When the disease creeps in and attacks the joints, it robs you of sleep and tranquility and life loses its vivid colors. When exercise is no longer fun, come to ORTOMED-SLINI.
- Upper limb lymphostasis
- symptoms
- What is Keller disease type 2 or Freiberger disease?
- The course of type 2 Keller disease can be divided into four stages:
- Treatment
- Conservative treatment:
- Transverse flatfoot
- causes
- Consequences of flat feet
- Treating and slowing the progression of transverse flatfoot
- Morton's neuralgia
- The most common are.
- Latest updates.
- My subscriptions:
- Type of itching in the genital area
- Itching and burning in the vagina after urination
- Vaginal redness in diabetes
- Treatment of itching in the vagina
- About the disease
- Thumb bandage (left) T-02: function
Upper limb lymphostasis
Lymphostasis is a disease of the lymphatic system associated with an imbalance in lymph flow and retention of lymph in the body. The pathology is accompanied by thickening of tissues, persistent swelling and thickening of the limbs, reduced mobility, characteristic ulcers of the skin, and darkening of the skin.
Lymphatic drainage disorders and lymphatic congestion in the limbs are often the result of
- impairment of the excretory function of the kidneys;
- circulatory insufficiency or chronic venous insufficiency;
- postthrombotic syndrome;
- damage and blockage of the lymphatic vessels;
- fistulas in arterial and venous structures;
- Suppression of lymph flow by tumors, inflammatory tissues, infiltrates;
- Malformations of the lymphatic system, etc.
The exact cause of the condition can only be determined by taking a medical history and identifying the underlying condition that caused the lymphatic flow disorder.
symptoms
The development of the disease is indicated by a number of characteristic symptoms:
- Pronounced swelling of the limbs that appears in the evening and disappears in the morning;
- Increased swelling during physical exertion, prolonged restriction of arm movement, etc.;
- Persistent swelling;
- A noticeable mark left on the skin when pressing on the swollen area of tissue
- The skin at the site of lymphatic congestion becomes tight and thickened, accompanied by severe pain.
In more severe cases that require immediate specialist medical attention, it comes to
- irreversible disorders of lymph flow;
- Symptoms of benign cystic and fibrous accumulations in the tissues;
- limb dysfunction;
- loss of contour of the arm;
- Occurrence of contractures due to restricted mobility;
- Symptoms of trophic ulcers, eczema and rust inflammation;
- Symptoms of tissue sepsis.
What is Keller disease type 2 or Freiberger disease?
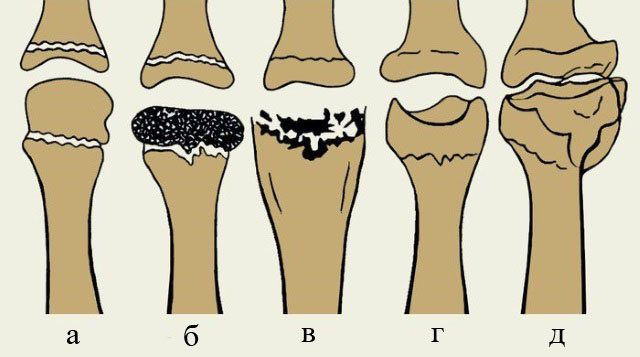
Keller's disease type 2 or Freiberg's disease is a relatively rare non-communicable disease and belongs to the group of osteochondropathies. The head of the metatarsal bone begins to die off as a result of circulatory disorders, which are due to one reason or another. In 95 % of the cases, the head is affected by 2 or 3 metatarsal bones, aseptic necrosis in the others cannot be ruled out.
Although the disease was recognized and described more than 100 years ago, little is known about it to this day.
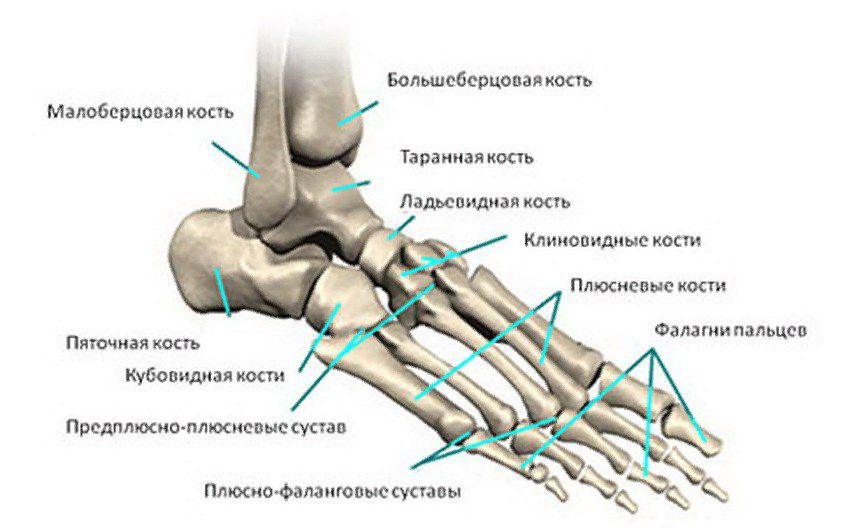
The tarsal bones are a group of 5 long bones located in the midfoot. They connect the pontics to the back of the foot. The heads of the metatarsal bones form the metatarsophalangeal joints with the distal phalanges that allow the toes to move and maintain normal support. Aseptic necrosis of the head of the second metatarsal is most common in adolescent girls aged 10-15 years. It is also at this age that it is most often discovered. However, Keller's disease type 2 does not occur for the first time in adults, although it is often diagnosed in cases where appropriate treatment has not been received in adolescence. However, there are reports of cases when the pathology first appears in 20-25 year olds, but this requires more detailed investigation.
The course of type 2 Keller disease can be divided into four stages:
- Aseptic necrosis. This stage is characterized by the destruction of the bony ridges in the bone that provide strength, ie the development of local osteoporosis. As a result, the affected metatarsal head loses its density and is no longer able to withstand the loads placed on it.
- Compression fracture – results from the destruction of part of the remaining bony trusses inside the head or newly formed bony trusses. This causes them to break, wedge into each other, and drastically reduce the height of the bone.
- fragmentation or resorption. Changes in the metatarsal bones lead to the formation of osteoclasts (special cells that resorb damaged bone rays). This leads to a reduction in the size of the head and even to its almost complete resorption.
- Recovery and Consolidation. The body tries to repair the damage by trying to rebuild the lost bone. As a result, the metatarsal head gradually rebuilds, but this is often difficult because it is severely deformed by the pathological fractures and defragmentation that have occurred, and the repair process itself requires a good blood supply, which is not available if Keller's disease is left untreated .
Treatment
The prognosis for Keller's disease is very favorable, especially if the disease is diagnosed and treated early. If this is the case, then patients have every chance to get rid of the excruciating pain in the foot and the need to limit physical activities.
The type of treatment largely depends on the stage of the disease, the presence of complications and the age of the patient. While conservative treatment is sufficient in the early stages, advanced cases may require surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment:
- Immobilization of the foot with a cast in the form of a shoe for a period of 4-6 weeks. In particularly difficult cases, immobilization can be extended to 12 weeks. During this time mobility is ensured with the help of crutches.
- Wearing orthoses. These help to properly distribute the load on the foot and eliminate movement anomalies. Their use eliminates the symptoms of the disease and drastically reduces the risk of complications. To be effective, however, they must be tailored to the individual patient.
- The pharmacological treatment aimed primarily at eliminating the symptoms of the disease, especially pain, by taking NSAIDs and improving the metabolic processes in the foot. Therefore, additional preparations are prescribed that activate calcium metabolism and improve peripheral blood circulation. In this way, an attempt is made to influence the causes of the disease.
- Physiotherapy, which includes massage, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, iontophoresis, laser, shock wave therapy, foot baths, etc., is also used. The aim of these treatments is to improve blood circulation in the feet, eliminate inflammation and reduce pain. Physiotherapy is very effective against Keller's disease.
- The therapy consists of an individual exercise program that improves local blood circulation, increases the range of motion of the big toe metatarsophalangeal joint, strengthens the foot muscles and prevents flat feet from developing.
Transverse flatfoot
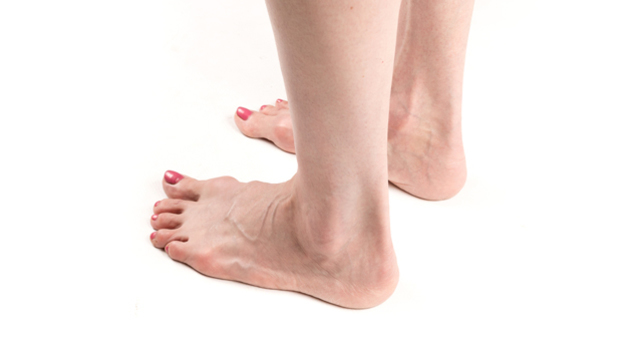
Women are doomed to suffer a lot in the name of beauty. But as we all know, all patience has an end. What does it matter if you wear high heels and pumps, if the 'bone' sticks out unsightly, widens the foot and literally doesn't take another step. The cause of this deformity is transverse flatfoot.
Our feet are made up of many bones connected by joints, ligaments and tendons. Ideally, the metatarsals (where the pontics attach) should be parallel to each other and held in place by ligaments. In practice, the bones are often fanned out, which is only acceptable up to a point.
When the supporting bones are too far apart, the following happens: the first metatarsal, to which the big toe attaches, deviates significantly from the rest, and the foot muscles are redistributed. The tendon, previously stretched longitudinally, reverses direction, following the deviated metatarsal and pulling the toe outward. This deviation of the thumb is called hallux valgus. It causes the head of the metatarsal to shift and protrude. Because the shoe is in constant contact with this area, abrasion and eventually inflammation of the joint occurs. As a result, osteochondral hypertrophy occurs, popularly referred to as 'bunions'.
causes
Most commonly, transverse flatfoot is due to an inherited weakness of the musculoskeletal system. In addition, inheritance occurs in the female line. In men, this form of flatfoot is less common, mainly as a result of trauma. The ratio of affected women to men is 8:2. Standing work (the forefoot is loaded during the day) and uncomfortable footwear exacerbate the problem.
Many people rely on the miraculous effect of supination, which redistributes the load on the foot. However, the disadvantage of supination is that it only relieves the symptoms without eliminating the cause. So how can you strengthen your muscles?
With a longitudinal flatfoot (when the foot does not have a steep arch and the legs tire quickly), the effect is achieved by strengthening the foot and shin muscles with exercises. With transverse flatfoot, the situation is unfortunately different. The muscles responsible for causing the condition are very small and manageable. However, strengthening exercises are useful. By combining foot exercises (right, left, up, down and circular movements) with daily warm baths and foot massages, the growth of stubborn bunions can be stopped permanently.
Popular and this recipe: apply a net of 10%iger iodine solution to the 'bone'. This really helps reduce inflammation and thereby stop cartilage growth. Just don't use a more concentrated iodine solution or you could get skin burns. Ditto for vinegar compresses - unfortunately they don't help.
There are many ointments available today that relieve joint inflammation and improve tissue nutrition. However, it is better if the ointment is selected by an orthopedist.
With both forms of flatfoot, it is advisable to wear low-heeled shoes (up to four centimeters). It is also advisable to change footwear throughout the day. Staying in shoes at work is uncomfortable and unhealthy. Always bring comfortable, breathable shoes to change into.
When the cartilage that has grown at the head of the metatarsal bone turns into bone tissue, the 'bone' becomes a constant source of pain. In this case, only surgery can help.
Consequences of flat feet
Flat feet have very serious consequences for the entire body. It is an apparently localized pathology that affects almost the entire musculoskeletal system and accelerates its degradation.
The main consequences of flatfoot.
- Spinal disorders and postural disorders (curvatures, osteochondrosis, herniated discs, radiculitis).
- Excessive stress on the joints and the resulting premature wear (arthrosis, arthritis of the joints) due to additional lateral stress.
- Diseases of the pelvis (coxarthrosis).
- Foot deformities result in 'neurological disorganization' due to distortion or misinterpretation of nerve impulses from the foot receptors. This leads to balance and coordination problems and reduced movement efficiency.
- Imbalances in the muscles lead to painful 'trigger points'. The fluid gait is impaired and slackening occurs over the years. Flat feet reduce the efficiency of the venous pumping mechanism of the calf muscles, resulting in blood congestion in the legs that causes varicose veins in the lower limbs.
- Another consequence of flat feet is a disease of the plantar tendon and foot nerve (Mardan neuralgia) - heel spurs, accompanied by burning pain.
- As a result of the slowed blood flow in the lower limbs, the functioning of the entire circulatory system is impaired.
The impaired functioning of the circulatory system, in turn, leads to chronic hypoxia in the tissues of the lower limbs. This contributes to the development of varicose veins. A vicious circle is created. In elderly people with an initial circulatory disorder and in diabetics, such disorders often lead to pathological edema, trophic disorders and ulcers on the feet and lower legs.
Treating and slowing the progression of transverse flatfoot
Conservative treatment aims to halt the progression of flatfoot and relieve pain. In the early stages, treatment consists of the fabrication and wearing of custom orthopedic insoles or pads under plantar compression. In advanced stages (severe deformities) of transverse flatfoot, patients wear orthopedic shoes adjusted to individual measurements, strictly adhering to the recommendations of the orthopedist/traumatologist.
Conservative treatment includes. Physical exercise, massage and physical therapy, and warm footbaths (which help relax muscles and thereby reduce pain). Conservative treatment of these deformities is a prophylactic measure that supports the function of the deformed toes and feet under static and dynamic loads, thus improving the patient's quality of life and slowing down the progression of the foot deformity. However, if the flat foot has already resulted in a toe deformity (hammer toe), surgical methods of correction and elimination of secondary soft tissue changes are of priority.
The surgical treatment of transverse flatfoot is performed when there is significant pain that cannot be relieved by conservative treatment methods. Treatments on the toe joints to correct the valgus deviation of the first toe are carried out as an independent procedure or as part of a reconstructive operation to correct the entire forefoot. First and foremost is the Schede operation.
The surgery is performed on the bones and ligaments of the foot. Typically, the cartilage at the ball of the metatarsal (the bony part) is cut away, the bone smoothed, and the tendon reduced so it can hold the first toe in a straight position. All this is fixed with a special splint. The operation is complicated but effective.
Morton's neuralgia
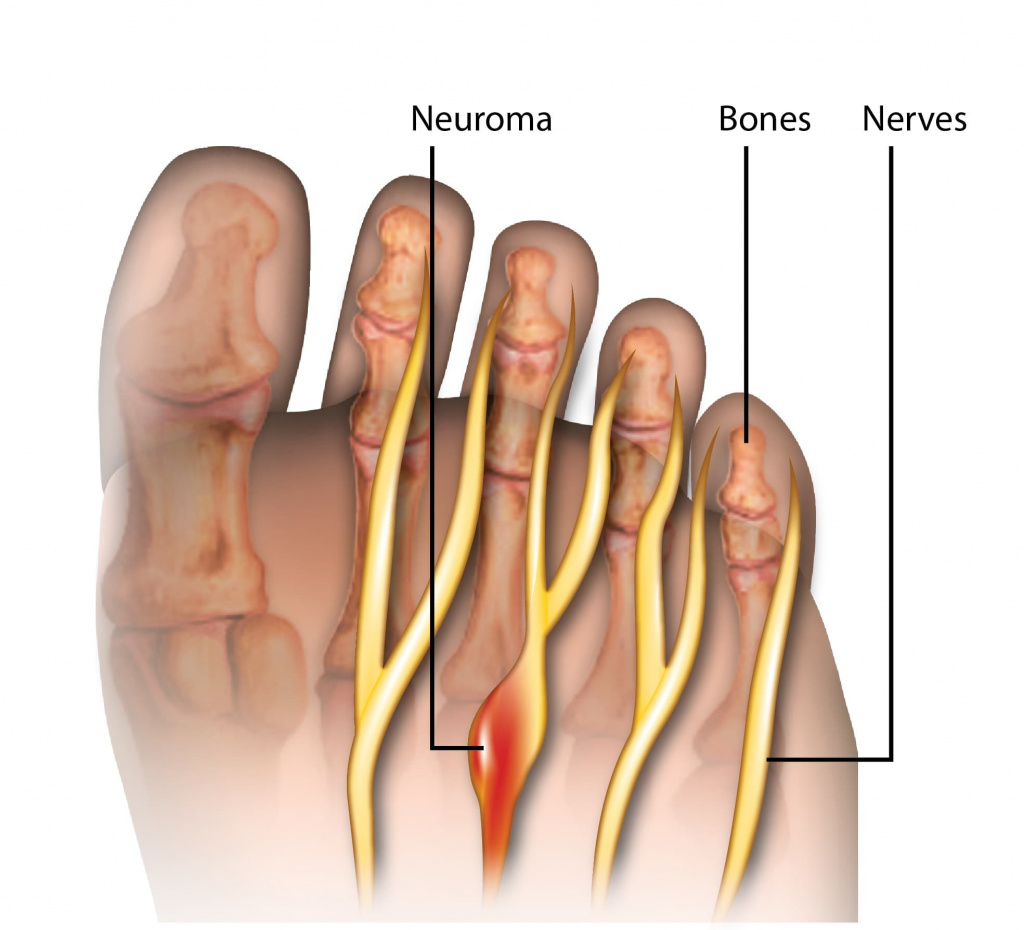
Morton's neuralgia, also known as Morton's neuroma (Morton's neuroma)is often the cause of pain in the metatarsal area. It is caused by the transverse ligament pressing on the carrying nerve, which eventually becomes inflamed. Describe patients with Morton's disease. The pain in the foot is described as stabbing or even burning. Factors that cause Morton's neuralgia include bunions, transverse flat feet, and hammer toes. Obesity can also be one of the causes and the habit of walking in high heels.
The most common are.
Neither I nor Sting nor McCartney know the secret of a hit' – Igor Sarukhanov on the making of a hit. Unformatted. Excerpt from the broadcast of March 17, 2023.
'I want to know who a rat is! Polina Gagarina let off steam on the set of the show 'Voice 11'. Excerpt from the broadcast of March 17, 2023.
'I treat my age with great respect'. – Irina Ponarovskaya talks about compliments and the age limit. tonight show Abstract.
'Every child in Georgia should play the piano'. Brandon Stone opens up about having a love of music in his blood. anecdotes. Excerpt from 03/10/2023.
'You have become unhappy!' A divorced man reveals how his daughter sees him. Psyche. Excerpt from 03/12/2023
Latest updates.
Are Ultraviolet Light Bulbs Dangerous; milk oolong green tea; arthritis in the lower back; lose the excess - the beginning of a project. Live healthy!
- about the company
- promotion a
- Special Projects
- OTT version of channel one
- online cinema
- HbbTV Interactive television
- Channel One applications
- Casting for Channel One
- Tell your story about a World War II veteran
- All Movies
- Switch to digital broadcasting
- Your ideas for Channel One
- Working at Channel One
- TV ratings
- User Agreement
- Contact
- make contact
My subscriptions:
© 1996-2023, Channel One. All rights reserved.
Total or partial reproduction of material is prohibited.
Compatible use of material on this site requires a link to the resource in question.
The code to embed videos in blogs and other resources on our site may be used without permission.
Broadcasting online without permission is strictly prohibited.
broadcast request.
Type of itching in the genital area
The type of itching in the female genital area can be constant or intermittent and only occurs under certain conditions – e.g. B. after a hot bath, on the beach or during sexual intercourse. Even with intermittent and seemingly insignificant itching, a specialist doctor should be consulted, since such a symptom may indicate a health problem and the need for treatment. If it starts to itch 'there', don't hesitate to consult your doctor.
Itching and burning in the vagina after urination
More frequent occurrences of this symptom after going to the toilet can indicate a bladder infection (cystitis). This condition is manifested by frequent urges to urinate, which is irritating and gives the impression that the inflammatory process is concentrated in the genital area.
Discomfort in the genital area is also caused by inflammation of the urethra, that is, inflammation of its walls, in which various bacteria and viruses are involved.
Almost any disease of the excretory organs, causing dryness of the mucous membrane, leading to micro-injuries and accompanied by discharge, can cause discomfort in women. Penetration of urine into the area of microtrauma causes irritation, which leads to discomfort.
Vaginal redness in diabetes

Diabetes causes changes in the way the entire body functions. With this disease, small blood vessels are damaged, the local immune defense is reduced, the acid-base balance is disturbed, the skin and mucous membranes become dry, scaly and easily form microcracks, which become infected with pathogenic flora and fungi, leading to inflammatory diseases . And, of course, the woman can be plagued by discomfort in the genital area, manifested as itching and painful sensations.
Treatment of itching in the vagina
The treatment program is developed by the doctor depending on the causes that led to the unpleasant symptoms. If it is not possible to eliminate the symptom by not using perfumed intimate hygiene gels and wearing synthetic underwear, the woman may need medication. Dysbacteriosis requires diet and pro- and prebiotics, thrush requires antifungals, age-related changes require hormones, and if an STD is the cause of the condition, both partners should be treated.
Application of topical drugs is complicated by a biofilm, which is a community of microorganisms on a surface, in this case living tissue. iv This is one of the main survival strategies of bacteria in infected organisms - they join together and 'try' to survive by sticking to each other. v This property in many cases prevents the use of vaginal suppositories, pills, and other topical medications for STDs.
Viral infections can be treated with systemic drugs. One such drug is VIFERON. It is an antiviral and immunomodulating drug with indirect antimicrobial action, which has a number of unique pharmacological properties. It contains interferon alfa-2b, which helps stop viruses from multiplying and also helps the body's immune system function properly.

VIFERON suppository suppresses viral activity and strengthens the body's immune response to pathogens, so it can be used in infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract (chlamydia), infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract (chlamydia, cytomegalovirus infection, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, gardnerellosis, papillomavirus infection, bacterial vaginosis, recurrent vaginal candidiasis, mycoplasmosis) in complex therapy.
About the disease
This clinical syndrome, in which the foot has a horse-like appearance, may result from paresis of the foot or ankle contractures. The severity of the deformity can vary. In some (lighter) cases the heel is only slightly raised in relation to the supporting surface, in other (more severe) cases the heel is significantly raised and the person only stands with their toes on the ground.
With a unilateral pathological process, walking function can be preserved, but it is difficult. With a bilateral equinus (right and left foot), the affected person has great difficulty walking. The diagnosis of this syndrome is made on the basis of an objective examination and palpation, as well as additional tests. X-rays, CT scans and MRI scans help to visualize the deformity of the foot. Electromyography and podiatry are also indicated as part of the differential diagnosis.
Foot paresis and persistent ankle contractures can be treated using a variety of methods. In some cases, a conservative approach and the choice of orthopedic shoes is enough, in other cases, foot paresis surgery is indicated. Your doctor can help you choose the best treatment program.
The symptoms of clubfoot, like the symptoms of foot paresis, include subjective and objective symptoms:
- limited mobility of the ankle;
- Gait impairment (moderate to severe);
- lack of dorsiflexion (both voluntary and passive);
- Curvature of the foot with the toes below the heel, the degree of elevation can vary widely;
- pronounced rejuvenation of the skin on the most stressed sole of the foot (toes, metatarsal bones);
- thinning of the skin in the heel area;
- sharp raising of the lower limbs when walking with a strong flexion in the knee and hip joints (this is a forced action to prevent the foot from catching on a horizontal surface when walking);
- Pain when walking (both local and throughout the leg).
The causes of horse foot can be congenital or acquired, the latter being the most common variant. This deformity can occur in isolation or in combination with other foot deformities, such as: B. the corso-varus (the foot is not only in sole flexion, but also turned outwards).
Acquired deformities are usually the result of neurological disorders (palsy of the foot). However, other causes are also possible:
- Joints - deforming ankle arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis;
- Muscular – inflammatory lesions of the muscle compartment of the lower leg, traumatic muscle injuries, including from external immobilization devices;
- scarring – after deep burns and wounds;
- Compensatory - the horse's foot is formed on the shortened limb with the normal length of the other leg (this reaction is intended to ensure gait).
Thumb bandage (left) T-02: function
T-02 thumb bandage (left):
– Allows the abduction of the first finger, which has a positive effect on valgus deformities.
– Allows the big toe to be fixed in a medium physiological position.
– Reduces the symptoms of valgus deformity.
– Prevents the occurrence of a valgus deformity at risk.
– Prevents the development of the condition and the aggravation of concomitant diseases.
Buy the big toe bandage (left) T-02 in our orthopedic shop. You can place your order by phone during shop opening hours, but you can also leave a request via the shopping cart at any time of the day. We will process your order immediately and send your package to the address you provided. Delivery will be made as soon as possible, please contact our manager, it depends on the region where you live. There is a toll-free number for regions 8 800 550-52-96.
You can ask us any questions about the product or the shop.
Our qualified professionals can surely help you.
Read more:- Morton shoe inserts.
- Pain in the heel bone of the foot.
- Morton's Neuroma Ointment.
- metatarsal bones.
- Treatment of metatarsalgia of the foot.
- metatarsalgia.
- tarsal and metatarsal joints.
- tarsus.
