Some skin diseases cannot be prevented, especially genetic abnormalities or skin problems related to various internal diseases. But some skin problems can be prevented if you know what causes them. This is especially true for infections with skin lesions:

- 20 examples of body language and what they reveal
- The power of body language
- Types of mycoses
- How are they developing?
- Swelling and pain in the feet: disease-related causes
- Lower leg edema: causes and drug treatment
- diagnosis
- Treatment of Restless Legs Syndrome
- Endomorph body type
- What can I eat if I have gout?
- Diet for gout - a diet example
- What are skin diseases?
- How are skin diseases treated?
- What is gout?
- How long does a gout attack last?
- What to do after vaccination?
- What not to do after the DPT vaccination
20 examples of body language and what they reveal
Do you want to understand what those around you really want? This is easy if you understand body language. The words of a partner, boss, friend or acquaintance may seem very true, but turn out to be a complete lie. Body language, facial expressions and gestures are another matter. It is the non-verbal language that confirms or denies the meaning of what is being said.
Everything matters: from the slightest body movement and posture to eye contact, spatial distance and voice volume.
How much credibility can you give body language? Practically 100%!
Of course, there are people who intentionally use certain non-verbal signals to mislead others, but with the right practice and knowledge, these are easy to decipher. We have prepared 20 body language examples for you that will help you better understand people's true motivations.
The power of body language
More than one book has been written about the power of body language. It should be noted that incredible opportunities sometimes open up for the holder of this power of knowledge. It can be compared to magic or sorcery. But no, it is much more effective!
Imagine: You can achieve what you want with positive body language signals. For example, to get a job, sell or buy something cheap, win an argument, or start a relationship easily. But don't get too euphoric, because there are also negative signals that can betray you and prevent you from achieving your desired goal.
The fact is that it is very difficult to control your own body language (although it is possible if you practice it regularly and acquire the right skills). You can use certain signs, but your true intentions will be clear even to people who know nonverbal language.
Be careful when judging other people's body language. Always remember: a gesture or facial expression can mean different things to different people.
Types of mycoses
There are several groups of microorganisms that attack the epidermis. They attack different parts of the body and cause associated diseases. The most important pathogens of mycoses are Trichophyton, Verrucosum, Microsporum and Epidermophyton.
- Dermatomycosis of the beard and mustache;
- trichophytosis of the scalp;
- ringworm;
- Dermatomycosis of the groin area;
- dermatomycosis of the feet;
- interdigital dermatitis on moist areas;
- Onychomycosis of the nail plate.
Treatment depends on the location. While antifungals are sufficient on the head and exposed skin, drying agents are required in damp areas. In such cases, it is not only important to kill the pathogens, but also to make the environment inhospitable to their reappearance.
How are they developing?
Direct epidermal contact with the area where the pathogens accumulate is enough to cause a fungal infection. Transmission is possible from person to person or through contact with household objects. The disease does not begin with every contact with the fungus. With strong immunity, the organism shows resistance to the pathogen.
For active growth and reproduction it requires a slightly alkaline or neutral environment. Normally the pH value of the skin is 5.5, which corresponds to an acidic environment. However, if it becomes moist and does not receive oxygen, the pH rises to the alkaline range.

Another important requirement for mushroom growth is a low temperature. At 75°C they die within minutes, so cooking and ironing will stop the spreading process.
Swelling and pain in the feet: disease-related causes
Not everyone deals with the problem of swollen feet responsibly. However, the causes and treatment can be much more serious than just fatigue or excessive fluid intake - swollen feet can be both a secondary and primary symptom of disease.
They can indicate the presence of a number of diseases:
- Kidney disease - characterized by poor urination, lower back pain and high blood pressure;
- Heart failure – with palpitations, shortness of breath, constant weakness and severe tiredness;
- Bone and joint diseases – accompanied by pain in the upper and lower limbs and impaired motor function;
- Nervous system disorders - Patients with neurological disorders complain of movement disorders, speech and coordination disorders, involuntary muscle spasms, tics, tremors, decreased sensitivity to touch, headaches, behavioral problems and insomnia;
- Varicose veins and CVI (chronic venous insufficiency): The first symptoms of venous disease are swelling in the legs. They are minor at first, but become more severe as the disease progresses. The leg swelling associated with varicose veins or CVI is characterized by easing or disappearing at night and increasing during the day. Over time, the swelling is accompanied by radiating pain and night cramps in the calf muscles, as well as the appearance of small reddish-blue spider veins on the skin and later dark blue and tortuous veins. In advanced stages, the skin of the lower legs becomes dry and shiny, and pigmented brown islands are formed, preceded by trophic ulcers.
Each of the above-mentioned diseases can manifest itself with symptoms such as swelling in the legs. The causes and treatment of swelling are determined by an experienced phlebologist from the Jusupovsky Hospital on the basis of a comprehensive examination using modern diagnostic equipment in the clinic
Lower leg edema: causes and drug treatment
Treatment of edema of any cause in the phlebology department of the Yusupovsky Hospital includes a comprehensive approach. The treatment regimen is developed by phlebologists and a team of specialists from various medical disciplines individually for each patient depending on the diagnosis and stage of the disease. In general, pharmacological treatment is chosen for patients with venous, cardiac and renal diseases, which are most often accompanied by the development of leg edema.
Severe leg edema caused by heart or kidney disease usually cannot be resolved with topical treatment (gels, ointments, or massages). Eliminating such edema requires restoring the normal functioning of internal organs, which requires normalizing the water and salt balance.
Diuretics (potassium-sparing, loop, thiazide), cardioprotective drugs and potassium preparations are prescribed (the latter are contraindicated in patients with kidney failure).
Leg edema caused by venous disease can be treated with both external and internal (systemic) medications.
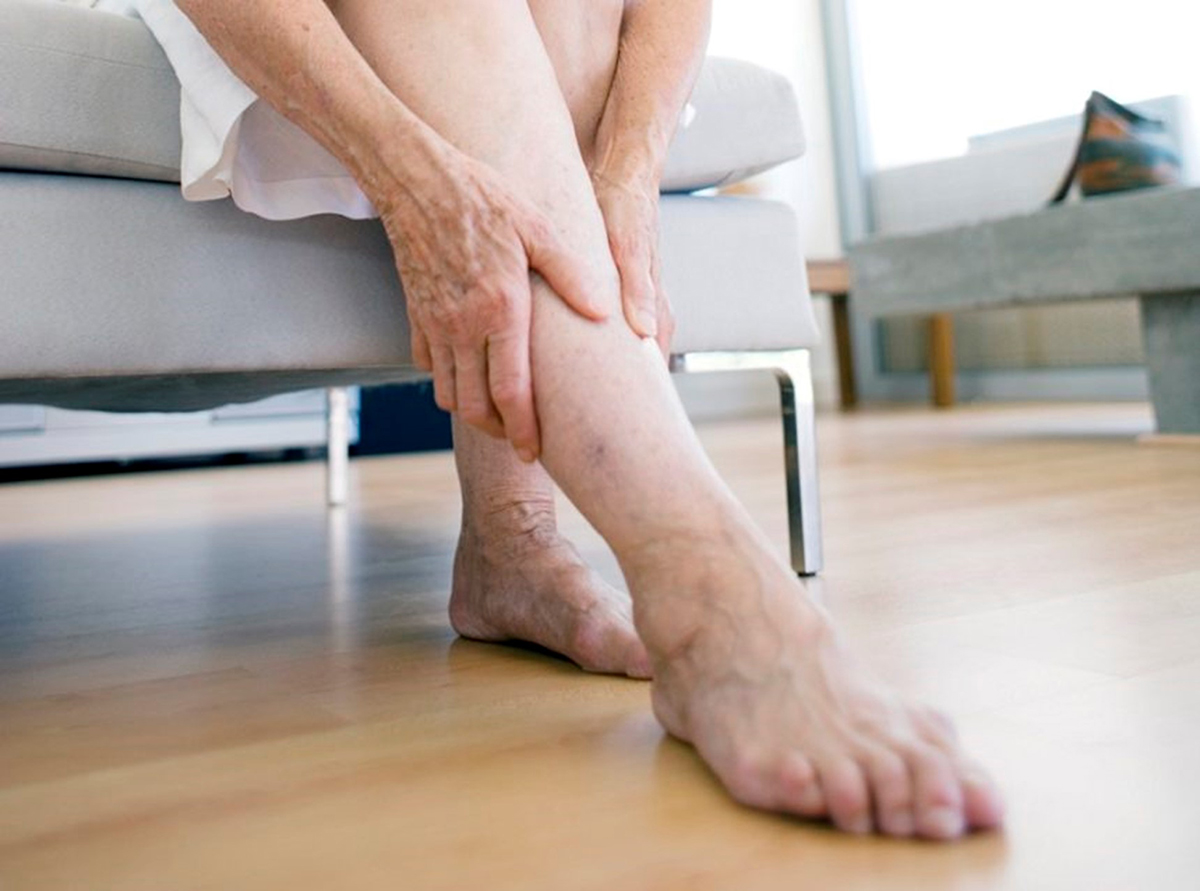
The use of external agents (phlebotonics) relieves symptoms, improves blood microcirculation, reduces the likelihood of blood clots, and reduces inflammation and edema.
The use of systemic drugs (venotonics, angioprotectors, antiaggregates of the latest generation) is recommended by the phlebologists of Yusupov Hospital for the prevention or treatment of varicose vein disease.
Swelling as a symptom should not be taken lightly, especially if the feet are acutely swollen. The causes of this symptom can be varied, so it is important to make an early diagnosis and initiate early treatment of the condition that caused the swelling.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of restless legs is made based on the patient's characteristic symptoms, standard examination and neurological examination. Two tests are recommended for confirmation:
- Electroneuromyography: Detection of the contractility of the leg muscles;
- Polysomnography: Recording the basic indicators of body performance (pulse, breathing) as well as movements during sleep.
In addition to the basic diagnosis, the doctor will try to find the cause of the abnormality. For this purpose, the following examinations can be recommended:
- General and biochemical blood tests (determination of hemoglobin, ferritin, uric acid, glucose, trace elements, etc.).
- General urine examination;
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain;
- Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the lower limbs (to detect varicose veins and thrombophlebitis);
- Blood tests for thyroid hormones, etc.
If necessary, the patient is referred to specialists (endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, urologist, etc.).

Treatment of Restless Legs Syndrome
Treatment requires a multidisciplinary approach. If it is a primary pathology, the following drugs are used:
- Antiparkinsonian drugs (levodopa, bromocriptine and others): They normalize dopamine metabolism in tissues and eliminate the effects of dopamine deficiency;
- Antiepileptic drugs (carbamazepine, phenobarbital, etc.)
- Benzodiazepines: relieve seizures and normalize sleep;
- Local anesthetics in the form of gels and ointments (Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen and similar);
- anti-inflammatory drugs in tablet form.
The first three groups are prescription drugs. They should only be taken as directed by your doctor. In severe cases, opioids are used, but their use is severely limited.
If the disease arose against the background of another pathology, means are prescribed to eliminate the cause:
- Metformin: a drug that normalizes blood sugar levels;
- Antianemic drugs to increase iron levels in the blood (Fenuls, Ferrum preparation);
- Iodine preparations to stabilize the thyroid;
- Vitamin and mineral supplements for vitamin or micronutrient deficiencies.
Physiotherapy (magnetic therapy, darsonvalysis), massage and exercise therapy can improve the effects of medications. These treatments are complementary.
In the long term, a spa treatment to strengthen the nervous system is advisable. Mud baths, pine baths, hydrotherapy and lymphopressure help normalize the psychological state, improve sleep and reduce the frequency of attacks.
Endomorph body type
Key Features of Endomorph Body Type:
Hipsters are characterized by a slow metabolism, which means they gain weight quickly. This type is not characterized by endurance and usually has low strength values. Endomorphs are naturally inactive and sedentary, like to eat a lot and prefer sweets and fatty foods.
To quickly build an ideal body, men of this type need to follow a strict diet. This is the only way to achieve a flat stomach. It is particularly important to keep an eye on the glycemic index of carbohydrates and to limit carbohydrate intake in the evening to a minimum.
Cardio exercise is preferable as it burns fat effectively. The main goal of exercise for endomorphs is to combat excessive obesity. Muscle mass is hidden under a layer of fat, so the relief achieved may simply not be visible.

The most effective training is bicycle training. They help you remodel your body to gain muscle mass and relieve stress. There are good reasons to consult a trainer and nutritionist to help you create a sensible and effective weight loss program.
The recommended training frequency is 3-4 times per week. Training should be varied and include fun sports, outdoor exercise, swimming and so on.
Good nutrition is just as important as exercise. Do not resort to rigid diets that restrict nutrition. Starvation can reduce not only fat but also muscle, and the weight lost comes back quickly.
It is necessary to limit the amount of carbohydrates consumed: no more than 100 g per day. It is best to consume this amount 40 minutes before training so that energy is used efficiently. The diet should contain sufficient amounts of calcium, magnesium and amino acids.
What can I eat if I have gout?
The following foods should be included in the diet to prevent gout and relieve its symptoms:
- vegetarian soups: cabbage soup, vegetable soups, okroshka, beetroot, etc;
- lean boiled or fried meat, poultry and fish;
- dairy products, milk, quark;
- eggs (one egg per day);
- grains (in moderation);
- Fresh, cooked or pickled vegetables;
- fruits and berries;
- Root vegetable;
- bread (2 types);
- Lean fish;
- chicken, turkey, rabbit;
- plums;
- cherries;
- citrus fruits;
- Nuts – hazelnuts, almonds, cashews, walnuts and pine nuts;
- Chicory;
- weak green teas and herbal teas;
- mild coffee with fat-free milk;
- Honey, marshmallows and jam.
- Drink at least 1.5 to 2 liters of water per day, or even three liters per day in times of exacerbation.
Studies have shown that purine-rich vegetables such as asparagus and spinach do not increase the risk of gout or trigger gout attacks.
These seafood include shrimp, mussels, scallops, anchovies, sardines, tuna and trout. The overall health benefits of consuming them may outweigh the risks associated with gout. Therefore, you can include fish and seafood in moderation in your diet - of course, taking your body's reaction into account.
In addition to diet and medication for gout, your doctor may recommend taking vitamin C because it helps excrete uric acid.
Diet for gout - a diet example
Manuel Pevzner, a Soviet nutritionist and gastroenterologist, has developed a special diet - Table 6 - which is prescribed by the doctor for disorders of purine metabolism and increased uric acid levels in the blood. This diet virtually eliminates the absorption of purines into the body through food.
The general principles of the gout diet are similar to those of a healthy diet.
Diet for a week for gout sufferers
- cheesecake, fruit gum/honey, kefir;
- cottage cheese casserole, carrot and apple juice;
- oatmeal with apple, homemade compote;
- Buckwheat groats, toast with jam, fat-free milk.
- Fat-free yogurt with breakfast cereal;
- boiled egg, carrot and pumpkin salad;
- breakfast cereals with fat-free milk;
- Milksoup;
- fruit with fat-free cream;
- Tea with jam, honey or marshmallow.
- Milk soup, zucchini schnitzel with potatoes, homemade compote;
- zucchini soup, boiled fish, mashed potatoes;
- vegetable soup, coleslaw, tomato juice;
- buckwheat groats, beef cutlet, cabbage stew, juice;
- Vegetarian borsch, carrot schnitzel, milk;
- stewed vegetables, kefir;
- Potato soup with barley, pancakes, compote.
- Vegetarian vegetables, weak tea or herbal mixture;
- salad (egg, carrots, croutons, sour cream), corn porridge, quinoa;
- oatmeal, fried vegetables, weak tea;
- Rice with peppers, pancakes with fruit, compote;
- Fresh vegetable salad, boiled or fried chicken fillet, homemade cornichons;
- Cheesecake with banana, herb mixture.
A varied menu can be put together for every day from the dishes listed.
Western experts also suggest their own daily menus:
What are skin diseases?
All skin diseases can be divided into two large groups:
- Permanent illnesses whose symptoms occur and persist over a long period of time (even until the end of life),
- Temporary changes that are short-lived and disappear with (or without) treatment.
Permanent lesions. Some chronic skin processes may be present from birth, while others may appear suddenly at any age, from infancy to old age. The cause of these problems is not always clear and obvious, for many there is no effective treatment and they require constant care and hygiene measures. However, for most chronic skin diseases, effective remedies have been found to achieve long-term remissions. However, such diseases are considered incurable, and exacerbations, i.e. the flare-up of new skin rashes, are possible at any time.
- Psoriasis (psoriasis) with plaque or teardrop-shaped rashes, joint and scalp lesions;
- atopic dermatitis and eczema;
- Rosacea with typical skin rashes on the face and body;
- Systemic lupus erythematosus with the typical 'butterflies' on the face and internal lesions.
Temporary skin lesions. There are a variety of temporary skin lesions associated with adverse external influences - infections, allergies, irritations, burns, contact with chemicals or cosmetics, medications. Transient skin reactions are also possible with the development or aggravation of systemic diseases - liver problems, viral infections (including the so-called 'skin infection') and the development or aggravation of a disease. childhood), poisonings and allergic diseases.
Some skin diseases have an occupational cause, such as: B. contact dermatitis. It arises from frequent skin contact with chemical, biological and irritating substances. Problems appear within minutes or hours of skin contact and resolve quickly once the causative agent is eliminated.
How are skin diseases treated?
Most skin diseases, both acute and chronic, can be cured and almost completely eliminated. However, it is important to consult a doctor to determine the exact cause of the skin lesions, conduct a comprehensive examination and exclude systemic changes and concomitant diseases that could complicate therapy.
Important!!! Any treatment should be prescribed by a doctor, even if it is a topical treatment. The situation is even more serious when oral medications, especially hormonal drugs, are required.
Common therapies and approaches include the following:
- Systemic treatment with oral medications;
- physiotherapy and device therapies;
- surgical and microsurgical techniques (not applicable to all diseases)
- Topical therapy and skin care with medical cosmetics.
Among the drugs used in dermatology, the most commonly used groups are:
- antihistamines;
- topical and systemic forms of antibiotics;
- antiviral medications – topical and oral;
- Corticosteroids – usually topical, in very rare cases short oral or injectable treatments;
- medicated creams, ointments, lotions, lotions, etc;
- Vitamins – topically or by injection;
- certain prescription medications (immunosuppressants, biologics).
Laser, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation and minimally invasive methods of lesion removal, as well as phototherapy (UVB, red light) are also commonly used for treatment.
Unfortunately, not all skin diseases can be treated radically and completely. Some can resolve quickly and even without intervention, while others persist and recur despite extensive treatment. That's why it's so important to achieve lasting remission and maintain good skin care going forward. It is also important to know and eliminate all possible triggers for skin diseases and to protect yourself from stress and a weakened immune system.
What is gout?
Gout is a disease of the joints because urate is mainly deposited there. The disease also affects the kidneys, ligaments, bones and liver.
The cause of gout is the constant increase in uric acid in the blood. It is caused by the breakdown of purines (nitrogen-containing compounds that come from food and/or are synthesized by the body). Normally it passes from the bloodstream to the kidneys, where it is filtered and excreted in the urine. However, if there are metabolic disorders, excretion is disturbed. As a result, the concentration of uric acid increases. Their salts settle as crystals and cause gout.
Don't have time to read long articles? Follow us on your social networks: listen to background videos and read short articles about health and beauty.
Mega pharmacy on social networks: VKontakte, Telegram, OK, Viber
How long does a gout attack last?
A characteristic feature of the disease is that the joints are affected asymmetrically. The thumb of one of the lower limbs is often affected first. The phalanges and wrists can also be affected. Later the disease often spreads to other joints.
- Severe pain in the joint;
- lividity of the skin and swelling in the affected area;
- chills, fever of 38 degrees or more;
- Complete loss of joint mobility.
The pain increases with the slightest touch to the joint and is not always relieved by painkillers. Their intensity decreases slightly during the day and increases again at night. The severe pain lasts up to 3 days and then gradually subsides. On average, an attack lasts between 3 days and a week.
The frequency of attacks can vary from once every six months to several years. Their frequency increases as the disease progresses. Over time, the flare-ups become less severe but longer lasting, and the process spreads to more and more joints. With a long course, 50-60 % patients develop tofus - white or yellow nodules in which urate has accumulated. They occur on the fingers and toes, auricles, feet, knees and elbow joints. Tofus are painless, but sometimes they open spontaneously and cause quite a bit of pain.
Gout cannot be completely cured. However, a good diet and avoiding bad habits can reduce the frequency of attacks.
What to do after vaccination?
If your child is allergic, they should remain under medical supervision for the first 30 minutes. Once at home, it is advisable to take an anti-allergic drug and give an NSAID drug such as Nurofen. The medication not only has an antipyretic effect, but also a pain-relieving effect, as the leg can be very painful in the first 24 hours. Measure your body temperature regularly for the first 2-3 days. If necessary, it should be lowered.
If the child has a temperature above 38˚C, an antipyretic agent should be given as there is a risk of febrile seizures.
What else should you do after a DPT vaccination? It is important to follow a hypoallergenic diet and drink more fluids.
After the DPT vaccination, you can go for a walk outside, but only in areas that are not crowded. Vaccination lowers immunity and increases the risk of respiratory disease.
If a large lump appears at the injection site that does not shrink spontaneously within 2-3 weeks, magnesia compresses can be applied. This will speed up absorption.
What not to do after the DPT vaccination
- soak the injection site on the first day
- take a steam bath, take a hot bath for the first 2-3 days (a shower is better)
- Overheating or excessive cooling
- overfeed the baby
- introduce new foods
- Eating foods that cause allergies
- Walking in crowded spaces
Complications after DPT vaccination cause fear. However, it is important to use common sense and understand that while negative reactions after vaccination can be prevented, they do not otherwise protect you from deadly diseases!
Read more:- What types of doctors are there and what they do.
- What types of doctors are there.
- types of toes.
- What other names are there for doctors?.
- What kind of doctor treats knee joints.
- What shoes should you wear if you have osteoarthritis of the knee?.
- What kind of doctor treats the joints.
- Which muscles hurt after running?.
