Orthopedic shoes support the rear and midfoot with a firm heel. The arch of the foot is supported by spinal insoles, which evenly distribute the weight of the body and prevent further deformation, correct the shape of the foot, improve posture, stabilize blood circulation and reduce joint wear.

- Toe nodules (nodules, cones), causes, diagnosis and treatment
- Causes of Toe Bunions
- Verified article.
- Causes of nodules on feet
- Surgical procedures to treat 'bumps':
- signs
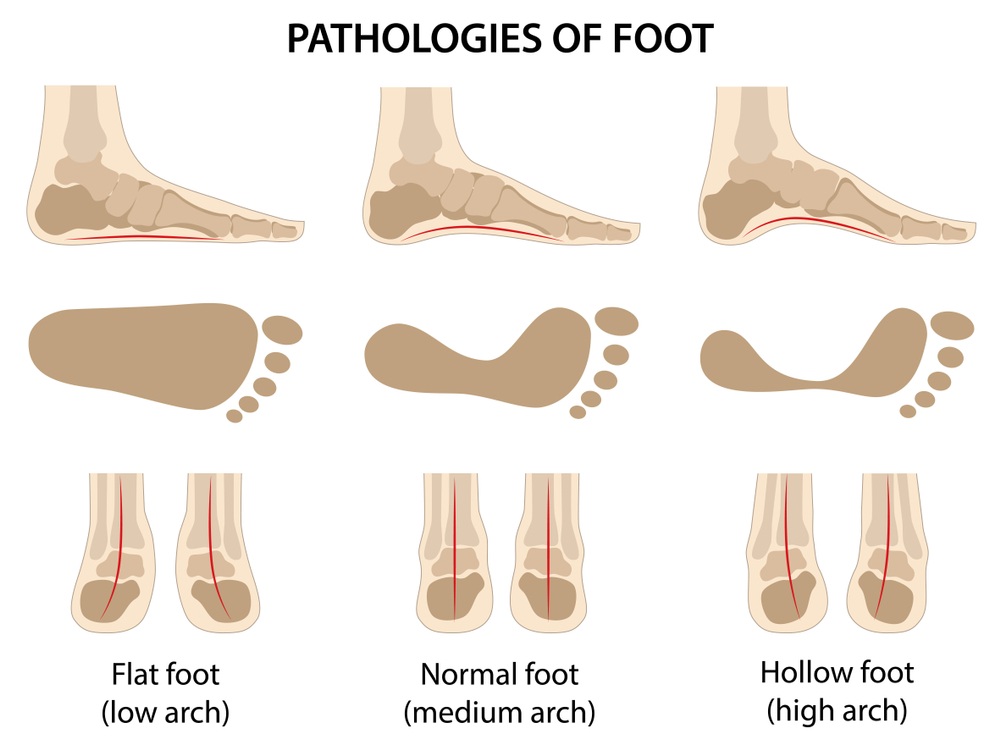
- Why does a transverse flatfoot occur?
- Bones in the foot: causes
- Bone pain in the foot: what to do?
- Why are the metatarsals and toes curved?
- What other causes are there for the disruption of the vaults?
- Causes of valgus foot
- What should I do if I have an ingrown bone in my foot?
- Overgrowth of the foot
- Gout (gouty tophus)
- Treatment tactics:
- Big toe: other causes
- Prevention: Can bunions be prevented?
- rehabilitation period after the operation
- Contraindications to the operation
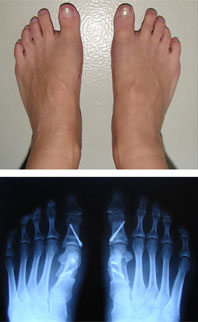
Toe nodules (nodules, cones), causes, diagnosis and treatment
Toe nodules are areas where the metatarsal bones are displaced. In their normal, physiological position, the metatarsal bones should be parallel to each other, but when they change their angle, unsightly growths - nodules - form. The degree of visual severity of the deformity and the intensity of the symptoms depend on how badly the bone has deviated. There are 4 degrees of deformity:
I – the deformity does not reach more than 20 degrees and there are no symptoms;
II – the deviation is close to one degree, the feet hurt after walking for a long time;
III – the deviation is less than 50 degrees, pain often occurs when walking, it is difficult to find footwear;
IV – the deviation of the bones is more than 50 degrees, there is a deformation of the foot and other toes, the pain syndrome persists even at rest.
Athletes, women who constantly wear uncomfortable shoes, and people with standing jobs are at risk of developing this problem. In order to avoid constant pain and deformity of the foot caused by thickening, it is important to consult an orthopedist in a timely manner and receive the recommended treatment.
Causes of Toe Bunions
- Diseases. This group of causes includes gout, osteoarthritis, hygroma, Taylor's deformity and other diseases. These can be inflammatory and non-inflammatory growths.
- Standing work. This problem often affects salespeople, hairdressers, baristas, teachers and other professions that spend more than eight hours a day on their feet and put excessive strain on their feet.
- Sporting activity. Professional athletes who play football, run, cycle and engage in other sports that primarily involve the feet are at risk.
- Wearing uncomfortable shoes. Shoes with narrow toes, high heels and uncomfortable heels increase the load on the foot and distribute it unevenly. Wearing uncomfortable shoes regularly can cause deformation of the metatarsal bones, growths, and pain.
- Hormonal changes. The strength of bone structures is influenced by hormones. When the body undergoes hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause or teenage restructuring, this can cause deformation of the bone structures of the foot.
Verified article.
Causes of nodules on feet
- Joint diseases, arthritis of any kind, exostosis, bunions, flat feet and others can cause bony enlargement of the foot;
- Genetics: In many cases the condition is inherited;
- Endocrine system disorders;
- Tight or ill-fitting shoes (this risk area includes women who neglect their health and prefer high heels);
- Various injuries to the foot or lower leg, congenital defects as well as the effects of dislocations or impaired bone healing after bone fractures;
- Certain activities (e.g. ballet) place increased pressure on the forefoot and may increase the likelihood of developing a deformity.
- Applying various fabrics (e.g. felt) to reduce pressure on the bony area of the foot.
- Physiotherapy treatments such as lasers and ultrasound are used to relieve the inflammatory and dystrophic symptoms of the disease.
- Any blisters or abrasions that also cause pain should be treated.
- To prevent deviation of the first toe, it is advisable to wear physiological, properly fitting shoes.
- If the toe deformity is large, the shoes, especially the toe, should be well stretched to relieve the pressure on the bone.
- It is advisable to wear custom-made insoles to distribute the load on the foot when walking and running.
- Range of motion should be improved through physical therapy and foot massage.
Surgical procedures to treat 'bumps':
The following procedures are used in the CM Clinic to treat valgus deformity of the first toe. Corrective osteotomies. These operations eliminate the deformity and preserve the joint. It is not enough to saw off the 'hump'; the deformation of the 1st metatarsal must be corrected by fixing the fragments with special screws and spikes.
The day after the operation, the patient can walk independently wearing special postoperative shoes: Baruca shoes. After the operation, the patient will remain in the hospital for a maximum of 2 days. During this time, appropriate pain treatment, antibiotic therapy, bandaging and exercise therapy should be carried out.
If you have pain in your big toe, come to the SM Clinic on Klara Zetkin Street and have modern surgery!
To learn more, make an appointment with a specialist or a home visit with a doctor at +7 (495) 292-39-72
signs
The first symptoms of the disease are unremarkable. Prolonged walking is accompanied by discomfort in the toes, heaviness in the legs, mild pain and swelling. Usual shoes are uncomfortable to wear due to the widening of the foot. As the arch of the foot flattens, the symptoms of paraplegic flatfoot increase:
- The feeling of heaviness in the feet is constant, regardless of physical activity.
- The lower leg muscles hurt, the foot hurts, the calf muscles hurt.
- The rapid fatigue of the legs leads to a loss of performance and chronic fatigue.
- The gait becomes stiff and angular and mobility is lost.
- The bones in the feet are constantly irritated by the pressure of shoes. In response, the periarticular capsule, which protects the big toe joint from overload, becomes inflamed.
The foot deformity is visually noticeable (see illustration). The foot enlarges, the wide foot does not fit into normal shoes and the inside of the heel wears out quickly. Dry calluses and corns form on the heels and soles of the feet. The angle of the big toe increases significantly. The second and third toes become crooked and the phalanges of the toes bend (hammer toe).
If you notice the first symptoms of flatfoot, you should not delay treatment. The abnormal distribution of body weight on the foot sets off a pathological chain. Pain occurs in the knee joints and sacral area, and pressure on the intervertebral discs increases. There is an increased risk of developing osteochondrosis, spinal fractures and spinal curvature.
Why does a transverse flatfoot occur?
In 8 out of 10 people, the bony arch of the foot drops as a result of overloading the foot, reducing muscle tone. The inside and the phalanges of the toes are tensed and the foot is flattened. Main causes of foot deformity:
- Weakness of the connective tissue, genetic defects.
- Weakening of muscles and ligaments due to lack of physical activity.
- Carrying and lifting heavy weights, weight training, being overweight.
- Standing on your feet for long periods of time (tour guides, salespeople, welders, waiters, hairdressers).
- High heels, tight and small shoes.
- Injuries to the ankle joint, torn tendons and ligaments in the arch of the foot.

Bones in the foot: causes
Doctors refer to the degenerative process as the formation of the 'valgus foot'. As mentioned, weight gain and wearing uncomfortable, wobbly shoes are among the causes, but these causes are not at the top of the list. Both an overweight man and a woman wearing high heels can have completely healthy feet.
Medicine has not yet given a clear answer to the question of the causes of corns. However, an analysis of statistics shows that the most common causes are:
- Genetic predisposition. The structure of bone tissue and therefore the tendency to form corns is hereditary;
- Traumatic impacts on the foot;
- Congenital deformities;
- Certain types of arthritis, particularly rheumatoid arthritis, which involve severe and deep inflammation;
- Poliomyelitis and other pathologies affecting the nervous system and muscles.
Bone pain in the foot: what to do?
It is better to start treatment at the first signs of bone protrusion, when there is no or little pain sensations. The treatment methods are as follows:
- Correct choice of footwear. It is worth avoiding heels that disrupt stability, models with narrow toes that put pressure on the toes. By themselves they are unlikely to provoke the formation of bunions, but they can be an additional factor in their development. Optimal footwear is loose and has a low heel. Typical examples are good running shoes with cushioning and a slightly raised heel. Sneakers, on the other hand, are not 'good' footwear because they have a completely flat sole;
- Insoles. It is best to use. custom insoleswhich are made based on an impression of the foot. The insoles ensure the correct alignment of the foot and minimize pressure on the big toe joint;
- Silicone based toe spacers. The soft insoles also reduce pressure and help the big toe to be in the anatomically correct position;
- Lifestyle adjustments. Lifting weights, long-distance running, standing for long periods of time, and similar activities make the situation worse.
If a protruding bone causes not only discomfort but also severe pain, you should consult your doctor. Based on an x-ray, the doctor will draw conclusions about the exact nature of the joint deformity, advise orthoses, buy them - to make life much easier and get rid of the pain. Orthotics are a much more sensible and appropriate solution than taking medication to relieve pain. The use of such preparations must be closely monitored by a specialist, otherwise the consequences will be extremely negative! Insoles, on the other hand, are completely harmless to health and can be used permanently and without restrictions.
Why are the metatarsals and toes curved?
There can be factors that promote the development of misalignments of the metatarsal bones:
The metatarsals are an important part of the arch of the foot. The main cause of metatarsal deviation is a disruption in the elastic properties of the ligaments, tendons and muscles that support these bones and the arch of the foot.
In these disorders, the arches are unable to maintain their correct shape when the load is relieved and the metatarsals do not return to their original position'. The vaults gradually lose their cushioning function and become flattened. The tarsal bones and toes deviate and a 'vicious circle' is set in motion.
What other causes are there for the disruption of the vaults?
Other factors that contribute to arching of the foot and deviation of the metatarsals and toes are high static loads.
Increased stress on the ligaments, tendons and muscles of the foot, such as these, also lead to arch prolapse:
Regardless of the congenital or other factors that lead to the development of the deformity, metatarsal and toe deviation and arch prolapse, treatment of the deformity is possible. Eliminating these harmful factors is an important part of the treatment complex.
Causes of valgus foot
The valgus defect develops slowly. This has more disadvantages than advantages: the disease is difficult to detect in the early stages. At first, your usual shoes become uncomfortable, then your feet start to hurt. The main symptom of hallux valgus - an outward deviation of the big toe with the formation of a bony protrusion at the base - only becomes apparent gradually. Where is the cause?
The largest percentage of patients with valgus deformity are women over 30 years old. Have you already guessed why? True, it all depends on your shoes. If you wear shoes with high heels and/or narrow toes every day, the likelihood of bunions is high.
In addition, the causes of this condition can be:

- congenital weakness of connective tissue;
- Being overweight – increases the strain on the feet;
- inherited predisposition;
- sedentary lifestyle due to sedentary work and weakened leg muscles;
- flat feet;
- Injuries to the ankles;
- Ballet and dance lessons, as you often stand on your toes.
What should I do if I have an ingrown bone in my foot?
Problems associated with ingrown bones are not just cosmetic. Patients often complain that they have difficulty fitting into shoes and that their feet become tired when walking. In addition, valgus foot deformities are often accompanied by problems such as the formation of painful calluses and corns. Conclusions. Something has to be done.
The answer to the question 'Can you cure bunions with iodine?' is: No. The same applies to other home remedies: They can only temporarily relieve the feeling of pain.
The first step is to visit a podiatrist. He or she will make the necessary diagnosis and prescribe treatment, which may be conservative or surgical. Today there are so many treatment options that surgery can be avoided. Surgical intervention is only necessary in very advanced cases.
The treatment of valgus defects is lengthy and not easy. It includes the selection of suitable orthoses, physiotherapy, anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving medications as well as massages. In addition, the doctor prescribes a complex of therapeutic physical exercises. It is advisable to visit the clinic at an early stage of the disease for faster results.
Overgrowth of the foot
A hygroma is a 'protrusion' of the joint capsule or tendon sheath. The growth can form on the back of the foot from the ankle to the toes.
- It forms on the dorsal surface of the foot. An exception is the hirgroma on the sole of the foot.
- At first it appears sporadically and disappears, then it becomes permanent.
- It is painless, dense or soft-elastic and often mobile.
- When rubbing against footwear, symptoms of inflammation may occur: redness, pain and swelling.
- Causes discomfort and pain when wearing tight shoes.
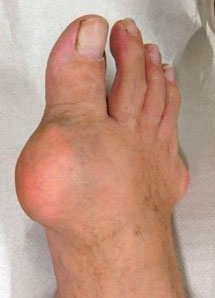
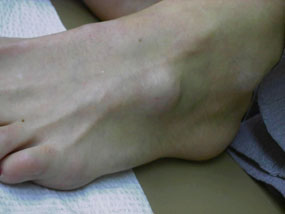 | 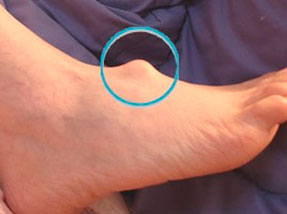 |
| Appearance of the foot with holograms | |
|---|---|
Gout (gouty tophus)
Gout is a disease associated with a disorder of purine metabolism. The tophus in gout are deposits of uric acid salts in the tissue.
- Gout is more common in men, and tophus is the main reason for visiting an orthopedist;
- The location of the tophi varies greatly and extends from the toes to the earlobes.
- Their size varies from a few millimeters to gigantic proportions;
- Tophi tumors are dense and painless;
- When chronically traumatized by footwear, they can become inflamed, infected, and infectious;
- When the tophi open, a white mass (urate crystals) is released from them;
- 15-20 % of gout patients carry urate stones.
 | 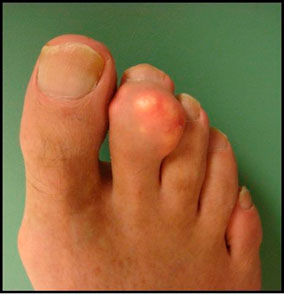 |
| The appearance of a foot with gout tofu | |
|---|---|
Treatment tactics:
- After conservative treatment and stabilization of the urea level, removal of the tophus is indicated.
- The operation is best performed when the tophus is small, without waiting for it to grow or for purulent complications to appear.
- The operation is localized and individualized depending on the size and location of the tophus.
Big toe: other causes
If the bone of the big toe is swollen, it may be due to more than just a valgus deformity. Diagnoses also mentioned include:
- Gout. It is caused by the accumulation of uric acid salts in the joints and is manifested by severe, sudden pain. The attack can last up to 5 days and is one of the main symptoms to distinguish gout from hallux valgus.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Affects all joints and parts of the legs. Symptoms include calluses on the soles of the feet and claw-like deformities of the toes. Rarely, a bunion typical of hallux valgus occurs.
- Osteoarthritis of the big toe joints, hallux rigidus. Symptoms include pain at the base of the phalanges, swelling of the big toe, subcutaneous protrusions, and tuberosity.
Despite the differences, it is difficult for patients to distinguish valgus from gout and osteoarthritis. A consultation with an experienced orthopedist can be helpful. The doctor will diagnose the problem, examine x-rays, make a diagnosis and suggest treatment.
Prevention: Can bunions be prevented?
Simple preventive measures can reduce the risk of bunions developing into thickened, deformed bunions. Patients are recommended to:
- to eat healthily – avoid obesity, vitamin and mineral deficiencies;
- Wear comfortable shoes and orthopedic insoles so that the joints are always in the correct position;
- Exercise – to strengthen the muscles and ligaments in the legs.
At the first signs or suspicion of an abnormality, you should immediately see your doctor for examination and treatment.
rehabilitation period after the operation

During the first 24 hours, the patient is recommended to remain in the clinic under the supervision of the surgeon. The patient receives a special orthosis, the Baruca shoe, which takes the pressure from the forefoot and toes onto the heel when walking. This shoe must be worn for at least six weeks. In severe cases, crutches may also be used and physical activity may be limited.
After the operation, the following is recommended for 2 weeks:
- Bed rest;
- In addition, a pillow or pad should be placed under the legs to facilitate the drainage of excess fluid;
- If the pain is severe, apply cold compresses for 30 minutes up to four times a day.
To relieve pain, the doctor will prescribe medication individually and calculate the dose for use at home. The swelling will go away on the 3rd to 5th day after the operation. After 14 days, another visit to the surgeon is required to remove the stitches from the skin.
After 6 weeks, the patient is sent for another X-ray examination. Walking without a corrective orthosis with a toe support is allowed if the patient has a positive tendency and there are no contraindications.
In some older patients, swelling may persist for a long period of time due to decreased venous tone in the limbs. In this case, lymphatic drainage therapy and contrast foot baths are recommended.
Contraindications to the operation
Absolute or temporary limitations to foot osteotomy surgery are.
- osteoporosis and reduced bone regeneration;
- worsening of rheumatoid arthritis;
- Obesity grade 3 – 4;
- Acute stage of infectious diseases.
Minimally invasive procedures are permitted for varicose veins, arthritis and bursitis.
Taylor syndrome results in a painful growth at the base of the little finger, swelling, blistering. New surgical treatments can eliminate complications and restore ease of gait.
Read more:- What is the name of the ankle bone?.
- Medial and lateral side.
- foot bone in Latin.
- Growth zones of the foot bones.
- The ball of the foot grows.
- Lower leg and foot bones and their connections.
- Shapar joint.
- foot bone in Latin.
