Reflexology, physical therapy, and other methods can also be used. The orthopedist develops an individual correction plan for each patient. If you have a similar problem, we recommend that you make a free appointment with an orthopedist in our chiropractic clinic in Moscow.
- What to do if your legs are crooked
- Procedure for Correction
- If it is rickets
- Avoid tight wrapping
- Bar osteosynthesis
- Ilizarov osteosynthesis
- Incorrect curvature of the lower limbs
- Correction of lower limb curvature
- DIAGNOSIS OF LEG CURVE IN A CHILD
- REHABILITATION MEASURES
- Ratings and Comments (54)
- Blog (Foot Correction)
- Possible causes of X-shaped feet
- Symptoms and diagnosis of leg curvature
- Why does femoral neck deformity occur?
- Varus Deformation of the Neck of the Thigh (Femur)
- Leg exercises in remission
- Can exercise help?
- List of Sources
What to do if your legs are crooked

- information
- techniques
- conditions of treatment
- doctors
- history of the center
- our strengths
- Certifications and Patents
- Cooperation
- Clinical Center
- News
- Left
- Contact us
- processing of personal data
- Correction of the foot
- Correction of foot deformities
- Growth enhancement (leg lengthening)
- BONE AND JOINT TREATMENT
- Treatment of discounts
- X and O shaped foot curves
- False and real bends in the foot
- Express methods for correction
- Image gallery
- Registration for treatment
- FAQ
- blogs
- letters from patients
- advice for patients
- geography of our patients
- computer modelling
- Patient Testimonials – Correction of Leg Curvature
- How to choose a clinic
- Survey
- Stories from the center
- patient blogs
- scientific publications
- Popular publications
- Other Publications
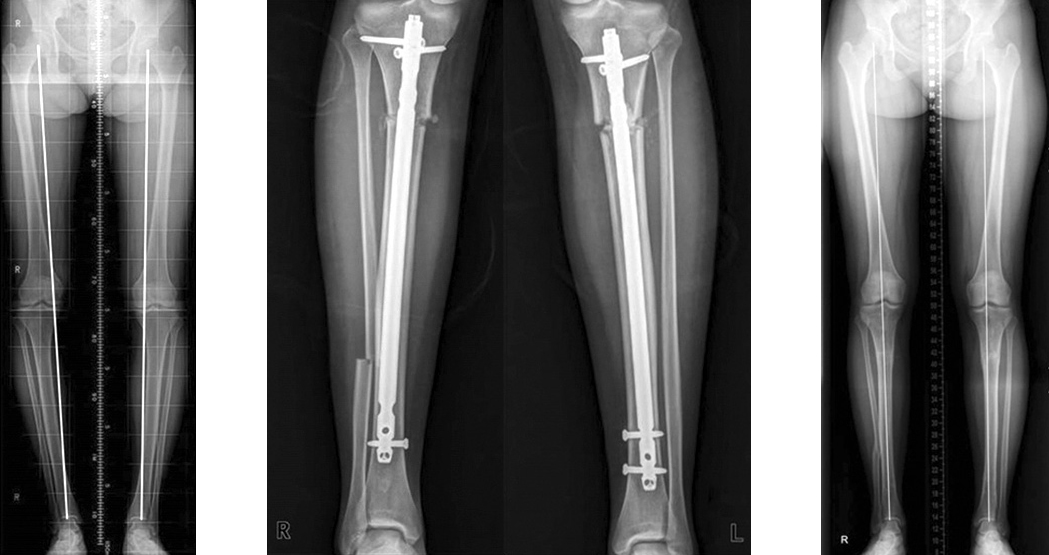
Surgical correction of bowlegs and knock knees (leg straightening, correction of leg curvature)
The center for cosmetic and anthropometric (orthopedic) corrections offers you a unique opportunity

Condition before and after correction (leg curvature correction)
Cosmetic correction procedure (curvature) is carried out by experienced podiatrists using a specially developed correction method correction famous Volgograd doctor, Honored Inventor of the Russian Federation, Doctor of Medical Sciences Michael Fedorovich Egorov
Procedure for Correction
Correction of the foot (The correction of the curvature of the feet.) is performed on both feet at the same time and consists of three steps:
1 – surgery. The operation is performed alternately, first on one foot and then on the other. First, a special orthopedic bandage is attached to the leg below the knee. Thin but strong pins made of safe, special medical steel are inserted through the bones at the top and bottom of the lower leg. The pins are then firmly inserted into the rings of the splint, creating a solid splint-bone system. An osteotomy (bone removal) is then performed. The osteotomy is performed using a special orthopedic drill using the method of corticotomy (partial cutting of stronger bone elements with minimal trauma to the surrounding tissues). The operation ends with the insertion of a cosmetic suture;
2 – Correction. During this period, a gradual During this period there is a gradual correction of the shape of the legs, The correction takes place over several days. Correction usually starts on day 5-7 after the operation. The duration of the correction depends on the extent of the original deformity. The gradual correction enables a very precise correction of the curvature with an accuracy of a few tenths of a degree. It is currently the most precise technology available. Together with the patient, the doctors decide on the completion of the correction, taking into account the patient's wishes and the results of the computer simulation.
3 – fixation. This phase is the longest. During fixation, the bones are held in the corrected position by the appliance until they have healed. The duration of fixation is about 1 month. During this period, patients are most mobile, walk without crutches and have practically no pain. Our patients can be found in almost all important facilities in the city. They visit numerous cinemas, shopping centers, parks, museums and, of course, Mamaev Kurgan. Many of them say they just forget about the prosthetic legs. Once fixation is complete, X-rays of the tibia are taken and the quality of the anastomosis is determined. When the resulting bone regeneration is sufficiently dense, the device is removed.If it is rickets
Rickets is a disease of infancy characterized by disturbances in phosphorus-calcium metabolism [1]. The most common cause of classic rickets is vitamin D deficiency. It 'directs' the absorption of calcium, which in turn affects the absorption of phosphorus.
In the first years of life, the child grows particularly quickly, and the phosphorus and calcium deficiency clinically manifests itself so clearly and specifically that it stands out as an independent disease.
As a rule, the first signs of the disease appear at the age of 2-3 months. The most noticeable manifestations of rickets are softening of the bones, which is manifested by softening of the edges of the fontanel and sutures of the skull, flattening of the occiput, and in severe cases, curvature of the spine and legs, and deformation of the pelvic bones.
Rickets [2] should be prevented during pregnancy by taking vitamin D. By the time the infant is one month old, at least 400-500 IU of vitamin D should be given daily. Vitamin D is also a medicinal treatment for rickets [3].
Avoid tight wrapping
You may still hear from grandmothers that crooked legs can be 'corrected' by tight swaddling. Such outdated measures do not bring positive results, but a lot of problems.
Modern medicine is against swaddling because it impedes blood circulation in the limbs, causes delays in physical development and makes breathing difficult due to the pressure on the baby's chest. Clothing with a sling should be preferred to loose undershirts, pajamas or baby overalls. The arms and legs should remain free.
Bar osteosynthesis
This technique is used less frequently than the other two (plates and staples). The undoubted advantage is the stable fixation, which makes it possible to operate on both limbs at the same time and to ensure early function and use of the bone. In this method, after drilling the bone canal, a pin of the appropriate diameter is inserted into the femoral or tibial intramedullary canal.
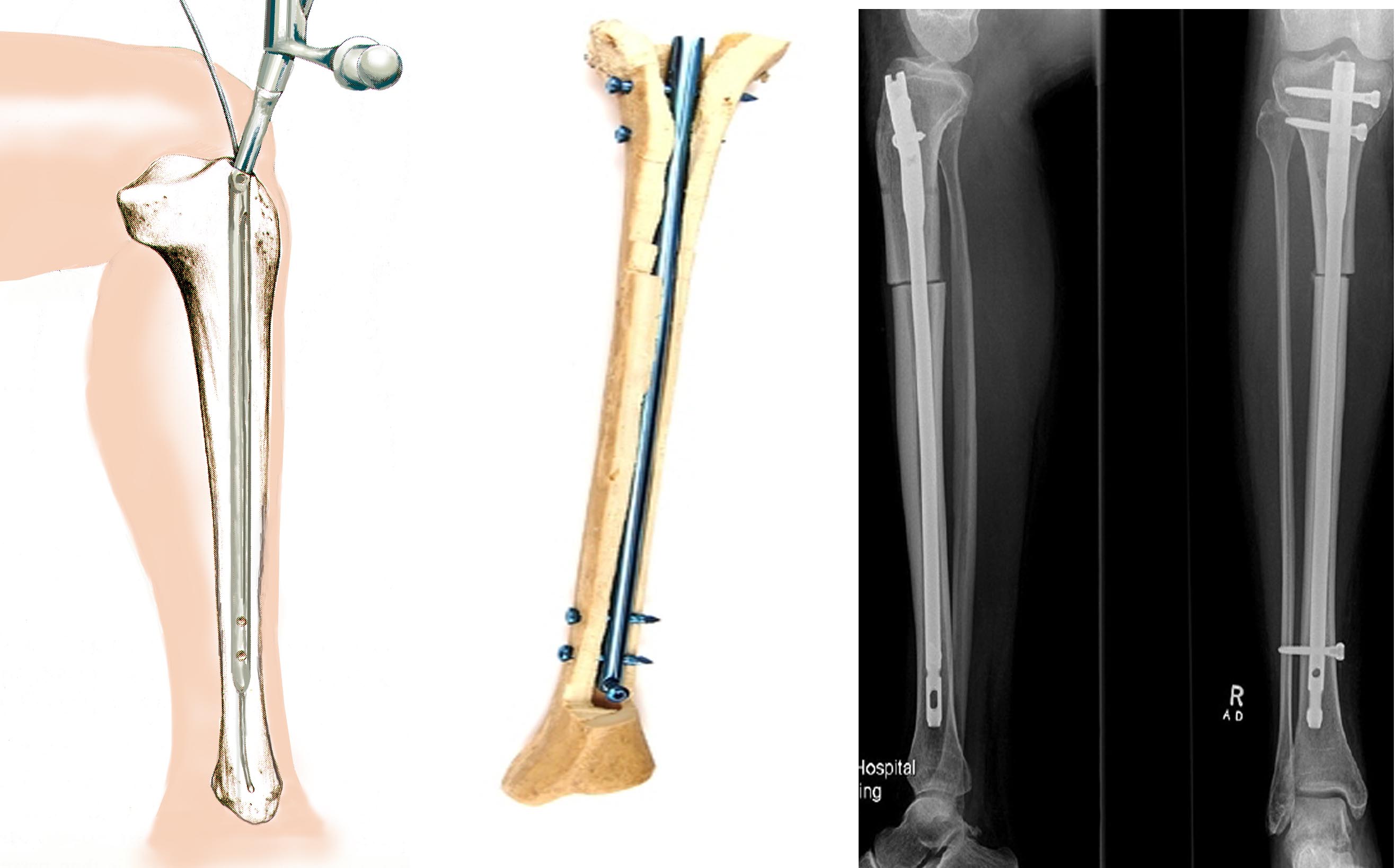
Path of insertion, position of the post in the bone and post-operative X-rays
Although the pins are inserted through a small incision, they cannot be considered minimally invasive. There is a risk of serious complications. For example, while with the Ilizarov appliance the inflammation or induration is local and superficial and heals easily, with intramedullary fixation the induration can spread to the entire medullary canal. Also, it is very difficult to achieve symmetrical correction of both limbs, which is important in cosmetic surgery.
Given the risk of serious complications, we would not recommend this technique for aesthetic leg shape correction. The use of pins in lengthening is justified when long periods of fixation with the Ilizarov apparatus significantly reduce the quality of life of patients.
Ilizarov osteosynthesis
The Ilizarov apparatus is the most commonly used method for correcting severe and complex limb deformities. The extent of correction or correction of deformities in other planes is unlimited. Medialization, rotation, subluxation of the fibular head, and limb lengthening can be performed simultaneously with correction of angular misalignment. The full load of the limbs is possible in the next few days after the procedure.
The main complication that occurs with external osteosynthesis is inflammation in the joints. These are not difficult to deal with. The incidence of bone inflammation in the spine is less than 1.5 percent. Although the bone is already inflamed, it locally heals completely.
The main disadvantage of the Ilizarov supports is their sheer presence and the limitations associated with clothing and footwear. The solution to this problem is to replace the round supports with monolateral mini fixators that attach to the anterior surface of the tibia. These are much smaller and do not affect the full function of the knee joint.
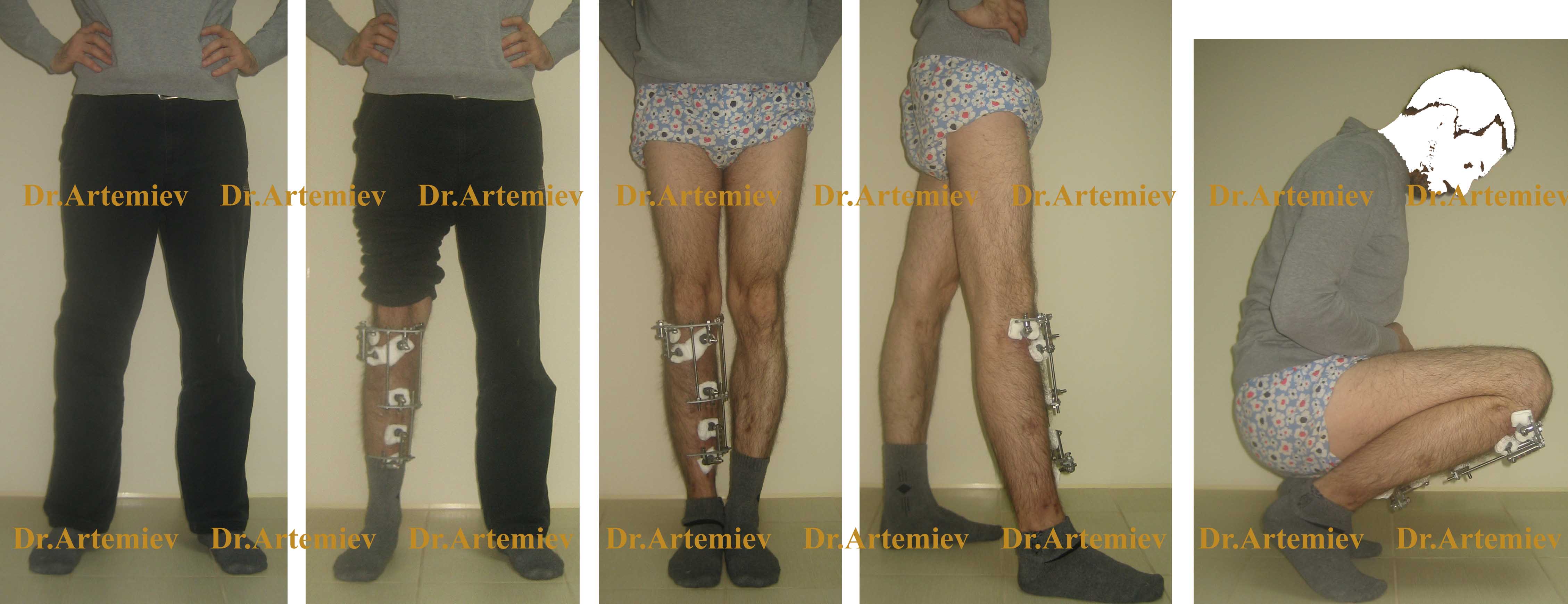
Appearance of a patient with a mini fixator on the lower extremity during the correction of a tibia deformity
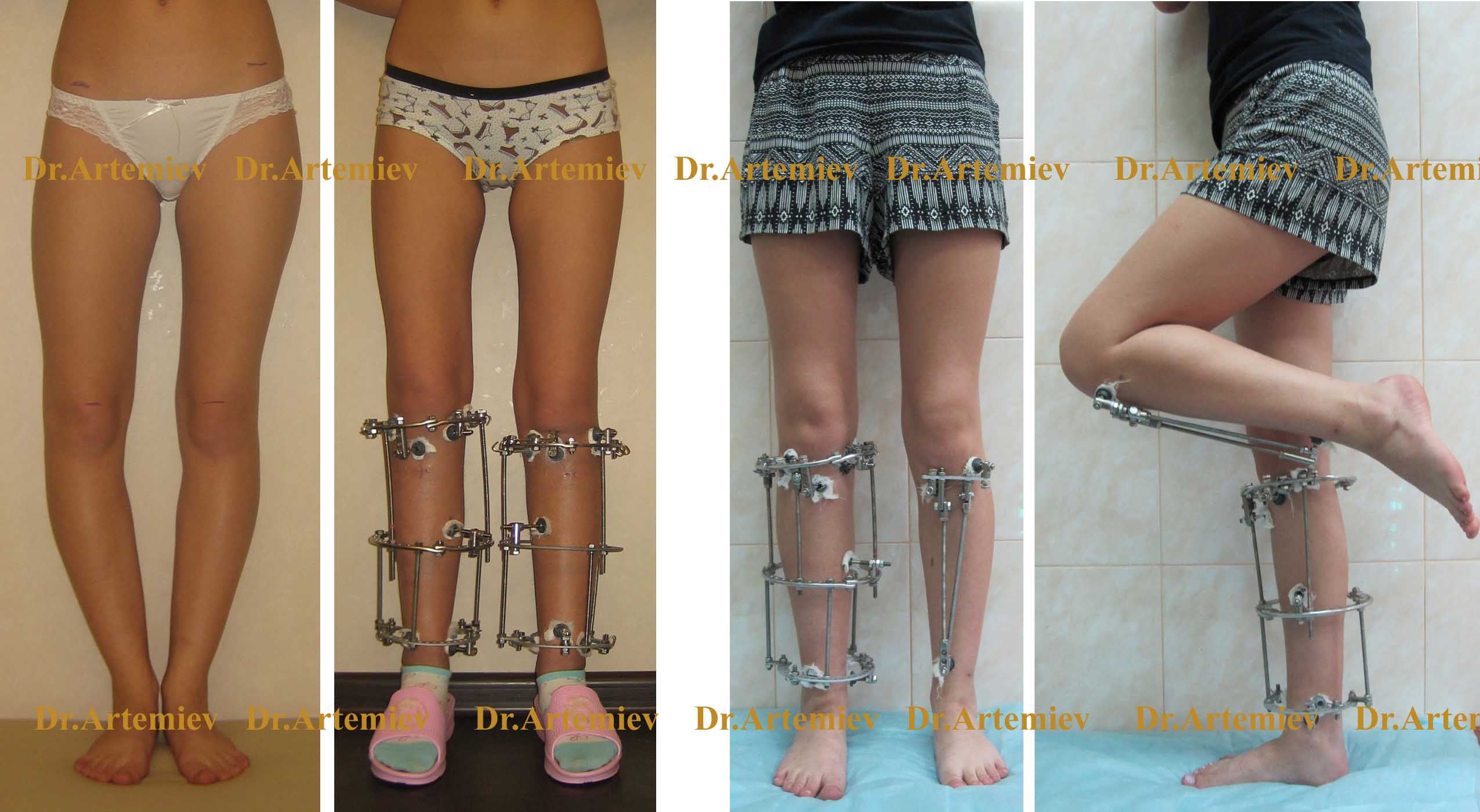
Appearance of a patient with varus deformity of both tibia using a mini fixator
Changing from Ilizarov ring braces to mini fixators makes sense 1.5-2 months after the operation if there are already signs of regeneration in the osteotomy zone. For surgeries on both limbs, mini fixators allow the legs to be closed at the knee joints and the final shape of the legs to be assessed before they are fully healed.
Incorrect curvature of the lower limbs
Doctors classify this type of defect as a cosmetic defect because the soft tissues of the lower limbs are not positioned correctly, giving the impression that the shape of the leg is abnormal (crooked) - however, upon diagnosis, the bones themselves are found to be intact are. The main indicator of a misalignment is that the soft tissues in the lower leg area are not growing together.
The problem of leg curvature is noticeable from adolescence, and often it is not even necessary to visit a medical institution to diagnose this defect, since it is visible to the naked eye. The main reason for the curvature of the legs is the lack of important vitamins and micronutrients in the child's diet. Vitamin D and calcium are involved in the development of bones and in maintaining their strength. Therefore, in order to prevent bone loss in childhood, it is important to monitor the child's diet and saturate it with the necessary substances. It is also necessary to spend more time outdoors and in the sun, which leads to enrichment of the body with oxygen and normalization of metabolism.
A fairly common cause of tibia curvature (not only in children but also in adults) is trauma, particularly when the tibia, femur, or knee joints are affected.
Intrauterine development can influence the development of the defect: for example, if the mother is seriously ill during pregnancy or if there is a genetic factor.
Correction of lower limb curvature
The most common method of correcting leg shape and lower leg curvature is surgery, which is associated with better results and greater effectiveness. It is virtually impossible to correct anomalies through motion alone.
If a patient is diagnosed with an improper curvature of the lower limbs, they will be offered a shin contouring technique. Doctors note that not only people with cosmetic flaws, but also professional athletes resort to this method of correction to give their legs the necessary contour. However, this technique is only applicable if the lower leg bones are not deformed.
Another method of correcting a false curvature of the lower leg is prosthesis, ie implantation of prostheses under the skin in the area of the calf muscle. Silicone implants are used as prostheses. This material is characterized by high elasticity and strength, so they are not visible. After such a correction, the doctor will definitely inform you about any limitations in the physical stress on the lower leg area. With implants, it is possible not only to correct the shape of the lower legs, but also to add volume to slender legs.
If the defect cannot be corrected with the above methods, orthopedic surgery is performed, in which the doctor performs a corrective osteotomy by cutting the bone, followed by Ilizarov compression-distraction osteosynthesis. The same method can also be used to increase the height and adjust the length and shape of the bones.
The operation of the curvature of the lower leg is only suitable for patients who are at least 18 years old.
- Asian eye incision
- freckles
- wolf lips
- double chin
- Generalized periodontitis
- Hyperkeratosis on the feet
- hyperpigmentation
- Deformation of the auricle
- skin sagging
- Sagging skin on abdomen
- Oily skin
- Oily eyelid hernias
- curvature of the nose
- apron of fat on the skin
- small chin
- Droopy upper eyelid
- problematic skin
- Systemic Scleroderma
- Thin Lips
- Sensitive skin
DIAGNOSIS OF LEG CURVE IN A CHILD
In the case of congenital anomalies, the problem can be diagnosed in the first few months after birth, but usually the curvature of the legs becomes clearly visible in children by the age of 1 year, when they begin to walk. In most cases, the diagnosis is finally made by the age of 2 years.
How is O and X curvature diagnosed in children?
Diagnosis mainly involves observation by an orthopedist, rudimentary examination, and motor tests. Hardware diagnostics is used to study the pathology in more detail.
X-rays are a common examination of bones and joints that provide an immediate indication of the condition of the hard tissue. Read more below
Ultrasonography or arthroscopy of the joints is a safe and quick way to determine the cause of the pain and assess the condition of the joint. Read more below
Computed tomography provides a three-dimensional model of the examined area and can reveal changes such as inflammation, injuries, malformations, etc.
REHABILITATION MEASURES
If there is no longer any doubt about the curvature of the child's legs - how to correct it? Depending on the stage, treatment can be conservative or surgical.
With a mild pathology, treatment can be limited to manual therapy and therapeutic massage. However, when the leg curvature has progressed to a more complicated form, conservative treatment is required.
Teipes are self-adhesive tapes. They are attached to the body and relieve the painful joint, injured muscle or ligament. They facilitate blood and lymph flow and accelerate healing. Read more
Used to correct bad posture and flat feet. Also recommended for people who are on their feet for a long time to prevent back problems. Read more about it
Gymnastics not only has a positive effect on muscles, ligaments and joints, but also on the nervous system. Read more
The massage calms the nervous system, increases blood microcirculation and improves metabolism…
Ratings and Comments (54)
Only registered users can leave comments. Please sign in.
Natalia 11:05 Oct 18, 2020 Wow?wonderful I didn't know about these surgeries ❤️
Annaast 23:06 14 April 2017 There are even promotions for such operations?
I had my curvature corrected a few years ago. The rehabilitation period is difficult, but worth it. I am very satisfied with the result! 1Seema 12:01 13 December 2016 Hello everyone. I'm new here:)) I would like to participate in this surgery because I have had a leg complex since childhood, everyone around me is looking at me and I can't go to the beach and wear a skirt, so I would like to as woman wearing skirts ((((
MarinaMalina 22:55 23 April 2016 I have a friend who had surgery and had to wear an Elizarov brace for 3 months. But the operation was paid for by the government).
Sayhopee 11:08 Jan 2 2021 How did the state pay for this?
Olga 00:41 30 Jan 2016 I think it's a serious operation
Tyusha 13:49 3 Jan 2016 Hello everyone. I dream of participating in this operation because I have O-shaped legs, a complex since childhood would also add a few centimeters to the height. Am willing to attend any session. If this operation is not expected in the coming year , please advise me on the price and suggest a good doctor . Thank you.
Summers 00:24 14 August 2015 The second video is great, very positive girl) I remembered myself after the operation, I was also running, jumping, too hurt that no one gave way on the subway))))
Alina 19:26 20 November 2014 Can you also apply if you don't have a deformity but only need to lengthen your legs?
zuma 19:12 21 April 2014 Hello, I'm new here :)) can you tell me if there are any stocks for this treatment?
Inspiration 17:20 6 December 2013 yes it's a good procedure) I had it done + extension
Blog (Foot Correction)
- Valgus deformation of the toe ? My Operation Author Post Farida 23 Oct 2021
- A year after my surgery.
 Flight normal.??? Author post Natalia??? 24 Jan 2020.
Flight normal.??? Author post Natalia??? 24 Jan 2020. - 7 months after my surgery at Makinian Levon Gagikovich.
 Emotions, impressions, feelings. Written by Natalia??? on August 6, 2019.
Emotions, impressions, feelings. Written by Natalia??? on August 6, 2019. - Surgical treatment of valgus toe misalignment – 'toe bones'. Author Entry Nina? on July 22, 2019.
- One month after surgery to correct a forefoot deformity.
 Recovery author of the entry Natalia??? March 24, 2019.
Recovery author of the entry Natalia??? March 24, 2019. - How I examined myself for the operation.
 Interesting information. Written by Natalia??? January 22, 2019.
Interesting information. Written by Natalia??? January 22, 2019. - Day 2.3 after surgery with Levon Gagikovic
 Conditions at home, rehabilitation. Written by Natalia??? on January 20, 2019.
Conditions at home, rehabilitation. Written by Natalia??? on January 20, 2019. - My forefoot deformity correction surgery by Dr. LG Makinian at the Galaxy Clinic.
 Part 2. Written by Natalia??? on January 18, 2019.
Part 2. Written by Natalia??? on January 18, 2019. - My forefoot deformity correction surgery by Dr. LG Makinian at the Galaxy Clinic.
 Part 2. Written by Natalia??? on January 18, 2019.
Part 2. Written by Natalia??? on January 18, 2019. - My surgery with orthopedic trauma surgeon Makinian Levon Gagikovic at Galaxy Clinic
 Part one Natalia??? January 18, 2019.
Part one Natalia??? January 18, 2019.
Possible causes of X-shaped feet
X-shaped feet can be physiological or pathological. The former affects children between the ages of 3 and 5 years. During this period of lower limb development, about 85 % of the children have a slight X foot deformity. By school age, this deformity should have completely resolved itself through the build-up and strengthening of the muscular skeleton in a natural way.
In an adult, this deviation is acceptable at 5-8°, while in a woman after childbirth, a valgus deviation of the tibia up to 10-12° can persist within 3-4 years. Greater angles of inclination are considered abnormal and result in misalignment of the tibial condyles in the joint capsule. This affects the meniscus and synovial layer of cartilage.
In patients with valgus torsion, knee joint deformity can develop as early as 20-25 years of age. By the age of 35, this leads to persistent persistent pain and the development of grade 3 osteoarthritis of the knee. Therefore, the condition of the lower limbs should be closely monitored.
All risk factors and potential causes for developing knock-knee deformity should be eliminated for active prevention. Below are only the main types of negative influences that can provoke this pathology:
- Congenital anomalies in the development of the bones and cartilages of the lower limbs (as a rule, the first signs of this appear in the first year of the child's life);
- Early positioning of the child, when the musculo-ligamentous apparatus is weak, the tibial and femoral condyles are displaced, and the foot is misaligned;
- Wide leg position when standing and walking;
- Inappropriate choice of footwear for constant wear and sports activities (this problem often occurs in adolescents when, for fashion reasons, they do not want to wear comfortable shoes);
- Obesity, since each extra kilogram creates a significant load on all bones of the lower limbs, which gradually slip, so there is a compensatory load distribution;
- asthenic constitution with poorly developed tendon and ligament apparatus;
- Dystrophy and atrophy of the muscular apparatus of the lower limbs (caused by a sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work, or impaired innervation and blood supply)
- metabolic diseases such as angiopathy and diabetic nephropathy;
- Alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking also lead to toxic and vascular inflammation of the muscles of the lower limbs and progressive deformity of the limbs;
- Peculiarities of the female pelvis can cause misalignment of the legs; in girls, this pathology begins to manifest itself in early school age
- Calcium and phosphorus deficiencies, which can be caused by nutritional disorders, bowel dysfunction, or vitamin D deficiency;
- kidney disease, in which there is an increased excretion of calcium and phosphorus salts;
- Rickets before 3 years of age
- poor heredity (if the parents suffer from valgus deformities of the lower limbs, then there is a high probability that the child will be affected by the same disease)
- Anomalies in the ossification process of the outer border of the femoral or tibial condyle;
- valgus deformity (primary or secondary) of the femoral neck;
- Consequences of trauma (usually intra-articular fractures, tears of the ligamentous and tendon apparatus of the knee joint with subsequent bicatrial deformity);
- Tumors of the musculoskeletal tissue around the knee or ankle.
Symptoms and diagnosis of leg curvature
X-shaped legs are often visible to the naked eye. However, in the initial stages, it is worth paying close attention to the specific symptoms of knock knees, which can manifest themselves as follows
- increased fatigue of the lower leg muscles with usual physical activity;
- Pain in the legs that occurs after standing for a long time
- cramps in the calf muscles;
- impairment of gait, feeling of instability;
- Loss of muscle tone in the legs.
The X-shaped leg curve is visible to the naked eye when the degree of deviation is significant. However, in order to make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to see an orthopedist. The doctor conducts a comprehensive examination to determine not only the degree of deformation, but also the possible cause of the deformation.
Anatomical changes in the knee joints and spine lead to secondary clinical signs. Tension of the medial collateral ligaments leads to instability of the joint in lateral projection. Hyperextension can fracture and tear the tibial and femoral condyles. This then leads to deforming thickenings in the form of bony prominences and nodules.
Flat feet are another distinctive feature of X-shaped foot deformity in both children and adults. Severe flat feet cause persistent foot pain, muscle tension in the arch of the foot, etc.
The inclination of the trunk to one side or the other when walking causes scoliosis, destruction and twisting of the pelvic bones, and deformation of the hip joints. With unilateral deformation of the limbs, pronounced claudication is observed.
Diagnosis begins with a comprehensive examination by an orthopedist. It is he who determines the extent of the deformity and the possible negative consequences of this pathology. This is followed by an X-ray examination in several projections. From this it is possible to deduce the extent of deformation and the presence of secondary pathological changes.
Why does femoral neck deformity occur?
Primary femoral neck deformity occurs only as a congenital anomaly that may not become apparent until adulthood. The gradual deformation of the femoral neck is a consequence of such negative factors as:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- excessive body weight;
- smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- foot misalignment when walking and running;
- Heavy physical work that puts a lot of strain on the hip joints;
- femoral neck fractures;
- Wearing high-heeled shoes.
Secondary femoral neck deformities always develop against the background of other diseases of the lower limbs. The most likely pathologies include:
- Deforming arthrosis of the hip (cocarthritis);
- Deforming arthrosis of the knee (gonarthrosis);
- curvature of the lumbosacral spine;
- Inflammation of the pubic conjunctiva and detachment of the pubic bones in women during pregnancy
- foot deformities in the form of flat feet or club feet;
- Tendinitis, tendonitis, synovitis, bursitis and cicatricial deformations of the soft tissues of the lower limbs.
Risk factors should also be considered. These include intrauterine bone abnormalities, rickets in early childhood, osteoporosis in middle and older age, vitamin D and calcium deficiencies, endocrine diseases (hyperthyroidism, diabetes, adrenal hyperfunction, etc.).
Successful treatment of hip deformity requires elimination of all possible causes and negative risk factors. Only then can a positive result be achieved.
Varus Deformation of the Neck of the Thigh (Femur)
There are two types of hip deformity: valgus and varus, with the former being an X-shaped deformity and the latter being an O-shaped deformity. Both forms are accompanied by a change in the angle between the femoral head and the diaphysis of the femur. Normally this is between 125 and 140 degrees. Increasing this value to 145-160 degrees results in an O-shaped curvature. Decreasing the angle leads to a varus deformity of the femoral neck, in which rotation of the lower extremity is severely limited.
Abduction of the leg from the body is impaired in a varus hip deformity, causing severe hip joint pain. Therefore, the initial diagnosis is often wrong. The doctor suspects destruction and deformation of the femoral head and the hip socket. To confirm the diagnosis of deforming arthrosis, an x-ray of the hip joint is taken in several projections. This laboratory examination also reveals a varus deformity of the femoral neck, which is clearly visible on the X-rays in the straight and lateral projection.
Several stages can be distinguished in the development of hip curvature:
- A slight deformity with a change in angle of 2-5 degrees does not cause discomfort and does not lead to visible clinical symptoms;
- The middle stage is characterized by severe curvature and causes problems with some movements in the hip joint;
- A severe deformity leads to a shortening of the limb and a complete blockage of twisting and rotational movements in the hip joint assembly.
In adults, varus deformity is often the result of aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. Also, this pathology is accompanied by mucopolysaccharidosis, rickets, bone tuberculosis, chondroplasia and various other serious diseases.
Leg exercises in remission
If you're only exercising to compensate for a sedentary lifestyle, you can move on to full-body exercise More exercises for your leg muscles. The exacerbation complex is suitable as a continuation of the warm-up training. The most important thing is to follow the technique closely and not try to increase the load when the body is not ready for it.
- Do 15-20 squats: Make sure your knees don't fall in and go forward past your feet.
- Sit in a chair and place one foot on top of the other. Then raise the other leg to the maximum height, you can stay at the highest point. Repeat the exercise 10 times, then switch legs.
- Leg raises (you can lean against a wall or chair): Forward, backward, sideways 15 times, then switch legs.
- Run a few laps around the room by stepping on tiptoe, then hop for 30 seconds without falling back on your heels.
- Finally, run in place for 2-3 minutes.
Can exercise help?
If you don't feel like exercising at home, moderate exercise is a good idea. Nordic walking, swimming and yoga can help. If you're feeling good, you can start jogging, biking, and skating, or play some outdoor games: soccer, volleyball, and basketball.
Most importantly, for the sake of your health, don't overindulge in exercise, because heavy training is sure to hurt an unprepared body. Physical activity benefits your whole body, and after a while you can start to get closer to more serious results. Or maybe you'll transition from the five-minute exercises at home to a healthy, athletic lifestyle. Either way, even a simple routine of exercise will help you feel better and is the first step in recovery from illness.
List of Sources
- Git VD healing of the spine. – Moscow: Labyrinth Press, 2006. – 256 с.
- Abelskaya IS, Mikhailov, OA // Degenerative lesions of the spine and joints: Ml. conf. / ed. by AN Mikhailov and VD Pilipenko – Mn., 2001. – С. 12-15
- Kosheleva LP Proper Posture as a Pledge of Human Health // International Journal of Applied and Fundamental Research. – 2014. – № 12-2. – C. 215-217.
- Volkova AY, Solomotina NB, Zhuravskaya NS Description of complex exercises to strengthen the muscles of the back girdle in postural disorders and osteochondrosis // Scientific Journal. 2015
- Pjastolowa NB Physical rehabilitation of spinal curvature // Wychowanie fizyzyczne. Sports. Tourism. Physical recreation, 2019. ref.
- Epifanov VA Therapeutic physical training. Handbook / VA Epifanov, M: GEOTAR-Media, 2006. 568 с.
- X-shaped legs photo.
- legs x.
- Shoes for crooked feet, how to choose them.
- Crooked big toe.
- How much does crooked leg surgery cost?.
- Why are a teenager's toes crooked?.
- How to tell if your legs are long.
- The baby has short legs.
