It is also advisable to teach children first aid for sprains, bruises and other injuries so that they can remain calm in stressful situations and provide proper first aid to themselves or others.

- Injuries leading to hip dislocations
- Symptoms of a thigh muscle strain
- Function of the gluteus maximus muscle.
- How can you tell if you have glute major weakness?
- Classification of musculotonic syndromes
- diagnosis
- Structure of muscles, muscle biology
- Nocturnal cramps in pregnant women
- treatment methods
- Creatine helps build muscle
- The key to building muscle mass is strength training.
- Legs
- Hamstring biceps
- Which muscles are most likely to shorten?
- Why do muscles shorten and shorten?
- Exercises for the quadriceps muscles of the thigh (quadriceps)
- Lean on a support
- Bulgarian lunges
- Exercises for the glutes
- Deadlift with dumbbells
- Kicks
Injuries leading to hip dislocations
It is not uncommon for athletes to suffer hip dislocations, which are treated by trauma surgeons. This injury most commonly occurs during lunges, leg raises, and squats.
If, after performing an exercise, there is severe pain that is so severe that the exercise can no longer be performed, it is a sprain. But do not panic or worry, if all therapeutic measures are carried out at once, you can quickly return to an active lifestyle. If we turn to the anatomy and see the cause of the pain, the situation is as follows. There are three muscle groups in the hip area:
The adductor muscle guides the hips, the other two are responsible for extending and flexing the legs. Since the quadriceps and posterior muscles pass through the hip and knee joints, they are more prone to injury than the others. In addition, these muscles are constantly exposed to high loads, especially during vigorous physical movements, fast running or walking, high and long jumps and sports games (volleyball, basketball, football). The back and thigh muscles can be stressed or stretched to varying degrees, with 3 degrees:
- Severe pain but no bruising;
- There is severe pain and bruising.
- The muscle is completely torn and there are many large bruises.
In the latter case, it can take up to several months to regain the same physical shape.
He specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory and allergy diseases and has knowledge in the areas of external respiratory function testing, allergen testing, autohaematology and specific and non-specific immunotherapy.
Symptoms of a thigh muscle strain
To diagnose a biceps brachii or iliolumbarus strain, several symptoms should be noted: First, there is a 'clicking' sensation; secondly, there is severe pain and it is painful to touch the injury; third, there is visible bruising, and sometimes a large bruise.
After the injury, it is difficult to continue moving, let alone playing sports. There is a greater risk of the same injury causing permanent damage in the future, which is why it is especially important to follow all doctor and trainer recommendations. Further diagnosis is carried out by a surgeon or trauma surgeon.
The doctor must find out under what circumstances and with what movement the injury occurred, what type of tenderness the patient is experiencing, and how large the bruising is. The doctor will ask the patient to bend and straighten the leg at the knee and hip joints, and then make a diagnosis. These symptoms of a hamstring strain should be taken into account and an x-ray should also be taken.
Function of the gluteus maximus muscle.
The gluteus maximus muscle is very important for activities such as standing, walking and running. The function of this muscle in these activities is to participate in extension of the leg, straightening of the body, abduction and alignment of the hip to the body, hip rotation to and from the center of the body, and stabilization of the pelvis. This muscle may also play a role in stabilizing the knee during extension.
For example, when standing, the gluteus maximus plays an important role in hip extension and pelvic stabilization. When running, this muscle stabilizes the trunk and also helps extend the hip when accelerating and inhibit the leg when stopping movement.
A weak gluteus maximus therefore impairs the ability to carry out many of our daily activities effectively and safely. Weakness in the muscles can lead to difficulty performing certain movements that require the use of those muscles, such as walking. B. when standing up, getting up from a sitting position, walking or running. Sometimes weakness in the glutes can be accompanied by back, knee, and hip pain.
How can you tell if you have glute major weakness?
Here's a quick and easy test to find out if you have glute weakness.
Lie on your back and bend your knees to at least 90 degrees. Tighten your glutes. Slowly lift your hips off the floor and then straighten your right knee so your hips are parallel. Try not to change the height of your pelvis or rotate your hips. If the pelvis tilts or rotates to one side when the leg is extended, there is definitely glute muscle weakness. However, women should not do this test until six weeks after delivery.
To determine gluteal muscle weakness, the doctor can use other manual and dynamic diagnostic techniques:
- Manual diagnostic procedures include observing the correctness of the exercise, the presence of movement errors, or determining the compensatory involvement of other muscles in the execution of the movement.
- Dynamic techniques include digital video analysis of movement execution, which allows the physiotherapist to view the movement in detail. This video analysis allows the physical therapist to assess the gluteal muscles in the kinetic chain and dynamically observe the function of the pelvis and lower limbs throughout the gait cycle.
Classification of musculotonic syndromes
There are several types of musculotonic pain syndromes. They are classified according to their localization:
- Anterior lumbar muscular compression syndrome: It affects the III-VI cervical vertebrae area and the upper rib. Muscle contraction compresses the subclavian artery and brachial plexus.
- Pear muscle syndrome: The sciatic nerve and inferior gluteal artery are compressed.
- Facet syndrome: Local tenderness and stiffness in the metatarsophalangeal joints of the spine. It is accompanied by subluxation of the vertebral segments and rupture of the joint capsules. Depending on the location of the affected facet joint, the pain can radiate to the head, shoulders, chest, lumbar spine, sacrum, hips or buttocks.
In addition, the trapezius, the largest chest muscle (pectoralis major), the lumbar muscle (quadratus lumborum) and the shoulder extensor (scapulae) are often affected. The pain syndrome can be both primary (affecting only the cramped tissue) and secondary, that is, occurring outside the area of injury.
diagnosis
Diagnostic measures include:
- the clinical examination
- Assessment of the symptoms and clarification of the neurological anamnesis
- functional x-ray of the spine
- MRI
- Electroneuromyography (examination of bioelectrical muscle potentials used to diagnose lumbar muscle tone syndrome and symptoms of radiculopathy)
MRI is considered the most informative, safe and painless method of neuroimaging. It provides the most accurate assessment of the condition of the spine and spinal cord, can detect intervertebral protrusions and herniations and determine their size and location.
Spinal rehabilitation: material from the specialists of the rehabilitation center's movement laboratory
Download a detailed rehabilitation program
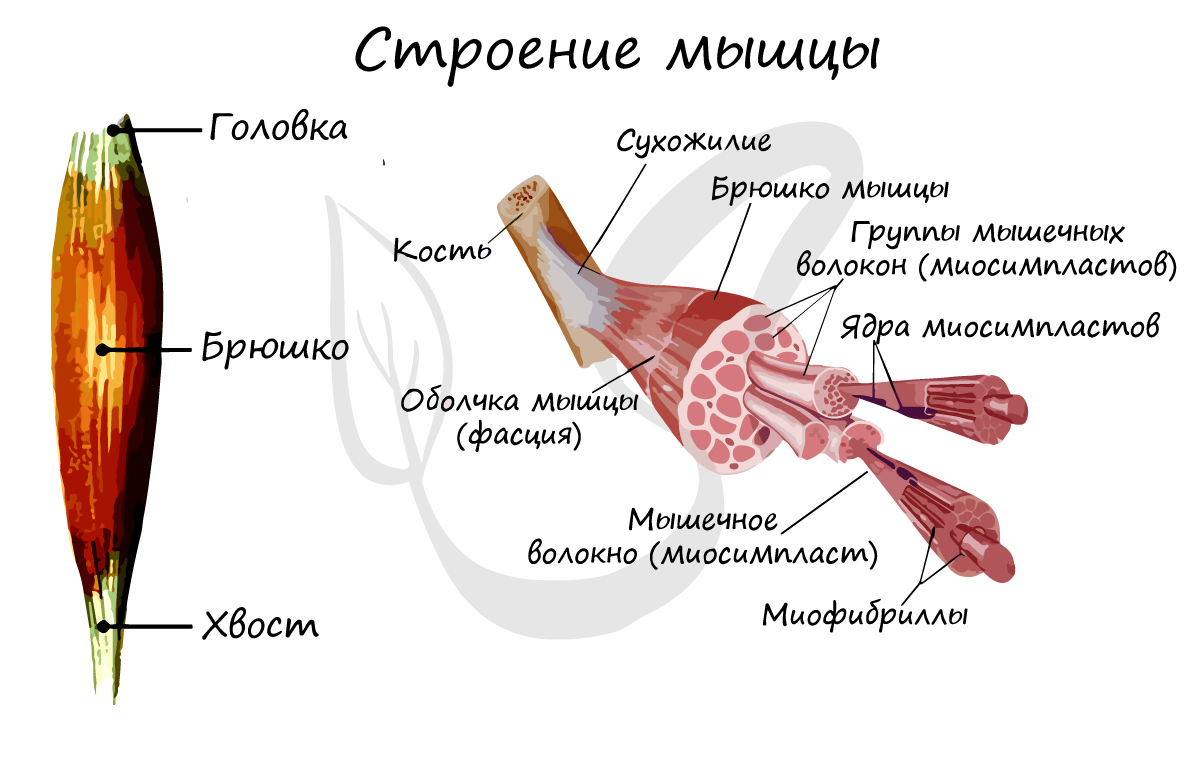
Structure of muscles, muscle biology
Muscles are the active part of the musculoskeletal system. When they contract, they set the bony levers in motion: movements are created that move the body and its parts through space.
building the muscles
Muscles are made up of a series of muscle fibers that form the belly of the muscle. The muscle is divided into a head and a tail: the head is connected to the fixed part of the muscle, while the tail pulls on the movable part of the skeleton when the muscle contracts.
In the muscle tissue section, we learned in detail about the structure of the striated muscle tissue, which enables us to move voluntarily (under conscious control). The striated muscle tissue consists of long, multinucleated fibers - myofibrils - which are striated transversely by an elementary unit - the sarcomere. Sarcomeres join together to form myofibrils, which in turn form myofibrils.
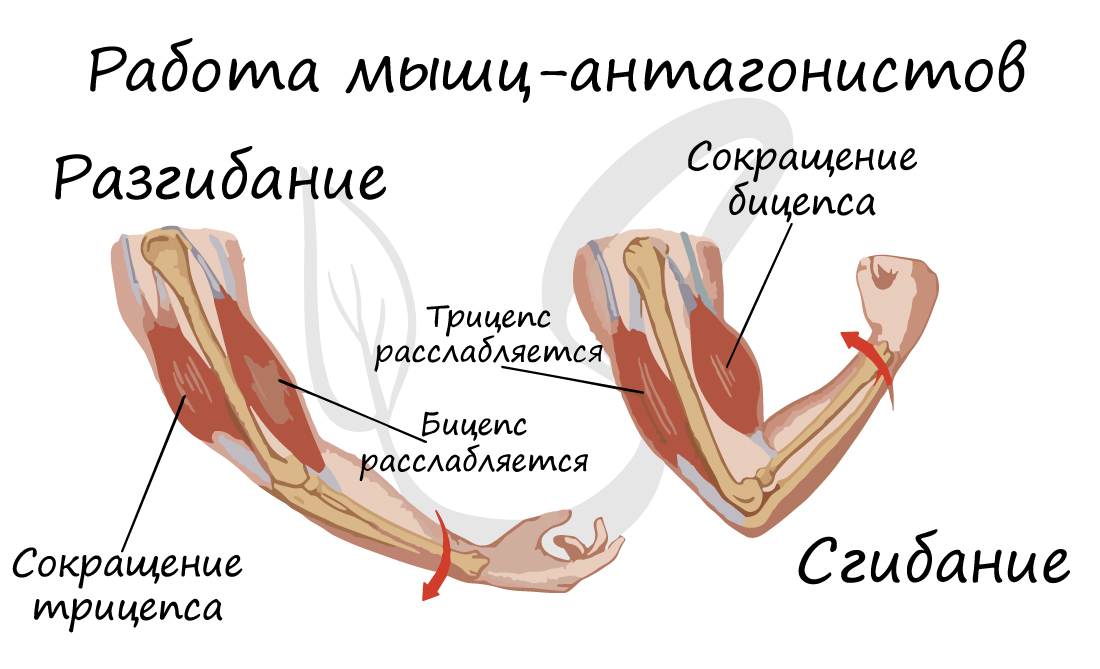
antagonists and synergists
A distinction is made between antagonistic and synergistic muscles. Antagonist muscles (from the Greek antagonistes - antagonist) are muscle groups that stand parallel to each other and, by contracting, cause the bone levers to move in opposite directions. Simply put: one bends and the other straightens the limb. The most obvious examples of antagonistic muscles are the biceps and triceps.
Synergistic muscles (from Greek synergos - working together) are muscles that work together to perform a specific movement. Examples of such muscles are the brachialis and biceps.

Nocturnal cramps in pregnant women
During pregnancy, the intake of micronutrients is significantly increased. Calcium, potassium and magnesium are essential for fetal growth and development. If the expectant mother's body is deficient in these substances, it signals this with muscle cramps. Eat a healthy diet, avoid coffee and fast food, and limit your salt intake. Ask your doctor to prescribe a vitamin and mineral complex.
In the second trimester of pregnancy, the woman's weight increases. The legs, especially the feet, are put under additional strain, which hinders blood circulation. If cramps occur, do exercises for pregnant women, including stretching exercises. Do not take any medication during pregnancy without consulting your doctor.
treatment methods
Treatment of cramps should be comprehensive: follow a healthy diet, take vitamin and mineral complexes, wear comfortable clothing, drink enough water, limit the consumption of coffee and alcoholic beverages, do not take over-the-counter medications and don't do too much exercise.
If the cramps are caused by kidney disease, endocrine disease, or varicose veins, you should treat the underlying condition.
To relieve cramps, you can try pinching your foot, placing a cold towel on it, or standing on a cold floor.
To prevent cramps, you can take warm foot baths, stretch and knead your legs before bed. Place a pillow under your feet so that they are slightly elevated. This improves blood circulation.
Creatine helps build muscle
Anyone who trains in the gym to get a beautiful, shapely body should know that muscle building is supported by creatine. It is a chemical that occurs naturally in the muscles and brain. But you can also get it with food, e.g. B. with red meat or seafood.
When muscles contract and relax (e.g. during exercise), heat energy is released. When a large amount of it is released, the blood vessels that innervate the muscle help redirect this energy into the skin, preventing the muscle from overheating.
The key to building muscle mass is strength training.
No other type of exercise is better for building muscle than strength training. You should literally be at the limit because it is the only exercise that causes hypertrophy (i.e. enlargement) of the muscles. Your muscles are used the most when you exercise with dumbbells or lift weights.
Fitness experts say that each workout should last no longer than 90 minutes. Anything beyond this time will have a negative impact.
Legs
Leg training generally refers to the development of the quadriceps and biceps thigh muscles. For both quadriceps and biceps, trainers try to do several exercises for each.
As the name suggests ('quadro' means four), this muscle consists of four heads, each of which has its own origin, but which all converge in the knee area and flow into a common tendon that surrounds the kneecap and attaches to the tibial tuberosity.
The main function of the quadriceps muscle is to extend the lower limbs in the knee joint. As you may have guessed, this extension is achieved by the combined action of all four heads as they are connected by the same tendon. Isolated work on the individual heads for lower leg extension exercises is not possible, and the lower and upper quadriceps muscles cannot be trained separately.
The width of the foot position and direction do not distribute the load between the muscle heads of the quadriceps, but in some exercises can influence the activity of other muscles involved, such as the biceps and gluteus maximus. Quadriceps exercises are generally only differentiated based on whether they are core exercises (multi-joint) or isolation exercises (single-joint).
Since not only the knee joint but also the hip joint is moved during these exercises, in addition to the quadriceps, the hip extensors (not to be confused with the extensors of the lower limbs) are also actively involved: M. gluteus maximus, M. gluteus adduction, M. biceps femoris, M. semitendinosus. In my opinion, to effectively train the quadriceps, you should always combine core exercises with isolation exercises, as both have their advantages and disadvantages.
And you can make do with just a few exercises - a basic exercise and an isolation exercise (squat plus shin extension on one machine). Separately, I would like to point out one of the benefits of compound exercises for the quadriceps. This is glute training. This particular muscle group is not specifically trained, but should definitely not be forgotten. An athlete with his jeans hanging off his butt looks ridiculous, the gluteus maximus has to have its place!
Hamstring biceps
Because the muscles of the hamstring cross at two joints, when the pelvis is at rest they work together to flex the tibia at the knee joint and lengthen the thigh, and when the tibia is at rest they work together with the gluteus maximus to lengthen the trunk. The range of movements that target the biceps femoris is therefore very diverse.
These include the trainer shin splits, straight-leg deadlifts, hyperextension, and weighted squats. All of these exercises effectively develop the biceps, the only difference is how many other muscle groups are involved. Movements that extend the hip to the torso or the torso to the hip also work the glutes and erector spinae. Therefore, when choosing your exercises, you need to decide what is more important in this phase: isolated or compound load.
If your hamstring workout includes core quadriceps exercises in which the biceps plays an active role, such as: For example, if you do all squats and leg presses, you can limit your workout to one biceps isolation exercise. This allows you to perform a total of three exercises in one workout: a core exercise for the quadriceps and an isolation exercise for the quadriceps and biceps.
Which muscles are most likely to shorten?
The back and psoas muscles (iliopsoas, quadriceps, erector spinae) are most prone to shortening.
In the upper body – Trapezius muscle of the upper back, pectoralis minor muscle, sternal part of the pectoralis major muscle (which raises the scapula), transversus thoracic muscle, rectus abdominis and obliques, nuchal lattice muscles, suboccipital muscles, sternoclavicular muscles, flexor joints of the upper limbs.
In the lower part of the body – Calf muscle, hamstrings, gluteus medius muscle, thigh adductors, camel toe muscle, tibialis anterior muscle.
But basically every muscle in our body can shorten if its biomechanics are disturbed.
Why do muscles shorten and shorten?
Now we come to the heart of the matter. The cause of the problem is the same in most cases. Hypotonia (weakness), reduced functioning of the antagonist muscle.. The weakness of at least one muscle in the body inevitably leads to a tightening of another muscle, which takes over the load of the weaker muscle. The result of chronic overstretching is spasm, shortening of the muscle.
An illustrative example. When the gluteus maximus is weak, it leads to overstretching and shortening of the lumbar spine muscle. Why? The main antagonist of the gluteus medius muscle during walking is the gluteus maximus muscle. When we take a step, the gluteus maximus muscle contracts and pulls the leg backwards, while the lumbar spine helps bring the leg forward. Walking is essentially an alternating contraction and relaxation of the gluteus medius and lumbar muscles. The worse the gluteus maximus works, the more the lumbar muscles shorten.
What is the danger? There is a gradual destruction of the cartilage of the hip joint (coxarthrosis), micro-injuries of the intervertebral discs in the lumbar spine, which entails the risk of disc bulging and herniation.
Or this example. Shortening of the pectoralis minor muscles is caused by weakness of the rhomboid and middle trapezius muscles, resulting in the so-called pectoralis minor syndrome, numbness in the fingers and pain in the hand.
Exercises for the quadriceps muscles of the thigh (quadriceps)
Lean on a support
This exercise works all the leg muscles and even the abdominal muscles, but your quadriceps are particularly stressed. You need a hard surface to stand on - a chair, stool, bench, box.
- Starting position: legs together, back straight.
- Inhale, place one foot on the surface and let the other foot hang back for a second.
- As you exhale, return to the floor and do the same exercise with the other leg.
Perform the step-outs in 15-20 steps per leg, 2-3 approaches, one minute between each step. For additional load at the top, you can hold the exercise for 30-40 seconds, regularly cushioning the supporting leg.
Bulgarian lunges
This isolation exercise has a visible toning effect on the quadriceps area without overloading or pumping it. The difficulty level of the exercise is high because, in addition to performing the lunges, you also need to focus on maintaining your balance.
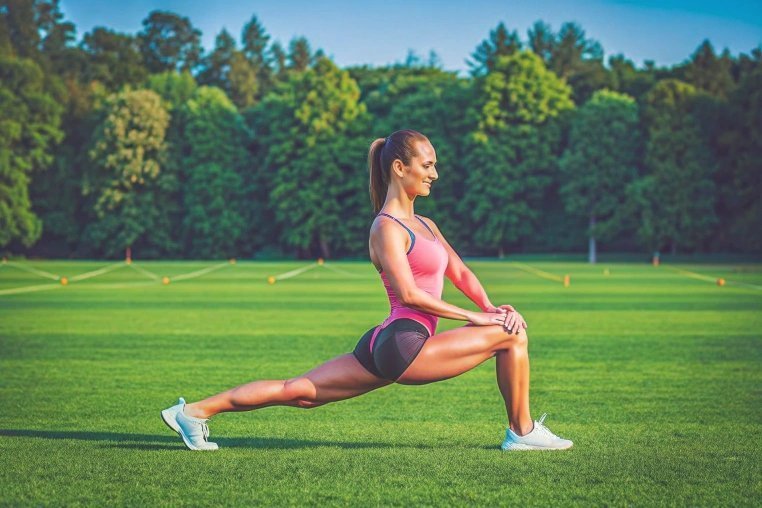

- Take the starting position - the left leg rests on a support, the right leg is relaxed and stretched forward.
- On an inhale, lunge with your right foot until your knee forms a 90-degree angle.
- The foot rests on the heel. On the exhale, return to the starting position.
For visible results, perform 15 to 18 lunges on each leg, performing 2 to 3 of these steps with a minute's rest between each approach.
Exercises for the glutes
Deadlift with dumbbells
Dumbbell deadlifts work the glutes and provide additional stress on the back of the thighs. The dumbbells can be heavy weights, at least 4 kg each.
Stand up straight, feet hip-width apart, toes pointing slightly inward to take pressure off your lower back. Hold the dumbbells in your hands and place them on the front of your thighs. Bend forward with your knees straight. If you find it very difficult to keep your knees straight, you can bend them slightly.
Lower your hands with the dumbbells from the hip joint to the middle of the shin, then raise them again. It is important that you keep your back straight and naturally arch your lower back.
Perform this exercise 15 times, for a total of 2 sets.
Kicks
This exercise is also a compound exercise that works the glutes and activates the hamstrings and front thighs.
The starting position is standing on all fours. Hands firmly under your shoulders, pelvis over your knees. Head in line with body, do not raise or lower. Alternately perform a straight leg push upwards with maximum amplitude.
Breathe freely, with the leg going up as you exhale and down as you inhale. Perform the exercise 10 times in 3 sets.
Read more:- The flexor muscles of the foot.
- How muscles and bones are related.
- muscles in the legs.
- Shin extensor muscles (tibialis extensor muscles).
- muscle work while running.
- Which muscles of the anterior tibial group do you know?.
- Anterior tilting of the pelvis.
- Lift your heels off the floor during the squat.
