The insole has the following structure:

- What are the advantages of anatomical shoes - let's look at their characteristics
- Features of the anatomical shoes
- What is an insole?
- What is it made of?
- Functions of the insole in the shoe
- Types of supinators
- How do I choose the right footwear with insoles?
- To what extent is an insole mandatory in children's shoes?
- Which shoes should I choose for my child?
- Shoes for the winter season
- Do shoes have to have an insole (padding on the inside of the sole)?
- Should I look for shoes with a hard sole?
- What is an orthopedic insole?
- types of deposits
- Which shoes should I choose for my child?
- winter
- Sports
- How to support the foot in shoes without insoles?
- contraindications
- diversity
- prophylactic
- correction
- therapeutic
- Chiropodist duties
- When an orthosis is required
- What is an insole and what is it for?
- What insoles should be included in children's shoes?
- For what purpose is soft supination used?
- What is the difference between therapeutic and therapeutic?
What are the advantages of anatomical shoes - let's look at their characteristics
There is hardly a parent these days who does not know about orthopedic shoes. Apparently they are useful and everyone needs them, and even if not, they have magical properties. The opposite is true for anatomical shoes. Very few people are familiar with the term. We will devote the next 7 minutes of reading to understanding these terms and explaining what these shoes are.
Let's start with the simple things - let's talk briefly about orthopedic shoes. We want to dispel a common myth and remind you that orthopedic models are designed to heal. They are prescribed by the doctor and can be worn at any age, they are not suitable for prevention.
These shoes help correct defects in the musculoskeletal system. They are rarely available in normal children's shops, but are made to order in special ateliers. Therefore, a specific model is designed for a specific person.
Features of the anatomical shoes
What we used to call orthopedic shoes are actually just anatomical variants. Such models are used to prevent possible problems. Here are the characteristics that each specimen exhibits:
- Shoes are made of natural, breathable materials - leather, suede, cotton. If they are made of artificial materials, then they are of high quality and have perforations for ventilation.
- They have a fixed cuff on the heel so that the heel is well supported. It shouldn't be too high. The heel counter is usually made of a soft material that does not pinch the heel.
- The sole is firm and springy but not stiff. The shoe should also not sag in the middle.
- Wide toe box. A narrow toe is not acceptable in children as they need freedom of movement. It is better if the nose is closed.
- He doesn't have high supination. A large insole can be misplaced and cause unnecessary deformation of the foot instead of helping it.

You can buy good children's shoes in a normal shop. Orthopedic' shoes – Only in special shops.
What is an insole?
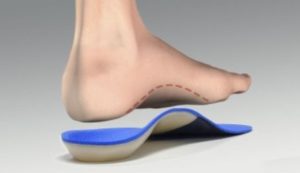
An insole is the protruding part of the footbed or a separate cushion inside the shoe. Attached to the front, middle or rear of the foot, it supports the arch of the foot and evenly distributes the load while walking.. Another function is to maintain the stability of the sole shape, which is particularly important when the foot is deformed.
There are two types of shoe inserts: plain and insoles. They are available as a separate part of the actual shoe, as a finished shoe with an insole, or as an orthopedic insole.
Important!!! It is a misnomer to call an orthopedic footbed an insole. It is only the protruding part of it.
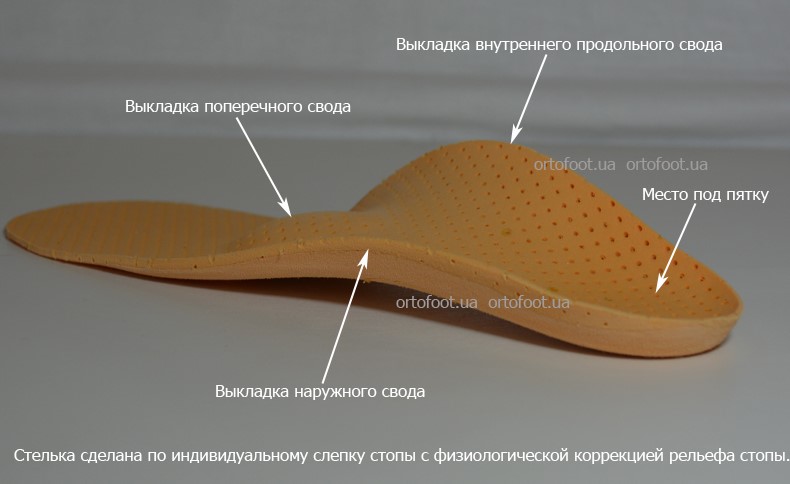

What is it made of?
The components differ not only in location and purpose, but also in the materials:
Gel insoles are sold separately or together with an insole. They are rarely found in finished shoes. They often consist of a sheet of metal or plastic bent into an arch shape and covered with leather.
Functions of the insole in the shoe

It is designed to support the foot and reduce pressure on the spine and joints. Some types of footbeds are made of elastic material. In the case of flat feet, it supports the arch of the foot and helps to shape the longitudinal arch. Metal plates not only support the foot, but also increase the life of the shoe by reducing deformation. Therefore, the price of such shoes is higher than shoes without gaiters, which wear out quickly and require the purchase of a new shoe.
Types of supinators
The most common type is a metal plate bent in the shape of an arc. It is attached between the sole and the actual insole and covered with leather or oilcloth. There are insoles made of leather, cork or plastic.
How do I choose the right footwear with insoles?
The choice of footwear with an insole depends on its purpose. For a healthy, anatomically correct foot, choose shoes with orthopedic prophylactic insoles – VP-1 and VP-6. VP-1 has inner longitudinal vault sealing, while VP-6 has transverse and inner vault lining. Both variants are used to maintain the correct foot shape. Useful for heavy and constant strain on the ankles - athletes, hairdressers, shop assistants, pregnant women and overweight people..
Important!!! A distinction is made between valgus and varus deformities. In valgus deformity, the foot flexes inward, while in varus deformity, the foot flexes outward. A varus deformity is referred to as a valgus foot, while a valgus deformity is referred to as a flat foot.

With a valgus deformity, shoes with VP-2 and VP-5 inserts are used, with the VP-2 model having a heel insert and the VP-5 model having a heel and forefoot insert.
As already mentioned, An important criterion when choosing a shoe with a heel cushion is the intended use.. And if you need a prophylactic pair, you can choose it yourself. The most important thing is to make sure that the size fits perfectly and that the foot pinator hits the right spot on the foot. However, with any type of deformity, only the doctor can prescribe insoles, which are made individually based on an impression of the foot.
To what extent is an insole mandatory in children's shoes?
The supinator in infancy is not an essential element. First and foremost, footbeds like orthoses are chosen by the orthopedist when the child has a foot deformity.

Unless your child has such problems and their feet are not developing abnormally, they usually do not need foot supinators. In addition, sometimes such a device can even interfere with the formation of the arch of the foot, so parents can buy healthy children's shoes without an insole.
The manufacturers of children's shoes are increasingly offering sandals and shoe models with a special insole that supports the longitudinal arch of the foot and is intended to prevent flat feet from developing. It should be noted that high-quality orthopedic insoles should only support the arch of the foot when the child is putting all of their body weight on one foot. Otherwise, they do not prevent the foot muscles from working properly.
However, if the arch of the foot seems too stiff and high, the child's arch will always rest on this support and the muscles will not work properly. Over time, the musculature of the arch of the foot can become so weak that longitudinal flatfoot develops. In other words, a poor-quality insole not only fails to perform its function, it actually makes the situation worse.
Which shoes should I choose for my child?
Of course, the need for an insole for shoes is a very controversial topic. Some experts say healthy feet don't need prophylaxis, while others say feet won't stay that way for long without support.

Ultimately, it is up to the mothers and fathers to decide which shoes their offspring should wear. However, if parents think their kids need Supinator shoes, there is one thing they should keep in mind. The shoe should always be the right size because it is important that the insoles are where they should be.
However, parents often buy shoes for several seasons in advance in search of savings. It is therefore often the case that a child's feet are not yet mature and the season has already begun. However, such a situation is unacceptable! Such shoes can be dangerous for your child's health because the the insole and their supine padding are designed for a specific sole length.
The big manufacturers have long since switched to producing shoes without a separate insole, but instead use a profiled insole. Its shape, which is perfectly adapted to all the anatomical features of the foot, is designed with heel recesses and a moderate lining of the inner arch. But there are still a few nuances in certain types of shoes.
Shoes for the winter season
Of course, the winter boots for boys and girls must also be selected taking into account certain orthopedic requirements. Indeed, there is no lack of that.

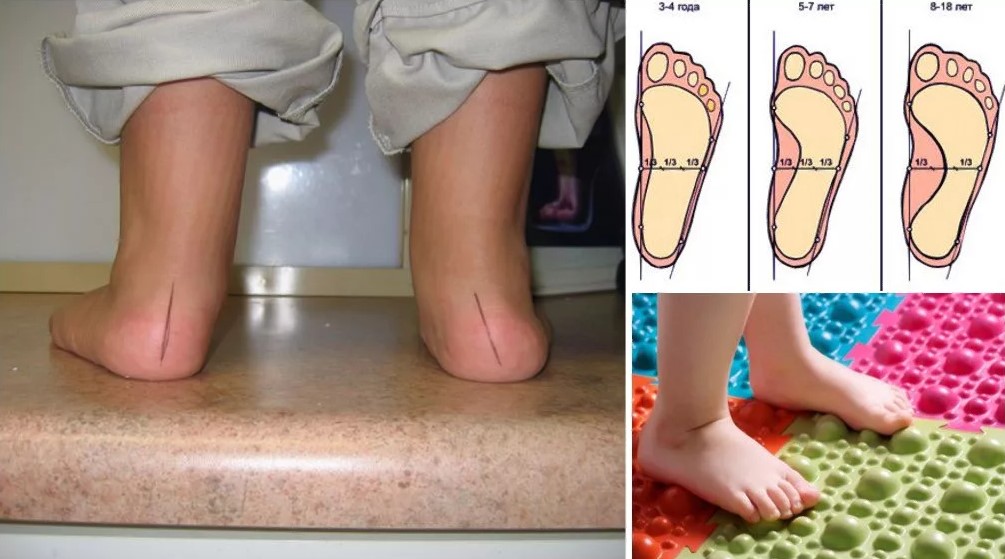
Do shoes have to have an insole (padding on the inside of the sole)?
This is a misconception that has settled not only in the minds of parents but also in the minds of some doctors. The insole is apparently mass-produced in the shoe factory and serves to support the arch of the foot and prevent flat feet in the child. That's not the case! It is important to know that all children up to the age of 3-4 have what is known as a physiological flat foot. In infants, the arch of the foot is filled with fatty tissue and the foot appears flat. This layer of fat is a kind of 'natural support' that keeps the arch of the foot in the right position when walking and running. As the child grows and moves more, the layer of fat thins and a longitudinal arch forms (where the arch supports the insole).
Wearing shoes with an insole puts unnecessary pressure on the fat pad. The child feels uncomfortable: to relieve the feeling of pressure, he may begin to bend over. When parents take off such shoes, they see a red spot on their child's foot, right where the insole is compressed.
After all, the foot is a system of three arches supported by three points. Simply supporting an arch of the foot is definitely not enough. Therefore, the pad on the insole (supinator) in mass-produced children's shoes has nothing to do with the treatment and prevention of flat feet.
Should I look for shoes with a hard sole?

The sole should be flexible and soft, not 'shockproof' and inflexible. When checking the flexibility of the sole, make sure that it gives where the foot rolls off, which is at the base of the toes. This gives your child's feet the right amount of movement and optimal foot control.
A paragraph is a must! The lack of a heel counter leads to overloading of the heel area. It also prevents the child from falling backwards. For small children, the heel should be as wide and stable as possible, 5-15 mm high. For older children, the heel is not necessary as a design element - the difference in height between the front and back of the shoe is decisive.
What is an orthopedic insole?
Orthopedic footbeds are products designed to support the arch of the foot (transverse or longitudinal). Put simply, an orthopedic insole is usually an insole that is placed in normal or special footwear (orthopedic shoes, sports shoes or hunting shoes). It is necessary when the foot is tilted inwards or when the person has been diagnosed with flat feet.
So why are pronators and supinators so important? First of all, it is good to understand the difference between the two. Pronators generally support the front of the foot, which is important in the case of a transverse flatfoot. In supinators, they often provide support along the arch of the foot or near the heel. Flat feet are indispensable because they disrupt the spring function of the feet. This transfers the entire impact load to the joints, spine and brain, as each step in this situation creates a micro-shock.
In such cases, orthoses are indispensable as they reduce the intensity of pain when walking and protect the foot from possible deformities, such as e.g. B. a flattening of the foot protect. They also normalize the entire musculoskeletal system.

In other words, footrests are necessary in the following cases:
- to normalize blood flow;
- with transverse flat feet;
- to improve general well-being;
- to counteract excessive leg fatigue;
- after injuries or fractures of the bones of the feet and lower legs;
- to support the arch of the foot in the longitudinal plane (in the case of longitudinal flatfoot);
- reduce stress on the ankle, knee and hip joints and spine.
types of deposits
There are many different types of supinators. There are molded insoles made of cardboard (although they are of little use), insoles made of leather, cork and plastic. Sometimes you can also find supinators made of silicone or metal. In recent years, the most popular is the leather supinator with a metal plate adapted to the shape of the arch of the foot. Externally, almost every supinator is covered with leather, oilcloth or foam.
As previously mentioned, there are two main types of foot supinators:
The latter are particularly necessary for women, since forefoot deformities are often caused by wearing shoes with heels for a long time. While orthotics can be used with foot supports in shoes and boots, this is virtually impossible in sandals. That is why many women are seriously considering how to make their own supinators for forefoot support. But you don't have to reinvent the wheel.

Luckily, there are gel supinators on the market that can solve such a problem. Gel shoe inserts have a self-adhesive surface that allows them to be held in place. There is a wide range of gel supinators. They are easy to attach to the front of sandals or open shoes, but there are also gel inserts for the heel or for longitudinal arch support.
If you have a longitudinal foot problem but don't like gel insoles, you can also use other models from proven manufacturers. Strutz insoles, for example, have been particularly popular lately. The peculiarity of these products is that they do not fit into shoes or boots, but are worn on the foot, which radically changes the principle of distributing the load on the foot. Each of these 'insole' consists of an elastic band (either black or nude) to which is attached a soft cushion that, when worn, nestles under the arch of the foot. These insoles do not need to be adjusted and are a good solution for people who spend a lot of time on their feet.
Which shoes should I choose for my child?
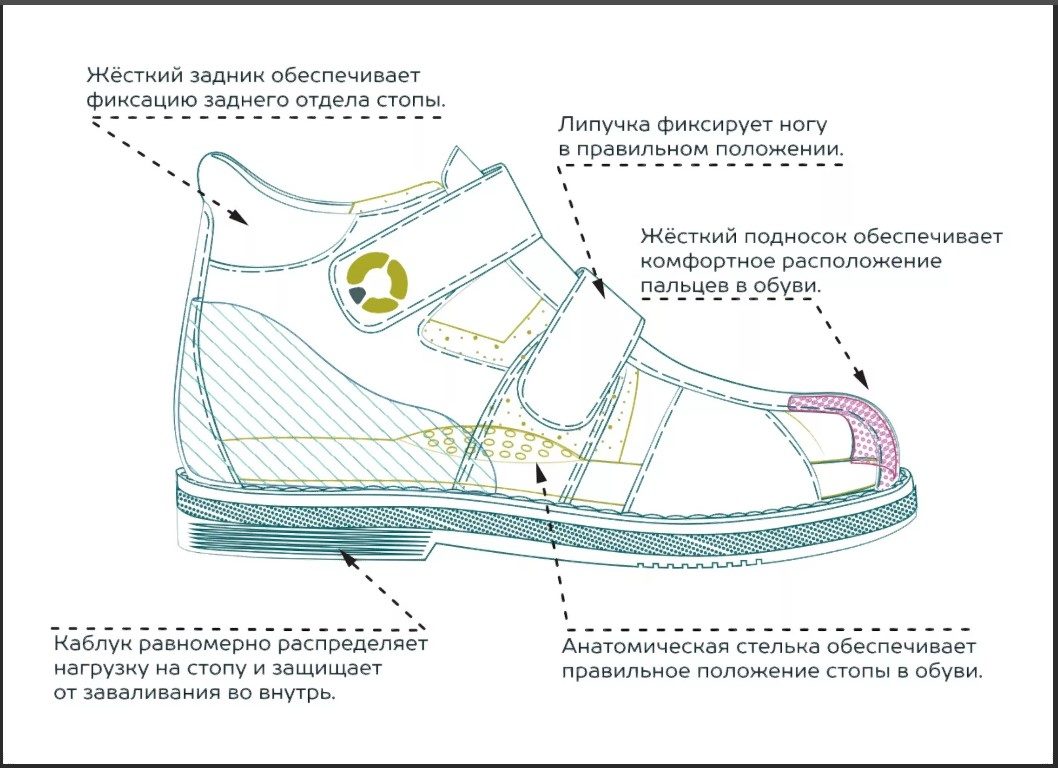
- Therapeutic or orthopedic shoes.
- Prophylactic shoes. They are age-appropriate and serve to prevent the development of foot pathologies:
- The upper is soft and natural;
- the sole is flexible and non-slip; the toe area is raised;
- the toe is wide;
- the heel is 5 to 10 mm;
- the heel is closed, rigid;
- Velcro closure, easy to adjust and fix.
winter
- Round toe, hard heel;
- thick sole;
- stable heel;
- stable lace closure and secure fittings;
- mandatory insole;
- Insole, if present, in the form of a slight elevation on the inside.

A notice!!! In most cases, warm children's shoes do not have insoles, since woolen socks have no function. And in winter it is better to wear special shoes at home, where the child spends most of the time.
Sports
Children nowadays often wear sneakers because parents believe that these are the most comfortable shoes. But don't forget the most important selection criterion - and stiff backs and supinators. These are only required for occasional use, so to speak.
There are special requirements for sporting activities:
If it is a child it is better to defer such an article 'until later'.
Read more:Important!!! Consult your doctor when buying ice skates and buy orthopedic insoles to counteract the negative effects on the foot.
How to support the foot in shoes without insoles?
When buying orthopedic shoes for the first time, the question does not arise where to get a shoe supinator, what it is and what it looks like. Unfortunately, not all manufacturers offer beautiful shoes, sports shoes or boots equipped with them. If upon checking you find that your newly purchased pair of shoes doesn't have a supinator, don't fret because you can:
- Buy special orthopedic insoles that have a Gelenoc. A good option is a half insert. This is a regular insole with no flap at the front, just a bead at the inner arch and a cut-out for the heel. It is ideal for open shoes (sandals and sandals).
- Stock up on removable insoles for your shoes. When they wear out, they can be easily replaced, while a native supinator's wear and tear requires the immediate purchase of new shoes.
Supinators are usually made of leather or silicone. These models are more suitable for prevention, but for the treatment and elimination of deformities, doctors recommend gel shoe inserts. They distribute pressure better and relieve fatigue due to their stiffness.
Factory insoles, which are not made from the patient's mold, have a similar design. The insert is placed on the inside of the shoe to slightly raise the heel-to-toe area while the heel area is recessed. Some models have so-called pelotics that support the transverse arch. In addition, aids such as wedges are essential in the treatment of flat feet. These change the angle of the foot, allowing the heel to return from its retracted position.
contraindications
Children should only buy orthopedic insoles with a doctor's prescription. Since every foot is different, choosing the wrong product can lead to various anomalies in the formation of the arch of the foot. The use of orthotics with supinating shoes is not recommended. And in children with diagnosed pathologies such as flatfoot or clubfoot, these products must be selected individually.
As a rule, there are no contraindications to the preventive use of high-quality insoles. In rare cases, the child may have an allergic reaction to the material from which the pads are made. Silicone or hard plastic products are not recommended for small children. If the child has wounds, scratches or inflammation of the skin on the foot, insoles should not be used until they have healed.
diversity
In very young children, insoles are usually only used prophylactically. Infant feet are immature, so they are rarely diagnosed with flat feet or other pathologies. In addition to prophylactic insoles, there are also corrective and therapeutic insoles. They are prescribed by the doctor when there are severe foot deformities.
prophylactic
There is a large selection of prophylactic devices from various manufacturers in specialist shops and specialist shops. They are designed to prevent foot deformities and help the child develop proper arch and gait. Appropriately selected insoles help to relieve the foot and help it to adopt a physiologically correct position when walking.
correction
Special insoles with an anatomical shape are used for the early correction of malpositions in children. These should be selected by the doctor after an examination. Typically, these insoles correct the alignment of the foot with a semi-rigid framework that prevents the development of flat feet. Supporting the arch of the foot with a spinator will help reduce stress and eliminate pain during running and long walks.
Corrective items should be selected even more carefully than prophylactic items. The physician should determine the height of the insole, the depth of the heel indentation, and the presence of wedges to prevent valgus deformity. These items must be worn with closed-toe shoes, which must have a firm back and a small heel.
therapeutic
Orthoses are used for severe foot disorders such as valgus deformity, flatfoot or clubfoot. Their special feature is that they have to be made individually. Only by adapting to the shape of the foot can they help treat the pathology. Such aids have to be replaced after a certain time because they no longer fulfill their function of correcting the misalignment.
Chiropodist duties
Healthy feet have an arch shape that straightens as you walk. This process is called pronation. After this, the foot returns to its original shape, which is known as supination. This foot mechanism reduces stress on the joints and spine. With flat feet, natural pronation-supination does not occur, so the shoe must have a small underfoot roll on the insole. This has a cushioning function and minimizes the impact load.
Therapeutic insoles are only available with custom made insoles. Their shape and size is determined by the individual foot.
Mass orthopedic shoes for children with supination do not have therapeutic properties. They promote the anatomically correct foot position when walking, but do not correct any deformities.
When an orthosis is required
All young children are diagnosed with congenital flat feet. This is normal and does not require treatment. A shoe is not necessary up to the age of 2 years. The muscles and ligaments should develop naturally and without external influence. As the child grows and flat feet do not go away, children's shoes with a stiff supinator and an adjusted heel will be required.
The shoe or other pair with an instep should fit the child's size. If the shoe is too big or too small, the supinator will shift under the foot. As a result, the arches of the feet form incorrectly.
When choosing children's shoes, pay attention to the type of insole. A flat piece does not provide good cushioning, and a piece that is too high (5 mm or more)一 provokes muscle weakness. The insole should be moderately soft and spring under pressure. The optimal height 一 no more than 4 mm.
For a child who is just starting to walk, children's shoes without an insole are quite suitable, but c but with a solid heel. Such a firm heel keeps the ankle secure and prevents dislocation.
At Krasnodar TD ≪Standard≫ you can buy anatomically correct shoes, boots and sandals for children of all ages. If necessary, an orthopedic pair will be made to order.
What is an insole and what is it for?
When walking and running, the foot performs many movements that represent a complex biomechanical process. The inner arch of the foot is flattened as it absorbs the shock (like the springs in a car). This cushioning mechanism is called pronation. In order to take the next step, the body's center of gravity must shift and enough energy must be stored in the leg to push off. The muscles of the lower leg and foot engage, moving from the mobile system state to a rigid support state, and the arch of the foot returns to its original arched state. This process is called supination.
The pronation-supination of a healthy foot helps mitigate the effects of hard surface contact during walking and running. These processes reduce the pressure on the spine and ankles and prevent micro-shocks.
However, the inner arch of the foot does not work properly for everyone. With flat feet, the pronation-supination process does not work, so the foot cannot absorb loads. This is why people with flat feet (the arch of the foot is not or only insufficiently developed) tire quickly when walking and have joint and spinal problems. To improve the condition of a patient with this orthopedic pathology, it is necessary to artificially reproduce the processes of supination and pronation, including through specially selected footwear.
A supinator is a special protuberance, a seal on the footbed in the form of an asymmetrical roll. Depending on the version, the Supinator has the following objectives:
- Restoring and maintaining the anatomically correct arch of the foot (rigid orthopedic models are used only in insoles for therapeutic shoes);
- provide additional cushioning (used in preventive and casual shoes).
What insoles should be included in children's shoes?
Standard models of children's shoes often have soft supinators. These have nothing to do with orthopedic therapeutic supination.
For what purpose is soft supination used?
The purpose of a soft, prophylactic insole is to provide additional cushioning for the feet during heavy use. A soft insole is suitable, for example, for children who are actively involved in sports (running, football, basketball) that put a lot of strain on the lower limbs. Even if children spend most of the day in shoes (e.g. in kindergarten), a soft, prophylactic footbed cannot do any harm. This ensures that the arch of the foot is anatomically correct.
What is the difference between therapeutic and therapeutic?
Therapeutic traction insoles are only necessary for children with diagnosed arch developmental disorders. They are made individually for children's shoes.
Important! The degree of stiffening, size and shape are determined by the orthopedist after visual inspection and hardware diagnosis of the arch disorder. When determining the supination configuration, its parameters are calculated in such a way that they correct the specific deformity of the child's foot. Therefore, you will not find mass-produced children's shoes with therapeutic supinators in your nearest store, nor do you need to look there.
If your child is healthy and their feet are developing normally, neither a soft nor a therapeutic orthopedic supinator is necessary. Children under the age of two do not need supinating shoes. Giving the child the opportunity to move actively even without shoes (at least at home) is enough to form an internal arch, while a rigid orthopedic supinator shoe can even cause damage (especially if the pair not the right size).
- Supinator or foot pinator.
- The shoe inserts are.
- What is an insole in a shoe?.
- This is what the insole looks like when the shoe is removed.
- What is pronation and supination?.
- pronation and supination.
- Ortho insole.
- What is a shoe insert?.