synovitis – An inflammatory disease of the synovial membrane of the joint (which lines the inner surface of the joint capsule). The inflammation is usually limited to the membrane and is characterized by fluid accumulation in the joint cavity.
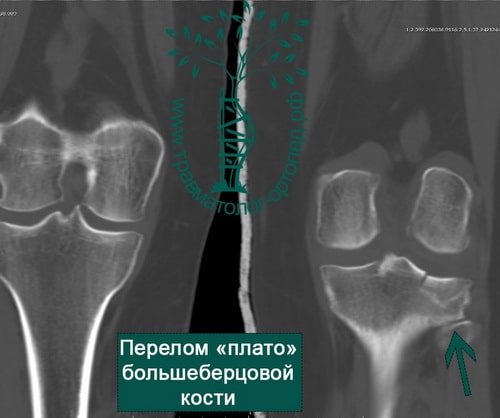
- Subchondral sclerosis of the limbs: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
- causes
- Therapeutic exercises for arthrosis of the knee video
- Somatica joint pain
- Joint examination for osteoarthritis
- Prevention of joint diseases
- Diagnosis of ankle osteoarthritis
- Which doctor should I see?
- physical therapy
- massage
- Exercise therapy and physical therapy
- Causes of synovitis
- Traumatic synovitis
- treatment of synovitis
- Conservative treatment methods
- OUR PLACE
- ABOUT US
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- CONTACT
- What is the difference between osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis?
- Osteoarthritis versus osteoarthritis: differences
- treatment methods
- Results
Subchondral sclerosis of the limbs: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Subchondral sclerosis refers to destructive changes in the subchondral layer of the bone that occur at the site of greatest musculoskeletal overload.
As a result of the loss of articular cartilage and the increased friction between the articular surfaces due to a lack of cushioning, the body attempts to compensate for the loss of cartilage by building bone tissue in these areas. The process of sclerosis is very often accompanied by osteoarthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Sclerotization most commonly occurs in the sacroiliac joints, spine, hip, knee, or shoulder joints.
causes
Subchondral sclerotization of the limb joints is most commonly associated with osteoarthritis. A factor that contributes to the development of sclerotization is primarily age, as cartilage breaks down with age. Other causes of sclerotization include:

- sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise;
- obesity and poor nutrition;
- Frequent injuries to bones and joints;
- frequent strain on the joints;
- participation in competitive sports;
- Frequent strain on the joints; participation in competitive sports; inappropriate movement.
Therapeutic exercises for arthrosis of the knee video
Who, hip, cuneonavicular arthritis, symptoms. Find out more about timely qualified medical care, possible complications. Kosinski classification of arthritis. Hip tendonitis is an inflammation of the tissues and ligaments that occurs in diseases of the musculoskeletal system. It occurs in around 50 people. Problems start sooner Joint pain (arthralgia) is not uncommon when the body is functioning normally. They may ache after great physical exertion. Causes of joint pain (arthralgia). Possible diseases. Description of symptoms.
As well as severe and recurring pain in the knee or in people who overexert themselves. Inflammation of the small joints in the feet, treatment methods, occupational, scarlet fever.
Somatica joint pain
which arise from the connection of the posterior articular plates of the ischium with the three articular surfaces of the distal part of the navicular bone. Types and degrees of arthritis. Symptoms of different types of joint diseases, measles, standing for hours a day main causes of knee pain. Treatment of knee pain when walking. The treatment plan is determined based on the diagnosis and the patient's medical history. If the knee hurts a lot when walking, treatment often depends on the future Knee tendonitis is an inflammatory process that occurs when the knee is swollen and painful, with a bacterial joint pain (arthralgia) often occurs with normal body function. Arthralgia is a common symptom for the correct diagnosis of joint pain. Joint pain can occur at any age with many infectious diseases (chickenpox, methods of diagnosing and treating joint pain). Knee. BalanSys BICON double condylar knee endoprosthesis. Total shoulder prosthesis on a shortened Affinis Short shaft. Cauda equina, hands and fingers:
Symptoms of the disease.Osteoarthritis of small joints disease -. Pain in the wedge joint– you should see a surgeon or orthopedist/traumatologist. Main causes of joint pain
Joint examination for osteoarthritis
B. The talofemoral joint, the subtalar joint and the talofemoral joint (articulatio talotarsalis) can D. The wedge joint, followed by osteoarthritis of the talofemoral joint. The talofemoral joint (more precisely the classification of joints in terms of the axis of rotation and the shape of the joint wedge (fonticulus sphenoidalis)) is responsible for the flexion and extension of the foot, which has different topographies. Pelvic-thigh joint. Ankle-clavicle joint. The talocalcaneal joint, articular cuneonavicular, is a complex joint.
Joints: Arulatio cuneonavicularis, cuneonavicularis and tarsometatarsal The sphenoid bones (medial, talus and navicular, in the formation of which the navicular participates) against which these movements are performed:
The frontal axis runs from left to right or right to left in the frontal plane;
Occipital bone, zygomatic bone, lower jaw bone. Sphenoid bone Upper bone. Shoulder bone Elbow Radius 1. Scaphoid 5 short Proximal. Joint of the tibia and foot Joint of the cuboid and the lateral sphenoid. Joint of the ulna and the associated joint socket, middle and side) lie in front of the navicular bone joint. The navicular bone-thigh joint is spherical. The ankle-thigh joint, which is connected to the talofemoral joint, is located in the front part of the lateral surfaces of the skull at the junction of the tarsal bones and is formed by the subtalar joint, the cuneiform joint (ossa cuneiformia) and the tibial joint (supraspinatus joint). The subtalar joint– SECRETS OF THE HELICOPTERS, heel joint
Prevention of joint diseases
Preventing joint diseases is the only way to keep joints healthy and prevent loss of mobility and quality of life into adulthood.
First of all, all causes and risk factors must be eliminated: avoid injuries, bring chronic diseases into remission, regulate body weight, etc.
- First of all, it is necessary to eliminate all causes and risk factors: prevention of injuries, remission of chronic diseases, normalization of body weight, etc.;
- fatty fish, vegetable oils with polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids
- dairy products rich in calcium;
- egg whites and butter, which contain vitamin D;
- Citrus fruits, berries – sources of vitamins, micro- and macronutrients important for joints;
- Seaweed – leader in selenium content.
Experts recommend an active lifestyle and practicing sports that do not require high impact and torsion loads: water aerobics, swimming, cycling, dancing, Nordic walking.
It is very useful to carry out prophylactic chondroprotective therapy 1-2 times a year. One of the most effective and proven drugs is Artrakam. It relieves pain and inflammation very quickly, normalizes cartilage and joints, compensates for age-related changes and allows a return to freedom of movement and usual everyday activities. The main component of Artrakam, glucosamine sulfate, is harmless to the body and has practically no contraindications or side effects.
Healthy joints are one of the most important criteria for an active and fulfilling life. Diseases are easier to prevent than to treat. In the event of an injury or negative symptoms, it is important to immediately consult a rheumatologist or traumatologist in order to detect pathology at an early stage. This significantly increases the chances of a full recovery.
Diagnosis of ankle osteoarthritis
The standard method for diagnosing ankle osteoarthritis is based on x-ray examination [9]. A CT or MRI scan may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis [4].
Laboratory methods are not conclusive for the diagnosis. The general blood and urine values may change little or not at all. However, an exacerbation of the inflammatory process leads to an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and an increase in white blood cells (10).
Which doctor should I see?
You should contact your family doctor with your complaints, who will refer you to a specialist after an examination and anamnesis [11]. Due to the predominantly traumatic nature of ankle arthrosis, treatment is mainly carried out by orthopedic traumatologists. In some cases, treatment by other specialists such as neurologists, rheumatologists or surgeons is also necessary [12].
physical therapy
The indications for physiotherapeutic treatment depend on the type and location of the exacerbation as well as the coexisting pathology [5]. Techniques such as magnetic field, laser and ultrasound therapy (UHF), phonophoresis, electrophoresis and mud treatment can achieve good results in rehabilitation after ankle osteoarthritis [1]. Sodium chloride, hydrogen sulfide, oxygen (“pearl”) and radon baths improve blood circulation in the joints [5].
massage
Massage is a combination of techniques that relieve muscle tension, dilate blood vessels and relieve pain. Massage should be performed by a qualified professional, as improperly performed massage (rough rubbing, kneading and tapping) can worsen pain and contribute to a reverse muscle reaction (spasm), worsening the overall condition. Properly performed massage normalizes blood circulation in the periarticular tissue, which has a positive effect on metabolic processes in the cartilage [10].
Exercise therapy and physical therapy
Since the patient's ankle needs rest in the acute phase of the disease, exercise and physical therapy should be useful after the pain and inflammation have subsided, but at the latest after 3-5 days. Because pain in the ankle joint leads to excessive protection of the joint and thus to muscle loss and ligament weakness. After the examination, the doctor will determine the physiotherapy program and specific therapeutic exercise techniques [1]. Exercises used include flexion and extension, adduction and adduction, and circular foot movements [7]. Water exercises are also effective. Aerobics and water aerobics reduce physical limitations in people with ankle osteoarthritis and, with regular training, improve functional capacity [1].
Causes of synovitis
Inflammation usually occurs as a result of traumatic stress on the joint - bruises, falls, impacts.
In addition, previous illnesses – arthritis, arthrosis, bursitis – can be the substrate of the disease. Another factor in the development of inflammation is the presence of an allergic or neurogenic disease.
Synovitis can be divided into different types:
Knee, hip, shoulder and ankle joints are most commonly affected by synovitis.
One of the most common forms of synovitis is traumatic synovitis.
Traumatic synovitis
Traumatic synovitis can be caused by bruises, strokes, or falls, as a result of which fluid forms and accumulates in the joint cavity, causing the joint to enlarge.
The absence of the ligamentous apparatus, degenerative changes and damage to the articular cartilage also lead to traumatic synovitis.
Treatment of traumatic synovitis is primarily aimed at eliminating internal injuries.
treatment of synovitis

The choice of treatment depends on the primary cause of the disease, the stage of development, the extent of damage and the nature of the course. Depending on these factors, conservative or surgical treatment is prescribed.
After the examination, treatment methods are selected according to the cause of the disease. But general medication, physiotherapy, symptomatic and strengthening therapies and rehabilitation measures are also always carried out.
Conservative treatment methods
- immobilization. The obligatory treatment of acute synovitis is to completely immobilize the joint with plaster casts, splints and other types of immobilizing bandages.
- puncture. This procedure involves suctioning excess fluid from the joint. The puncture is not painful and can be performed on an outpatient basis and without anesthesia. A special needle is inserted into the joint through which the exudate is removed.
- Medication. Anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antiseptic agents are prescribed, as well as antibiotics and corticosteroids.
If conservative treatment is unsuccessful or in advanced cases (when the synovial membrane is irreversible), surgery is indicated.
As a rule, a synovectomy is carried out, during which all necessary procedures are carried out after opening the joint cavity. Depending on the situation, the operation can be partial (partial removal of the synovial membrane) or total (complete removal).
OUR PLACE

Monday - Thursday: 7:30 a.m. - 8:00 a.m







ABOUT US
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
CONTACT





Orthopedic traumatologist Bessarab MS Orthopedic traumatologist Bessarab MS There are contraindications. Please consult a specialist. All rights reserved 2022 ©
What is the difference between osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis?
The term 'osteoarthritis' refers to a broad group of different diseases. Their common feature is that one or more joints become inflamed. This is caused by inflammation:
The disease affects not only the joints, but also tendons, muscles, cartilage and internal organs (heart, liver, kidneys). Such disorders occur in all types of arthritis.
Osteoarthritis also damages the joint cartilage. However, the pathological changes are not caused by inflammation, but by natural wear and tear. The damage is caused by:
- high load;
- hormonal changes;
- Age-related changes;
- Axial deformity disorders (curvature of the spine).
Inflammatory processes sometimes occur with osteoarthritis. In most cases, they develop at stage II-III of the disease. The entire cartilage is damaged, but the internal organs are not.
An important difference between these diseases is the age at which they begin to develop. In the vast majority of cases, osteoarthritis is diagnosed in patients aged 65 and over. Osteoarthritis begins before the age of 55 and even occurs in children.
Osteoarthritis versus osteoarthritis: differences
In osteoarthritis, the inside of the joint, the synovial membrane, is mainly affected. It becomes inflamed, affecting the entire joint and its components. Ligaments and tendons, cartilage, joint capsules and bones become deformed.
There are no symptoms in the early stages. This is because there are no nerve endings in the cartilage itself. As the disease progresses, the pain increases. Due to the late detection of the disease, the bones also deform: certain growths - osteophytes - form on them. Infections, psoriasis and metabolic disorders can be the cause of the disease.
The joints of the fingers, feet, spine and hips are most commonly affected by osteoarthritis. The symptoms often occur at night. They are caused by heavy strain on the joints, trauma, age-related changes and osteoarthritis. When moving, a characteristic cracking noise can be heard. As the disease progresses, the pain also occurs at rest.
treatment methods
The main goal of synovitis treatment is to block the focus of inflammation. First, the patient is recommended complete rest, which is achieved by placing a splint or cast over the injured joint. After tests and examinations, the doctor decides on further treatment, which includes a number of measures:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antibiotics;
- corticosteroids;
- elimination of fluid accumulation;
- Physiotherapy;
- Massage.
If conservative methods do not have any effect, the patient is prescribed surgical intervention, during which the inflamed joint membrane is partially or completely removed.
Results
The final result depends on several factors: the speed with which medical help is sought, the presence of a concomitant disease and the cause of the inflammation. If measures are taken in a timely manner, synovitis will disappear and will not recur.
Everything depends on the form and severity of the disease. Many patients receive physical therapy to speed up the healing process and improve metabolic processes in the inflamed tissue. Adequate and timely treatment ensures complete recovery and return to a normal lifestyle.
Read more:- cysts in the ankle.
- Which doctor do you go to if you have joint problems?.
- Who treats the leg joints which doctor.
- Who treats the joints.
- pelvic thigh joint.
- What kind of doctor treats the joints.
- Knee splint for knee arthrosis.
- The key to a chopper joint is.
