The doctor first collects the medical history and conducts an examination. The specialist assesses whether the patient's bones are anatomically correct, makes predictions about possible anomalies and selects diagnostic methods.

- Modern orthopedics in Moscow
- The main areas of interest of our orthopedic clinic are
- The orthopedic specialist
- What does an orthopedist treat in adults?
- organs
- Diseases
- What the orthopedist treats
- Orthopaedist/Dentist
- What the patient should know
- When it is important to see an orthopedist
- Which diagnostic methods does the podiatrist use?
- Consultation of an orthopedist: diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system
- diagnostic procedures.
- What methods are used to treat orthopedic diseases?
- The first visit to an orthopedist
- Examinations recommended by the orthopaedist
- Who is an Orthopedist?
- What does an orthopedic surgeon do?
- Podiatrist and podiatrist - what is the difference?
- podiatry
- Visit to an orthopedic surgeon, rheumatologist
- How to live pain free
- telefonic consultancy
- Consultation with a doctor
- course of treatment
- treatment at home
Modern orthopedics in Moscow
Orthopedics is a branch of medicine that deals with problems of the musculoskeletal system. Every year there is an increasing need for qualified orthopedic surgeons. Osteoarthritis and arthritis, back pain, foot deformities, torn ligaments and tendons, fractures and dislocations - this is not a complete list of ailments that patients need to see a doctor for. This is an incomplete list of complaints with which patients come to the doctors of the Paul Ehrlich European Medical Academy.
The clinic actively cooperates with leading orthopedic surgeons in Germany. Patients who wish to travel abroad for treatment but have high hopes for Western medicine can get equally effective treatment at our center by turning to us and saving a household budget.
We regularly invite qualified orthopedic surgeons from leading clinics around the world for consultations and help patients to book appointments with internationally renowned professors.
The center is equipped with the latest diagnostic devices and high-quality medical technology of the latest generation. Our doctors have unique methods to ensure that a high percentage of patients return to an active life after treatment.

The main areas of interest of our orthopedic clinic are
- treatment of the spine;
- treatment of joint pathologies;
- treatment of foot and hand injuries;
- accident surgery;
- arthroscopic surgery;
- rehabilitation after operations, severe bruises and injuries;
- prevention of diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- Custom made insoles with unique technology;
- A wide range of physiotherapeutic treatments;
- repair of soft tissue;
- development of individual treatment and recovery programs based on diagnostic data;
- the opportunity to obtain a 'second opinion' in cases of doubt.
The range of complaints with which patients present in the orthopedic clinic is quite wide. The most common complaints include:
- joint pain and inflammation;
- muscle pain and cramps
- limb deformities;
- unstable gait;
- side effects of surgical interventions;
- curvature of the spine;
- pain in the foot area;
- bunions in the big toe;
- ineffective rehabilitation after fractures or injuries;
- protracted healing of wounds and bruises;
- back pain;
- limited joint function.
The specialists will not only determine the cause of the discomfort, but will also suggest the best treatment program. Experienced doctors work according to the latest findings and a holistic therapeutic approach leads to excellent results. In our center we not only take care of the staff, but also of the equipment. We have the latest generation of diagnostic and therapeutic equipment with medical imaging from renowned international brands.
The orthopedic specialist
orthopedist – An orthopedist is a medical specialist who specializes in the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. These include congenital diseases, infectious diseases, acquired diseases, various types of defects, adverse effects of surgical interventions, serious injuries, etc. The podiatrist examines, diagnoses and treats the patients.

Depending on the work and tasks of the podiatrist, the following areas of orthopedics can be distinguished:
- outpatient – The treatment of complaints is carried out exclusively conservatively in various institutions: trauma department, home treatment, day clinic, etc. Follow-up examinations are usually also carried out and attention is paid to prevention.
- endoprosthetics – This procedure is performed when the damaged joint or bone cannot be healed by other, gentler methods. This includes surgical endoprosthetics, that is, the replacement of various joints.
- surgical – Surgical treatment of pathologies and many common diseases. Ligaments and joints are most commonly treated through orthoscopic surgery. Routine surgeries are performed on: hands, feet, etc.
- traumatology – Injuries of everyday life such as broken bones, torn ligaments and contusions are treated here. It also deals with specific diseases such as injuries that are closely related to dangerous professions: stuntmen, athletes, dangerous jobs. They also correct old bone formations and defects.
- Pediatric Orthopedics – Age-related peculiarities of the musculoskeletal system, their active growth and increased muscle tension lead to various dangerous disorders and even disabilities.
What does an orthopedist treat in adults?
orthopedists – Orthopedists are highly specialized doctors with expertise in various fields: surgery, traumatology and sports medicine.
An orthopedist treats everything - bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons and the nerve endings connected to them.
organs
Movement disorders in adults always negatively affect the proper functioning of internal organs. These organs can be retracted or compressed.
- upper limbs, lower limbs;
- Bones of the shoulder girdle: clavicle, scapula;
- spine, pelvic bones;
- foot, heel, metatarsal, toe pontics;
- Ligaments, cartilage, tendons.
Diseases
The orthopedist treats the following diseases:
- broken bones;
- scoliosis, kyphoscoliosis, osteochondrosis;
- contortions;
- flat feet, pronounced clubfoot;
- cures polio, acts on the spinal cord, so the effects are lifelong;
- Baker's cyst, osteogenic sarcoma, Ewing's tumor;
- Treatment of numerous congenital diseases: torticollis, dysplasia, etc;
- Treatment of joint deformities: arthrosis, arthritis.
 flat feet
flat feet  Baker's cyst below the knee
Baker's cyst below the knee  arthrosis
arthrosis  gout in the legs
gout in the legs  dislocation of the ankle
dislocation of the ankle  Development of spondylitis and osteochondrosis
Development of spondylitis and osteochondrosis  Ring finger fracture
Ring finger fracture  Fracture of the heel bone
Fracture of the heel bone
What the orthopedist treats
- Osteoporosis. It is a polyetiological, chronically progressive systemic and metabolic disease of the skeleton or a clinical syndrome that is manifested by other diseases. Osteoporosis is characterized by a decrease in bone density (microarchitectural abnormalities appear differently and depend on the prevailing risk factor for the pathology), increased bone fragility and a long latent course of the disease. Older age, larger height and lower body weight are risk factors for developing the disease. The pathology occurs three times more often in women than in men and is found mainly in Caucasian and Mongoloid individuals.
- Osteochondrosis, a syndrome of dystrophic changes in articular cartilage. Pathology is associated with an upright posture and develops with age – with age there is a physiological decrease in the vascular bed in the intervertebral discs, which leads to their diffuse nutrition and causes dystrophic changes (the cartilage loses strength and elasticity, its texture and shape changes). It can occur in any joint, but the intervertebral discs are most commonly affected. Depending on the localization of the pathology, cervical, thoracic and lumbar osteochondrosis is distinguished. Dystrophic changes are aggravated by improper diet, poor posture, insufficient warm-up, use of soft pillows and mattresses, carrying bags over the shoulder. Flat feet and obesity contribute to the development of osteochondrosis.
- flat feet. Is a change in the shape of the foot that manifests itself as a prolapse of the longitudinal and/or transverse arch. It can be primary flatfoot, transverse and longitudinal arch prolapse, or a combination of both. Transverse flatfoot is accompanied by a flattening of the transverse arch of the foot, the forefoot rests on the heads of all five metatarsal bones, the fan-like spreading of which in connection with an outward deviation of the first toe and a hammer toe deformity of the middle toe leads to a shortening of the foot. Longitudinal flatfoot is characterized by a flattening of the longitudinal arch, in which almost the entire surface of the sole touches the ground and the foot length increases. Pathology is directly related to body weight – the higher the weight, the more pronounced longitudinal flatfoot (more common in women). Depending on its origin, it can be congenital (aged 5-6 years), traumatic, paralyzed, shaky, and static.
- Hollow foot is a pathology in which the height of the arch of the foot is abnormally increased (the opposite of flatfoot). It results from trauma to the foot, is caused by certain disorders of the neuromuscular system, and can be inherited. In addition to the external deformation, the patient suffers from pain and fatigue when walking.
- Valgus deformity is a pathology in which the metatarsophalangeal joint of the first toe is curved and the other toes are depressed (a 'bump' gradually forms at the base of the big toe, making it difficult to wear normal footwear). The disease is associated with rapid fatigue in the legs and pain in the ankles.
- Herniated disc caused by displacement of the nucleus pulposus of the disc and rupture of the fibrous ring. The lumbosacral area of the spine is most often affected, much less often the cervical and thoracic areas. It is manifested by localized pain in the area of the projection of the damaged disc or referred pain, numbness, weakness and sensory disturbances in the limbs, etc.
- Periarticular inflammation is a degenerative lesion of the tendons where the tendons attach to the bone. It is accompanied by the development of reactive inflammation in the affected tendon and localized serous sheaths.
- Neuromyelitis is a symptom of spinal cord injury and is characterized by pain along nerve roots and nerves. Sensory disturbances occur and movement disorders can occur. As a rule, it is an acute disease, but it often turns into a chronic condition, with phases of aggravation.
- spondyloarthritis. It is a chronic degenerative disease of the spine that develops when the discs shift and thin. The increased pressure on the facet joints leads to a loss of the elastic properties of the hyaline cartilage, leading to the gradual formation of osteophytes (bone ridges). Osteophytes can significantly limit the mobility of the affected part of the spine. As the process progresses, there is reactive inflammation and a complete loss of mobility in the affected area.
- Heel spurs (plantar fasciitis), an overgrowth of the heel bone. The hypertrophy is located near the insertion of the Achilles tendon or near the tuber on the soleus side and takes the form of a spur or wedge. It occurs as a result of foot and heel trauma, circulatory disorders, metabolic disorders, obesity, etc.
- Scoliosis is a triplanar spinal deformity that can be congenital, acquired, or post-traumatic.
- Arthritis. This term refers to any disease (lesion) of the joints. Arthritis can be acute or chronic, affecting one or more joints.
- osteoarthritis. This degenerative-dystrophic joint disease is characterized by damage to the cartilage tissue of the joint surfaces, followed by an inflammatory reaction.
Orthopaedist/Dentist
An orthopedic dentist is a professional who makes dentures (rebuilds the outer and inner parts of the tooth).
He examines the condition of the patient's mouth and jaw, as well as the entire body before performing the prosthetic work, makes the necessary preparations, takes an impression and makes a prosthesis adapted to the patient.
- micro dentures. The treatment involves the preservation of a large part of the tooth (inlays and ceramic veneers).
- Removable dentures. A prosthesis can be partial (bridge) or complete. It consists of a nylon base and artificial teeth and is attached with special masses or brackets. Removable partial dentures are even used in children to maintain normal dentition after losing a baby tooth.
- Fixed dentures (crowns and bridges).
What the patient should know
Fresh injuries are best treated, so don't hesitate to see your doctor. Many people prefer to treat the symptoms themselves after a fall, and that's one of the biggest mistakes: home accidents and falls can result in broken bones, dislocations, torn ligaments, and other subtle injuries with symptoms similar to a simple contusion.
If the diagnosis is not made early enough, the consequences can be dangerous: the bones cannot heal properly and rough scars can form at the fracture site, restricting freedom of movement.
When visiting the orthopedist, it is important to talk about the true causes of the complaints and to describe the symptoms in detail.
Depending on the specificity and complexity of the disease, the orthopedist can also schedule an examination by other specialists: a neurologist, rheumatologist, endocrinologist or traumatologist. This ensures that the disease is treated holistically.
The most important thing for the patient is to follow the recommendations of the orthopedist and not neglect physical therapy and orthopedic devices. The more carefully the treatment program is followed, the quicker recovery will occur.
When it is important to see an orthopedist
Here are some symptoms of the most common diseases that require a visit to an orthopedist for adults or children: flat feet, clubfoot, dislocated hips, scoliosis and kyphosis, torticollis, joint diseases.
Flatfoot is manifested by pain in the feet and a change in their shape. You may also experience swelling and pain in your feet after moderate to heavy exercise. Clubfoot can be congenital or acquired.
Clubfoot is always a congenital condition, a type of fetal abnormality. The external symptom of clubfoot, which is the reason for visiting a pediatric orthopedist, is the child's incorrect foot position. There are different degrees of clubfoot, but if you visit an orthopedist in time and follow all his recommendations, the foot can return to its normal position.
Hip dislocation is another very common congenital disorder. It is also called hip dysplasia. It is only detected during a special examination of the newborn by an orthopedist. In this case, too, it is important to consult a specialist at an early stage. Judging by the feedback received by orthopedists from parents of children with dysplasia, in most cases the condition is successfully corrected.
Scoliosis and kyphosis is a curvature of the spine that can be congenital or acquired. There are different degrees of scoliosis and kyphosis. In most cases, the curvature of the spine is visible to the naked eye. These conditions are treatable and should be evaluated by an orthopedic surgeon. Congenital scoliosis and kyphosis are often detected in the maternity ward or during one of the routine check-ups of the newborn at the health center during a visit to the orthopedist.
The main symptom of torticollis is an obvious deformation of the neck, causing a constant tilt of the head to one side. This condition can be congenital or acquired in old age.
In the case of instability of the joints (or just one of the joints), swelling or enlargement of the joints, pain in the joints when moving, cracking noises, an orthopedist should definitely be consulted.
Which diagnostic methods does the podiatrist use?
In his work, the podiatrist uses exclusively instrumental diagnostic methods: MRI, CT, X-ray, ultrasound and endoscopy (if there is a suspicion of a joint disease).
The orthopedist always examines the patient before referring him for an examination, listens to the complaints and, after the examination, makes a preliminary diagnosis. To clarify the diagnosis and determine the severity of the disease, the above diagnostic methods are used.
Consultation of an orthopedist: diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system
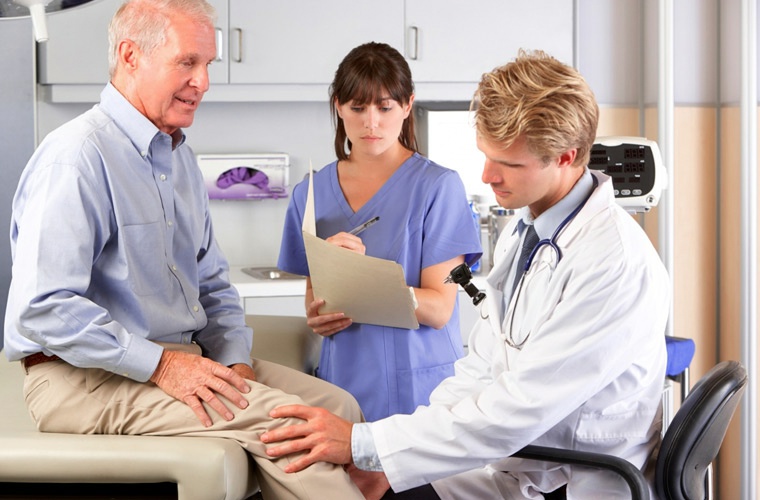
diagnostic procedures.
As a rule, to establish the diagnosis, the orthopedist uses instrumental methods of examination: ultrasound, X-ray, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Arthroscopy is one of the latest diagnostic procedures in orthopedics. A flexible tube with a lens attached to the end is inserted into the joint cavity. This method allows surgical treatment in combination with diagnostics.
Laboratory tests cannot assess the condition of your musculoskeletal system. For this reason, as part of the initial diagnosis, the orthopedist will not usually arrange for examinations, but will assess the general condition of your body if surgery is required.
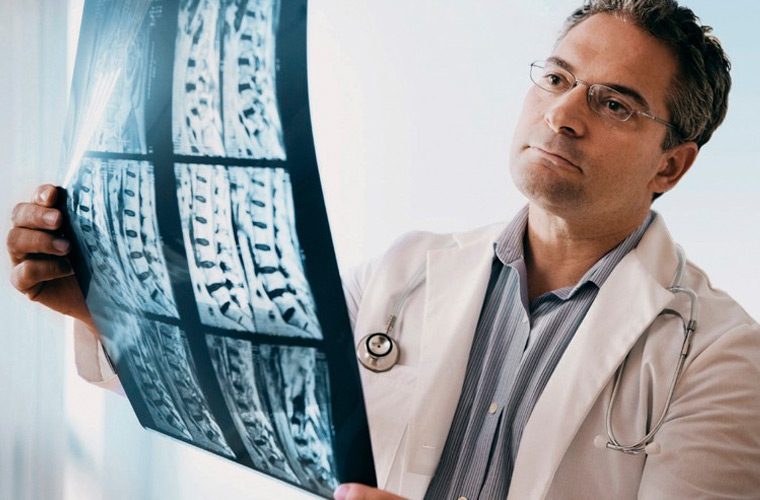

What methods are used to treat orthopedic diseases?
To alleviate the above conditions, the orthopedist can use two types of methods:
- Conservative treatment (conservative treatment). It is a long-term therapy in which the patient is involved. Plaster casts are used to ensure immobilisation of the deformed area. With pathologies of the lower limbs, orthopedic shoes and orthoses are often recommended. Exercise therapy, physiotherapy and massage are also common.
- surgical treatment. This treatment is carried out when the pathology cannot be eliminated by conservative methods. During the operation, prostheses can be inserted and muscles and ligaments can be sewn up. In modern orthopedic surgery, innovative techniques are used that have made complex operations such as joint replacement possible.
The first visit to an orthopedist
Patients are often interested in how the first visit to an orthopedist goes. We will therefore outline the main points to consider during an initial consultation with a specialist:
- Visual assessment of the anatomical structure relevant to the skeletal system (normal or abnormal); this activity is especially important when examining a newborn;
- Determination of the range of motion relevant to the affected joints;
- recommendation of fluoroscopy to clarify or refute the suspected diagnosis;
- Complex forms of pathology may indicate the need for investigations such as CT and MRI (which then require a CT or MRI scan).
Examinations recommended by the orthopaedist
Despite the profile of this specialist, which one could mistakenly presume to exclude investigations aimed at completing the general clinical picture, its traditional and specific forms cannot be dispensed with either. In particular, the orthopedist may need the results of the following examinations:
- general urine and blood analysis;
- blood clotting time data;
- activated partial thromboplastin time data;
- Prothrombin index as well as prothrombin time and prothrombin time + fibrinogen.
Who is an Orthopedist?
An orthopedist is a doctor who treats musculoskeletal disorders caused by deformities or diseases. The pediatric orthopedist examines the causes of congenital skeletal and muscular abnormalities, corrects deformities and restores the function of the musculoskeletal system. He uses both conservative treatment methods (physical therapy, physiotherapy, orthoses, braces, splints, prostheses, cast, manual therapy) and surgical interventions: osteotomies and tendon transplants.
Training to become an orthopedic surgeon takes place as part of specialist training or postgraduate studies at a medical university. As part of their studies, they learn disaster surgery, prosthetics and rehabilitation. Orthopedists work in endopedic clinics, rehabilitation centers, orthopedic spas and polyclinics. Orthopedics is one of the most sought-after and complex medical specialties. Most patients become disabled due to musculoskeletal disorders.
The examinations by a pediatric orthopedist are obligatory at the age of 1, 3 and 9 months and before admission to kindergarten. A pediatric orthopedic consultation is essential when a child has poor posture at school, starts playing sports or dancing, has difficulty with everyday movements, is uncoordinated and clumsy, or has pain in the feet when walking. The podiatrist is responsible for all posture and gait disorders.
Ukrainian orthopedists are increasingly being trained in western European countries. Advances in orthopedics in our country allow effective prevention and treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, as well as rehabilitation after injuries. Some clinics offer medical services at the level of European clinics. There is an exchange of experiences, internships and exchange programs.
Most orthopedic patients are treated in outpatient clinics. Surgical intervention is not as common as it might seem at first glance.
What does an orthopedic surgeon do?
The orthopedist treats flat feet, scoliosis, injuries and congenital defects with physical therapy, manual therapy or surgery. He treats clubfoot, torticollis and joint anomalies and corrects misalignments. The orthopedist treats injuries: sprains, bruises, dislocations, fractures and burns.
The spine pays the price for our ability to walk upright from the moment we take our first steps. She is exposed to enormous stress throughout her life. The orthopedist also deals with problems related to the spine. The most common problem in childhood is scoliosis.
For children and adults with diseases of the musculoskeletal system, the orthopedist can prescribe individual orthoses. He can also recommend exercise therapy and therapeutic measures for home and sports injuries.
In advanced cases, the patient ends up in the hands of orthopedists who specialize in endoprostheses (replacement of a joint with an artificial joint). This can e.g. B. be necessary in osteoarthritis, when the articular cartilage wears out, or fractures, z. B. the femoral neck. The orthopedist is also responsible for treating deformities of the neck and chest. A pediatric orthopedic surgeon works with a neurologist to help children with complications from cerebral palsy and polio get back on their feet. The orthopedic examination plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of hip dysplasia and hip dislocation. The orthopedist also treats rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and synovitis - inflammatory and degenerative joint diseases.
If there is a neurological disease in your family or if you have had an accident in the past, you should not forget to visit your orthopedist once a year. This is how you can protect yourself from complications.
The orthopedist examines the joint on the couch, assesses the mobility of the joint and prescribes an ultrasound, X-ray, MRI or CT examination of the joint.
He has been treating wounds and fractures since the time of the ancient Incas, who were able to operate on the skull, straighten dislocations and repair bones.
Podiatrist and podiatrist - what is the difference?
podiatrists – Podiatrists are specialists in a new branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the foot, ankle and lower leg. They offer conservative and surgical treatments for various complications of the bones, muscles, blood vessels and nerves.
podiatrists – are specialists who deal primarily with nursing. Podiatrists perform instrumental and instrumental pedicures, take care of ingrown toenails, conduct hygienic treatments using special substances, and provide advice on the choice of shoes. Podiatrists face problems that are easily solved with the right care.
A podiatrist is not always a doctor. In some cases, podiatrists may also be hardware pedicure specialists. The podiatrist carries out aesthetic corrections. Patients often go to a podiatrist first. The podiatrist assesses the condition of the foot and, in the event of a serious pathology, refers to a podiatrist. This means that podiatrists and podiatrists work together.
podiatry
Podiatrists treat patients of all ages with the following conditions:
- fractures and dislocations. The most common ankle and foot disorders that podiatrists encounter in practice. Because they often work in sports medicine, treating athletes and developing methods to prevent and avoid injuries
- Bunion deformity, hammer toe. Podiatrists perform conservative treatments and surgical procedures for a variety of deformities and provide rehabilitation services after surgery.
- Osteoarthritis that develops into osteoarthritis. Prolonged inflammation of the joint leads to wear and tear. Podiatrists offer conservative, including physical therapy, and surgical treatments for arthritis and osteoarthritis.
- pain syndrome. In children and adolescents with congenital deformities, pain is often the main symptom. The podiatrist recommends a series of exercises to correct the condition and makes custom orthotics. If conservative methods are ineffective, resort to surgery.
- Discomfort, pain in the heel. Caused by heel spurs, calcium deposits in the lower part of the heel bone. They can be caused by running, improper footwear, or obesity. Another condition that causes heel pain is plantar fasciitis. This is an inflammatory and degenerative process that occurs in the connective tissue along the sole of the foot.
- Morton's neuroma. A benign neoplasm of the neural tissue of the metatarsal bone, usually between the second and third, third and fourth toes. The therapy is conservative, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs to combat pain and orthoses. If the therapy is unsuccessful, an operation is indicated.
Visit to an orthopedic surgeon, rheumatologist
An orthopedic trauma surgeon deals with the treatment of orthopedic diseases. You can also make an appointment with a rheumatologist in our clinic who deals with trauma problems (gout, rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, etc.).
At your first visit, the doctor will question you in detail about all your symptoms, conduct a visual examination, and prescribe additional tests if necessary. The treatment program is designed individually and as gently as possible, taking into account the peculiarities of your body.
Remember that orthopedic diseases are quicker and easier to treat in the early stages, when surgery is not yet necessary.
How to live pain free
Fill out the form or give us a call +7 (843) 562-00-90

telefonic consultancy
1) You tell us your problem, the age of the disease and the preferred doctor (if you go to a specific doctor who has been recommended to you). 2) You make an appointment. 3) Before your appointment, you will be reminded of your appointment by the receptionist. If you need to reschedule your appointment, please give us a call.
Consultation with a doctor
1) The doctor will ask you about your symptoms, your medical history and possible causes. He or she will read your test results. If necessary, he will order additional examinations and tests or refer to the necessary specialists. 2) He diagnoses and prescribes treatment (if the condition is amenable to our treatment methods). The attending physician monitors the course of treatment and adjusts it if necessary.

course of treatment
1) Your condition will be treated by 3-5 specialists in different treatment methods. 2) An instructor teaches you how to do the exercises correctly, at a pace and at an intensity that you can continue at home. After completing the prescribed physiotherapy, you will receive recommendations on how to continue exercising at home.

treatment at home
At this stage, you can independently follow the recommendations you received at the end of the full therapy, without the supervision of our therapists. If physical therapy has been prescribed, do it at home, observing the intensity and intervals. If you have any questions or doubts about the correctness of your exercises, we recommend that you make an appointment with a specialist doctor to clarify and eliminate your concerns.
Read more:- orthopedist, the.
- Who is the orthopedist.
- Who is the orthopedist?.
- What an orthopedist treats and what symptoms to report.
- Orthopedist who treats children and with what.
- What does the orthopedic traumatologist treat?.
- Traumatology orthopedist which doctor.
- What does an orthopedist examine?.
