Less commonly, flat feet require surgery. There are about 500 types of operations to correct foot deformity. They are performed on both soft and bony structures. Surgery is performed when conservative treatment has proven ineffective or the condition is very serious. The operation is followed by a long recovery period and special rehabilitation is required. Not all medical centers perform such complex operations.

- Symptoms of Flat Feet
- Advice before visiting the orthopedist
- symptoms
- This article has been reviewed by
- types of disease
- Specialists
- podiatrist
- orthopedist
- Which doctor should you see if your child has flat feet?
- Symptoms of flat feet in children
- Diagnosis of flat feet in children
- Causes of flat feet
- types of flat feet
- symptoms
- Causes of flat feet
- Causes of flat feet
- Treatment of flat feet
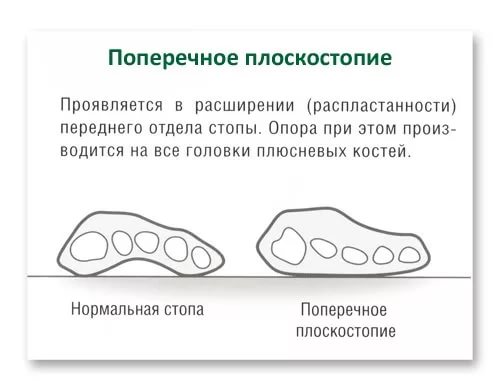
- How does a transverse flat foot manifest itself?
- What are the causes of transverse flatfoot?
- Symptoms of the disorder
- Types of juvenile flatfoot
- What is the risk of flat feet?
- Causes of flat feet
- types of flat feet
- flat feet
Symptoms of Flat Feet
- pain in the foot
- Heavy strain on the feet
- Changed posture
- Weakness of muscles
- Lower back pain
- Headache
- Cramps in the limbs
- knee pain
- curvature of the spine
- hip pain
- Swelling in the limbs
- Deformed toes
- Deformed feet
- Fatigue when walking
- clubfoot.
If you notice these symptoms, you should not wait, but consult a doctor immediately!
Advice before visiting the orthopedist

Orthopedists diagnose, prevent and treat congenital and acquired deformities of the musculoskeletal system, including the effects of trauma. There are pediatric orthopedists and adult orthopedists. For children, examinations by an orthopedist are recommended as a preventative measure: at the ages of 1, 3 and 9 months and annually thereafter.
There are no special preparations for visiting the orthopedist. You should shower hygienically and wear clothing that you can easily remove during the examination. It is important that you bring with you any scans and CT scans that you have previously taken.
symptoms
Children complain of pain in the foot area when they stand on their feet for long periods of time.
This article has been reviewed by
Clubfoot in children develops due to
- overweight
- Frequent walking barefoot on a hard, level surface
- repetitive movements
- uncomfortable footwear
- Trauma to the feet
- inheritance
- rickets
- Musculoskeletal paralysis of the foot resulting from poliomyelitis or cerebral palsy
Congenital flatfoot is rarely diagnosed. The causes are prenatal fetal anomalies, bad habits of pregnant women and exposure to ionizing radiation.
In most cases, flat feet in children under 6-8 years old is a physiological phenomenon. When a child is born, he has flat feet without a pronounced arch, which is due to muscle weakness and the predominance of fatty tissue on the surface of the sole, which serves as a shock absorber. The large amount of soft tissue on the feet dominates until about 3 years of age, after which it gradually decreases. The ligaments also develop, which affects the arches of the feet.
types of disease
Depending on the changed arches of the feet, there are 2 types of flat feet:
In transverse flat feet, the transverse arch is missing. This pathology arises from a genetic predisposition in combination with external triggers. Gradually, the length of the sole decreases due to the fan-shaped spreading of the bones, its width increases, the big toe tilts outwards and the middle toe deforms.
Longitudinal flatfoot is characterized by a flattening of the longitudinal arch of the foot. The length of the foot increases and a club foot develops. This condition is characterized by rapid wear and tear of the sole of the shoe on the inside of the foot. With longitudinal flat feet, the ankle joint is very stiff.
Often, clubfoot can be diagnosed with early rebound, trauma, and ill-fitting footwear. It is characterized by the absence of the metatarsals, rotation of the heel bone and toes, and an axial shift in the ankle joint.
- First. Usually recognized accurately in childhood. Don't panic, but follow the recommendations of an osteopath or orthopedist.
- Secondly. The child's gait becomes clumsy and a club foot develops. When walking, muscle fatigue increases and pain occurs in the lower back, lower leg and foot.
- Third. It is characterized by a complete deformation of the foot, leading to poor posture, pain in the back and throughout the body, and neurological disorders.
Specialists
If you don't know which doctor at your primary care office treats flat feet, you should contact a surgeon. He or she will make an initial diagnosis and refer you to specialists.
podiatrist
Podiatry is a new medical branch that deals with the treatment of flat feet and a number of other foot diseases:
- Varus and valgus deformities.
- Abnormalities associated with diabetes.
- Ingrown nail plates.
- Plantar fasciitis – also known outside the medical community as heel spurs.
- Morton's neuroma.
- Osteoarthritis in the ankles.
Since there are few specialists in this field, you should visit large diagnostic centers and get a referral from a doctor there.
orthopedist
Solves problems related to the musculoskeletal system. The orthopedic specialty is often combined with traumatology because these specialties are related and a large proportion of bone problems in the lower limbs are caused by trauma. If you have a choice between a traumatologist and a subspecialty orthopedist, it is better to make an appointment with the latter.
Also read: What shoes should I wear if I have flat feet?
Which doctor should you see if your child has flat feet?
A foot deformity in a child noticed by observant parents. If your child has developed club feet while running and walking, you need to take him to a pediatrician. He or she will make an appointment with a doctor called a pediatric orthopedist.
The doctor examines the child himself and talks to the parents about the child's behavior, his condition and the severity of the troubling symptoms. If necessary, additional diagnostics are carried out to clarify the diagnosis and the extent of damage to the adolescent's foot system. Depending on the current situation, treatment is prescribed and the patient is monitored by the doctor until puberty. A timely visit to a good specialist stops the development of pathology.
Symptoms of flat feet in children
Congenital and acquired flat feet manifest themselves in different ways. In congenital flat feet, the foot is severely deformed, usually one foot: it looks like a cylinder, the sole is flat or convex, the back is slightly concave and the toes are turned outwards. When the child begins to walk, the deformity persists and worsens.
The acquired flat foot reflects the child's shoes: the inner edges of the sole and heel are tamped at the age of 6-7 years.
Depending on the severity of the symptoms and the height of the arch of the foot, doctors distinguish three degrees of flat feet in children:
- no deformity visible to the eye, arch height up to 35 mm;
- the foot is visually flattened, the height of the arch of the foot is from 25 to 17 mm, the medial part is widened, the ankle joint and lower back hurt, it is difficult to walk long distances;
- the deformity is large, the height of the arch of the foot is less than 17 mm, the legs and lower back hurt constantly, it is impossible to walk in normal shoes.
Subjective complaints associated with flat feet do not always occur. They usually occur when the foot is significantly deformed. Children suffer from constant foot pain, rapid fatigue and swelling that occurs when walking for long periods of time. This makes it difficult to walk long distances. The children refuse to leave and prefer to play in peace. Prolonged deformation leads to twisting of the fingers and the formation of blisters. Without treatment, posture problems and the development of scoliosis occur. Spinal diseases, especially osteochondrosis, rapidly develop or worsen, and herniated discs occur.
The child may complain of back pain that increases after physical exertion or when sitting for long periods of time. Gradually, the joints become affected and deforming arthritis develops - the mobility of the joints is restricted and the range of motion is limited. The pain becomes almost constant and fatigue increases.
Diagnosis of flat feet in children
Diagnosis and treatment of flat feet is carried out by a pediatric orthopedist. The diagnosis is made after the age of 5, earlier only in severe cases of congenital deformity. During the examination, the doctor looks at the length and width of the foot, the condition of the arch, the range of motion, the condition of the toes and the blisters. The pediatric orthopedist also assesses the wear of the footwear and characteristic abrasion areas.
For children older than 5 years, additional methods are used:
Plantography is a footprint and can be created on paper or electronically. In the paper version (Smirnoff), the foot is colored and the child is then placed on a piece of paper. The doctor analyzes the print.
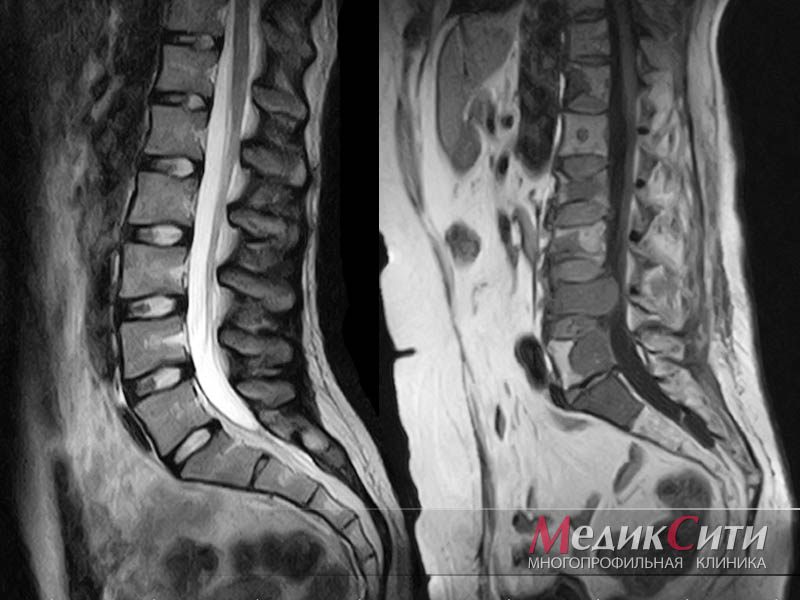
X-rays are taken in straight, oblique and, in some cases, lateral projection. Deformities, joint condition, cartilage, pathological ossifications and other details are assessed.
Causes of flat feet
A relatively common cause of flat feet is congenital characteristics and hereditary weaknesses of the connective tissue, including the foot. This is called subtlety. In the past, a foot with a molded flat foot was considered arthritic.
In most cases, however, flat feet are acquired, meaning they develop as a result of abnormal foot formation in childhood. The main mistake is usually children's shoes with the wrong orthopedic shape. In later adulthood, especially in girls, flat feet can be the result of shoes with a very narrow toe box and a high heel.
Sometimes flat feet are the result of poor posture or high or low muscle tone.
types of flat feet
Flat feet are divided into longitudinal and transverse arches, depending on which arch of the foot is lowered. There are also cases of combined flat feet. Transverse flatfoot is the most commonly diagnosed condition. The condition can be congenital or acquired. The first variant, which accounts for a minimum percentage, is believed to be the result of defects in the tissues of the fetus. Basically, the problem occurs throughout life. Specialists consider these variants of flat feet:
Fractures, muscle and ligament injuries cause traumatic flatfoot. Paralytic flatfoot is associated with poliomyelitis and paralysis of the tibial plateau and other muscles. The rickety shape is caused by brittle bones that deform under stress. The static form of the disease is diagnosed in 80 percent of cases. The causes for this are multifactorial.
symptoms
The symptoms of the disease are quite characteristic, so confirmation of the diagnosis by a specialist is not difficult. The patient may suspect a problem in the early stages. Common symptoms include:
General fatigue, sometimes called chronic fatigue syndrome, may occur as the disease progresses. The patient often complains of pain in the lower back when standing and walking. It's difficult to find shoes that are comfortable and don't cause pain. Thickened and rather rough patches of skin appear, especially on the big toe. The external symptoms of the disease include:
The patient often has poor posture and develops clubfoot. The gait becomes heavy and unnatural. The patient is then forced to put their feet in the wrong position to minimize discomfort. Pain is the main indicator of the problem. It is mainly located in the feet:
In later stages, the hip and knee joints as well as the local muscles also hurt. The sacral and lumbar spine are affected. The pain increases toward the end of the work shift and is particularly severe in patients who have to walk or stand all day, carry weights, and perform other physical labor.
Causes of flat feet
The factors provoking a pathological condition of the musculoskeletal system are divided into internal and external. The former include all types of anomalies and defects of the musculoskeletal system, including:
- connective tissue weaknesses;
- hereditary diseases;
- family predisposition;
- Weakness due to hypodynamics.
The number of extrinsic causes is also sufficient. In most cases it is an acquired disease that is provoked:
Flat feet are caused by both complete inactivity and excessive physical activity. Office workers, factory workers, athletes with injuries, and overweight people are often affected by flat feet.
Causes of flat feet
The best way to identify flat feet is to see a doctor. A child or adult will notice the following symptoms:
- Tiredness that sets in quickly, a feeling of heaviness in the legs when standing or walking.
- Cramps, swelling in the ankles and lower legs.
- In women: difficulty walking in high heels.
- Change in foot size.
- Difficulty choosing comfortable shoes.
- Club foot, discomfort when walking.
To diagnose flat feet at home, dip your feet in paint or oil. Then step on a clean piece of paper, first with your toes and then with your heel, to leave a clear mark. Paint or oil must not get on the sheet. Do not lean against a chair or table; the test is carried out while standing.
- Crescent footprint, no insole area - no flat feet.
- Completely hollow area of the foot – presence of flat foot, most likely valgus flat foot.
- A large gap between the forefoot and backfoot is also an indication of flat feet.
An interesting, but not very effective, way to determine if a child has flat feet is to ask him to step on wet sand on the beach.
Treatment of flat feet
When treating flat feet in children, it is important to remember that the foot continues to form and grow up to a certain age (3-4 years). Therefore, certain abnormalities in the structure of the foot are considered normal.
Therapy for children includes exercises on orthopedic mats, massage and wearing orthopedic shoes. The doctor prescribes a specific list of exercises and which shoes to buy for a child with flat feet. Many people wonder which doctor diagnoses and treats flat feet. This is an orthopedist or an osteopath.
Before treating flat feet in adults, the specialist must conduct a thorough diagnosis to determine the type and extent of the disease. After that, the doctor will tell you how to treat your flat feet at home using special exercises.
Complex exercises can help strengthen the muscles of the lower leg and foot to maintain correct posture. The patient must make an effort to achieve an effect - he must adhere to a program and regularly perform the exercises recommended by the doctor. Surgical intervention is very rarely performed for this problem.
How does a transverse flat foot manifest itself?
The human foot consists of a large number of bones connected by joints, tendons and ligaments. In a normal physiological state, the metatarsal bones are aligned parallel to each other and are held in this position by ligaments. In real life, bones often differ from each other, but this is considered normal within certain limits.
If the bones are too far apart, a transverse flat foot occurs. In this condition, the first metatarsal bone to which the big toe is attached is significantly different from the others, and the muscle attachments of the foot are distributed differently. The tendon that runs along the foot changes direction as the metatarsal bone deviates, pulling the toe outward.
The head of the metatarsal bone shifts and begins to protrude outward. Constant contact with this area can cause abrasions on the shoe and sometimes inflammation of the joint. In this way, a so-called transverse flatfoot more or less develops.
What are the causes of transverse flatfoot?
Transverse flatfoot of the first degree develops from a number of causes, the main of which is associated with injury to the ligamentous apparatus of the legs. It is inherited, but there are also other predisposing factors:
- Excess weight, which puts more strain on the ligaments of the feet;
- Paralysis and paresis in the leg muscles;
- prolonged wearing of uncomfortable and tight footwear or high-heeled shoes;
- Long-standing professions such as hairdresser, shoe salesman, etc.
Symptoms of the disorder
Clubfoot in adolescents aged 13 to 16 is always accompanied by a heavy and unsteady gait, and they feel uncomfortable even in comfortable shoes. In later stages, they may also have pain in the lower back, knees, and hips. Externally you can notice that the foot is flattened.
The first symptoms at the age of 14-16 are usually recognized by doctors visually:
- Shoes wear out quickly and irregularly;
- feet get tired quickly when walking;
- The lower limbs swell and shrink;
- Wearing high-heeled shoes causes excruciating pain.
The development of flat feet during puberty is very dangerous because the body's gravity shifts backwards and one has to bend forward to maintain balance. The spine takes on a comfortable shape, that is, it arches. This leads to intervertebral fractures, pinched nerve endings and scoliosis.
The uneven distribution of the load on the foot and poor cushioning lead to irreversible pathologies in the joints of the lower limbs. That is why the elimination of flat feet in children aged 14 to 16 years should be started as early as possible.
Types of juvenile flatfoot
In order to quickly get rid of flat feet in 13-16 year olds at home, it is necessary to recognize the form of the pathology, of which there are three in total:
With the longitudinal foot, the space between the surface of the foot on which you rest and the inside of the foot narrows. The edge of the arch of the foot at the longitudinal arch also disappears, resulting in cushioning.
With transverse pathology, the forefoot becomes flatter and wider and the bones spread apart. This causes the toes to tilt outward. There is also a combined form of flat foot, in which both longitudinal and transverse foot pathology are combined. Before treating flat feet after the age of 13, an orthopedist conducts an examination to determine the severity of the pathological deformity.
What is the risk of flat feet?
If we look closely at a healthy foot, we can see that there are two arches: a transverse and a longitudinal arch. These arches help us maintain balance while walking and cover long distances without fatigue.
If the arches of the feet are deformed, a person is diagnosed with flat feet. Some patients, upon learning of this condition, begin intensive treatment by any means necessary, while others do nothing at all. Both approaches are incorrect because a podiatrist should first be consulted to determine the degree and form of the pathology before treating the foot condition. On the other hand, if left untreated, flat feet will progress quickly and treatment will become more difficult.
Currently, between 40 and 60 people worldwide live with flat feet. The disease can lead to complications such as spinal curvature, radiculitis, osteochondrosis, intervertebral fractures, pelvic bone disease, knee joint disease and toe curvature.
Causes of flat feet
Flat feet and other foot diseases are often observed in people whose jobs involve constant stress on the feet: couriers, hairdressers, salespeople, etc. Wearing tight shoes or high-heeled boots also aggravates the foot, increases the load on the forefoot and leads to this that the foot bends inwards. Therefore, the optimal heel height for adults is 3 to 4 cm and for children 1 to 1.5 cm.
There are several factors that can lead to this type of foot problem:
- Pregnancy;
- overweight;
- Diseases that cause bone fragility (flu, rickets, etc.).
- genetic predisposition;
- underdevelopment of the musculoskeletal system;
- Various injuries (fracture of the heel bone, fracture of the ankle, damage to ligaments and muscles that strengthen the arch of the foot).
types of flat feet
According to the time of their appearance, flat feet are divided into two large groups: congenital and acquired.
Congenital flatfoot It arises from congenital foot defects and is quite rare, with only 3 % cases.
Acquired flatfoot Can occur at any age and includes the following forms:
Flat foot. Treatment of foot deformities and diseases
Clubfoot. Treatment of foot deformities and diseases
flat feet
Flat feet – a condition that progresses quite quickly. There are 3 degrees of this disease.
grade 1 (Slight flat tire.) is caused by a weakening of the ligaments. The shape of the foot does not change, but at the end of the day, after a long walk, pain appears in the legs. The pain usually subsides after a period of rest. In this condition, the gait is less springy and the foot swells in the evening.
grade 2 (combined flatfoot (combined flatfoot)). At this stage the flat foot is already noticeable. The foot becomes larger, the gait is difficult and walking becomes difficult. Pain increases, affecting not only the foot and ankle joints, but also the knee.
grade 3 (Extremely pronounced flat feet.). A severe foot deformity causes a change in the position of the toes, with the big toe tipping outward. There is constant pain in the feet, ankles and knees. Osteochondrosis, arthrosis, scoliosis and intervertebral fractures can occur. Walking is difficult, even at slow paces and short distances. The patient can no longer walk in normal shoes.
Read more:- Which doctor treats adult posture?.
- Which doctor treats the hip joints.
- Who treats the leg joints which doctor.
- flat feet (valgus foot).
- Traumatology orthopedist which doctor.
- Massage for flat feet.
- Photo of scraped feet.
- baby splashing.
