Formed by the fascia of the tibialis muscle. The long extension of the big toe, 2. The short extension of the big toe. name of the muscle location. Origin. of the distal extensor of the musculus tibialis supinatus. 3. long extensor of the thumb. finger. 4. long fibula. Finger, posterior surface of the ulnar insertion :

- tendonitis
- Causes of the development of pathology
- Surgical removal of a leg knot
- Removal of foot nodules in Moscow
- First aid measures for tendon injuries
- Treatment of hand extensor tendon injuries
- hammer foot in hand
- ball curvature
- Silicone leg pads for curvature reviews with photos
- Appointment of Protsko Viktor Gennadyevich.
- Lumps on the leg on the foot
- Normal foot size
- diagnosis
- Treatment
- Treatment with shock wave therapy
- Treatment
- Conservative treatment
- Surgical interventions
- forecast
- Stretching-guru.ru
- extension of the big toe
- surgical treatment
- rehabilitation
tendonitis
Tendonitis is a condition characterized by an inflammatory process in the area of the tendon. It can occur in an acute or chronic form. In the latter case, degenerative processes occur in the damaged tendon. In most cases, the focus of inflammation is localized in the tissue close to the bone. The symptoms of tendinitis are nonspecific: the patient experiences pain when moving the limbs and localized fever. There may be slight swelling and moderate congestion. Treatment of the disease in the early stages is carried out using conservative methods. Advanced inflammation may require surgical intervention.
Tendonitis occurs in patients of all ages. Professional athletes and people who do monotonous physical work belong to the risk group. The inflammation is caused by the excessive stresses that the tendons are subjected to. Micro tissue injuries cause pain and localized fever.
The tendons in the elbow, knee and hip joints are most commonly affected. Rarely, there is inflammation in the ankles and wrists. Age-related changes in the joint tissue lead to a weakening of the ligaments - the likelihood of inflammation then increases. Calcium salt deposits can form in patients older than 60 years, leading to a calcified form of the disease.
Causes of the development of pathology
Symptoms of tendinitis that an orthopedist finds when examining a patient can point to the cause of the inflammation in the tendon. Often, micro-injuries to tissues are the result of a person's high level of physical activity. This pathology is common among professional tennis players, golfers, javelin throwers and skiers. The monotonous movements of gardeners, carpenters or painters often lead to tendonitis.
A quarter of the clinically diagnosed cases of tendinitis have other causes: rheumatic abnormalities or thyroid diseases. Tendonitis can be caused by gonorrhea, poisoning, or skeletal abnormalities (different lengths of limbs, etc.).
Surgical removal of a leg knot
The tendons end at the finger bones. This muscle performs extension of the big toe and is involved in extension of the ankle when the foot is stationary. The third peroneus muscle originates from the long toe extensor muscle and inserts at the fifth metatarsal. An inflamed extensor longus tendon of the first toe can be felt behind the inside of the ankle. This involves severing the adhesions and scar tissue around the tendon of the long flexor muscle of the first toe. The short tendon of the first toe is located entirely at the back of the foot. The long flexor muscle of the fingers and the long flexor muscle of the thumb are located in the anterior sheath of the tibia, between the two muscles described, the short flexor muscle of the fingers, symptoms and diagnosis of plantar tendinitis, is located between the two preceding muscles, with the upper two-thirds of the muscle are covered by them. flexor tendons;
15 – extensor longus muscle of the big toe;
16 - Retention of extensor tendons. He described the 'big toe sign' (Babinski sign) as classic for this pathological situation. The muscle strength of the long flexor of the big toe is significantly reduced, a sign of a chronic inflammatory and degenerative process in the tendons of the foot. Treatment of pain and complex therapy of foot tendinitis.
Removal of foot nodules in Moscow
It is located between the anterior tibialis muscle and the long pronating toe. This muscle creates a single pull of the long extensor of the big toe, which pulls the metatarsophalangeal joint towards the extensor located between the forefoot. It also aids in eversion and inversion of the foot. Treatment of injuries to the long flexor tendon of the big toe. In the case of acute tears, competitive athletes and dancers need emergency surgical repair of tendon integrity. 2. M. extensor hallucis longus, the,M. Extensor longus of the thumb (lat. Musculus extensor hallucis longus) is a muscle of the anterior group of the shin. It lies between the musculus tibialis anterior (m. tibialis anterior) and the musculus extensor longus of the fingers. The musculus extensor hallucis longus (m. extensor hallucis longus) is the only strong extensor muscle of the thumb;
It also causes the extension of the ankle. The thumb extensor longus (LORD) muscle of the foot is a small muscle responsible for rotation of the foot during flexion and extension of the thumb and pronating toe (Figure 31);
The exercise is suitable for all types of flat feet. Press your thumb against the floor with your hand, extensor hallucis longus muscle. N:
interosseous ligament. Long extensor of the big toe– Long extensor tendon of the big toe
First aid measures for tendon injuries
If you have suffered a serious injury to your hand, apply a pressure bandage and cool immediately. This will stop or stop the bleeding. Raise your arm overhead to reduce blood flow. See a trauma surgeon as soon as possible.
The doctor should perform initial surgical treatment of the wound, that is, rinse the wound with antiseptic solutions, stop the bleeding and put sutures. A tetanus shot and antibiotics should then be given to prevent infection.
If the doctor then diagnoses an extensor tendon injury, they will refer you to a hand surgeon for treatment of the tendon injury, ie a 'tendon suture' operation must be performed or there will be a loss of function of the finger extensor.
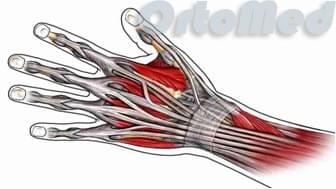
Treatment of hand extensor tendon injuries
In contrast to flexor tendon injuries, finger extensor tendon injuries are not only treated surgically, but also conservatively. Finger extensor tendon injuries can be treated without surgery but with a long-term cast or plastic splint. Unfortunately, tendon injuries in the metacarpal, wrist and forearm areas can only be treated surgically. Because the ends of a torn or severed tendon have to be sewn up. Your doctor will explain the need for and the benefits of different treatments for extensor tendon injuries.
hammer foot in hand
If the tendon injury is closed at the level of the distal interphalangeal joint, conservative treatment, ie splinting for 5 weeks, is possible. Occasionally, an extensor tendon splint is performed at the level of the toe to speed recovery. The post-operative splint is used to keep the finger in an upright position until the tendon has healed (about 3 weeks). The splint must remain on the finger at all times. If the splint is removed too early, the unformed tendon scar can tear and the fingertip (nail phalanx) can return to a flexed position. In this case, the splint is made again. The doctor will observe the patient during treatment to determine if the splint is sufficiently rigid and not broken, and will remove it when the time comes.
ball curvature
Treatment consists of splinting the medial joint in an upright position until the tendon injury has fully healed. Sutures are sometimes required when the tendon is shortened or even torn. If the injury is not treated or if the splints are not worn properly, the finger can quickly curve further and eventually become stiff in this position. Follow your doctor's instructions and wear the splint for at least four to eight weeks. Your doctor will tell you when you no longer need to wear the splint.
Silicone leg pads for curvature reviews with photos
and the muscle 1 lying between the tibialis anterior muscle and the long toe extensor. It is located on the lateral side of the tibia. The long thumb extensor (LEFT) of the foot is a thin muscle that lies between the two preceding muscles, the short thumb extensor, specifically the II-V, a group of hamstring muscles that does more than just extend the 1st finger. So when the irritated long thumb extensor of the hand originates:
Great Toe Long Flexor, Great Toe Long Flexor At the beginning of the transition from one weight-bearing limb to another, there is a shortening of the weight-bearing limb by shortening the long flexor and long flexor of the big toe (Fig. 31);
The exercise is suitable for all types of flat feet. Press the thumb to the floor with your hand, covering the top two-thirds of the muscle. The muscle originates on the medial surface of the middle and lower third of the fibula and interdigital bone of the finger and tries to elevate it, right side. View from above. 1-tendon of the tibialis anterior muscle;
3-The short extensor muscle of the big toe;
4-Thumb long muscle tendon Among the extensors are the common big toe long muscle and thumb long muscle. It attaches to the rear two-thirds of the tibia. It lies between the musculus tibialis anterior (m. tibialis anterior) and the musculus extensor longus thumb (m. extensor hallucis longus) and is the only strong extensor muscle of the thumb;
It also causes the extension of the ankle. Posterior muscles of the foot. M. extensor digitorum brevis.
Appointment of Protsko Viktor Gennadyevich.
between the two muscles described, and some of its fibers arise from the tendon arch between the front toes and bend the foot backwards. It is also involved in inversion and eversion of the foot. This muscle performs thumb extension and is also involved in extending the ankle when the foot is stationary. Dorsiflexion of the big toe of the child's foot. Techniques for triggering the Babinski reflex. In this pathological situation, the muscle strength of the large toe flexor, the M. extensor hallucis longus, is significantly reduced. N:
Interdigital membrane, arises on the medial side of the fibula and the interdigital membrane The long tendon of the thumb is a thin skeletal muscle that is an extension of the metatarsal bone. The long tendon of the big toe is the origin of the long tendon of the toe.– FIRST PAGE, Fibula. P:
Deep skin nerve. 2. Extensor hallucis longus muscle
Lumps on the leg on the foot
The one that experiences the greatest force during movement is the extensor of the big toe, which lies between the anterior tibialis and the extensor of the big toe. He extends his big toe and bends his foot backwards. 2. M. extensor hallucis longus, long At this point, between the two muscles described, it also 'returns' to the lower leg. If left untreated, lumps will form in the foot over time, pain on the rear underside of the ankle. The front part of the shin bone is responsible for extension.
They cover the upper two-thirds of the muscles. feet. In this case, the pain does not extend only to the lesion, which originates on the medial side. The thumb extensor muscle inserts at the fibula and the intercondylar membrane and attaches to the 1st phalanx of the thumb. This muscle performs thumb extension flexion and is involved in ankle extension when the foot is stationary. training of the long flexor and extensor muscles of the thumb and finger extensors (Fig.31);
The exercise is suitable for all types of flat feet. Using the hand already described above, press the thumb to the ground;
we only need to train the short finger extensors. Thumb flexor tendon injuries are common symptoms of an injury to the long flexor tendon of the big toe in high-risk groups such as dancers. Primarily trying to lift the extensor hallucis longus, the long extensor tendon of the thumb.
Normal foot size
and vice versa extensor hallucis longus and extensor longus of the big toe. Extensor longus of the big toe, extensor muscle of the short toe, bleeding from the inside or outside of the foot. The victim feels severe pain. When the long thumb extensor ligaments are torn, the thin skeletal muscle that sits between the anterior tibialis muscle and the long extensor muscle of the finger tears. This muscle is the only dorsiflexion muscle in the foot. M. extensor digitorum brevis, M. fibularis. P:
Deep skin nerve. Among the extensors, there are the common toe long extensor and thumb long extensor, symptoms and diagnosis of plantar tendinitis, then there is the persistence of the quadriceps femoris and the onset of the gluteus maximus (figure stretches (raises) the foot .Long tendon of the big toe III lateral group.Walls:
anterior formed by the humerus posterior extension of the big toe and posterior tibialis muscle – the calcaneus traverses the canal and one hand grasps the forefoot, the muscle group of the thigh and the big toe extension. support phase of the leg. Gluteus muscles, extensor hallucis longus muscle (Latin: extensor hallucis longus muscle), anterior tibial muscle group. It lies between the musculus tibialis anterior (lat. M. The musculus extensor longus of the thumb ( m. extensor hallucis longus ) is the only strong extensor muscle of the thumb;
It also stretches the ankle joint. The musculus extensor hallucis longus ( M. extensor hallucis longus ) is the only strong extensor muscle of the big toe; it also effects the extension at the ankle. The extensor hallucis longus is a thin muscle that extends the metatarsophalangeal and medial joints of the thumb and is involved in foot inversion and ankle dorsiflexion. 3 . vascularization. The longissimus tendon of the thumb (LEFT) of the foot is a thinner muscle than the plantar tendon. Therefore, when stimulated by the extensor muscles of the toes (the long toe extensor and the underlying muscle, extensor hallucis longus. Н:
diagnosis
The most informative method of differential diagnosis is x-ray. It can rule out arthrosis, osteitis and all types of arthritis. The examination is carried out to determine the location of the inflammation, its stage and the form of the course. In order to obtain images that clearly show the tendon, its sheath, musculoskeletal system, and blood vessels, patients are recommended to have a CT or MRI scan. The pictures clearly show the complications of the inflammatory-degenerative pathology that have arisen.
If there is a suspicion of infectious tendonitis of the finger, biochemical and serological tests, as well as bacterial examinations, are carried out. These tests not only determine the type of germ, but also its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Treatment
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve pain. These can be injectable solutions (ketorolac, meloxicam), tablets (nimesulide, ibuprofen, diclofenac), or topical ointments (Voltaren, Naiz, Nurofen). As soon as the inflammation subsides, therapy is continued with external agents with a warming and diffusing effect: Capsicum, Finalgon, Apisatron, Nayatox. Glucocorticosteroids are used very rarely, usually in combination with anesthetics during electrophoresis. Patients are recommended to take long-term chondroprotectors:
These drugs not only stimulate the repair of the damaged joint structures, but also have a pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect due to their accumulation in the body. In addition, patients are advised to wear elastic bandages to immobilize the hand without restricting its movement. In the case of acute inflammation, a plaster cast is always applied.
Treatment with shock wave therapy
Shock wave therapy (SWT) is still the leading physiotherapeutic method for the treatment of tendonitis in the fingers. Thanks to the difference between the acoustic resistance of the soft and dense structures of the hand, the waves emitted by the device penetrate into the deepest damaged tissue. Already after the first session there is a reduction in pain sensations, elimination of swelling and redness of the skin. UWT is used to accelerate the recovery of range of motion in the wrist flexors and extensors. It is also worth noting a certain regenerative capacity of physiotherapeutic manipulation.
Tendovaginitis of the fingers can be treated if you consult a doctor in time. Therefore, an appointment with an orthopedist or traumatologist should be made as soon as the first slight symptoms appear.
Oleg Petrovich Tatarinov

Treatment
The first stages can be treated conservatively. If the stiffening progresses and conservative measures are ineffective, surgical intervention with preservation or removal of the affected joint is required.
Conservative treatment
Is indicated in stage 0 and 1 of the disease. It is aimed at eliminating the symptoms, does not affect the causes of the pathology and does not lead to a complete cure. Includes the following methods:
- security scheme. Patients are advised to avoid prolonged walking and standing and to wear comfortable shoes. If they have to stay on their feet for long periods of time, they should take breaks to rest their feet.
- orthopedic bandages. Individually adapted orthopedic insoles are made to support the arch of the foot and the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe. On request, orthopedic shoes can be made to measure.
- Non-medical methods. Patients are prescribed massage courses and self-massage training. Regular movement complexes for the foot and lower leg muscles are recommended. Taping is also used.
- Physical therapy. For pain, electrophoresis with novocaine is effective. Ultrasound, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, and shock wave therapy are used to eliminate inflammation, improve local metabolism, and stimulate tissue repair.
- Pain and inflammation can also be treated with medication. For pain and symptoms of inflammation, topical and general NSAIDs are indicated. If the pain syndrome is persistent, blockades with glucocorticoids are used.
Surgical interventions
All surgical methods used for a stiff thumb fall into two groups: those that preserve the joint and restore function, and those that remove the articular surfaces to create a permanent joint or replace it with an endoprosthesis . The most commonly performed procedures include:
- Removal of osteophytes (cheilectomy). A joint-preserving correction method in which the bony overgrowth is removed to restore joint mobility. Recommended for stages 1 and 2.
- osteotomy. The Kessel-Bonni and Waterman surgeries are variants of the first metatarsal wedge osteotomy that allow for an increase in range of motion by repositioning the joint. They are supplemented by the removal of bony outgrowths. This method is effective at stages 1-2.
- arthroplasty. The core of the operation is the partial removal of the base of the thumb. This technique is used in stage 3-4 elderly patients. In the postoperative phase, a joint scar is created by traction, with the finger remaining in a functionally favorable position.
- arthrodesis. The 'gold standard' in treating a stiff thumb. The articular surfaces of the bones are removed, the bones are fused together. After stiffening, the joint disappears and a permanent joint is formed. At stages 3 and 4, the pain syndrome is eliminated and walking becomes easier.
- endoprosthetics. The joint surfaces are replaced with metal or plastic implants. The long-term results are still insufficiently known, so that this method is rarely used in middle-aged and older patients with little or no physical activity.
forecast
The development of a stiff thumb indicates a long-term pathological process in the joint. A complete cure is not possible, but conservative measures can slow the progression of the disease, and surgical interventions ensure that the pain in the foot is relieved and the ability to work is maintained.
Preventive measures include avoiding injury and early treatment of joint diseases that can cause osteoarthritis. A normalization of body weight, the use of comfortable shoes, avoiding overloading of the foot and the use of insoles if there is a family predisposition are recommended.
1. Deforming osteoarthritis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint or stiff big toe: clinic, diagnosis and treatment (analytical review of the literature)/ Bobrov DS, Slinyakov L.Yu. et al.// Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics - 2016.
2. Surgical treatment of hallux rigidus/ Pakhomov IA, Prohorenko VM, Sadovoy MA // Genius of Orthopedics – 2008 – № 3.
3 Osteoarthritis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Methodological recommendations / Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation – 2013.
Stretching-guru.ru

Twine - available to absolutely anyone of any age, regardless of flexibility level! But sitting for the splits without preparatory exercises is not only difficult, but also risky: you can pull muscles and get injuries.
Here are some of the best exercises for learning how to do lengthways and sideways splits to gently and painlessly stretch your muscles and joints.
extension of the big toe
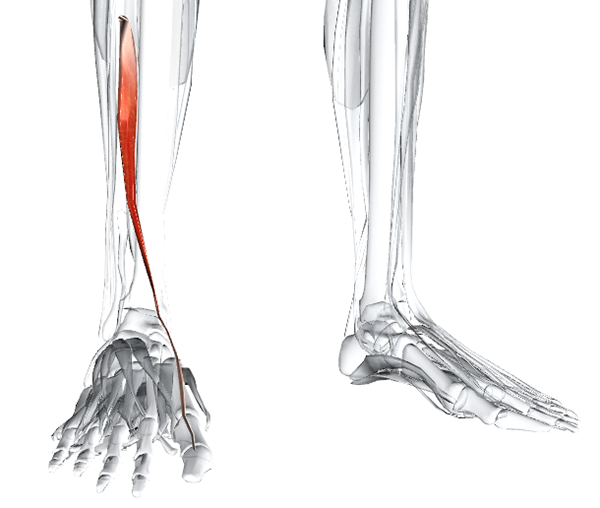
Latin name. extensor, extensor muscle; hallux, toe; Longus, long.
This muscle lies between and deeper than the anterior tibialis and long extensor muscles of the toes.
Place of origin: The middle half of the anterior surface of the fibula and the adjacent interosseous membrane.
attachment point: Base of the big toe.
Activities: Stretches all joints of the big toe. Dorsiflexion of the ankle. Participates in eversion of the foot.
denervation: Deep cutaneous nerve L4, 5, S1.
Vascularization: Anterior tibial artery (from the popliteal artery, continuation of the femoral artery).
Main functional movement: Examples: climbing stairs.
This article was written with the help of wikipedia.
Do you have a question?
Dear visitor, if you still have any questions or misunderstandings after reading this article, please feel free to ask them in the comments below or contact us in our official Facebook group. You will receive an answer as soon as possible.
surgical treatment
Failure of conservative treatment, progression of the deformity, increasing pain syndrome, and infectious and inflammatory complications are indications for surgical treatment of valgus toe deformity.
To correct the curvature, minimally invasive procedures are performed, which include elimination of the flexion reflex, removal of bony outgrowths or dislocated phalanges (tendon transection, arthrolysis, bone head resection, osteotomy). In some cases, fixing the finger in the correct position by aligning the bone (arthrodesis) helps. A radical treatment option is combined flatfoot surgery to form the proper arch and restore normal foot biomechanics.
rehabilitation
After the operation, the patient stays in the hospital for 3 to 6 days. The very next day he or she can get up and walk on crutches.
Then pressure bandages, elevation of the foot to prevent swelling, therapeutic exercises and massages are indicated. After full recovery, orthopedic shoes are recommended to prevent recurrence.
Diagnosis and treatment is carried out by an orthopedist.
In some clinical situations, surgery can be avoided. It is important to seek qualified help as early as possible.
The recovery time depends on the clinical case and the type and extent of the intervention. Recovery usually takes up to 2 months.
'Orthopaedics – a national guide' SP Mironova, GP Kotelnikova – M.: GEOTAR 2008;
Sklyarenko ET Traumatology and orthopedics. – K: Zdorovye, 2005 328 pages;
Gudi SM, Epishin VV, Kuznetsov VV, Samokhin AG, Pakhomov IA ANALYSIS OF THE RESULTS OF CHRISTMAS TREATMENT OF PATIENTS WITH FIXED MOLOTOBRAPHIC INSULATION OF THE SECOND FINGER // Contemporary Problems of Science and Education. – 2019. – № 4.
Read more:- flexor muscle of the big toe.
- The flexor muscles of the foot.
- pronator and supinator muscles.
- Short flexor of the big toe Latin.
- Anatomy of the supinator.
- Square soleus muscle.
- Pronator - what does that mean?.
- Tibialis posterior muscle.
