee joints to spring back. This puts unnatural strain on the ligaments and muscles of the knee joint.
Other examples are the unequal arches of the feet on the right and left, the different lengths of the legs, the pelvis, which should be symmetrical in space due to the upright posture of the trunk, develops a compensatory curvature to the side in the lumbar spine, ie scoliosis gradually develops. This leads to chronic pain in the spine. Herniated discs often develop.
The spine is also involved in maintaining balance and upright gait. The deformation of the foot increases the load on the spine. The lumbar spine is particularly affected. The problems arise because the spine must constantly maintain its cushioning function.
This foot deformity also affects the health of the most important organ in the human body – the brain.
Read more:- Longitudinal and transverse arches of the foot.
- Transverse orthopedic insoles.
- Valgus flatfoot (valgus flatfoot).
- Transverse arch of the foot Latin.
- Lift your heels off the floor during the squat.
- flat foot pronation.
- orthopedic insoles.
- Which doctor treats flat feet?.
