Shin fontanel
The newborn has no sutures, and the large spider-like spaces between the skull bones are called fontanelles. The presence of the fontanelles allows the shape of the skull to change during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal, making it easier for the baby to enter the world. The largest, frontal or anterior fontanelle, is located at the vertex, is diamond-shaped and does not disappear until the child is two years old. The smaller fontanelles in the occipital and temporal regions of the skull close two to three months after birth. Seam formation is complete between the ages of three and five. After the age of 30, the seams between the skull bones begin to thicken (ossify) due to the incorporation of calcium salts. This process occurs a little earlier in men than in women. As we get older, the human skull becomes smooth and the boundaries between the bones become virtually indistinguishable.

- Osteosynthesis of the lower leg bones
- Benefits of Tibial Osteosynthesis Surgery
- Examples of shin fracture treatment
- Clinical examples of intra-articular fractures of the tibia
- Main advantages of osteosynthesis for lower leg fractures
- Ultrasound-guided osteosynthesis
- Teeth
- Continuous cartilaginous connections
- Can lower back pain radiate to the leg?
- Herniated discs in the lumbar spine
- Inflammation of the sciatic nerve
- Effects on nerve endings
- osteochondrosis
- Non-orthopedic diseases
- muscles and tendons
- Arteries and veins of the lower limbs
- causes of injuries
- What types of ankle injuries are there?
- fractions
- Types of lower limb bone fractures
- Fracture in the upper, middle or lower part of the tibia
- The main symptoms of injury to the upper third of the bones of the lower limbs are:
- Fractures with and without dislocation
- signs
- Surgical technique.
- rehabilitation
Osteosynthesis of the lower leg bones
Tibial osteosynthesis is a surgical procedure in which bone fragments resulting from trauma to the tibia or fibula are reduced (put back into place) and securely fixed. The main goal of the procedure is to optimize the physiological conditions for the bones to grow together in their correct anatomical position. Such a radical intervention as tibial osteosynthesis is not recommended for all patients with fractures, but only for those for whom conservative measures are ineffective or, according to the findings, inadvisable (no fusion with a plaster cast).
Surgeons can use skeletal constructs or use only single fixation options to fuse the bone fragments as correctly as possible. The choice of specific devices depends on the size of the injury, the type of injury and location of the fracture, age, and additional medical conditions.

Benefits of Tibial Osteosynthesis Surgery
The main advantage of such an intervention is that it can create the conditions for the fastest and most complete healing of a fracture of the tibia. This is possible because two conditions are met. The first is that all bone fragments are fixed firmly and precisely. The second is the early restoration of tissue function with improved blood supply and accelerated regeneration. By using various structures, the bones are firmly fixed and the mobility of the limb is maintained.
These operations are performed for complicated fractures when both bones are damaged at the same time. In addition, osteosynthesis of the left or right tibia may be recommended if the ankle joint area is affected, if the fractures are displaced and the surrounding tissues are damaged.
Examples of shin fracture treatment
Patient R., 41 years old, injured as a result of a fall on ice skates. He was admitted to the hospital's emergency room.
After examination, he became one 4 hours after admission Metal osteosynthesis with a locking pin was performed..
The postoperative period was uneventful. The patient was mobilized and discharged from the hospital on the 5th day.
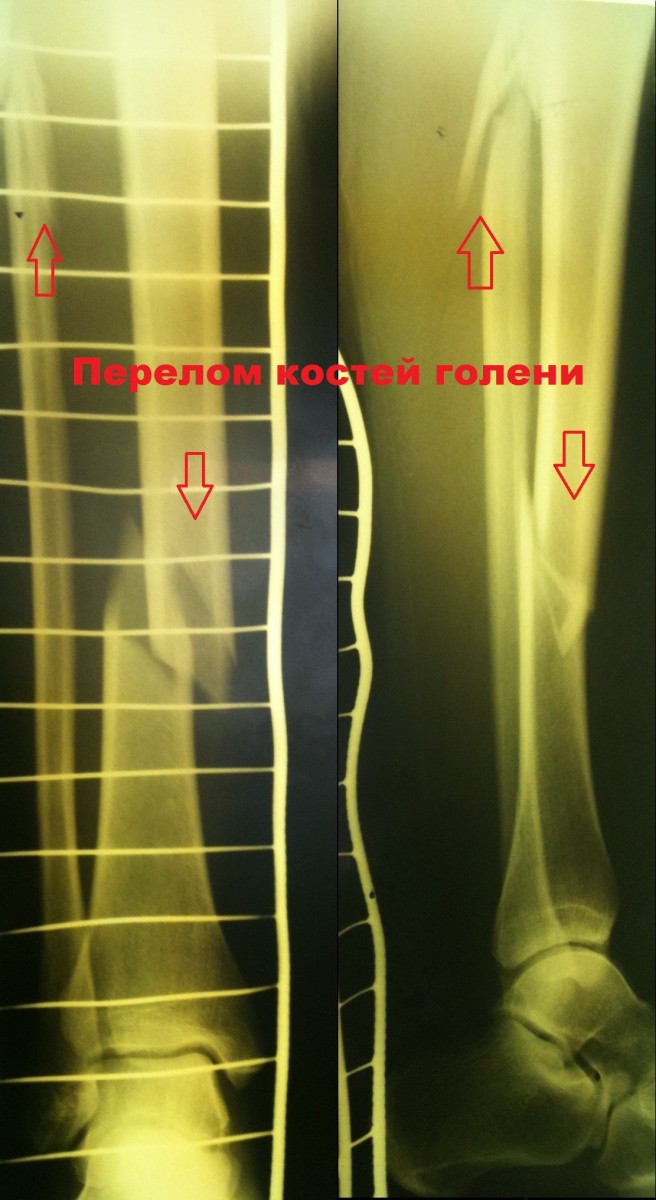
Patient C. Patient C. was 50 years old. The injury was caused by a car accident (passenger). The diagnosis was: Fragmentary fracture of the tibia..
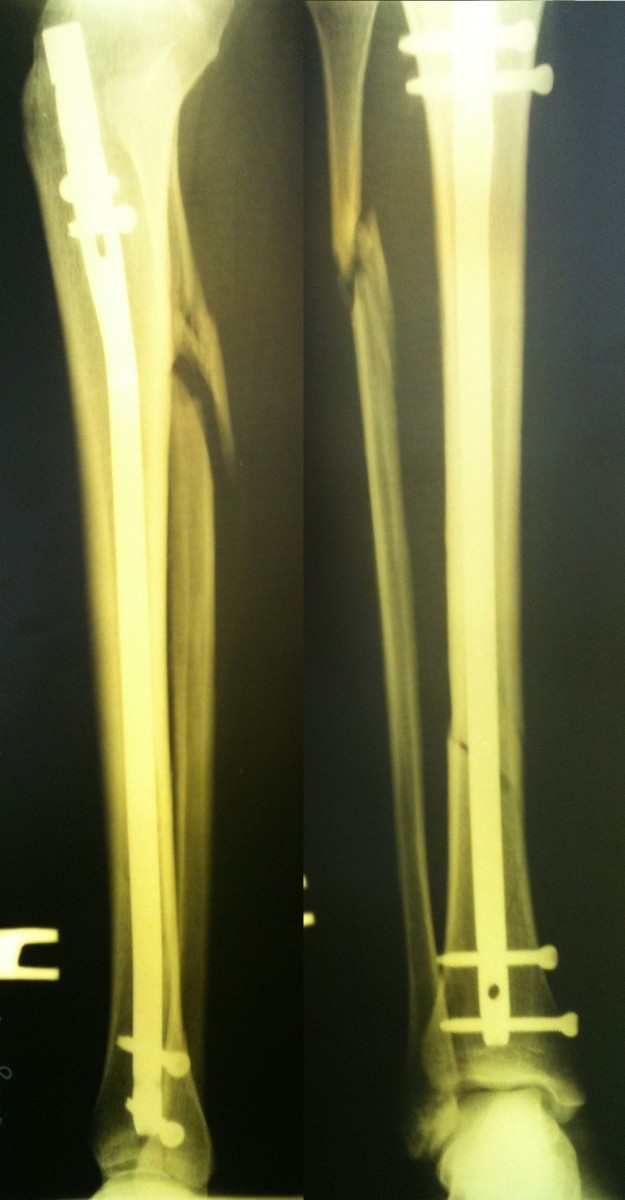
A closed reduction was performed Osteosynthesis of the tibia using a locking rod.
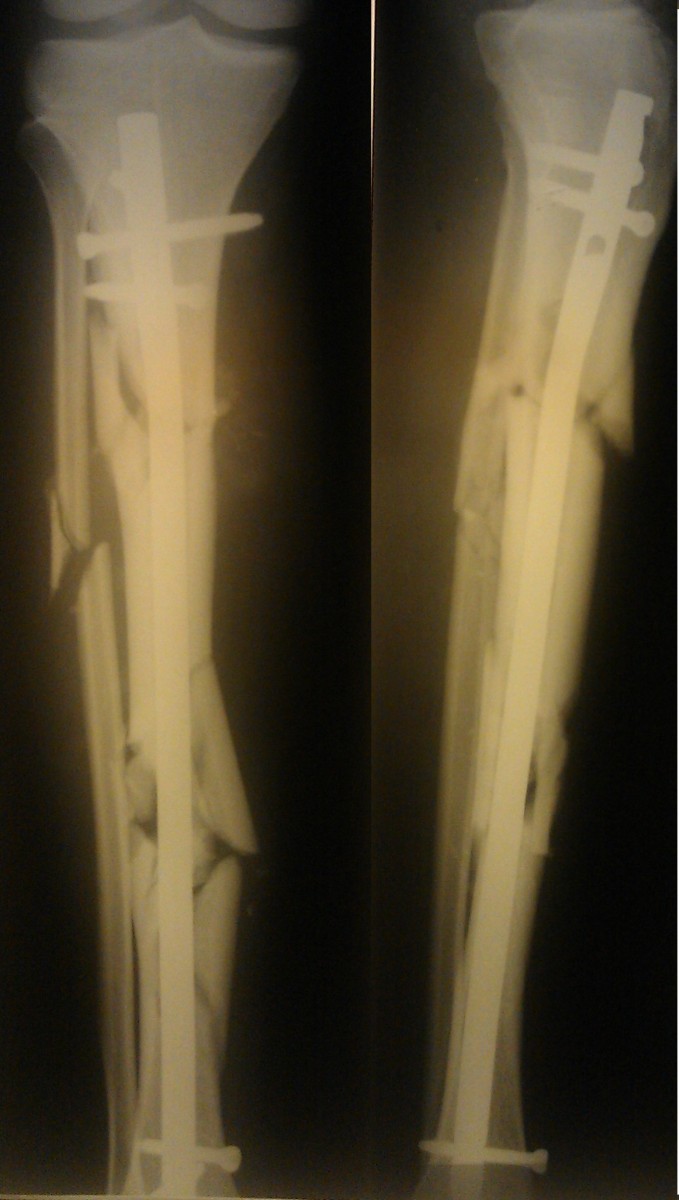
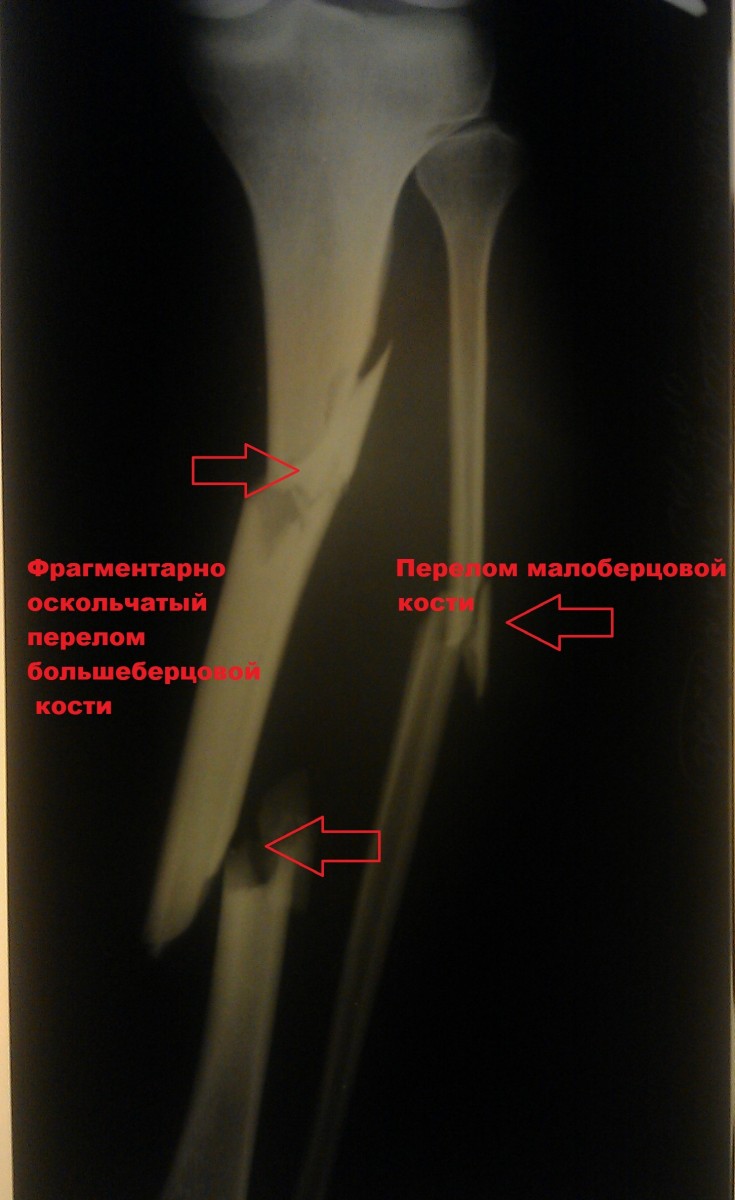
Patient K., 42 years old The patient was injured in a traffic accident (pedestrian). The diagnosis was: Isolated fracture of the tibia..
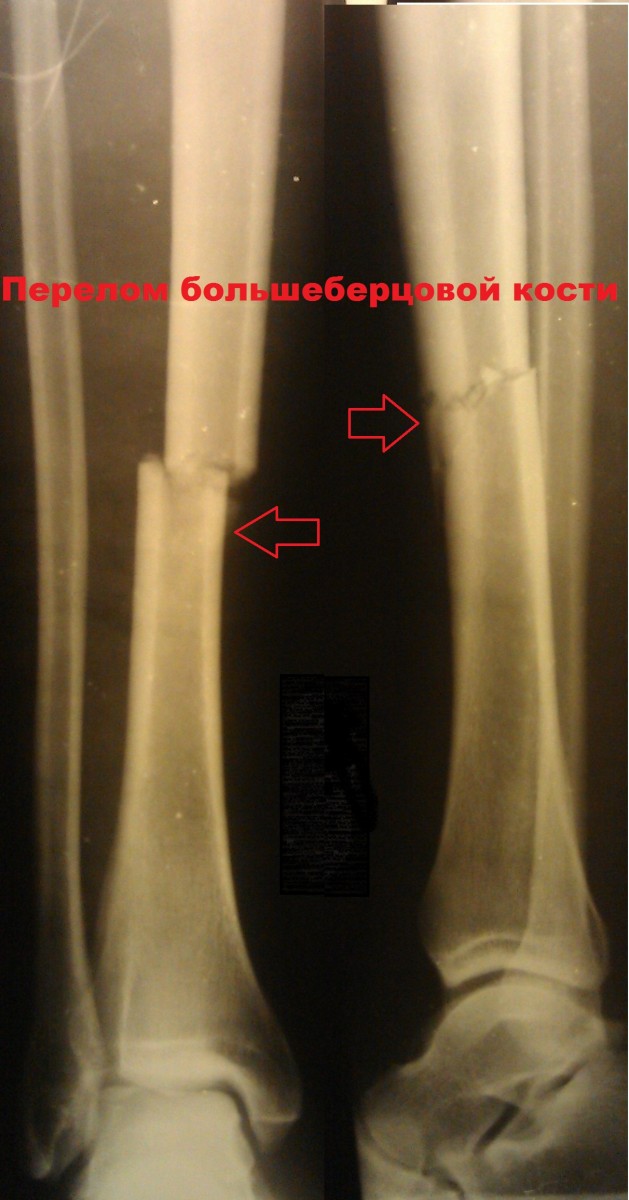
A was performed. Surgery to immobilize the fracture..
Clinical examples of intra-articular fractures of the tibia
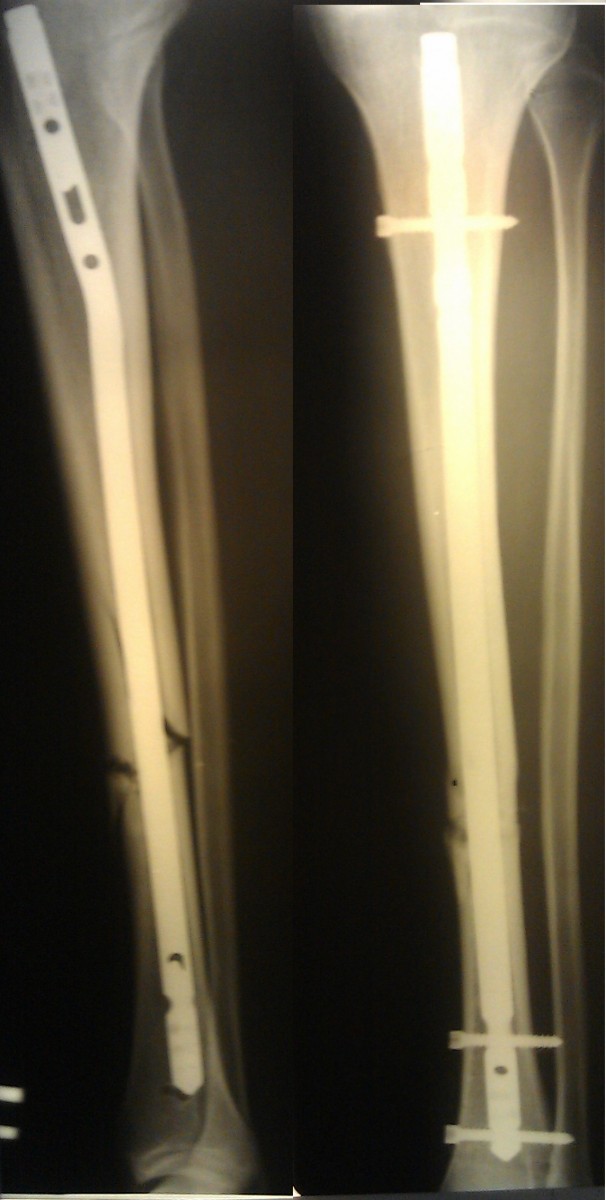
Patient L. is 37 years old. Injuries resulting from a road traffic accident. Surgical treatment was performed.
On follow-up P-graphs, the position of the fragments was satisfactory. The wounds healed with primary tension and sutures were removed on the 14th.
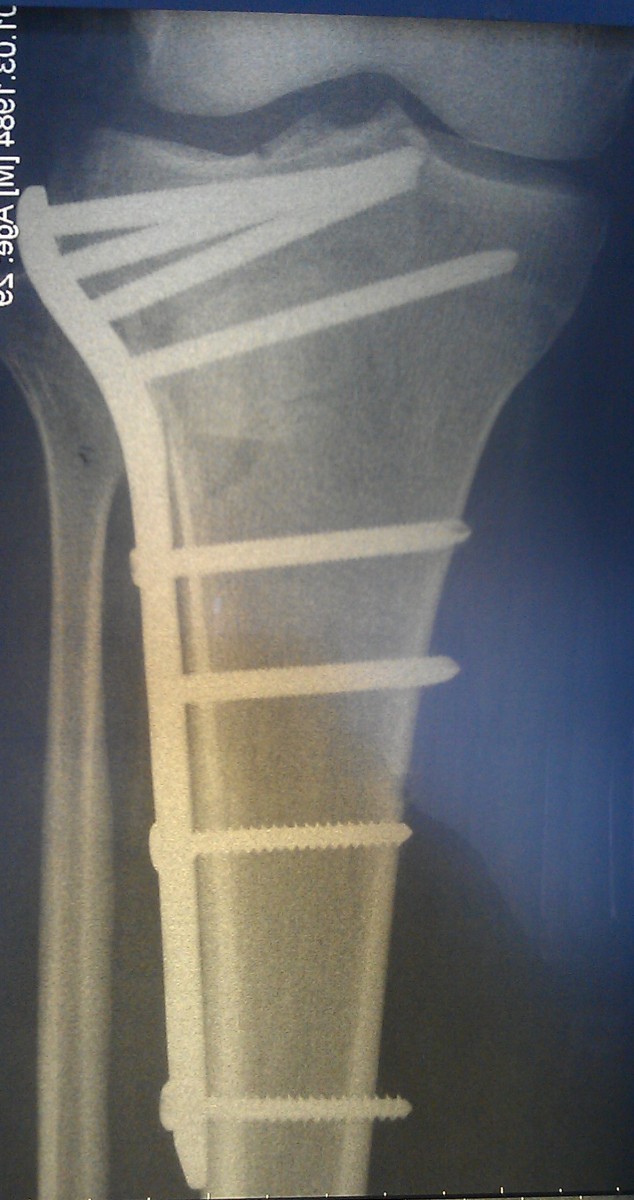
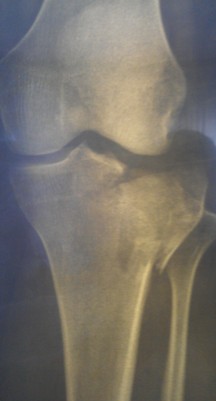
Patient M., 35 years old. Injury resulting from a fall on the street..
Closed reduction of the fracture was performed using a special device. In a second step, the fracture was fixed through minimal incisions with a plate and screws. Importantly, the fracture site itself was not exposed so that the blood supply and soft tissue relationships were not disrupted. The incidence of postoperative complications is extremely low with this surgical technique.
Main advantages of osteosynthesis for lower leg fractures
The main advantage of osteosynthesis is that it provides all the necessary conditions for restoring bone integrity. The fragments heal quickly and completely. Several factors contribute to this:
- Safe and precise repositioning, avoiding displacement of bone fragments.
- Targeted acceleration of bone tissue regeneration. Maintaining and improving blood circulation provides sufficient nutrients for regeneration.
- Mobility of the limbs. In contrast to plaster casts, mobility of the lower extremity is preserved, which is important for preventing contractures.
All consequences of the most serious injuries, fractures of the small and large tibia, can be corrected with this operation. It is also performed in cases where bone fragments have caused significant damage to the structures surrounding the soft tissues. In this case, there is no displacement of the fragments with even greater tissue trauma, the development of an inflammatory process, including an infectious component.
Ultrasound-guided osteosynthesis
Osteosynthesis of the hip, shinbone, humerus and other bone structures in the body can be performed using ultrasound. Under its influence, adhesion - the formation of bonds between heterogeneous solid surfaces that are brought into contact - is accelerated. The essence of ultrasound osteosynthesis of the lower leg:

- A special mixture of monomers is placed between the bone fragments;
- A generator produces a stream of electromagnetic waves, which is then converted into sound and directed at the injured area;
- By changing the structure of the monomer mixture, a conglomerate is created that firmly binds the bone fragments together;
- A seam is formed that is as strong as the bone itself;
- In addition, biochemical processes and cellular diffusion are activated, which has a positive effect on the regeneration rate.
After tibial osteosynthesis, each pore and canal is filled with a biopolymer material that has been hardened under ultrasonic vibrations. Although this method is effective, it is not used in all cases. It is a fact that atrophic changes are possible in the tissues adjacent to the artificial material. Therefore, ultrasound fusion of the lower leg is contraindicated in severe trauma and in immunocompromised states.
Teeth
Teeth are anchored in the maxillary sinuses (alveoli) by the so-called periodontium - bundles of strong fibers that connect the tooth root to the alveolar surface. Experts refer to this type of connection as 'embedding', although there is an anatomical discrepancy here: the teeth grow from inside the jaw, not from the outside!
Continuous cartilage-bone connections are characterized by strength, flexibility and low mobility, the extent of which depends on the thickness of the cartilage layer. One such connection is the intervertebral disc (see Fig. 1), which is 10-12 mm thick in the lumbar spine, the most mobile part of the spine. The intervertebral disc contains an elastic, gelatinous core at its center, which is surrounded by a strong fibrous ring. The core is highly compressed and constantly trying to expand so that it springs back and absorbs shocks as a buffer. When excessive stress or trauma occurs, the intervertebral discs can deform and shift, impairing the mobility and cushioning properties of the spine. As we age, metabolic disorders can lead to calcification of the intervertebral discs and ligaments as well as the formation of bony growths on the vertebrae. This process, called osteochondrosis, also leads to reduced mobility of the spine.
Continuous cartilaginous connections
Many continuous cartilaginous connections between bones only exist in childhood. As we age, these ossify and become continuous bony connections. An example is the fusion of the sacral vertebrae into a single bone, the sacrum, which occurs between ages 17 and 25. The formation of some cranial bones (e.g. occipital bone, temporal bone) from several separate parts is observed between ages 1 and 6 . With the fusion of the ends of the long bones with their middle part between the ages of 17 and 21 in women and the ages of 19 and 23.
Figure 2 Joint structure: joint capsule, bone, articular cartilage, synovial fluid, joint membrane
Joints are also cartilaginous connections between bones. However, in this case, there is a small fluid-filled gap in the thickness of the cartilage, which increases the mobility of the joint. The pubic symphysis (symphysis pubis) is the connection between two pelvic bones at the front. The possibility of a small gap between the pelvic bones near the pubic symphysis is important for women during childbirth.
The movable connections between bones are joints. These are discontinuous joints that always have a gap between the connecting bones. In addition to the joint cavity, the articular surfaces of the opposing bones and the joint capsule, which surrounds the joint on all sides, can be distinguished in the joint (Figure 2).
Joint capsule and cartilage
The articular surfaces of the bones that make up a joint are covered by a 0.2 to 6 mm thick layer of smooth articular cartilage, which reduces friction between moving bones. The greater the load, the thicker the articular cartilage. Since cartilage has no blood vessels, the synovial fluid that fills the joint cavity plays the main role in nourishing the cartilage.
Synovial membrane
The joint capsule surrounds the joint cavity and extends along the edge of the articular surface or slightly beyond it to the bone. The joint capsule consists of two layers: the outer layer, a dense fibrous membrane, and the inner layer, a thin synovial membrane. The synovial membrane is responsible for secreting a clear, viscous synovial fluid, which is a type of lubricant that facilitates the movement of bones against each other. The synovial membrane can form various protrusions: folds within the joint that cushion movements, and protrusions outside the joint capsule called bursa. The bursae lie around the joint as soft cushions under the muscle tendons and reduce the friction of the tendons on the bones during movement in the joint. Bruises can cause capsular inflammation (bursitis). In this case, the capsules (and the area around the joint) swell because the volume of the fluid they are filled with increases.
Can lower back pain radiate to the leg?
Yes, this is possible and a very worrying symptom. The spine is partly made up of interconnected nerves and has a very important function in every human body. Therefore, lower back problems inevitably affect overall health. Analyzing and deciphering the causes of lower back pain radiating to the leg is impossible without appropriate diagnostic tests and treatment. The spinal segment in question is the main cause of lower back pain that radiates to the leg and buttocks. However, its pathological conditions can be different.
When a bone becomes deformed or changes position, it is called an orthopedic problem. As a result, the bone begins to press on the nerve endings. There are the following diseases in which the pain in the lower back radiates into the leg:
Herniated discs in the lumbar spine
A herniated disc is a deformation of the intervertebral disc that occurs after long-term osteochondrosis or other pathological condition. This problem often causes pain in the lower back that radiates to the buttocks and legs. The pain is usually persistent but not particularly severe, and when it worsens it is unbearable.
Inflammation of the sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve is considered one of the most important parts of the spine as it is responsible for the movement of the limbs. If there is a problem with this nerve, lower back pain radiates into the legs and buttocks and is often accompanied by other, previously unconsidered complaints.
Effects on nerve endings
This is essentially the compression of nerves by tumors and bones. This is a side effect of orthopedic diseases that gradually deform the structure of the spine. You can roughly determine the source of your pain by analyzing which side your lower back hurts and which leg the pain radiates to.
osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a common cause of lower back pain that radiates down the leg. Osteochondrosis is a change in various tissues of the spine. It is often the cause of lower back pain that radiates to the legs and buttocks. The pain associated with osteochondrosis is usually incessant and annoying or acute in fits and starts.
Non-orthopedic diseases
This particular symptom is not always caused by orthopedic conditions. Lower back pain that radiates to the right or left leg is often caused by trauma or neurological problems. Symptoms are usually not limited to pain: the limbs may become numb and lose feeling.
Sciatica is a specific condition in which the sciatic nerve at the exit from the spine becomes inflamed. The pain often extends into the back. Lumboishalgia is one of the most common reasons why the lower back hurts, causing pain in the buttocks and leg.
muscles and tendons
The entire muscles of the lower shoulder girdle are divided into different sections:
Tendons are the immovable part that connects muscles and ensures that they function properly and are firmly attached to the bones.

Muscles are divided into two categories:
Each group of muscles connected by tendons has specific functions for that part of the lower limbs.
The muscles of the lower limbs and foot allow:

The main function of muscles is to control the bones as a kind of lever and make them move. The leg muscles are among the strongest muscles in the body because they enable walking.
Arteries and veins of the lower limbs
The lower limbs are put under a lot of stress, which is why the muscles need a constant supply of nutrients and a high blood flow that contains nutrients is required.
The venous system of the lower limbs is characterized by branching, there are two types:
- The deep veins. They ensure the drainage of blood from the lower limbs and drain the already filtered blood.
- Superficial veins. They ensure the blood supply to the joints and muscle tissue and supply them with vital substances.

The arterial network is less diverse than the venous network, but their function is extremely important. In the arteries, blood flows under high pressure while all nutrients are transported through the venous system.
There are four types of arteries in the lower limbs:
The main source is the aorta, which comes directly from the heart muscle area. When blood does not circulate properly in the lower limbs, painful, burning sensations occur in the joints and muscles.
causes of injuries
Most joint injuries are caused by excessive twisting of the joint.


- Hard physical work;
- walking in high heels;
- Improper alignment of feet when walking or running;
- Sports;
- Direct blows to the ankle;
- cross country running;
- Unfortunate landing.


Young people are particularly at risk (most injuries occur between the ages of 15 and 25).
What types of ankle injuries are there?
The type of injury depends on the type of force applied to the ankle joint.
fractions
The most common cause of this problem is an injury sustained while jumping or running. Twisting the foot shifts and rotates the ankle bone, resulting in a fracture of one or both ankles.
Often the injury is complicated by a ligament injury. Fractures can be closed (without soft tissue or skin damage) or open.


Clinical signs of ankle injuries include.
- Severe swelling of the ankle that increases rapidly;
- Severe pain that increases with movement;
- Deformity of the joint (if the injury is complicated by a dislocation of the foot);
- crepitations from fractures.
Fractures are clearly visible on x-rays.

Indirect signs of soft tissue injury:
To clarify the diagnosis, X-rays are taken in three projections.
Classification of fractures according to the mechanism of injury:

- Redression of displaced fractures;
- Immobilization in position with a cast or other device;
- Restoring the integrity of the ligament apparatus.
In the case of displaced bone fragments, osteosynthesis is performed to better fix them.

Types of lower limb bone fractures
- Open – with skin injuries; In this fracture, the fracture zone is in contact with the surrounding area.
- Closed – it is a complete or partial fracture of the bone in which the skin is not damaged.
- Displaced – when the bone fragments are displaced from their axis. This is a fairly serious injury as it takes a long time to heal.
- No dislocation - the fragments or bone remain in place.
Fracture in the upper, middle or lower part of the tibia
Depending on the location, the injury can occur in:
The main symptoms of injury to the upper third of the bones of the lower limbs are:
- Strong pain,
- swelling,
- Hematoma in the area of the knee joint,
- Malposition of the lower limbs,
- Limitation of the range of motion in the joint.
In the medial tibia, one or two tibial bones are injured. The fracture can be transverse, oblique or fragmentary. Symptoms of the injury include acute pain, bluish skin, mild swelling and deformation of the shinbone. The patient is still able to put weight on the foot. A plaster cast is applied for a period of one month.
All ankle fractures can result in ligament tearing, displacement of the fragments and displacement of the foot. With such an injury it is difficult to support the limb, and with a fracture with dislocation it is impossible.
Fractures with and without dislocation
In the event of an ankle joint injury with dislocation, the position of the fragments changes relative to one another. The characteristic symptoms are:
- the injured leg becomes smaller – shortening of the limb
- The lower extremity moves in an unnatural direction;
- Fragments can tear soft tissues and skin;
- strong pain;
- Impairment of range of motion.
Non-dislocation injuries are injuries to bones that remain in place. This injury is often confused with a tear in the ankle ligaments.
signs
Symptoms of a fracture can vary depending on the location of the injury. However, there are some basic symptoms that occur with any injury of this type:
- Severe pain that increases when you try to step on your foot.
- Swelling, swelling.
- Ankle deformities of varying degrees of severity.
- Bruises and hematomas may occasionally occur.
- Increased sensitivity to touch.
- Difficulty getting around.
- When moving the leg, a characteristic crunch of bone fragments can be heard.
- It is impossible to step on the foot.
The intensity of the pain depends on the pain threshold and the severity of the injury.
Surgical technique.
The procedure is carried out under anesthesia. The doctor cuts through the soft tissue in the area of the fracture, thereby gaining access to the damaged bones. As a first step, the fractures are gently compressed and if blood vessels, nerves, tendons, etc. are damaged, the anesthesiologist repairs them and restores continuity. – The fractures are carefully approximated, nerves, tendons, etc. are restored in their continuity. The actual osteosynthesis is then carried out, that is, fixing the fragments with metal structures. These can be placed in the bone (intramedullary osteosynthesis) or on the bone (osseous osteosynthesis). The choice of the specific type of procedure is made during the preoperative examination. After fixing the metal structures, the wound is sutured layer by layer and, if necessary, a drainage system is inserted.
External osteosynthesis is performed using an Ilizarov apparatus. Fixation spokes are inserted into the bone on both sides of the fracture and secured from the outside with special clamps or rings.
Take advantage of this unique opportunity and make an appointment for a free consultation about your planned operation. Read more.

Osteosynthesis of the shinbone prevents the fragments from moving again. This means that the affected person can resume physical activity much earlier than with classic conservative treatment. This avoids many of the problems associated with long-term immobilization, particularly muscle wasting.
rehabilitation
The patient remains in the hospital for 1-5 days, depending on the complexity of the procedure. After discharge, he will have to take medication and limit his physical activity. Until the stitches have healed, you should not bathe, overheat, go to the sauna or swimming pool, or swim in open water. Once the condition has stabilized, doctors recommend exercise, massage and physical therapy to speed up rehabilitation. Physical activities should be strictly dosed to avoid further damage to the bone. The leg cannot be put under full weight again until the fractures have completely healed, which is determined by x-rays.
If you want to find out the price of osteosynthesis of the tibia, ask questions about the operation or make an appointment, use the special form on the website or call the SM-Clinic Center for Surgery in Moscow.
Read more:- tibia and fibula.
- Bones of the tarsal bone of the hand.
- Corset for broken fibula.
- Fracture of the lateral condyle.
- The lateral ankle is.
- Fracture of the heel bone.
- fibula.
- Fractures of the tarsal bones.