That said, flat feet in five-year-olds are normal.
- What is a foot insole? Is it essential?
- How NOT to spoil children's feet
- Definition of a footbed
- Questionable usefulness of supinators in infancy
- How to choose the right shoes with cushioning?
- Why is the insole important in children's shoes?
- Features of the models for children
- What materials are they made of
- Benefits and possible harm
- Features of insoles for children
- How do you check the quality of an insole?
- When should you start wearing support shoes?
- What is an orthopedic splint?
- types of deposits
- Factors contributing to the development of this pathology:
- What orthopedic shoes for children should be
- hard heel
- insole
- Should you be looking for shoes with a hard sole?
- When should you buy shoes for your baby: when he's just starting to get out of bed or when he's already taking his first steps?
What is a foot insole? Is it essential?
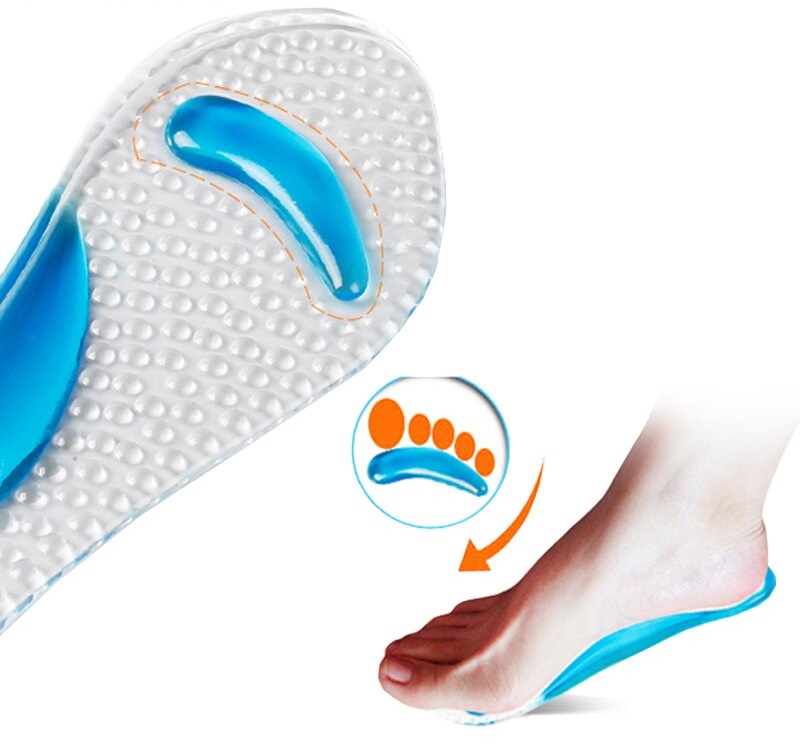
A supinator, a footrest, a gelenok, a lining for the inner arch - because that's the only part of the shoe that we don't call that. While some parents adore it and don't even bother looking at models without it in stores, others argue and prove that it's not that useful for healthy feet. In this blog article you will learn what it is, what it consists of and what its purpose is.
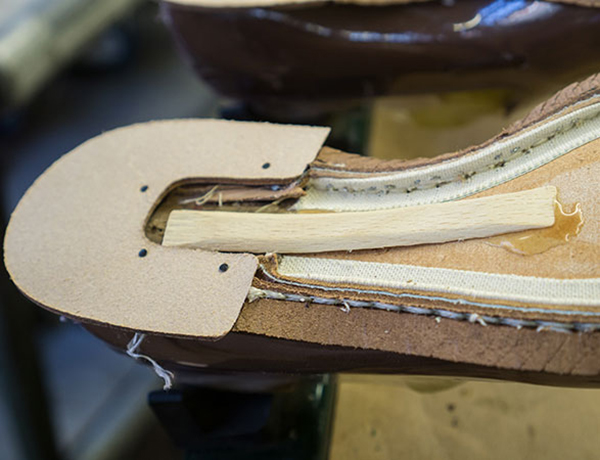
A shoe insert is the part of the insole, the convex part, that is usually attached closer to the back of the shoe or boot. It is made of leather, cork, metal or plastic.
According to podiatrist theory, it is required to keep the arch of the foot in the correct position. It is not usually flat but rather resembles an arch. When walking, it straightens up and immediately returns to its previous position - this helps to absorb the impact and relieve the spine. However, this is not the case for people with flat feet; Supinators help them restore flexion and keep the ligaments in the correct position.
These parts are quite rigid and are housed in custom-made special shoes. Normal children's shoes have soles - these are soft and only serve to cushion the feet.
How NOT to spoil children's feet
As we said above is the purpose of footbeds – They are designed to correct serious medical problems. They are chosen by a doctor, and the shoes themselves are usually made from an impression of the foot.
Children do not need them, as they can only cause harm. Some parents don't go into detail because they heard somewhere that 'shoes with insoles are useful'. The child is forced to wear shoes with rigid padding and the longitudinal arch of the foot no longer functions as physiologically intended.
The blood no longer circulates properly and the muscles and ligaments become weak and unable to support the foot properly. The result is that the child gets elongated flat feet. It's as if the parents want the best, but the result is 'the same as always'.
Only shoes that are the wrong size are worse. They slide under the foot, the child feels discomfort and pain, and the arch of the foot is anatomically incorrectly shaped.

A healthy child's foot does not need insoles - these must be prescribed by the doctor after an examination.
Definition of a footbed
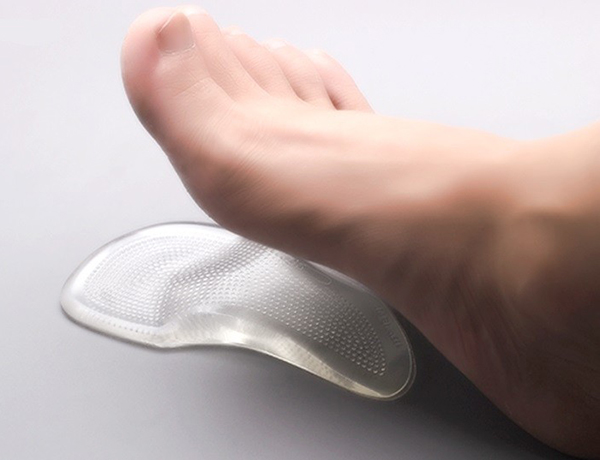
A footbed is a small bump on the inner edge of the insole. It should be just under the arch of the foot and flush with the outside edge.
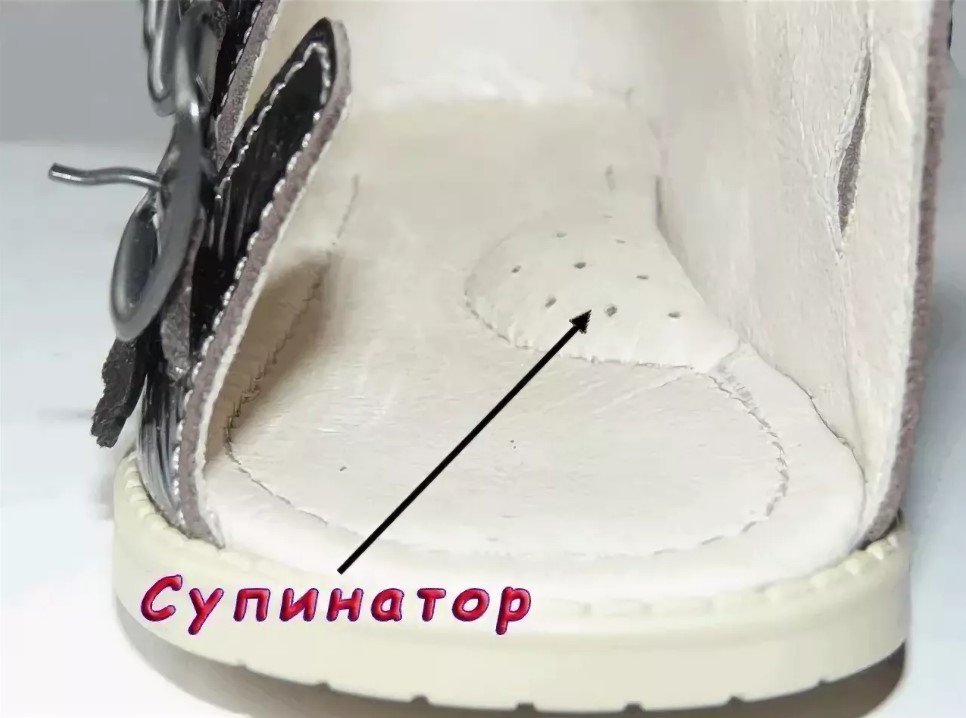

For preventive purposes, soft insoles of a small height are used so as not to injure the child and prevent sagging of the arch of the foot. They can be made of leather, cork, metal or plastic.
Questionable usefulness of supinators in infancy
If the child does not have problems with foot development, then they are basically unnecessary. In some cases, it even interferes with the normal development process, especially if the insole is of poor quality. A stiff and high insole weakens the arch muscles and causes abnormal arching.
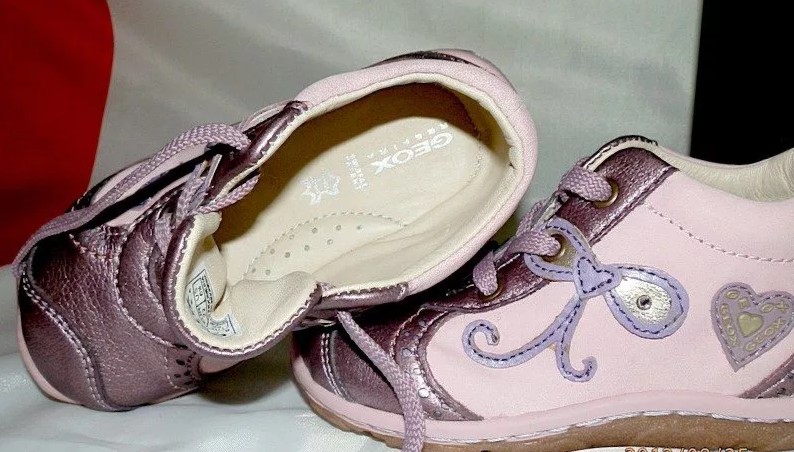

Podiatrists cite congenital weakness of the muscles and ligaments in the legs, accompanied by hypermobility of the joints, as one of the main causes of the problem. Regular barefoot walking combined with reasonable exercise (running, jumping, climbing stairs, etc.) helps muscles and ligaments to strengthen and function properly.
How to choose the right shoes with cushioning?
The choice of shoes with cushioning depends on their purpose. For a healthy, anatomically correct foot, choose shoes with orthopedic prophylactic insoles - VP-1 and VP-6. VP-1 has inner longitudinal vault sealing, while VP-6 has transverse and inner vault lining. Both serve to maintain the correct shape of the foot. Useful in case of high and long-term stress on the leg joints - athletes, hairdressers, shop assistants, pregnant women, overweight people.
Important!!! A distinction is made between valgus and varus deformities. With a valgus deformity, the foot bends inwards, while with a varus deformity, the foot bends outwards. The varus deformity is called clubfoot, while the valgus deformity is called flatfoot.

For the valgus deformity, shoes with VP-2 and VP-5 insoles should be used, with the VP-2 insole providing heel support and the VP-5 insole providing both heel and forefoot support.
As already mentioned, an important aspect when choosing helmeted shoes is the intended use.. And if you need a prophylactic pair, you can choose it yourself. The most important thing is to make sure that the size fits perfectly and that the foot pinator hits the right part of the foot. However, with any type of deformity, only a doctor can prescribe insoles, which are made individually based on an impression of the foot.
Why is the insole important in children's shoes?
Insoles in children's shoes are a separate and controversial topic. The fact that. essential in the event of a pathology or injury to the footis well known. With the so-called prophylactic supinators, the situation is much more complicated. Podiatrists' opinions are divided. Some believe that orthotics should be purchased for healthy children to prevent flat feet. Some orthopedists believe that using a shoe insert is important from the child's first steps.. They justify this by saying that a shoe insert:
- It supports the longitudinal and transverse arches of the foot;
- It relieves the child's sensitive spine;
- prevention of diseases associated with foot deformities;
- Creates a fusible foot shape with a pronounced arch;
- Makes walking easier with extra stability.

Other experts firmly reject this approach. They explain that wearing shoes with a closed arch in a healthy foot can cause longitudinal flatfoot for up to 7-9 years. This can happen because the muscles that are constantly in rigid support atrophy and no longer perform their function.
The well-known pediatrician Evgeny Komarovsky is skeptical about supinators in infancy. He says that this element doesn't shape the foot, just like gloves don't shape the hands and a hat doesn't shape the head.
Read more:The proof! We are born with a flat foot and have a pad of fat that acts like a roll. Only at the age of 7-9 years is the child's foot fully developed and resembles the foot of an adult. Then the use of insoles as a preventive measure is permissible. However, the insole must be low and soft.
Features of the models for children
Children's shoes with supinators are needed to form the correct arch of the foot, which is on the inside. This is a bulge that does not show when walking barefoot on sand or similar surfaces, indicating a lack of flat feet. Since children's feet are just forming, it is important to give them the right direction and shoes with an orthopedic insole should be chosen for this purpose.
It should be noted that all children up to the age of 2 have flat feet, which correct themselves. Therefore, it is not recommended for young children of this age to wear orthopedic shoes with a supinator. They are only chosen if the correct foot curve has not been formed by the age of 4.
The time frame for wearing these shoes is set individually for each child by the podiatrist. As a rule, all children of preschool age wear special orthopedic shoes or shoes with an insole. At the age of 6 or 7, you should consult your doctor again:
- If wearing shoes with a straight supinator has promoted arch formation, you can continue to wear shoes with a regular insole.
- If other defects have developed, a special custom-made orthopedic gaiter should be purchased. This is characterized by increased rigidity.
If there is a malposition, the child should always wear shoes with an orthopedic insole. To prevent flat feet, the insole can be used alternately with a normal sole. In one case or another, orthopedists do not recommend wearing soft rag slippers at home - it is better to walk on the floor barefoot or in socks to avoid foot curvature.
Another question is whether children's shoes should have insoles and whether these are necessary when the child goes to kindergarten. It is desirable for the child to be equipped with slippers, since he will be very active: when running, jumping and other physical games, the load on the feet should be evenly distributed. Rubber flip-flops are absolutely unsuitable for changing clothes. It is better to consider:
What materials are they made of
The shoe knot can be made of different materials:
- Metal. It can be combined with leather or plastic. The advantages are that it is a dense, rigid material that hardly flexes under pressure and provides good arch support.
- Leather. Used by most manufacturers in prophylactic models. Pros: This material is durable, easy to care for and prevents excessive slipping. In addition, a leather shoe sole absorbs moisture better than others and prevents odors from forming.
- Thick or thin plastic insoles. A classic option is the combination with leather. Advantages – attractively priced. Cons - quite fragile.
- Wood. Benefits - Material as dense as metal. Helps correct defects, used in Crockett & Jones footwear collections.
- fiberglass. Suitable for light summer footwear, most commonly used to prevent flat feet. However, it is not a universal option.
Leather is often used as an overlay by manufacturers of shoe inserts. It significantly reduces the cost of the product, but wears out very quickly.
Rigid materials are intended for the correction of curvatures that have already developed or for people who regularly subject themselves to great physical exertion. Supinator insoles made of gel or silicone are suitable for sports shoes. All soft models are suitable for children, including those made of leather or suede.
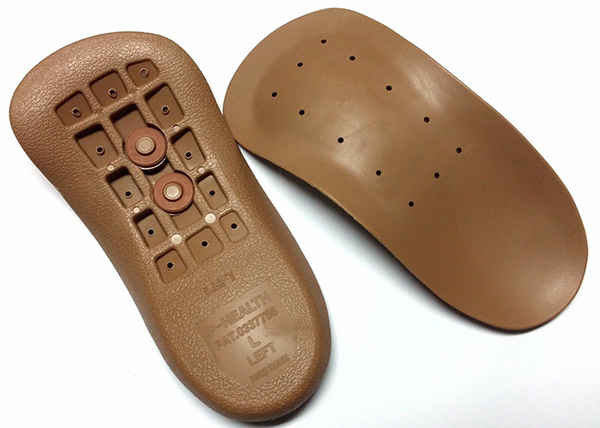




Benefits and possible harm
Pediatricians, physiotherapists and other doctors recommend orthotics with supinators as an effective way to reduce the intensity of pain in the feet. Wearing shoe inserts can also prevent pronounced discomfort, back pain, lower back pain, and knee pain. The advantages of shoe inserts are:
- Better cushioning, absorbing shock loads of the foot;
- Proper distribution of pressure, reducing stress on joints;
- Support of the longitudinal and transverse arches;
- pressure relief of the spine;
- strengthening weak ligaments;
- posture restoration;
- Stabilization of the foot during movement.
Despite the impressive list of benefits, there are potential downsides to wearing orthotics. An ill-fitting, unsuitable, or ill-fitting product can be inherently dangerous. The possible dangers of wearing insoles are described below:
Wearing standard insoles is acceptable in adults only if it is a preventive measure.
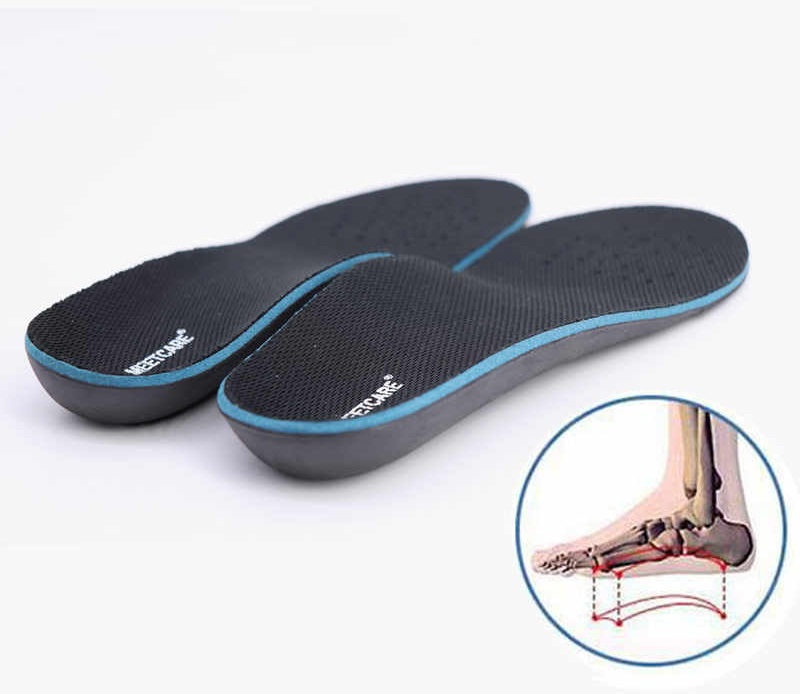
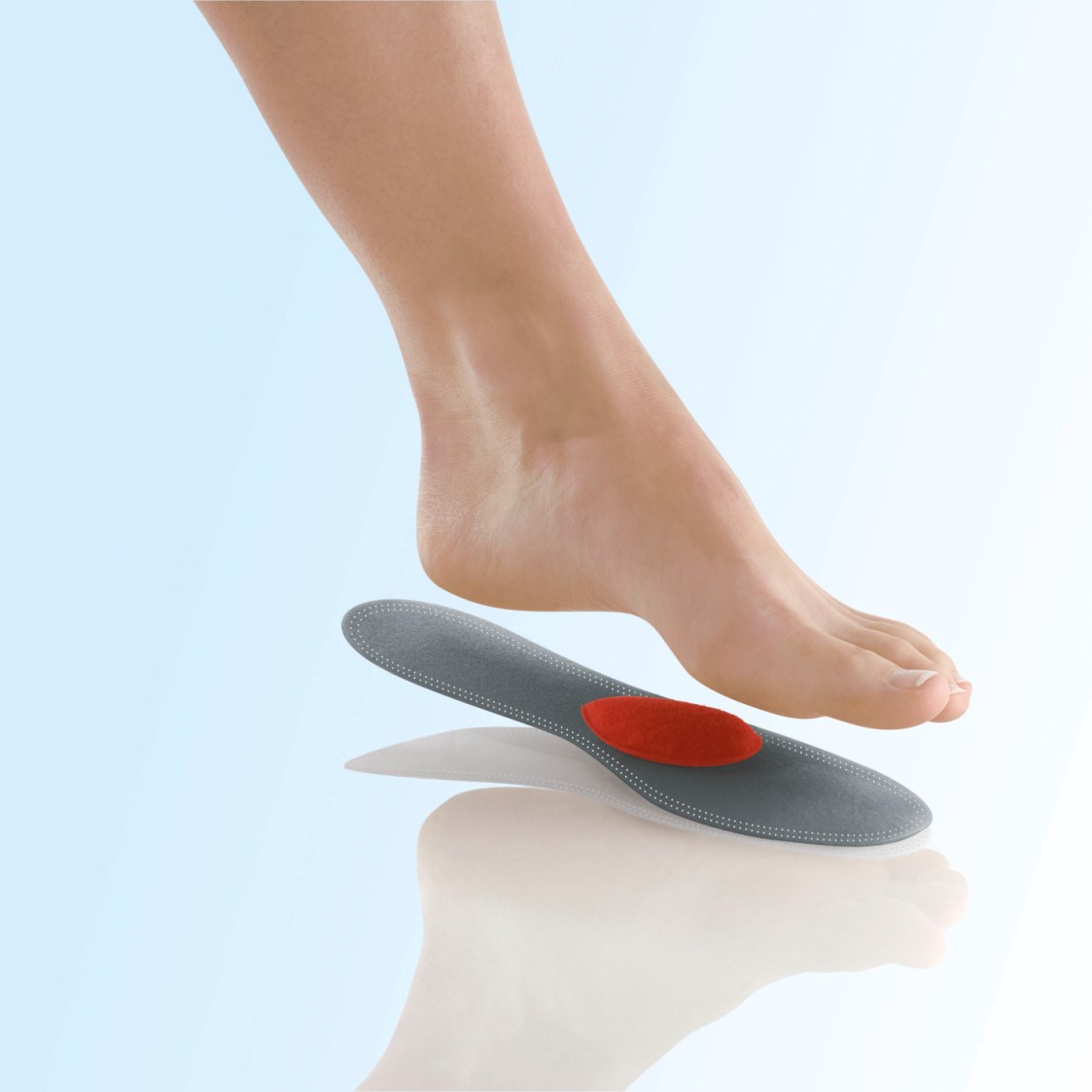


Features of insoles for children
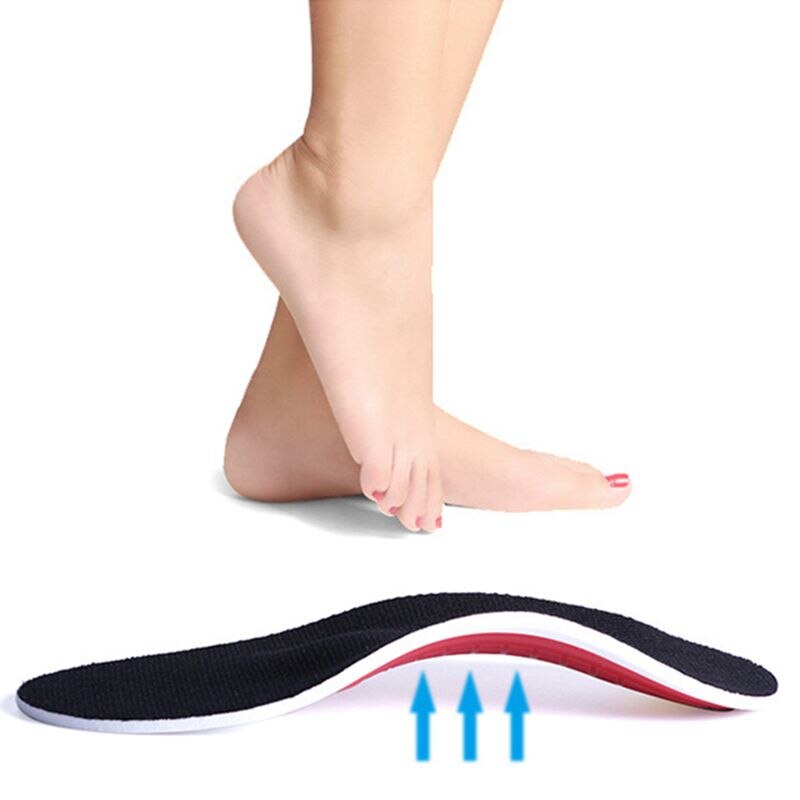
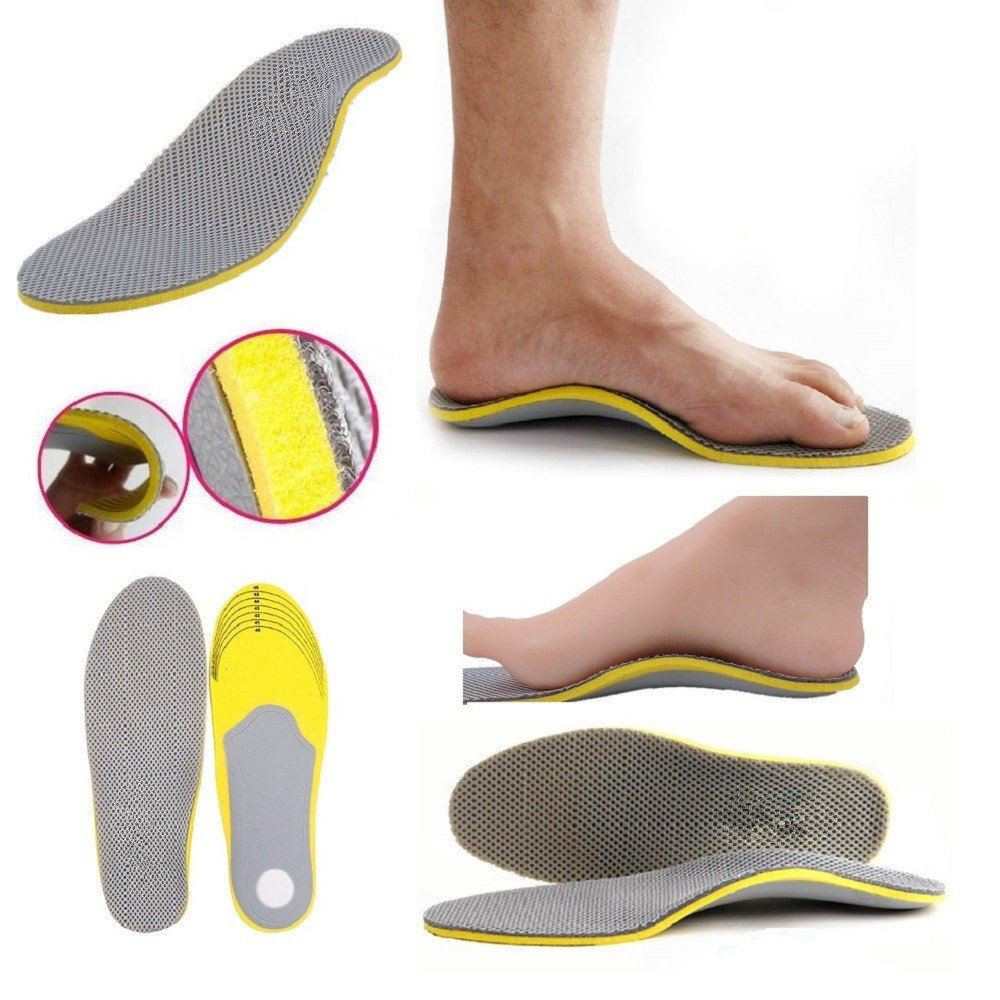
Due to the incomplete ossification process combined with high loads, children's feet may need additional support. The easiest way to ensure proper footwear alignment and reduce body weight pressure on the foot is to use special inserts. Diabetes, lower limb deformities, clubfoot and various forms of flat feet may require orthotics. Children need insoles that take into account the age parameters and all individual foot characteristics. Custom insoles for flat feet are usually made from a special thermoplastic material. The pad is heated to the required temperature and then adjusted to the child's foot.
Pre-made insoles are only recommended when custom manufacture is not possible for children under 7 years of age. Prophylactic insoles have been developed for children and young people without diseases of the musculoskeletal system and foot development. Their main purpose is to prevent problems and cushion when walking. Both soft and hard materials are used in production.
How do you check the quality of an insole?
You can check the quality of an orthopedic insole based on the following characteristics:
♦ The insole cushions when walking - this is necessary to activate the foot muscles during movement and to maintain blood circulation;
♦ the insole should have medium stiffness – too soft an insole does not support the arch of the foot, while excessive stiffness can cause pain and lead to improper load distribution;
The sole and orthopedic insole should be made of natural leather, preferably vegetable tanned, that is, without the use of chemicals in its manufacture, to avoid allergic reactions.
Beware of shoes of dubious workmanship. In such shoes, the insole may be in the wrong place. Incorrect placement can cause problems in the development of the foot, the child will complain of discomfort and rapid fatigue. This will only harm your child.
Children's shoes with cushioning should be purchased according to the size of your child's foot. With shoes that are bought 'in advance' there is a risk that the insole will not fit properly in relation to the foot. This can cause the foot to deform incorrectly.
When should you start wearing support shoes?
The age of five or seven should be carefully considered. During this period, children begin to take part in dance and sports activities, and the load on their feet increases. A shoe insert adequately distributes the shock wave and the increasing load and prevents the foot from being overstressed during physical activity.
An insole is a must when your child wears shoes outdoors, in kindergarten and at school. You can go barefoot at home. It makes sense to create natural conditions – an uneven surface. For example, with orthopedic mats that cause a natural massage and help keep feet healthy. Lay them out along the route that the child travels most often.
An insole prevents the emergence and development of flat feet, reduces the load on the spine and joints, thereby reducing the risk of osteochondrosis, arthritis and arthrosis of the joints, poor posture and other diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Children's shoes and Supinator insoles can be purchased at Ortix Orthopedic Stores.
Head of the Ortix training center, specialist in orthopedics, general practitioner
What is an orthopedic splint?
Orthopedic footbeds are products designed to support the arch of the foot (lateral or longitudinal). Put simply, a foot splint is usually an insole that is placed in normal or special footwear (orthopaedic shoes, sports shoes or hunting shoes). This is necessary if the foot is tilted inwards or if the person has been diagnosed with flat feet.
So why are pronators and supinators so important? First of all, it is good to understand the difference between the two. Pronators tend to support the forefoot, which is very important in the case of a transverse flatfoot. In supinators, they often provide support along the arch of the foot or around the heel. These aids are essential for flat feet as they result in a loss of spring function in the feet. This leads to the fact that all the stress of the movement is transferred to the joints, spine and brain, since each step in this state results in a micro-shock.
In such cases, orthoses are indispensable as they reduce the intensity of pain when walking and protect the foot from possible deformities, such as e.g. B. a flattening of the foot protect. They also normalize the entire musculoskeletal system.
In other words, footrests are necessary in the following cases:
- to normalize blood flow;
- with transverse flat feet;
- to improve general well-being;
- to counteract excessive leg fatigue;
- after injuries or fractures of the bones of the feet and lower legs;
- to support the arch of the foot in the longitudinal direction (in the case of a longitudinal flatfoot);
- to relieve ankles, knees, hips and spine.
types of deposits
There are many different types of supinators. There are ledges made of cardboard (even if they are not very useful), devices made of leather, cork and plastic. Sometimes you also come across a supinator made of silicone or metal. In recent years, the most popular is the leather supinator with a metal plate adapted to the shape of the arch of the foot. Externally, almost all insoles are covered with leather, oilcloth or foam.
As mentioned earlier, there are two main types of footbeds:
The latter are especially necessary for women, since the forefoot is often deformed by wearing high-heeled shoes for a long time. While orthotics with foot supports can be used in shoes and boots, this is virtually impossible in sandals. Many women are therefore seriously considering how to make their own supinators for forefoot support. But there is no need to reinvent the wheel.
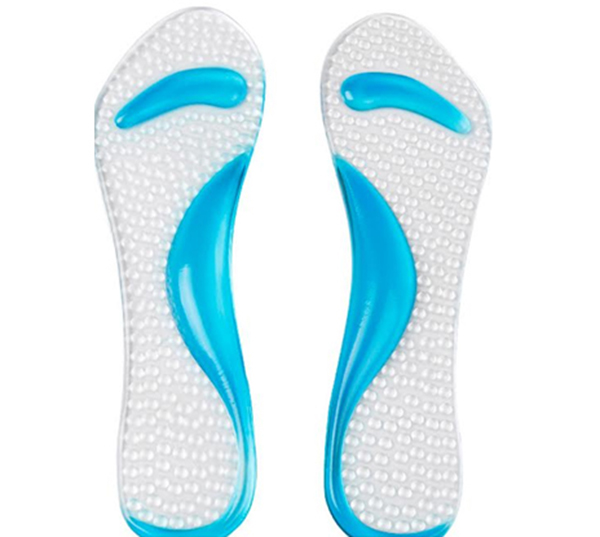
Luckily, there have long been gel supinators on the market that can solve this problem. Gel shoe inserts have an adhesive surface with which they can be fixed. There is a wide range of gel supinators. They are easy to attach to the front of sandals or open shoes, but there are also gel inserts that lie under the heel or provide longitudinal arch support.
If you have a longitudinal foot problem but do not like gel insoles, you can also choose other models from proven manufacturers. Strutz insoles, for example, have been particularly popular lately. The special feature of these products is that they do not fit in shoes or boots, but are worn on the foot and thus fundamentally change the principle of load distribution on the foot. Each of these 'insole' consists of an elastic band (black or tan) to which is attached a soft cushion that wraps under the arch of the foot when the device is worn. These insoles do not need to be adjusted and are a good solution for people who spend a lot of time on their feet.
Factors contributing to the development of this pathology:
- Weak muscles due to lack of exercise.
- Congenital weakness (underdevelopment) of the ligaments and tendons on the legs.
- Excessive strain on the ligaments of the foot due to overweight (obesity) in the child.
- Due to insufficient muscle tone (hypotension).
- Developmental disorders of the musculoskeletal system
- Often caused by wearing uncomfortable or soft footwear with insufficient foot support.
- Weakness of the body, prematurity and frequent acute respiratory infections at a young age.
- Scientists attach great importance to genetic (hereditary) predispositions, endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, diabetes) and bone formation disorders.
Let's understand these terms so that there are no wrong conclusions.
According to GOST 54407-2011, orthopedic shoes are shoes whose design was developed taking into account pathological abnormalities in the foot, shin or hip.
Such shoes are called therapeutic shoes and make it possible to correct the deformity and prevent its further development.
Wearing therapeutic shoes is recommended by an orthopedist only when diagnosing deformities and pathologies of children's feet (clubfoot, valgus deviations, congenital flat feet, cerebral palsy and others).
However, it is also generally accepted that the term 'orthopaedic footwear' refers not only to therapeutic but also to preventive footwear.
Prophylactic shoes are shoes designed to prevent foot abnormalities.
Prophylactic shoes are correct, anatomical children's shoes recommended for healthy children whose feet look the way they should at their age. These shoes can be worn by anyone. It is important to prevent foot deformities.
Therefore, 2 large groups can be distinguished: therapeutic and preventive.
What orthopedic shoes for children should be
Let's find out what details should be in children's orthopedic shoes:
It is very important that children's shoes are made of natural materials. Thin, soft leather with as few seams as possible should be used for the inside of shoes and sandals so that they do not pinch the foot. A genuine leather upper ensures that your feet do not sweat.
hard heel
Children underfoot must wear a solid heel! According to the state standard, shoes for infants and preschoolers cannot be made with an exposed heel. The child's heel must be immobile and unable to move side to side in order for the child to learn to place their foot in the correct position. Soft-backed or open-heeled shoes will not hold the child's foot in place and can cause the child to tip over or subluxate. Even a healthy foot cannot withstand the load and deform. When shopping for shoes, remember to check the heel - just press the toe against the heel with force. The heel of a good quality shoe should not bend.
Orthopedic therapy shoes have a higher heel pad than prophylactic shoes. The high, rigid supports of the shoe fix not only the waist, but also the ankle, which with constant wear ensures the correct development of the articular surfaces and prevents the further development of deformities.
In the case of sandals and therapy shoes, the rear part of the sole merges into a more rigid shoe on the sides, which also keeps the child's foot in the correct position. While such shoes are not always comfortable, many children can learn to place their foot in the correct position in this way.
At the same time, the stiffer heel shoe is the most comfortable shoe with soft piping on the inside of the back that prevents the child from rubbing against the shin during movements.
insole
What is the insole in children's shoes? A bumpinator is a special insert in the inner sole of a shoe. It is located on the inside of the insole, under the longitudinal arch of the foot. It maintains the spring function of the foot by reducing stress on the spine and joints, promoting proper arch formation and rotating the foot outward.
Should you be looking for shoes with a hard sole?
The sole should be flexible and soft, not 'shockproof' and inflexible. When checking the elasticity of the sole, make sure that it gives where the foot rolls off, namely at the base of the toes. This gives your child's feet the right movement and optimal foot control.
A paragraph is a must! The lack of a heel counter leads to overloading of the heel area. It also prevents the child from falling backwards. For small children, a wide and stable heel of 5-15 mm is advisable. For older children, the heel is not necessary as a design element - the difference in height between the front and back of the shoe is decisive.
When should you buy shoes for your baby: when he's just starting to get out of bed or when he's already taking his first steps?
To be honest, there isn't much of a timing difference between the two. Buying shoes for your child can be anything, but at the latest when they start to move actively on their feet.
Parents should adhere to the principle of maximum comfort and not maximum 'orthopaedic':
3. the back of the shoe should be no higher than the ankle, keep its shape and securely fasten the heel.
4. the toes should be wide enough for the child to wiggle their toes in the shoe.
5. Shoes should not be bulky or heavy so that they do not restrict freedom of movement.
6. It is important to choose the correct shoe size as children's feet should not 'ride' in them.
Neither the brand name, nor the high price, nor the cool look of the shoes and certainly not the use of the term 'orthopaedic' guarantee the right quality. Only by trying on and feeling a few pairs can you find a really good and reliable pair of shoes for your child.
- Supinator or foot pinator.
- What does the insole of a child's shoe look like?.
- Insoles are suitable for.
- What is a shoe insert?.
- Hypopronation shoe inserts.
- Manufacture of shoe inserts.
- orthopedic insoles.
- Argo shoe inserts.