Reasons for visiting an orthopedist can be:
- What does an orthopedist treat?
- What is orthopedics?
- Anatomy of the hip joint
- Some features of the hip joint in newborns
- What problems can an orthopedic dentist help with?
- How does an orthopedic dentist restore teeth?
- What orthodontists and prosthodontists have in common
- QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
- What does an orthodontic dentist treat?
- When to See an Orthopedic Dentist
- sports orthopedist
- Orthopedic Arthrologist
- What you should know about orthopedic dentistry
- Indications for visiting a trauma dentist
- Physical examination
- Pediatric Orthopedic Services at GMS Hospital
- Cost of pediatric orthopedic treatment
- Responsibilities of the Orthopedist
- liability of the orthopedic surgeon
What does an orthopedist treat?
An orthopedist is a specialist in the treatment of disorders and degenerative changes in the musculoskeletal system. He studies the formation of bones and muscles and the complications that develop as a result of infectious diseases, congenital defects and injuries in the home and in sports. The knowledge gained through years of practice allows him to lift patients with chronic diseases and serious injuries and to make life easier for people with skeletal disorders.
In this article, you will learn who an orthopedic trauma surgeon is, the types of treatments they deal with, and the diseases they treat.
What is orthopedics?
Orthopedics is the branch of medicine that deals with the study of causes and methods of correction and prevention of acquired and congenital pathologies and diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
reference. The name 'orthopaedics' was coined by Nicholas Andra in the mid 18th century. He defined what an orthopedic surgeon does and what diseases he treats. The term is made up of two words of Greek origin, which literally translated mean something like 'train' and 'straighten'. So, orthopedics deals with the problem of skeletal curvatures and muscle deformations and develops methods to eliminate them.
This science is part of clinical and sports medicine, traumatology and rehabilitation.
In practice, the causes and prerequisites for pathological changes include:
- trauma and injury;
- heredity;
- congenital diseases;
- inappropriate lifestyle;
- excessive physical exertion.
Anatomy of the hip joint
It is difficult to understand hip dysplasia without knowing the anatomy of the hip joint. The terminology can be difficult for parents to understand, but it's important to become familiar with it to better understand the situation.
The hip joint has two articular surfaces. One is the rounded head of the femur. The second surface is the acetabulum. It is formed by the surfaces of the pelvic bones and has the shape of a hemisphere. The pelvic bones in the joint area are connected to each other by Y-shaped cartilage. The inside of the hip socket is lined with hyaline cartilage. A cartilaginous lip made of cartilage is attached to the periphery of the acetabulum. It is necessary to deepen the acetabulum.
Some features of the hip joint in newborns

The femoral head is formed by cartilage tissue in a baby's first month of life. He gradually ossifies. It develops faster than the hip socket. In children, the femoral head is not sufficiently embedded in the socket, especially in the first months of life. This is particularly pronounced in girls.
In newborns, for example, only half, sometimes a third, of the femoral head is covered by the socket. This is known as articular surface malalignment. As the child grows, both the femoral head and socket develop proportionally and more evenly.
In addition, attention is paid to the features of the femoral neck. It is short and made of cartilage. The ligaments that strengthen the joint capsule are underdeveloped in children in the first months of life.
What problems can an orthopedic dentist help with?
The best way to understand what orthopedics is in dentistry is to list the problems that only an orthopedic dentist can treat. It should be pointed out right at the beginning that only an orthopedist can solve these problems: surgery and therapy have little effect in these situations:
- Severe tooth decay due to caries or mechanical damage that cannot be repaired with a filling.
- Pathological processes in the hard tissues of the tooth.
- Necrosis of the tooth structure.
- Anomalies that affect the shape of the teeth.
- Pathological abrasion of the teeth.
- Gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal diseases - prevention and prosthetics when teeth have already been lost.
A prosthodontist is also needed when minor cavities need to be corrected: chipped, scratched, misaligned healthy teeth and other problems.
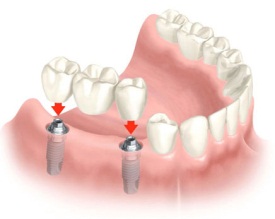
How does an orthopedic dentist restore teeth?
We have learned that a prosthodontist is necessary when a filling and superficial restoration cannot save the tooth. To restore a tooth, the dentist uses:
- Veneers – thin ceramic or porcelain plates. First of all, they have an aesthetic function - they are most often used to correct the appearance of the front teeth.
- Inlays – are used when the crown of the tooth is at least partially preserved.
- Crowns – are suitable for restoring teeth that have had their pulp removed. In a few sessions, the orthodontist prepares the tooth, takes an impression, and then inserts a prosthesis that fully matches the lost crown.
What orthodontists and prosthodontists have in common
What the orthodontist and prosthodontist have in common is that they only work on normalizing the dentition, which leads to a more harmonious alignment of the teeth and the restoration of chewing function.
Perhaps the biggest difference is that in addition to the orthodontist, there is also an orthodontist with a general specialty.
The orthodontist fixes the teeth in the correct position and aligns the bite, but without changing the shape of the teeth themselves.
The orthopedist, on the other hand, rebuilds teeth with dentures and replaces lost teeth, restoring chewing function and psychological comfort.
In general, there is a big difference between orthopedics and orthodontics in dentistry and the specialist treats them differently, so we hope you are not confused now.

QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Why do these two very different disciplines have similar names?
In Greek, oros means right, straight. Both a prosthodontist and an orthodontist correct teeth, just each in their own way, hence the similar names.
Can a dentist be both an orthodontist and an orthodontist?
Yes, if the doctor has studied both specialties, that is possible, but usually there are doctors who are more specialized.
If I need both orthodontic and orthopedic treatment, who should I go to first?
As a rule, the bite is first corrected by an orthodontist and then the fixed anchorage by an orthopedist. However, in some cases, temporary restorations are made with temporaries prior to treatment to prevent the teeth from being lost during the long-term orthodontic process.
What does an orthodontic dentist treat?
Orthodontic dentistry specializes in restoring teeth and preventing tooth decay. The primary goal of an orthopedic dentist is to ensure the integrity of the dental arch, even when a tooth is severely damaged or missing.
Among the problems that the specialist in orthopedic dentistry deals with are:
- caries as a result of dental disease;
- trauma consequences;
- loss of individual teeth;
- Missing parts of a tooth.
Significant damage to even a single tooth will inevitably have an impact on the individual. They usually cause psychological discomfort and sometimes even more serious problems. In addition, chewing activity is restricted, which can have a negative effect on digestion. An additional negative aspect is the increased pressure on the remaining teeth.
Orthopedic treatment aims to eliminate the problems that sufferers face. An orthopedic dentist can restore the joy of smiling, the comfort of communication, and a familiar way of life. Therefore, it is important to see a specialist in good time at the first sign.
When to See an Orthopedic Dentist
Dental care should not be put off, especially if a tooth is damaged or missing. An appointment with the dentist or orthopedist should be made in the following cases
- The tooth has partially decayed;
- A chip has formed on the tooth;
- A crack has developed;
- A bent tooth;
- Another problem of an aesthetic nature;
- Complete missing of a tooth.
Modern orthopedic dentistry can solve most aesthetic problems related to tooth loss. If you want to straighten your teeth and stop worrying about your smile, make an appointment with an orthopedist.
Treating a missing tooth early is just as important. With the latest orthopedic technology, it is possible to restore not only the crown of the tooth, but also the roots of the tooth. A new tooth can be placed in the place of the missing tooth, replacing it perfectly. Special designs are able to restore the integrity of an entire row of teeth.

sports orthopedist
The tasks of the sports orthopedist include the monitoring of athletes and the early detection of desired and pathological changes in their physical condition. The sports orthopaedist constantly monitors the performance of his patients and is directly involved in the development of training programs. In addition, the sports orthopedist specializes in developing courses that facilitate and accelerate an athlete's recovery after an injury. All this allows gymnasts and athletes to perform better without jeopardizing their health.
Knowledge of sport and exercise is essential for every modern orthopedist.
Orthopedic Arthrologist
An orthopedic surgeon is a medical specialist who diagnoses and treats degenerative and inflammatory diseases of the joints and spine. A good adult orthopedist will successfully diagnose and treat common conditions such as valgus deformities, osteoarthritis, polyarthritis, and osteoarthritis.
This doctor specializes in detecting and treating diseases of the human spine. The most common diseases of this organ include herniated discs, osteochondrosis and scoliosis.
You can find out more about advice, diagnosis and treatment here.
What you should know about orthopedic dentistry

If a person loses one or even several teeth, the dentition must be restored immediately, which is carried out by a specialist. The specialist, if he has mastered his craft, quickly decides on the treatment tactics and clarifies all the important points.
Now that you definitely know who and what he treats and know the key points of orthopedic dental treatment, let's briefly talk about treatment at Apex Dental Clinic.
Indications for visiting a trauma dentist

The traumatologist treats patients for emergency and elective indications. Emergencies may involve treating a broken bone, dislocation or serious injury. Such diseases require urgent examination and treatment.
An orthopedic trauma surgeon should be seen as an emergency if you have the following symptoms:
- bone, joint or muscle pain;
- crunching of joints when moving;
- limited movement of joints, stiffness;
- curvature of the spine, poor posture;
- pain in feet when walking;
- clubfoot.
Consultation with a trauma surgeon is indicated for long-term injuries and habitual dislocations. You should bring the results of previous examinations, scans and conclusions from other specialists to your first appointment.
Physical examination
The doctor first examines the patient's complaints, his age and dynamics. The doctor then collects the anamnesis - peculiarities of lifestyle, working and rest times, occupation, intensity of physical activity, diet. After that, the doctor carries out an objective follow-up examination.
During the examination, the traumatologist performs the following actions:
- Visual assessment of the patient's posture and gait, detection of limping, hunching;
- He examines the skin around the joints;
- He feels the joints, notes pain, swelling and range of motion;
- palpation of limbs, verification of bone integrity;
- Examines the spine, identifies pain points;
- determines the extent of movement in the spine;
- assesses the condition of soft tissues, the presence of hematomas, swelling;
- checks the severity of the tendon reflexes.
Pediatric Orthopedic Services at GMS Hospital
In our center for traumatology and orthopedics, diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system of various causes and severity are comprehensively offered. If you need the services of a pediatric orthopedist, contact the GMS Hospital. We offer you the best that modern medicine has to offer:
- Use of the latest medical advances and innovative treatment and diagnostic equipment;
- the development of personalized treatment and rehabilitation programs;
- modern, gentle treatment methods that maximize success
- advanced rehabilitation measures.
Make an appointment with one of the leading specialists at the Moscow GMS Hospital or call a pediatric orthopedist at home when it suits you best.
Cost of pediatric orthopedic treatment
The prices given in this price list may deviate from the actual prices. Please call +7 495 781 5576 (24 hours) or visit the GMS Hospital at 45 Kalanchevskaya Street.
| Surname | Price |
| Initial consultation with a leading surgeon/traumatologist/orthopaedist | RUB 15,851. |
| Initial consultation with a surgeon/traumatologist/orthopaedist | 11 095 rubles |
| Re-consultation with a leading surgeon/traumatologist/orthopaedist | 13 473 rubles |
| Repeat visit to a surgeon/traumatologist/orthopaedist | 9 430 rubles. |
| Extended consultation with a leading surgeon/traumatologist/orthopaedist | 28 541 rubles. |
Dear customers! Each case is individual, and the final cost of treatment can be determined only after a personal visit to a doctor of the GMS hospital.
The prices shown refer to the most requested services. You can purchase optional health insurance, pay for each visit individually, contract for an annual health program, or pay a deposit and receive the services at a discounted rate. On weekends and public holidays, the clinic reserves the right to charge additional fees according to the applicable price list. The services are provided on the basis of a signed contract.
Responsibilities of the Orthopedist
Orthopedic responsibilities include:
- General examination of the patient (determination of body weight, shape of the thorax, physique), collection of the medical history.
- Assessment of the musculoskeletal system: measurement of muscular strength and mobility of the spine, measurement of posture, plantography, angulometry.
- Preliminary diagnosis, prescription of the necessary examinations, interpretation of CT, MRI, X-ray, joint and Doppler ultrasound, densitometry, etc.
- Clarifying the final diagnosis in the ICD system, independently or with the help of other specialists, and drawing up a treatment plan according to recognized protocols.
- Recognition of disease complications and critical conditions and measures to eliminate and prevent them.
- Prescribing drug therapy, physical therapy, reflex therapy, exercise therapy, surgical, prosthetic and osteoplastic treatment, and intra-articular drugs when indicated.
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment and rehabilitation and revision of the plan previously prepared.
- Applying various types of bandages, including on purulent wounds.
- Immobilization with the help of splints, corsets and other constructions.
- Preparation of expert opinions for forensic examinations and the personal involvement of the orthopedist in this process.
- Selection of orthopedic shoes, prostheses, orthotics, etc.
- Advice to other general practitioners, filling out diagnostic and billing documents, filling out medical records and prescriptions.
- Regular accreditations every 5 years and mandatory medical examinations for further practice as an orthopedic surgeon.
- Patient education, discussions with the nursing staff about the prevention of accidents at work.
- Compliance with labor regulations, medical ethics and safety procedures.
liability of the orthopedic surgeon
According to Russian law, a doctor is liable for the following violations:
- Untimely or inadequate performance of his professional duties;
- failure to comply with or inaccurate execution of management's instructions;
- professional errors in the work of the staff subordinate to the orthopedist;
- Inadequate medical records and inaccurate data in reports;
- Abuse of official authority to the detriment of the employer for personal gain;
- Non-compliance by the doctor or his subordinates with the rules on the safe use of medical equipment and fire safety, failure to report violations to the management of the medical institution;
- Non-compliance with the labor regulations established in the medical institution.
The orthopedist is punished for mistakes made in the performance of his professional activity, depending on the seriousness of the violation. This may be an oral or written reprimand, loss of an award, demotion, dismissal or other administrative, disciplinary or financial sanction. Serious violations can be punished with withdrawal of approval, compensation for material damage and even imprisonment.
Before signing the employment contract, you should carefully study the duties of an orthopedic surgeon as described in the job description. Discuss disagreements with hospital management. This will help you reach agreement with your colleagues and avoid professional misconduct.
Read more:- Who is the orthopedist?.
- What an orthopedist treats and what symptoms to report.
- What does an orthopedist examine?.
- What is the name of the orthopedist in the health center?.
- What is another name for an orthopedist?.
- orthopedist, the.
- orthopedist.
- The orthopedist is the one who.
