The human foot consists of the tarsal, metatarsal and toe bones, which are connected by numerous joints. With the help of a system of ligaments and muscles, the foot forms arches, the so-called arches. There are two in total: the main longitudinal arch runs along the inner edge of the foot, the transverse arch is under the toes. Concavities can be straightened out either by a misalignment of the bones or by a defect in the support system. Put simply, when the muscles and ligaments are stretched, they can no longer hold the arch of the foot in place…. The result is flat feet.

- Flat feet: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
- Symptoms of Flat Feet
- ICD-10
- causes
- Causes of flat feet
- pat anatomy
- longitudinal vault
- transverse vault
- Treatment
- forecast
- symptoms
- Treatment
- Showers in exchange for a supinator
- complications and consequences
- Treatments in the Health Energy Clinic
- degrees of severity
- diagnosis
Flat feet: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
A flat foot is a condition in which the arch of the foot becomes flat. As a result, the foot loses almost all of its cushioning properties. After walking for a long time, the feet become very painful. Women are four times more likely to suffer from this condition than men. In the advanced stage, flat feet lead to arthritis, arthrosis, back and calf pain and curvature of the spine.
The human foot is unique: due to its structure, it is springy. The foot has two arches: the transverse arch, which lies between the balls of the toes, and the longitudinal arch, which runs along the inner edge of the foot. The arch of the foot is supported by a system of ligaments and muscles. No animal, not even a kangaroo, has a springy foot.
A healthy foot helps people keep their balance and reduces tremors when walking. When the foot's musculoskeletal mechanism is weakened, the foot becomes flat and unable to support the load. This leads to the development of flat feet.
Symptoms of Flat Feet
The disease develops gradually and is often not noticed by those affected. First, the affected person feels a slight pain in the legs and feet. Feet tire more quickly after walking or standing work. At the end of the day, feet swell and feel heavy. Symptoms subside after rest or massage.
With flat feet, shoes wear out faster, especially on the inside. The foot gets longer or wider and you have to buy bigger shoes. Women find it difficult to walk in high heels.
ICD-10
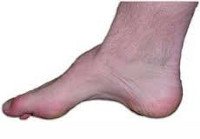
Beggar's foot is an enlargement of the arch of the foot. It can occur in various diseases of the nervous system and the musculoskeletal system. It can occur after severe trauma to the foot (contusions, severe fractures of the tarsal bones), especially in childhood. Sometimes inherited. Is associated with rapid fatigue and pain when walking. Causes blisters and deformities on toes. In some cases there is no functional impairment.
The reason for treatment is usually the severe pain in the feet and the inability to wear appropriate footwear. Conservative treatment is carried out for mild or moderately pronounced pes cavus. If the deformity progresses, surgery is indicated. Orthopaedists/traumatologists are involved in the treatment. If the pathology is caused by a disease of the nervous system, neurologists simultaneously treat the underlying disease.

causes
The exact mechanism for the development of pes cavus has not yet been clarified. It is believed that the pathology is most commonly due to muscular imbalance resulting from hypertonicity or paretic weakness of certain muscle groups of the lower leg and foot. However, experts note that when examining patients with pes cavus in some cases, it is not possible to detect a clear increase or decrease in muscle tone.
Cavus foot can occur with a number of diseases and neuromuscular abnormalities, including. Poliomyelitis, muscular dystrophy, spinal dysraphism (incomplete closure of the medial spinal cord suture), Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (hereditary sensorimotor neuropathy), polyneuropathy, syringomyelia, cerebral palsy, Friedreich's ataxia (hereditary ataxia caused by damage to the spinal cord and cerebellum), Meningitis, encephalitis, malignant and benign spinal cord tumors. In rare cases, the pathology is caused by burns on the foot or improperly healed fractures of the heel and calcaneus. In about 20% of the cases, the factors causing the deformity remain unknown.
Causes of flat feet
Arch thickening can be congenital or acquired. Congenital flatfoot accounts for 3 % of all cases. The most common form of acquired static flatfoot (80 % of all cases) is caused by weakness in the bones, muscles, and ligaments of the foot and lower leg. There is a hereditary predisposition to the pathology due to hereditary ligament weakness.
The risk of static flat foot increases with obesity, physical inactivity in sedentary jobs, 'standing work' (salespeople, hairdressers, assembly line workers, weavers, etc.), uncomfortable footwear and with age. Static flat feet can also develop from constant wearing of high-heeled shoes (due to the excessive stress placed on the forefoot). Other causes of acquired pathology include:
- traumatic injuries. Ligament weakness and changes in the anatomical relationships between the different parts of the foot occur after fractures of the heel bone, ankle, and tarsal bones.
- poliomyelitis. Poliomyelitis causes paralysis of the muscles of the foot and lower leg, leading to a redistribution of the load during walking, weakening of the ligaments and disruption of the relationships between the structures of the foot.
- rickets. The bones of the foot are weakened and can no longer bear the normal physiological loads. Today, rachitic flatfoot is rare.
pat anatomy
The foot supports the weight of the body, prevents falls while walking, and serves as a shock absorber and lifting mechanism. Central to all of these functions are the arches of the foot, which are both rigid and flexible and are made up of the bones of the foot, its ligaments and muscles. There are two arches in the foot: the transverse arch (the arch between the 1st and 5th metacarpal bones, which becomes visible when you hold the foot with your hand on the sides and push across) and the longitudinal arch (the arch at the inner edge of the foot) . The function of the arch of the foot is to maintain balance and protect the body from impact when walking.
When the musculoskeletal structures of the foot are weakened, the muscles and ligaments cannot withstand a heavy load, the foot becomes flat and 'sits'. At the same time, the cushioning function of the foot decreases. The impacts that occur when walking are transmitted to the higher parts of the body (spine and joints of the lower limbs), where, as a result of constant overload, degenerative changes (arthrosis, poor posture, osteochondrosis) develop.
longitudinal vault
The most well-known foot arch is the longitudinal arch. It can be easily seen and felt by running your hand along the inner edge of the sole. In this way, an arcuate indentation can be seen. This is where the cushioning takes place – the foot springs back under pressure. When this arch is flattened, all of the impact inertia is transferred through the foot to the joints and spine.
The longitudinal arch starts at the heel bone and runs through the foot to the toes. Its height is greater on the inside than on the outside. Depending on the number of metatarsal bones, experts distinguish five such arches. They extend from the heel bone to the toe joints. Their arched shape ensures flexibility when walking and absorbs shocks. The highest arch is that of the second metatarsal, the lowest that of the fifth. This area forms the outer edge of the foot and is the base of the foot when walking.
With normal development, the height of the arch of the foot should not be less than 35 mm at the inner edge. The angle of the arch of the foot can also be determined using an X-ray. It is formed by lines drawn from the calcaneus tuberosity and the joint of the first toe to the inferior edge of the wedge joint of the calcaneus. Normally this angle should not be greater than 130 degrees.

The transverse arch is located at the base of the toes and distributes the weight of the foot forward.
transverse vault
The transverse arch of the foot is hardly visible from the outside, but it has an important function. It is located in the forefoot at the base of the toes. The transverse arch is perpendicular to the longitudinal arch and is formed by the heads of the metatarsal bones. It distributes loads evenly and allows the foot to push off the ground when running and jumping. The foot rests on only two points: the heads of the 1st and 5th metatarsal bones. All others form a vault and act like a spring.
However, sometimes when the metatarsal bones are overstressed or the ligaments that hold the metatarsal bones in the correct position are weakened, the transverse arch becomes flattened. In this case, with each step, not only the 1st and 5th toes touch the surface, but all the others. The focus is shifted forward. As a result, the cushioning function is impaired and the forefoot no longer has the same elastic effect.
Treatment
The basis of treatment is a combination of conservative or surgical treatment aimed at eliminating the cause and suppressing the severity of unpleasant symptoms.
In the event of an acute exacerbation of osteoarthritis or the development of an acute process, the first principle is to limit the load on the foot during the acute phase and to avoid permanent trauma to the foot.
In addition, rehabilitation measures are required to restore foot function (normalization of gait and improvement of mobility). If necessary, surgical treatment may be recommended if conservative treatment has not brought the desired result.
Crutches may be prescribed to relieve the affected leg if the condition is unilateral, and immobilization with a cast or elastic bandages is also indicated. A special diet is only required if gout or metabolic disorders are diagnosed. Other patients need more protein and fresh fruits and vegetables, bone broth, fish dishes, a restriction of fatty and spicy foods and fried foods in the diet.
Non-steroidal drugs (NSAID group), which have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, are primarily used to relieve pain. They are prescribed by the doctor, and the method of administration depends on the severity of the pain. Depending on the severity of the pain and inflammation, injections or oral forms may be prescribed. It is not uncommon to combine injections with a switch to oral forms.
For those who don't like pills or want to get the fastest effect possible, Dialrapid sachets for preparing an oral solution come in handy. The drug is based on diclofenac potassium and helps to quickly and reliably stop pain.
In some situations it may be advisable to inject glucocorticoids into the joints. When the acute symptoms subside, the doctor prescribes chondroprotectors, physiotherapy, physical therapy, foot massage.
In addition, the footwear must be chosen very carefully. They must be of the right size, with a low heel and firm sole. In addition, patients are advised to wear pads and supinators.
forecast
Without treatment and elimination of the underlying causes that lead to damage to the ankles, the pathology can progress. The joint deforms and its mobility is restricted. With proper monitoring and following all medical advice, foot deformity can be significantly slowed down and pain eliminated, improving the quality of life.
Without proper treatment and following all doctor's recommendations, the damage to the joint will progress, which can lead to disability and the inability to move independently due to severe pain and changes in the foot. Deformities in the toe and metatarsal joints can lead to changes that cause spinal problems.
symptoms
- plantar fasciitis;
- plantar fasciitis;
- Achilles tendinitis;
- keratosis;
- varus heel;
- pain when walking.
Many patients with a severely arched foot take their time with treatment and ignore the symptoms. In order to avoid progression of the pathology to the second stage, when surgery is required, it is important to consult an orthopedist at the first worrying symptoms. The doctor will take your medical history into account and recommend special tests, e.g. B.
- X-rays. To confirm the presence of a high arch and determine the degree of deformity.
- plantography. Refers to examining the footprint and assessing changes that have occurred in the foot.
In the case of old foot injuries and problems with the neuromuscular apparatus, an MRI or CT scan is also performed. If the cause of the pes cavus cannot be found, an oncological examination is required to rule out a malignant tumor in the spinal column.
Treatment
If the patient consults a doctor when the first symptoms of cavus foot appear, the treatment will be conservative. The specialist prescribes a massage for the patient, teaches him effective gymnastics and selects suitable footwear or insoles for the high arch of the foot. The latter are primarily aimed at reducing the load on the toes and heels when walking.
The earlier the therapy is started, the greater the chance of success. If the patient is helped in the first stage of the disease, there is a 98%ige chance of a complete cure.
The doctor decides whether an operation is necessary for a high arch of the foot. In most cases, surgery is performed when conservative methods have failed or the disease is advanced. An operation of the pes cavus is possible, e.g. B:
During the rehabilitation period, the patient is recommended to take antibiotics and painkillers. In addition, to avoid complications, it is necessary to wear special footwear, which will be selected by the doctor.
Showers in exchange for a supinator
The official inventor of the supinator is Salvatore Ferragamo (1898-1960), an Italian who by 1924 had become the favorite cobbler of Hollywood stars and who invented more than three hundred models, including the heeled shoe and the sandal. He was the subject of legends. It was said that God himself gifted Salvatore with his talent. Some believed he sold his soul to the devil for the secret of the comfortable shoes. In reality, however, things were much simpler. Master Salvatore studied anatomy at the University of Southern California and received his degree in chemical engineering from the University of Pennsylvania. After understanding the structure of the human foot and the resilience of materials, Ferragamo realized that shoes would be much more comfortable if a small cushion was placed under the arch of the foot. Thus the first padded shoe was born. Since then, many shoe manufacturers have actively incorporated this innovation into their products.
In addition to the supinators, there are other ways to make life easier for people with flat feet. In the most severe and advanced cases, only a surgeon's scalpel will help, but if the disease has not progressed too far, special massage and exercises for the feet will help. However, don't get your hopes up too high. Flat feet cannot be completely cured, only the process can be stopped and its dangerous effects on the body, especially the spine and brain, reduced.
As a side note, conscripts with Grade I and II flat feet are not discharged from the army, but those with Grade III and IV flat feet are not called up in peacetime.
complications and consequences
Flat feet only appear to be a harmless ailment at first glance. The abnormal distribution of loads on the feet and joints and the lack of adequate cushioning inevitably affects not only the musculoskeletal system, but the entire body.
Without treatment, humans develop:
- compulsive clubfoot;
- valgus deformity of the foot;
- arthritis and arthrosis of the foot, knee and hip joints;
- Herniated and bulging discs, lower back pain, neck pain;
- Headache;
- varicose veins of the lower limbs;
- heel spur.
Treatments in the Health Energy Clinic
Health Energy Clinic orthopedic traumatologists are ready to help with all forms of flat feet. Patients are offered:
- Advice on choosing shoes, orthoses and lifestyle correction;
- Sports courses under the guidance of a trainer and learning basic exercises for training at home;
- selection of painkillers;
- Physiotherapy treatments to reduce stress;
- Therapeutic massage courses.
Regular check-ups with our specialists will help you reduce the pain and severity of your feet and reduce the risk of complications.
degrees of severity
- First degree – discomfort and pain in the feet appear in the evening or after sports. The gait changes and the ligaments weaken, but the external changes are hardly noticeable.
- Second stage - the feet widen or lengthen and the sufferer feels increasing pain even without exertion. The pain is localized from the foot to the knee joint. Clubfoot develops gradually and leads to impaired gait.
- In the third stage, there is impairment of the musculoskeletal system and permanent foot deformity. The pain is severe and persistent, making it impossible not only to play sports, but also to stand or walk on your feet for a long time.
- Pain in the feet when walking, standing or running for a long time. Over time, it can cause pain in the lower legs and lower back. In some patients, flat feet cause back pain and headaches.
- Pain, stiffness, heaviness and swelling in the feet and lower legs in the evening.
- Shoes slip quickly. This is especially noticeable when the patient walks in high heels.
- Women begin to feel severe pain when wearing high heels.
- The foot appears to be enlarging. Previously worn shoes may be too small.
- Rapid fatigue of the leg muscles.
- The outside of the foot clearly shows lateral growth of the foot.
- The big toe tips outward and a bony 'lump' grows.
- Corns form on the skin of the sole of the foot at the base of the toes, similar to calluses.
- There is a deformation of the toes that resembles a hammer toe.
diagnosis
- Plantography is the simplest method of diagnosing flat feet. The doctor takes a paper impression of the patient's sole and then assesses it.
- Podometry is the measurement of foot parameters and the calculation of indices. These are used to assess the degree of arch depression.
- Podography is an examination that uses special footwear and a treadmill. The foot is examined in motion.
- X-ray. Photos of the foot are taken in lateral projection to determine the condition.
Based on the results, the doctor determines the flatness of the foot and assesses its degree. The multidisciplinary CELT Clinic has the most modern equipment to achieve the most accurate results.
Read more:- The longitudinal arch of the foot is.
- Longitudinal and transverse arches of the foot.
- Which ligaments strengthen the transverse arch of the foot?.
- Determining the number of longitudinal arches in the human foot.
- Structure of the human foot.
- flat feet (valgus foot).
- The foot takes on an arched shape.
- Which doctor treats flat feet?.
