The diagnosis in children has some peculiarities, because the foot of a child under five years old is a weak structure (weak muscles, very malleable bones and ligaments).

- Treatment and prevention of flat feet
- The goals and tasks of therapy include:
- Valgus (X-shaped curvature of children's feet). What is it.
- Valgus (X-shaped curvature of the feet in children). treatment methods.
- 1. Osteopathy method.
- 2 Conservative method (therapy).
- 3. surgical method.
- Costs for our Services
- Why is physical therapy so important for flat feet?
- Documents for admission and payment
- Stages of development of flat feet
- Clubfoot in children and adults
- Treatment of flat feet in children
- Symptoms of Flat Feet
- Treatment of flat feet
- use of the product.
- Pharmacological Effects
- Possible complications
- How is this disease treated?
Treatment and prevention of flat feet
Before treating flat feet, the podiatrist examines the symptoms and anamnesis, conducts palpation, visual inspection and instrumental examination. Only after determining the severity and cause of the pathology, he chooses the best method of treatment.
It should be noted that full healing does not occur before the age of 18 when the foot is not fully formed. In adults, correction of the foot can only be aimed at stopping the further development of the disease, eliminating unpleasant symptoms and preventing the occurrence of complications.
The goals and tasks of therapy include:
- controlling pain and swelling
- elimination of muscle spasms
- cessation of deformities;
- restoration of metabolism;
- strengthening the musculoskeletal system of the foot;
- development of a correct gait pattern;
- Strengthening of the immune system.
In the treatment of flat feet, as a rule, conservative methods are used:
For severe foot deformities that cannot be corrected conservatively, the orthopedic surgeon may recommend surgery.
Valgus (X-shaped curvature of children's feet). What is it.
valgus (Valgus is a lower limb deformity in which the legs curve inward relative to the midline, known as an X-curvature. This deformity affects the knees, feet, and big toes.
Valgus deformity is quite common and begins in infancy. With early treatment, the patient has a good chance of recovery.
Valgus (X-shaped curvature of the feet in children). treatment methods.
1. Osteopathy method.
An advanced method that has become popular worldwide. Osteopathy is a method that uses original techniques to enable the patient's body to heal itself without the need for physical therapy, traditional healing programs or surgery. Osteopathy acts gently on the problem areas, without trauma and pain.

2 Conservative method (therapy).
The method is effective for 1-3 stages of the disease. Depending on the degree of curvature, it can take a long time for the lower limbs to return to their normal appearance and function.
Conservative therapy consists of a series of physiotherapeutic treatments with paraffin, medicinal mud and ozokerite. Electrophoresis, magnetic field therapy and diadynamic therapy (impulse therapy) are also used in the treatment. Foot baths, massages, physical therapy, swimming and gymnastics, orthopedic shoes, orthopedic insoles, etc. are indicated.
3. surgical method.
Rarely, only in cases where the curvature (valgus) of the X-shaped legs is so severe that any conservative treatment does not have the necessary effect.
After the operation and the removal of the cast, the patient undergoes a long and obligatory rehabilitation, which includes improving the blood supply to the lower limbs, physiotherapy and a bandage, which is later replaced with orthopedic shoes.
Costs for our Services
Individual physiotherapy and massage
A valgus foot deformity is a pathology in which the foot is turned outward so that the distance between the ankles is more than 5 cm. There is an X-shaped curve and an O-shaped curve, which are divided into three stages: mild (arch angle up to 140), moderate (arch angle up to 160), and severe (arch angle over 180). Babies show signs of slouching when they first try to walk, around six months after birth. Doctors make the diagnosis in infancy. It can be congenital or acquired. The occurrence of a valgus foot deformity can have various causes: prematurity, intrauterine hypotrophy, congenital weakness of the connective tissue, rickets, musculoskeletal trauma, putting the child on its feet too early, wearing unsuitable or inferior footwear. Cerebral palsy, osteoporosis, genetic abnormalities, congenital dislocation of the hip, poliomyelitis, and myodystrophy can also be causes.
Why is physical therapy so important for flat feet?
A good way to combat flat feet is with physical therapy treatment. Because joint, cartilage, and bone tissues can be easily corrected at a young age, a package of treatments is more effective. Depending on the degree of deformation, different treatments are prescribed. Therapy includes paraffin and mud wraps, therapeutic baths, therapeutic exercises, electrophoresis and magnetic therapy. The therapy helps strengthen ligaments and muscles, improves blood circulation and corrects the child's gait and posture. It also reduces joint pain and inflammation. The range of LFC exercises is usually supplemented by health massages. Regular special courses gradually bring the joints back into their correct position. Of course, in addition to the exercises, special orthopedic shoes and orthoses are also recommended.
Before you go to the sports classes, you should prepare yourself. An orthopedist should be consulted and all necessary examinations should be carried out. Only then can the doctor prescribe a suitable exercise program. For the first physiotherapy consultation, you should bring the clothes your child will be wearing, the ambulance card with the findings and the results of the examinations and tests. If necessary, the doctor will recommend further examinations. Physiotherapy is adapted to the child's age and the degree of foot deformity. During the first exercises, the specialist observes the patient and measures his blood pressure and pulse at regular intervals. The therapy can last between 14 and 30 days and should be carried out at the frequency recommended by the doctor. Do not give up after the first positive results, because the valgus deformity can develop over the course of life.
Documents for admission and payment
Write a letter to our e-mail address [email protected] - describe in your own words the condition of your child (what he can do, what he cannot do), your wishes for treatment ( what you want to achieve). Enclose your child's medical documents (discharge papers, findings from the neurologist and orthopaedist, EEG) and your child's birth certificate with your letter. Include the parents' full names and a contact phone number.
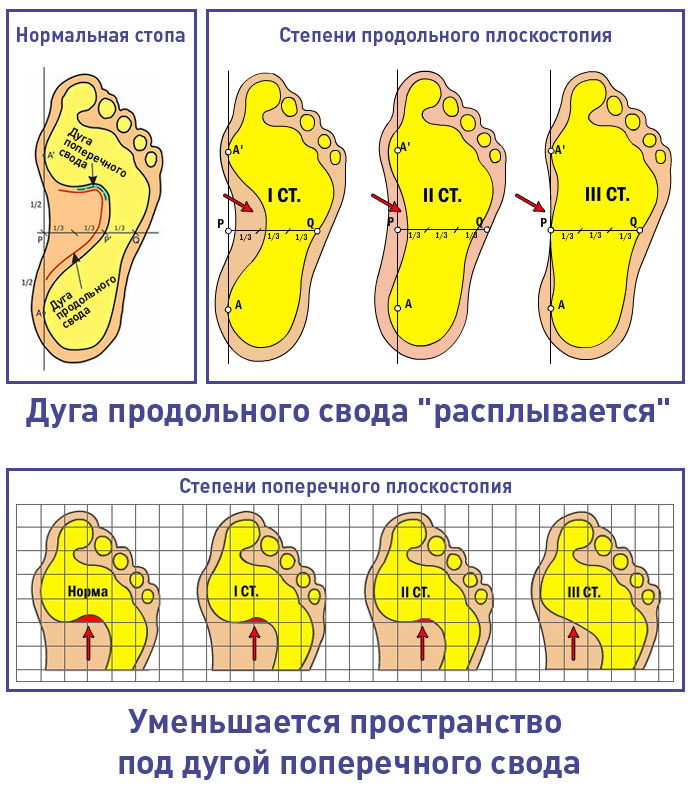
Stages of development of flat feet
As the disease progresses, the symptoms become more severe and the less treatable it becomes. Doctors repeatedly emphasize that the earlier treatment and prevention are started, the more complications can be avoided in the future.

- Grade 1 is the weakest. The muscles of the foot are weakened, the lesions are not yet visible from the outside, but the patient feels discomfort in the legs even after walking for a long time. The mild discomfort subsides with rest, so patients often ignore this symptom and dismiss it as simple fatigue.
- Degree 2 is already noticeable visually and the shape of the foot changes. The pain increases and radiates to the ankle and knee.
- Grade 3 is the most severe. The pain is permanent and the foot is deformed. Clubfoot affects the lower limbs, spine, back pain, headaches, difficulty walking and standing for long periods of time.
Clubfoot in children and adults
The syndrome occurs most frequently in childhood and is diagnosed during school years. In children, it is caused by rickets, trauma, polio, encephalopathy, and a flat foot (when the heel and toes turn outward).
The diagnosis is made in children after the age of five, since the symptoms are not yet recognizable at this age.
In adults, foot deformity develops for other reasons. Standing and working for a long time is usually an important factor. For example, teachers spend a lot of time on their feet and their feet lose their shape.
Interestingly, women are more prone to this condition. During pregnancy, women gain weight, which puts more strain on their feet, and their hormonal balance also changes.
Treatment of flat feet in children
Treatment of clubfoot should begin with an assessment and the development of an individual treatment plan. The following techniques can be used to treat flat feet in children:
- the use of orthotics;
- Therapeutic exercises and kinesitherapy;
- massage and osteopathy;
- electromyostimulation of the inner arch of the foot;
- Various types of physical therapy;
- Surgical interventions to restore the correct position of the foot bones (in the case of deformities associated with long-term flatfoot development).
Successful treatment of flatfoot deformities is only possible with conservative chiropractic techniques. If an operation or a temporary foot cast is performed, further degeneration of the muscle fibers of the inner arch occurs. At the end of the postoperative period, the flatfoot may worsen or secondary clubfoot may develop.
In our clinic, the treatment of flatfoot deformities is comprehensive. We give individual recommendations on the choice of footwear, the regime of movement, the development of special exercises that the patient can do at home.
In the treatment of flatfoot deformities in children and adults, we use massage and osteopathy, kinesitherapy and therapeutic exercises, electromyostimulation, physical therapy and many other proprietary methods. If you need the professional help of an orthopedist, we invite you to a free initial consultation with the doctor. Your first visit to our chiropractic clinic is completely free. The doctor will advise you individually and explain the techniques used in the correction of flat feet in children and adults.
Doctor of medicine, chief physician of the clinic
Symptoms of Flat Feet
Children usually don't complain about foot problems, and if they do, it's usually not a serious concern for parents.
Watch out for the following possible symptoms of flat feet:
- Unevenly worn slippers, the inner part of the sole and heel are more worn, one shoe is more worn than the other;
- Your child complains of aching or tired feet after playing or an active walk;
- If you look at your child's feet, you will notice a flattened arch.
If your child's gait changes, moves less, rests more after a walk or run, complains of tiredness and foot pain, your child should be seen by an experienced neurologist.
Treatment of flat feet
When treating our little patients, we follow a holistic approach and use the most gentle treatment methods:
- The child strengthens the muscles and ligaments of the foot;
- relieves pain syndrome;
- stops the progression of the deformity;
- restore blood circulation;
- improvement in muscle tone.
Our therapies that can be prescribed for flat feet:
- chiropractic;
- Osteopathy – treatment with the therapist's hands, gentle influence on the musculoskeletal system, nervous and vascular systems and internal organs;
- therapeutic massage;
- Acupuncture – impact on biologically active points with the help of microneedles;
- Laser reflex zone massage – painless treatment of reflexogenic zones and points;
- Tsubotherapy – gentle impact on the body's reflex points;
- Pharmacopuncture – injection of drugs of natural origin into the center of the problem;
- Plasmotherapy – injection of the patient's own purified blood into the focus of the disease;
- Isometric kinesitherapy – individual gymnastic techniques/exercises, possibly with elements of joint massage;
- Kinesiotherapy with the Exarta device;
- kinesiology taping;
- ozone therapy – treatment with active oxygen;
- Physiotherapy;
- Physiotherapy with enzyme preparations;
- shock wave therapy;
- Therapeutic intravenous therapy;
- hirudotherapy – treatment with medicinal leeches;
- botulinum toxin therapy - treatment with botulinum toxin;
- Intra-articular injection of synovial fluid from an endoprosthesis;
- Intra-articular blocks.
use of the product.
Clotrimazole cream is indicated for the topical treatment of the following skin infections:
- Tinea pedis, tinea corporis and tinea corporis caused by Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton Floccosum;
- candidiasis caused by Candida albicans;
- mycosis caused by Malassezia furfur;
- urticaria caused by Candida albicans;
Clotrimazole can be combined with betamethasone dipropionate and corticosteroids in some preparations.
When administered orally, clotrimazole is indicated as a prophylactic agent to reduce the incidence of oral and pharyngeal candidiasis in immunocompromised patients undergoing chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or steroid therapy for the treatment of leukemia, cancer, or renal transplantation. It is not indicated for the treatment of systemic mycosis fungoides.
Pharmacological Effects
Clotrimazole is a broad-spectrum antifungal that inhibits the growth of pathogenic yeasts by altering cell membrane permeability. Clotrimazole is fungistatic at concentrations up to 20 µg/ml and may be fungicidal at higher concentrations in vitro against Candida albicans and other Candida species. Unfortunately, resistance to clotrimazole, which was once rare, is now widespread in various patient groups.

Clotrimazole works well against fungi
Clotrimazole is generally considered to be a fungistatic rather than a fungicide, although this distinction is not absolute as clotrimazole exhibits fungicidal properties at higher concentrations.
The action of the drug is primarily due to damage to the permeability barrier in the cell membrane of fungi. Clotrimazole inhibits the biosynthesis of ergosterol, the main component of fungal cell membranes. If ergosterol synthesis is completely or partially inhibited, the cell is no longer able to form an intact and functional cell membrane. Since ergosterol stimulates the growth of fungal cells directly and in a hormone-like manner, the rapid onset of the above processes leads to a dose-dependent inhibition of fungal growth.
Although inhibition of lanosterol-14-demethylase (also known as CYP51), which is thought to be responsible for clotrymazole's antifungal properties, reduces ergosterol levels, the drug also has other pharmacological effects. These include: inhibition of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ -ATPase, depletion of intracellular calcium, and blockade of calcium-gated potassium channels and potential-gated calcium channels. The effect of clotrimazole on these complexes explains the other effects of this drug, different from its antifungal activity.
Possible complications
As a rule, with proper and timely treatment of strep throat, the viral form of tonsillitis is not dangerous and proceeds without complications.
SARS can be complicated by the appearance of a bacterial infection of the nasal cavity: the characteristic symptom is green nasal discharge. The prognosis is favorable, but treatment lasts a few days longer.
Influenza viruses are more likely to have complications than other viruses. These include pneumonia, lung abscess, hepatitis, heart disease and nerve inflammation. Adenoviruses can cause sinusitis and pneumonia.
A common consequence of viral tonsillitis is a fungal infection in the mouth and throat. Bacterial tonsillitis is not uncommon. Exacerbations of chronic diseases can occur.
How is this disease treated?
Viral strep throat in children is treated at home, following all the doctor's instructions. Herpes diseases and particularly severe flu require hospital treatment. The treatment regimen for tonsillitis includes bed rest, a bland diet, and medication.

For the first three to four days, the patient should stay in bed and rest. It is advisable to isolate him or her from the rest of the family to avoid contagion. During the illness, the diet should be maintained (porridge, mashed potatoes, soups, no hard, spicy or hot foods). Drinking plenty of fluids also helps speed recovery. Be sure to ventilate the room frequently.
With this disease, poultices or heat manipulations should not be used, as this can lead to severe swelling of the throat and further spread of the virus throughout the body.
- Antiviral drugs prescribed only by a doctor (Kagocel, Ergoferon, Grippferon and others);
- antihistamines (Zodac, Suprastin);
- antipyretics for fevers over 38°C;
- Regidron to avoid dehydration;
- Antibiotics are prescribed only in case of bacterial infection, otherwise they will be ineffective and only weaken the immune system and reduce the effectiveness of antiviral therapy;
- Throat rinses with antiseptics (Tantum Verde, Hexoral), lozenges (Pharyngosept, Lisobact), gargoyles with decoctions of sage, chamomile, Miramistin) are prescribed to relieve sore throat;
- Physiotherapeutic treatments should only be prescribed by a doctor and carried out in an ENT clinic. In the clinic, laser therapy in combination with ultrasonic medical rinsing of the tonsils and the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall, UVB (quartz treatment) of the tonsils and vibroacoustic therapy are very effective.
- X-shaped legs photo.
- Massage for flat feet.
- Shoes for valgus deformities in children.
- Orthoses for valgus in children.
- Massage for clubfoot in children.
- Osteopathic foot equinus.
- Clubfoot Treatment.
- Shallow valgus deformity in children.
