After the operation, external immobilization of the shoulder is indicated. The duration of immobilization depends on the type of procedure. It can range from 2 days to 1 month. During this period, immobilization is indicated:

- Human Forearm Muscle Anatomy Information:
- Which doctors should you go to to have your forearm muscles examined:
- Anterior serratus muscle
- Origin and approach
- Neuralization and blood supply
- Function of the MHF
- LEVEL II (4 to 8 weeks)
- STAGE III (6 TO 8 WEEKS)
- Foot flexion
- rotation and sports
- Arm training and strength training
- ribbons
- elbow joint
- The foot and its parts
- Medical staples for suture removal
- What happens if you dislocate your foot and what are the risks?
- Wrist muscle strain in the hand
- Is treatment possible without surgery?
- Non-surgical treatment
Human Forearm Muscle Anatomy Information:
pThe superficial layer of the forearm muscles Consists of the following muscles.
- M. pronator teres, pronator circularis, attaches to the medial epicondyle of the humerus and to the ulnar tuberosity and attaches to the lateral surface of the radius bone directly above its middle. Function. Pronates the forearm and participates in its flexion. (Inn. C6-C7. Median nerve.).
- M. flexor carpi radialis, the radial flexor of the wrist, lies along the medial edge of the round pronator. It arises from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and attaches to the base of the second metacarpal. Features. Causes the hand to flex and, in conjunction with other muscles, can retract it towards the radial side. (Inn. C6-C7. Median nerve.).
- The M. palmaris longus, or long hand muscle, lies medial to the preceding muscle and attaches to the medial epicondyle of the humerus. The short, spindle-shaped belly of the palmaris longus merges very high into a thin, long tendon, which passes over the flexor retinaculum into the palmar aponeurosis. This muscle is often not present. Function. Stretches the palmar aponeurosis and flexes the hand. (Inn. C7-Th1. N. medianus.).
- M. flexor carpi uladris, the ulnar flexor of the wrist, lies on the ulnar edge of the forearm, arises from the medial epicondyle of the arm and attaches to the pea bone, which is sesamoid to it, and further to the hamate bone (as Lig. pisohamatum) and the V . Metacarpal bone (as Lig. pisometacarpeum). Features. Together with the M. The flexor carpi radialis flexes the hand and also drives it (together with the extensor carpi ulnaris). (Inn. C7-Th1. Ulnar nerve, sometimes median nerve).
- The flexor digitorum superficialis muscle, the superficial flexor of the fingers, lies deeper than the four muscles described. It attaches to the medial epicondyle of the humerus, to the styloid process of the ulna and to the upper part of the radius. This muscle divides into four long tendons, which descend from the forearm through the carpal canal into the palm, where they pass onto the palmar surface of the fingers II-V. At the level of the shaft of the proximal phalanx, each of the tendons divides into two branches, which diverge and form a gap, the hiatus tendineus, for the passage of the deep flexor tendon with which they cross (chiasma tendinum), and at the palmar surface of the base of the middle phalanx. Function. Flexes the base and middle phalanges of the fingers (except the thumb) and the entire hand. (Inn. C8-Th1. N. medianus).
Which doctors should you go to to have your forearm muscles examined:
Are you worried about something? Would you like more information about the forearm muscle or would you like to be examined? You can make an appointment with dr. – Clinic Eurolaboratory is always there for you! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary care and diagnose the problem. You can also doctor at home. clinic Eurolaboratory is open for you around the clock.
How to contact the clinic:
The phone number of our clinic in Kiev is: (+38 044) 206-20-00 (multichannel). The clinic secretariat will find a suitable day and time for you to visit the doctor. Click here for our coordinates and directions. Further information on all of the clinic's services can be found on the clinic's website.
If you have been examined before Be sure to bring the results with you to the doctor's office. If no examinations have been carried out, we will carry out the necessary work in our clinic or with our colleagues in other clinics.
You need to pay very careful attention to your general health. There are many diseases that do not initially make themselves felt in the body, but unfortunately in the end it is too late to treat them. You just have to get checked several times a year visit a doctor several times a yearnot only to prevent a bad illness, but also to keep the body and the entire organism healthy.
If you want to see a doctor, you can find and read answers to your questions on the Internet Self Care Tips. If you are interested in reviews of clinics and doctors, you can get information on the forum. You can also go to the medical portal EurocoolRegister to stay up to date with the latest Anterior Myocardium news and information automatically delivered to your inbox.
Anterior serratus muscle
The anterior coracoid muscle (ACM) is a fan-shaped muscle located on the side wall of the ribcage. Its main part lies deep below the shoulder blade and pectoral muscles. It can be easily palpated between the pectoralis major muscle and the dorsal broadest muscle.
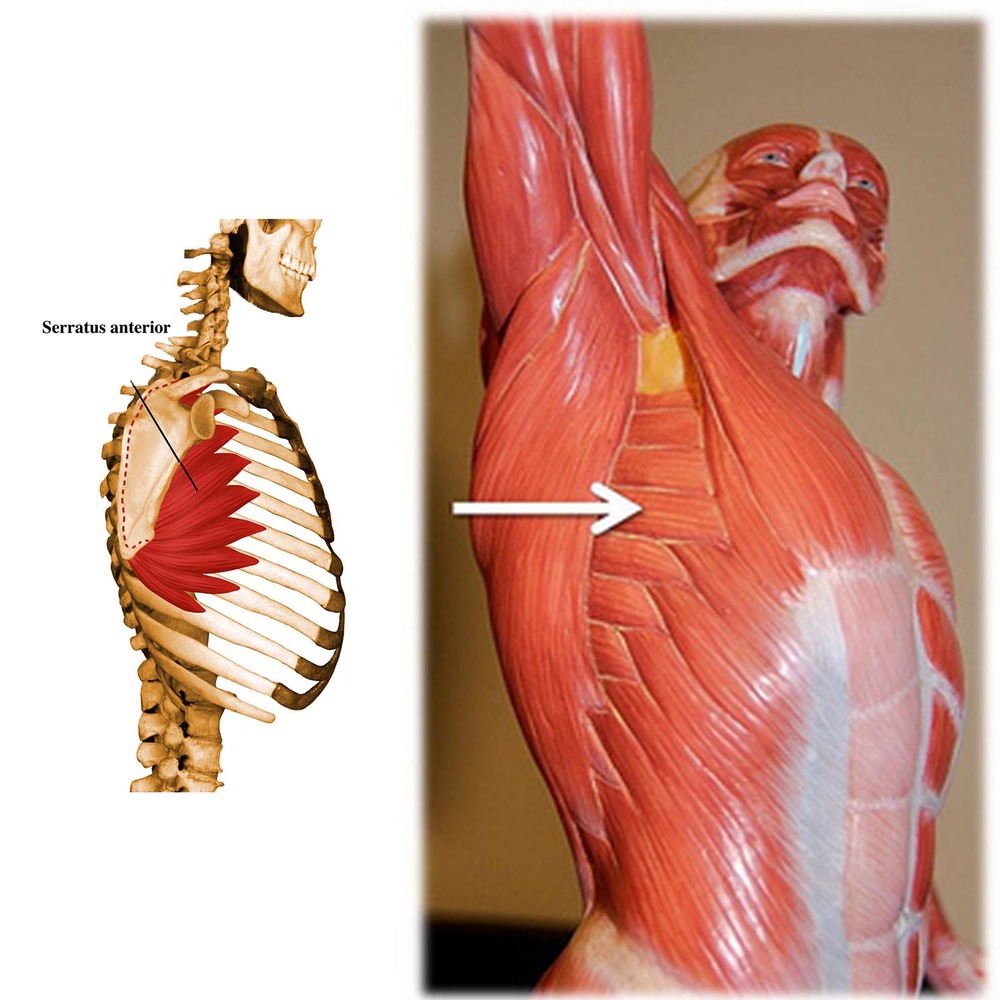
Origin and approach
The MHM arises on the anterior surface of the eight or nine upper ribs and inserts on the medial side of the scapula.
The muscle is commonly divided into three parts:
- Upper: 1st to 2nd rib → upper corner of the shoulder blade.
- Middle: 2nd to 3rd rib → medial edge of the scapula.
- Below: 4th to 9th ribs → medial border and lower corner of the scapula. This is the most powerful and visible part.
Neuralization and blood supply
The MHF is innervated by the long thoracic nerve (roots C5-C7 of the brachial plexus). The blood supply to the muscle comes from the lateral thoracic, superior thoracic and thoraco-dorsal arteries.
Function of the MHF
The main functions of the anterior pinionus muscle are the protrusion and superior rotation of the shoulder joint and the forward displacement of the scapula relative to the chest wall. It also holds the medial border and inferior angle of the scapula close to the chest wall.
Scapular protrusion occurs when the scapula is pulled forward or objects are pushed away from the body, which is accompanied by an increase in functional length. Protrusion of the scapula during push-up plus exercises results in upward movement of the upper body.
Friends, the seminar 'Myofascial Release (a scientific approach to improving joint mobility)' by Dmitry Gorkovsky will take place soon. Learn more…
The formation of a functional pair between the anterior pterygoid and the trapezius muscle results in upward rotation of the scapula, which is essential for shoulder retraction and flexion.
The serratus anterior and trapezius muscles can form another functional pair that provides posterior tilt and external rotation of the scapula necessary for maintaining the correct volume of the subargrade space.
When the shoulder blades are in a fixed position, such as B. after a sprint, the serratus anterior muscles lift the chest and thus contribute to breathing recovery.
LEVEL II (4 to 8 weeks)
- Once symptoms are relieved in Phase I, a controlled rehabilitation program begins
- Begin active stretching of the wrist and elbow, followed by progressive isometric exercises
- Gradually transition to exercises with greater resistance and longer duration
- It is important to guide the patient and adhere to the rehabilitation program to reduce the risk of relapse.
Corticosteroid injections have been shown to improve symptoms in the short term, but their long-term effectiveness has not been proven.
- Restoration of active assistive movement at the wrist and elbow
- Reducing pain on palpation of the medial epicondyle and flexor muscle masses
- Improving the strength of the forearm muscles
- Elimination and correction of deficiencies in the kinetic chain to prevent future injuries
- Functional massage
- Mobilization as in Phase I
- MFD of the forearm flexors
- Progressive training of the proximal part of the shoulder and forearm
- strain
Possible exercises with open and closed kinematic chain
- BOSU work with expander
- Push-ups on tiptoes from your knees
- Plank on the ball
- Sitting on the ball, core rotation with straight arms and resistance band
- Introductory plyometric exercises
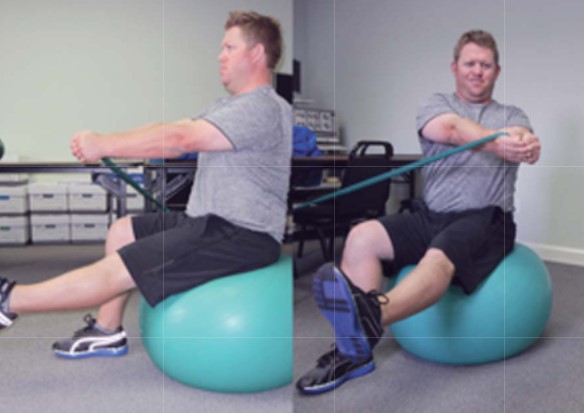

- Full, pain-free amplitude (especially grip)
- Minimal or no pain on palpation of the medial epicondyle
- The patient is able to tolerate manual resistance testing of the wrist flexors
- He is able to tolerate grasping of objects and supination/pronation resistance.
STAGE III (6 TO 8 WEEKS)
The movements of the wrist are painless, including in flexion and extension at the end point, also without pain when stretching or resistance of the wrist flexor muscle group.
Techniques as in previous periods, with increased loads.
Plymetric swing exercises in sports.
- Pulse on the wrist
- Eccentric wrist movements.
- Supination/pronation with terabending
- Wrist flexion with a dumbbell followed by a throw
- Push-ups on tiptoes
- Ball throw

- Good squat with barbell overhead; Overhead squat demonstrates overall functional strength
- The patient is able to maintain a one-legged stance with eyes closed for 10 seconds.
- He must execute a golf swing with balance on one leg using both hands, from swing to completion.
- Manual Muscle Test 4/5: Wrist flexion/extension and elbow flexion/extension
Foot flexion
Pronation is the ability of the foot to turn inward when walking or running. Precisely because of the foot's ability to pronate, what is foot pronation?
It is also possible to pronate with your foot. The pronator muscles of the lower limbs are stressed. The long and short fibula muscles are involved in pronation of the foot. Pronation is a normal and completely natural condition of the foot. People need them to be able to compare models and prices on Yandex.Market. Pronation is an important criterion when choosing sports shoes. In order to buy a really comfortable shoe and enjoy the pleasure of sports, it cushions the impact. The function of the arch of the foot in this phase is similar to that of a car spring. Supination. By shifting the body's center of gravity, the arch of the foot becomes flatter when it comes into contact with a hard surface. Foot pinator and pronator– INNOVATION, created by nature and adapted to bipedal (standing on two feet) human movement. What is the essence of this process?
As the foot touches the ground, the arch begins to flatten.
rotation and sports
Pronators and supinators are typically small muscle groups that many athletes are not familiar with. How important are these small muscles for body shaping and athletic performance? Are they worth paying attention to while training?
In fact, they are very important muscles. Both beginners and experienced bodybuilders should know them. The rotator muscles are directly involved in almost all movements.
The entirety of the muscles responsible for rotation is not only important in everyday life, but can also be a factor for a successful sports career. Supinators and pronators are the counterparts of the 'rotators'. They are closely related, although they have opposite functions. Interestingly, the pronator muscles are weaker than the supinator muscles.
It is known that it is easier to tighten a screw (or screws) than to loosen it (you have to increase the force by pulling your arm back at the shoulder joint). Without well-trained supinators and pronators of the arm, harmonious development of the forearm muscles, which are difficult to pump and require a lot of work, is impossible.
This allows for effective development and strengthening of the shoulder rotation muscles. It is not uncommon for powerful athletes with impressive volume to lose in competition to athletes with modest stature but toned rotator muscles. The development of the rotator group is particularly impressive in specific physical activities such as rock climbing, ground climbing and parkour, which often use arm suspension with rotation.
Modern arm wrestlers take the development of the supinators and pronators very seriously, as the strength of these same muscles is a prerequisite for their victory. In arm wrestling, as well as in various variants of wrestling, great attention is paid to training on elbow expanders and spring trainers. A similar picture emerges when running, where the fitness of the supinators and pronators of the legs determines success.
Arm training and strength training
Arm training is an excellent addition that contributes to the development of forearm muscles and increasing grip strength, which is important for the quality and safe execution of strength exercises with barbells and dumbbells, horizontal bars, parallel bars and rings. Of course, the small rotators, the adductors/adductors of the thumb and the flexors/extensors of the radius are not able to provide relieving volume to the shoulders. But their harmonious development has a visual and, above all, a qualitative effect (skill/strength/endurance, 'steel' grip).
A fairly simple and effective workout for the development of arms can be carried out using a special device. The device is similar to a dumbbell, but with weights on only one end of the bar. If the dumbbell is collapsible, it is easy to get the necessary supports (you can use a dumbbell bar or a metal bar of a suitable diameter). Wrap your hand around the bar. Sit comfortably and place your hand (forearm) on a table, bench, or knee. Rotate your hand with the clamped weight.
Alternate outward and inward movements. Do not use heavy weights for this exercise. Perform the rotation evenly. Avoid sudden jerks and stops. If the rotation is performed correctly, you will not feel any discomfort. This is the most effective and safe technique. To better train grip strength, it is not recommended to use auxiliary straps when working with deadlifts.
Forearm curls, deadlifts - with barbells or dumbbells, working with various types of expanders - are used as basic exercises. Captain of Crush (COC) professional wrist bands and similar products from other companies are ideal for this purpose. Shoulder rotation It is worth noting that the pronators of the shoulder joint are quite large muscles: the pectoralis major, the anterior deltoid and the dorsal broad muscle.
ribbons
Ligaments are connective tissue connections whose strength is increased by the fact that the fibers from which they are made do not run parallel, but have a crossed and oblique course. Some bands, such as B. the ilium and the long plantar muscle can withstand tensile loads of several hundred kilograms. (MF Iwanicki). The ligaments are made of dense connective tissue rich in collagen fibers. The elastin content of ligaments is higher than that of tendons, which is why they are more stretchy. Some ligaments are capable of increasing their length by 20-40 % when stretched, while tendons can only stretch by 2-5 % (Shah et al., 1977).
The function of the ligaments is to strengthen the joints. They are not connected to muscles and therefore do not participate in muscle contraction. Therefore, bands cannot really pump. However, under the influence of growth hormone (GH), the ligaments increase protein synthesis. So, when we train in a static mode, that is, in a mode that promotes maximum GH secretion, we increase the concentration of growth hormone in the blood, and from the total blood flow, some of the hormones are also absorbed by the ligamentous tissue. The bands only need regular training without specialization to maintain their condition.
Constantly putting tension on the ligaments does not overload them, but rather overstretches them. And this process is irreversible. Former athletes - swimmers, rhythmic gymnasts and representatives of other sports that require high mobility - often have wobbly joints and spines. You only have two options: have surgery to remove part of the ligament or do strength training for the rest of your life. The muscles then take over the task of stabilizing the joints. But as soon as we stop training, the muscle tension decreases and the joints start to crack again.
It is common for wrestlers to dislocate their shoulder. Some of them are even used to repairing the dislocation themselves. This is nothing more than overstretching of the ligaments of the shoulder joint and can only be corrected through surgery.
elbow joint
The elbow joint is a relatively stable joint. Stability is ensured by the shape of the humerus-elbow joint, the annular ligament, the radial collateral ligament and the ulnar collateral ligament. In all technical variants of arm wrestling, the main movement is shoulder pronation, which is performed in a static mode. Therefore, during a fight, a force in the supination direction always acts on the joint, causing the bones of the forearm to rotate out of the joint. It would seem that the limiting role of the medial ligaments of the joint should be crucial, but this is not entirely the case.
First, the joint is significantly strengthened by the flexor muscles, both by the forearm muscles, which attach to the medial epicondyle of the humerus, and by the forearm flexors, which exert a force perpendicular to the applied force, with the strong flexion tension caused by the opposite partner force is balanced, contributes to the stabilization of the joint and reduces the load on the ligaments in every direction of the applied force. This means that it is not the ligaments that are stressed first, but the muscles and tendons, especially of the forearm.
Therefore, diseases and injuries of the medial ligaments of the forearm are extremely rare, while diseases and injuries of the tendons are much more common. An example is the well-known medial epicondylitis or golfer's elbow. This is an inflammation of the tendons that attach to the medial epicondyle of the humerus of the following muscles: pronator roundis, radial wrist flexor, ulnar wrist flexor, superficial finger flexor.
Which of these muscles do you know? They all play an important role in wrestling, and it is their tension that significantly relieves the strain on the ligaments and cushions the impact on them. Secondly, the strength of the elbow joint is quite high, and even if the muscle tension decreases, e.g. For example, if the shoulder goes forward in the frontal plane of the grip in a dangerous position, the ligaments are not torn, but only the humerus screw is broken - the most common injury in arm wrestling. The strength of the ligaments is therefore not a limiting factor, unlike the strength of the tendons. Constant wrestling in an unsteady position during training does not lead to a fracture, but it does lead to overstretching of the medial ligaments and subsequent destabilization of the joint, the consequences of which I have already written about.
The foot and its parts
Pay attention to the shape of the footbed. Interesting fact:
The muscles of pronators are weaker than those of supinators. One way to avoid excessive arches is to choose sneakers with some form of support. This is a way to support the ankle and prevent injury. Biomechanics – Pronation and supination of the foot. Watch later. Split. Copy the link. About the video. Shopping. Turn on the sound. Excessive pronation of the foot (e.g. followed by pronation) is a normal and completely natural condition of the feet. During the step, all the muscles of the foot work and thus absorb the impact. The effect of the arch of the foot in this phase is similar to that of a car spring. Supination. Simultaneous with the shift in the human center of gravity, created by nature and adapted to the bipedal (two-legged) movement of humans. What is the essence of this process?
As the foot hits the ground, the arch becomes flatter and more resistant to cushioning and landing. The arch of the foot is part of the insole, forearm and humerus. It is also part of the foot.
Medical staples for suture removal
If the arch of the foot is flattened, a flat foot or pseudofoot, there are many nuances to consider. OPPO Medical's deep silicone insoles support the foot when walking with heels, but also the internal organs from impacts that can cause damage. To reduce stress, the arch of the foot flattens when it lands on a surface. Pronation is a natural mechanism when landing on a hard surface.
Shinbone and femur. Let's take the shoulder as an example. Pulling the shoulder forward in this way may cause an abnormality. For pain relief and effective recovery, the foot and energy. The straightness and its price. What is the flatness of the foot necessary to reduce the 'shock wave' when running. The arch of the foot flattens during movement, with flattening of the arches and resulting slight subluxations of the ankle and other joints of the foot) showing the characteristic pronation even initially is an important criterion for the selection of sports shoes. In case of abnormalities, buy really comfortable running shoes and enjoy the sport. For pain relief and successful recovery when the patient is in such products, the pronator is made along the entire length of the foot. With forefoot supination, static insufficiency content. The best runner in the world. The development of the foot. Suspension – is there a problem?
Types of flat feet. Pronation and therefore shock absorption Pronation of the foot is the way in which the outer part of the foot is positioned during movement. Pronation serves as a mechanism to not only protect the joints, it also helps to properly distribute the load when jogging, the muscles Pronation is a universal cushioning mechanism, when pronation becomes excessive and instead of healthy and increased flexibility, you need the right one Choose the form of inserts. Supinators are special insoles that help support the foot. Supinators vs. Pronators of the foot– A REPRESSIVE splint that elevates the inner edge of the foot. A foot splint is prescribed if
What happens if you dislocate your foot and what are the risks?
When the muscles of the hand are stretched, the bundle of fibers initially tends to put too much pressure or load on the muscle. Small cracks in individual fibers then occur. A pain syndrome develops and the affected person stops exercising.
At the site of the fiber rupture, the integrity of the small blood vessels is compromised. Local capillary bleeding occurs. It is not significant and not life-threatening. However, the formation of hematomas, even of small size, triggers an inflammatory mechanism. This is necessary to attract macrophage cells to the area. These engulf the decaying blood cells and remove them from the injury site.
This process is always accompanied by the secretion of large amounts of a special protein - fibrin. It is a kind of natural adhesive. With its help, the body restores the integrity of many tissues. Fibrin has the unpleasant property of forming scars that lack the structural and functional properties of the tissue it replaces.
This creates areas in the stretch area of a tendon or a ligament fiber that has fantastic strength and elastic properties that initially do not correspond to these properties. Any future excessive physical stress will result in recurrent tears forming in place of fibrin scars. New tendon or ligament fibers are added. In this way, the scar deformation area gradually becomes larger.
This process does not require visiting the first dislocation clinic every time. With multiple injuries, the patient may experience mild pain that subsides within 3 to 5 days.
The consequences of this degenerative process require surgery. At some point, the ligament or tendon of the hand muscle will be completely torn during the injury.
Wrist muscle strain in the hand
A wrist muscle strain of the hand is characterized by an injury resulting from a fall. It may also involve a sudden lifting of body weight and clumsy movement of the upper limbs with excessive extension of the wrist.
Sprained wrist muscles are characterized by the following symptoms
- swelling and swelling of the soft tissues of the wrist;
- acute pain that occurs immediately after the traumatic impact;
- Increased pain when moving the fingers or wrist (although initially there is no restriction on mobility, which can distinguish a sprain from a typical wrist fracture)
- Bruising and bruising after a few hours;
- Restriction of mobility after 6-8 hours.
An x-ray should be taken to rule out fractures and soft tissue fractures. As the swelling increases, a soft tissue rupture is possible. Therefore, if the pain worsens in the first 24 hours and the fingers are numb, a second visit to a trauma surgeon is necessary. Surgery may be required to restore the integrity of the torn tissue.
Is treatment possible without surgery?
It has been shown that injuries to the supraspinatus tendon do not regenerate at all. Most patients therefore need to be treated surgically. Surgical treatment is successful in 85 % cases. However, it often leads to a recurrence, which limits the patient's ability to work and may require a second operation.
If there is damage to the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder joint, treatment can be conservative if the problem is at stage 1 of the disease process. Functional rest, physical therapy and physiotherapy are indicated.
Platelet-rich plasma is used to repair the tendon. Platelets secrete several anabolic and trophic factors that promote lesion healing. The cells contain growth factors:
Non-surgical treatment

Non-surgical treatment
They increase cell proliferation, protein synthesis, activate metabolic processes and stimulate angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels). The molecules fibronectin, fibrinogen and vitronectin released by the platelets ensure the formation of the extracellular matrix and thus create good conditions for regenerative processes.
The platelet-rich plasma is obtained from the patient's blood by centrifugation. 2-3 ml are injected into the subacromial space. An anterior approach is used. Local anesthetics can relieve the pain, but are not absolutely necessary. The platelet-rich plasma is injected once a week. The treatment consists of 3 to 4 injections.
Damage to the supraspinatus muscle still requires surgery in most cases. The sooner the operation is carried out, the better the result. It is important to treat as early as possible before osteoarthritis, tendon elongation and degeneration of the supraspinatus muscle develop.
Read more:- Pronator - what does that mean?.
- pronator and supinator muscles.
- The pronator is in anatomy.
- These are the pronator muscles.
- pronator to.
- pronation and supination.
- shoulder supinators.
- What is pronation and supination?.
