At the first visit, tell the phlebologist about the possible causes of the seizures, indicating their location and duration. The doctor will prescribe these types of diagnostics:

- hyperkeratosis
- symptoms
- causes of the disease
- signs of pathology
- stages
- When the arch of the foot is high
- complications
- Treatment of foot deformities
- diagnostic procedures
- About foot cramps
- causes
- Causes of Boils
- Factors that contribute to the development of boils
- How does a boil develop?
- Change in eye refraction
- Other eye diseases
hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is the general term for a group of diseases whose main symptom is excessive keratinization of the skin. Under the influence of a certain factor, the cells of the outer horny layer of the skin divide faster and the shedding of dead cells slows down. As a result, the skin is covered with a horny layer, the thickness of which varies from fractions of a millimeter to several centimeters. Depending on the cause, keratosis can affect any part of the body.
A distinction is made between hereditary and acquired skin hyperkeratosis. Depending on the clinical manifestation, the pathology can take different forms:
- vesicular – scales from the sloughed epidermis clog the vesicle ducts, causing numerous small pustules to appear on the skin;
- lenticular – keratinized papules appear on the hair follicles of the lower limbs, which, when removed, leave small indentations on the skin;
- diffuse - short, thickened hair-like formations appear on the skin;
- seborrheic – scaly, greasy, easily removed scabs appear on the scalp and sometimes face, with red patches of skin underneath;
- diffuse - affects large areas of skin on any part of the body, sometimes the entire skin, the sebaceous glands stop working and the skin becomes dry and scaly;
- Warts - wart-like lesions appear on the skin but without the papillomavirus, and sometimes develop into tumors;
- The skin of the elderly develops senile, dark, calloused patches.
Diffuse and lenticular forms appear mostly in older men. Women and young people are rarely affected.
symptoms

The main symptom of hyperkeratosis is thickened, discolored skin over a specific area of the body, often with skin of a different color as the background. Initially, the skin appears rough, but later the stratum corneum thickens, sometimes to the point of becoming uncomfortable. In particular, advanced hyperkeratosis on the feet can lead to a changed gait pattern. The keratinized epidermis flakes off or partially detaches, and painful cracks may develop in thicker, drier areas that are slow to heal and become sites of infiltration. The pathology is often accompanied by dry skin and reduced function of the sebaceous glands.
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call +7 (495) 775-73-60
causes of the disease
Doctors believe the condition begins to develop as a result of abnormally healed foot fractures and due to muscle imbalances in the foot and lower leg. Neuromuscular pathologies that can lead to pes cavus include:
- muscular dystrophy;
- CEREBRAL PALSY;
- meningitis and encephalitis;
- Poliomyelitis;
- spinal dysraphism;
- syringomyelia;
- Friedreich's ataxia.
In 20 % of the diagnosed cases of pes cavus, the actual cause of the development cannot be determined.
signs of pathology
Discomfort when walking, easy fatigue and pain in the problematic lower extremity are considered the first symptom. Patients emphasize that they have increasing difficulties in choosing footwear - foot deformity makes it impossible to wear classic shoes, in advanced cases it is even impossible. As the disease progresses, the gait pattern changes and the sensitivity of the foot decreases.
The disease is diagnosed as follows:
- The doctor examines the foot and measures the height of the arch;
- X-rays of the foot and plantography are prescribed (for early treatment if lesions cannot be detected by physical examination);
- an X-ray of the spine and a general MRI scan are performed.
In most cases, an additional examination is carried out by a neurologist. If there is no obvious cause for the development of a pes cavus, the specialists speak of the high probability of a malignant tumor in the spine area - an examination and examination by an oncologist is necessary.
stages
- The first, or mild, stage consists of swelling of the feet in the evening that subsides in the morning. Swelling of the lower limbs can occur after prolonged immobility or excessive physical exertion. If the disease is at an early stage, it can disappear for a long time and only appear again after a few years;
- The second or medium degree of severity – the swelling does not go away even after rest, the skin thickens and becomes taut, pain appears. Pressing the swollen area with your finger leaves a permanent imprint;
- In the third or severe stage, lymphedema is irreversible and fibrocystic changes appear. In later stages, the pathology affects the knee joints and even the articular ligaments. The regional lymph nodes may be enlarged. In particularly severe cases, elephantiasis and lymphosarcoma occur. Sepsis can be fatal.
In the case of 'late' edema, initially only one limb is affected to a small extent. Eventually, over time, the disease spreads to the other limb. In most cases, the swelling of one limb is much more pronounced than the others.
When the arch of the foot is high
Finding the right shoes for tall women is a bit more difficult. The footwear industry focuses on the average fullness of the foot, which means you have to consider the interior features, such as B. insoles, even if you try on a pair one size larger.
If your new shoes feel tight when you try them on, that's bad. Don't expect them to 'wear out' over time and fit as shown, even if they look good overall.
Also, the wider appearance of some plus-size models is not a guarantee of a comfortable fit: each pair should be tried on. And before ordering from a photo in an online store, measure the height of the foot and read the reviews so that what looks beautiful in the photo does not disappoint when trying on.
A good choice for health are models with wide adjustable straps, Velcro, laces (preferably elastic), elastics on the lacing. It is advisable to look for manufacturers who offer not only beautiful models and a wide range of sizes, but also a choice of foot lengths.
complications
If a woman has a large bony prominence at the base of the big toe, deformed joints, pain - this means that there are consequences of long-term, although beautiful, but too tight shoes of poor quality.
If you understand your physiology and measure your size, it will be much easier to make the right choice among the many beautiful shoes. Poor quality shoes bought the wrong size can cause damage to the entire musculoskeletal system.
Finding this out yourself is uncomfortable.
Treatment of foot deformities
Each type of deformity requires individual treatment. For some conditions, conservative treatment may be sufficient, while in other cases, surgery is recommended.
With the congenital form of the disease, correction of the foot begins in the first days of the child's life. The pediatric orthopaedist manually positions the child's foot in the correct anatomical position and then fixes it with a plaster cast. Over time, the cast is replaced with a splint that is worn at bedtime. When the child is 3 years old, physiotherapy and massage are recommended.
Conservative treatment of acquired clubfoot includes the use of special orthoses and orthopedic shoes. Physiotherapy and physiotherapy are used as additional methods. If this treatment is not effective, arthrodesis is performed.
All types of flat feet are treated using conservative methods. Wearing orthoses, correction with plaster casts, therapeutic physical training, massages and apparatus-based physiotherapy are recommended for these patients.
This type of deformity is treated with splints and reduction bands, foot and toe corrections, orthopedic shoes, bandages, special sleeves and heel splints. If conservative treatment is unsuccessful, an ankle fusion is indicated.
The congenital form of the disease can be treated conservatively with plaster casts and immobilization splints. If the deformity is acquired, it can only be corrected surgically.
Physiotherapy, exercises, massage, anti-inflammatory ointments, bandages and splints are used to correct the thickening of the leg. If the condition progresses, the sufferer will be prescribed surgical treatment.
Surgical treatment of valgus deformity can be performed by the following techniques: phalangeal osteotomy; Removal (exostectomy) of the bony neoplasm; Division of the adductor muscle of the affected toe; Metatarsal osteotomy.
diagnostic procedures
This method is the simplest and most meaningful.
An impression of the foot is made using a special device (plantograph) to determine the degree of deformity:
- 1st degree - the indentation covers less than half of the foot;
- Second degree - the indentation covers less than a third of the foot;
- Grade III - no indentation.

About foot cramps
Foot cramps are often accompanied by unpleasant pain sensations, severe discomfort and the inability to move the limbs. This phenomenon is more common in older people, pregnant women and competitive athletes.
The phenomenon is characterized by a strong muscle spasm. The fabric becomes very stiff and feels dense. The cramp can affect the entire limb, the foot, or the muscles of the thigh. Most often, however, the cramps occur in the calf muscles. If this symptom occurs regularly, is accompanied by pain and affects the quality of life, it is important to consult a doctor to find out the cause of leg cramps and conduct timely treatment.
causes
Leg cramps can be caused by overactivity of the cerebral cortex. They can also occur when nerve fiber conduction is disturbed or when the level of ATP in the blood drops. These processes develop after intense physical activity, after traumatic brain injury, under stress or when wearing uncomfortable shoes. The causes of cramps can be different. The most common cause is varicose veins. A phlebologist can determine the trigger for this symptom after an initial diagnosis.

The most common causes of leg cramps during the day or at night include
- mineral and vitamin deficiencies. They can occur when the body is dehydrated, after intense physical activity, or when there is a lack of nutrients. This symptom can be caused by a lack of B vitamins or magnesium.
- Diabetes can cause hypoglycemia.. This is caused by the administration of insulin. It can only be treated by a specialist who will develop a treatment regimen and choose the optimal dose of insulin for each patient.
- Excessive physical activity.. Often occurs in people who play sports. Footballers, basketball players and weightlifters are at risk.
- Spasms can occur with thrombophlebitis, varicose veins, regardless of the stage of these diseases..
- Atherosclerotic diseases are associated with a high burden on the entire cardiovascular system. The heart and blood vessels are particularly affected. It is caused by hereditary predisposition, unhealthy lifestyle habits, unhealthy diet and high cholesterol levels.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels have a negative impact on blood flow. This is accompanied by swelling, pain and leg cramps at night and during the day.
- Hormonal changes can trigger leg cramps in women during labour. This problem can occur against the background of taking oral contraceptives, during menopause, during puberty, with drastic changes in the hormonal balance.
- With increased stress on the central nervous system, frequent severe stress, sleep disorders, muscle cramps can also be triggered.. This symptom spontaneously disappears when the stress can be managed and the regime restored.
Causes of Boils
- The most common cause of infection is Staphylococcus aureus, but other bacteria can also be pathogens.
- For example, enteric bacterial species such as Enterobacteriaceae and Enterococci are common causative agents of boils in the genital area and on the buttocks.
- Corynebacterium, Staphylococcus epidermalis (S. epidermidis), and group A beta-hemolytic streptococci (S. pyogenes) can also cause boil infections.
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is the most common cause of recurrent boils1.
Factors that contribute to the development of boils
In addition to direct contact with the pathogen, various triggers can contribute to the disease:
- Physical contact with infected people
- anemia
- Previous antibiotic therapy
- diabetes
- Poor personal hygiene
- Decreased immunity
- Skin diseases (atopic dermatitis, chronic wounds or leg ulcers)
- obesity and hematological diseases
How does a boil develop?

- A swollen and painful nodule (infiltrate) that is bright red in color.
- Accumulation of fluid in a closed cavity, indicated by a fluctuating (rippling) mark in the center of the nodule.
- Formation of a purulent-necrotic core (base of hair surrounded by pus and dead tissue).
- Opening of the furrow with detachment of the purulent-necrotic mass.
Change in eye refraction
myopia - A refractive disorder of the eye in which a person has difficulty seeing distant objects. In myopia, the image stops in front of the retina. Symptoms: poor recognition of objects in the distance, discomfort, rapid eye fatigue, pressure pain in the temple or forehead area.
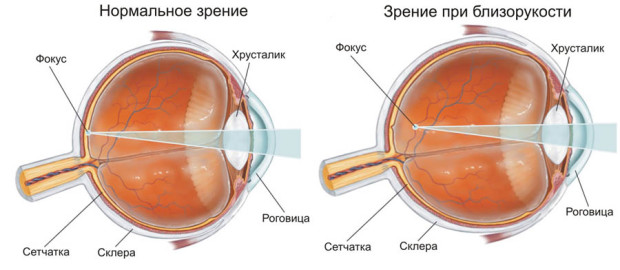
myopia
nearsightedness (hyperopia) – This is a refractive disorder in which the image is read behind the retina and is the opposite of myopia. In this case, the patient cannot see well both near and distant objects. Symptoms: Very often fog appears before the eyes, sometimes the patient squints.
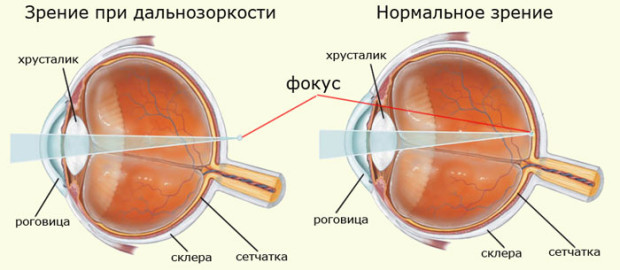
farsightedness
astigmatism – This disorder is characterized by the inability to focus light rays on the retina. It occurs most often in people with physiological disorders of the organs of vision: cornea, lens. Symptoms: blurred and unclear vision, easy fatigue, frequent headaches, tightening of the eye muscles when looking.
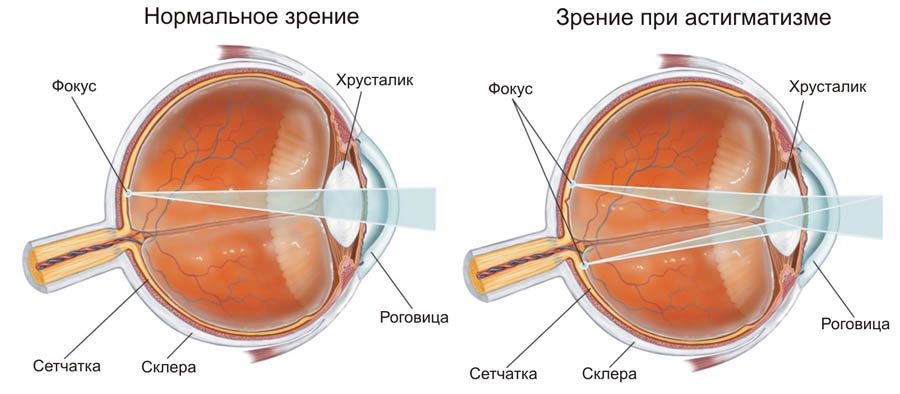
astigmatism
Other eye diseases
nystagmus – Uncontrolled oscillating movements of the eyeballs.
Lazy eye syndrome or amblyopia – is a disorder in which the eye stops working and moving due to muscle damage.
anisocoria – A discrepancy in pupil size. It occurs mainly as a result of various eye injuries. It is associated with acute photosensitivity and reduced vision. Sometimes this pathology indicates a violation of one of the brain departments - the cerebellum.

anisocoria
episcleritis – An inflammatory condition that forms in episcleral tissue. First, there is redness near the cornea, then this area swells. Symptoms: discomfort, bright light blinds the eyes. Connective tissue discharge may occur. In most cases, episcleritis resolves spontaneously.
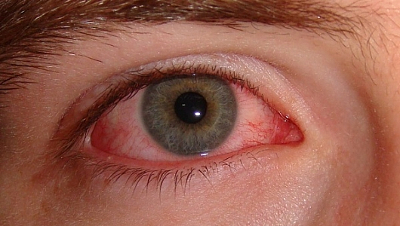
episcleritis
aniridia – Complete absence of the iris of the eye.
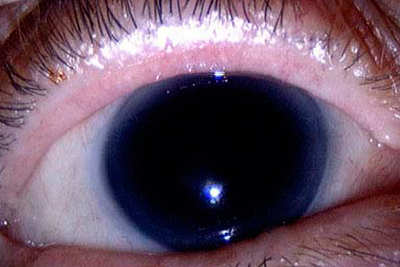
aniridia
polychory – An eye defect in which a person has more than one pupil.
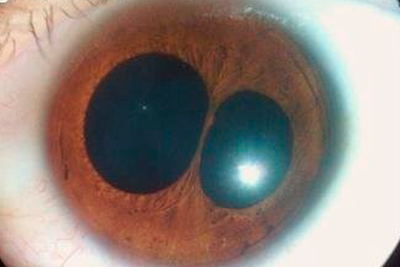
polychory
ophthalmoplegia – A condition in which the nerves in the eye that are responsible for moving the eye stop working properly. This leads to paralysis and the inability to rotate the eyeballs. Symptoms: Eyes turned to nose; this position should not be changed.
Read more:- The hock in which the person is located.
- The hock in which the person is located.
- A person walks on tiptoe.
- Photograph of a person's leg with a description.
- The cube on which a person's ankle is drawn.
- Marfan syndrome at a glance.
- How to remove a clubfoot.
- Why does a child develop clubfoot?.
