When suffering from joint diseases, it is important to ensure complete rest and minimize stress on the affected area. For this purpose, a rib bandage (e.g. model Orlett BAN-101(M)) can be used in acute conditions. The bandage made of thick and elastic material has a compressive effect on the ankle, which also prevents bleeding and the accumulation of blood in the joint cavity - the formation of hemarthrosis. In addition, four side stiffening ribs prevent the foot from bending during movements, which reduces pain.

- pain in the ankle
- Causes of ankle pain and associated symptoms
- Physiological edema
- The 'female' causes of swollen feet include:
- Clinical manifestations of valgus and spinal ankle
- What are the risks of ankle deformity?
- Signs of thrombosis
- Diagnosis of thrombosis
- ACCOUNTING
- GRIGORENKO Andrei Alekseevich
- Tereshkin Vitaly Vladimirovich
- SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT
- Recovery after a fracture
- Ankle splint for sprains – what you need to know
- Computed tomography of the ankle, safety
- How a CT scan of the ankle is performed
- medication
- Nutritional recommendations
- period of rehabilitation
- complications
pain in the ankle
The development of pain in the ankle joint has many different causes, which depend on age, lifestyle and accompanying pathologies. However, if there is no trauma, the development of pain in the ankle joint may indicate a number of pathologies - gout, bursitis, arthritis and many other problems. The most obvious causes of ankle pain are acute injuries (sprains, twists, fractures) caused by falls, traffic accidents or active sports and lifestyles.
Ankle pain also varies greatly: it can be stabbing or burning, painful or throbbing, and can occur gradually or suddenly. It is very important that the doctor diagnoses the cause of ankle pain and selects the appropriate treatment. Based on the type of pain and the accompanying complaints, symptoms and manifestations, the main causes of the joint problems can be identified and the treatment tactics, the scope of the necessary diagnostic measures and the subsequent rehabilitation can be determined. Sometimes treatment only requires rest and protection, but in some cases surgery may be the only salvation.

Causes of ankle pain and associated symptoms
The ankle joint is very complex. It consists of bones, cartilaginous structures and soft tissues (ligaments and tendons). Any injury or disease that affects the bones, articular surfaces, or ligaments can cause ankle pain. The patient cannot always associate the pain with a previous event, injury or illness, so the cause of the problem must be determined. The most common causes of ankle pain include:
Ligament sprains – damage to one or more ligaments as a result of various traumas (fall, walking on uneven surfaces, sports). A quick twist or twist of the ankle inward can damage the ligaments. Most commonly, the anterior ligament (talar-malofemoral ligament) is damaged, resulting in severe, throbbing pain on the outside of the ankle. There may also be bruising, swelling or instability of the joint. The medial ligaments are less commonly affected - the symptoms occur on the inside of the ankle.
Tendonitis is irritation and inflammation of the tendon that attaches muscle to bone. Ankle tendonitis is most commonly associated with damage to the tendon that attaches the ankle muscle to the surface of the bone on the outside of the ankle. It often occurs after exercise or when walking on slippery, uneven surfaces. With this type of injury, the ankle feels painful, and the feeling is bothersome, dull, lasts for several weeks, and increases with walking and standing. There may be swelling and a cracking sensation in the outer part of the ankle. Possible posterior tibial tendonitis, which typically causes pain and swelling on the inside of the joint and, if left untreated, can lead to severe loss of movement.
Osteoarthritis is an age-related change in the joint caused by the gradual destruction of cartilage and the rubbing of bones against each other. Damage to the Achilles tendon, which connects the muscles of the lower leg to the heel bone, causes a burning pain in the back of the ankle with tissue swelling and stiffness in the heel and calf. Such problems can occur during exercise, wearing ill-fitting footwear, and in the presence of bony heel spurs. Arthritis often causes ankle pain when walking and at rest. At this point, three types of osteoarthritis are possible. Over time, osteophytes (bony outgrowths) form, making movement difficult and causing discomfort. The pain occurs intermittently and gradually becomes constant and acute.
Physiological edema
Swelling in the legs can have physiological causes, that is, they are caused by certain circumstances affecting a healthy body and are not a manifestation of a disease. Such causes can be:
- Salty foods. Salt binds water. And if you eat a lot of salty foods, especially at night, you may experience swelling in the morning;
- Alcohol. Alcohol also binds water. That is why a person looks swollen after alcohol abuse. The problems are not limited to the face; the feet can also swell;
- hot weather. When it's hot, blood vessels dilate as the body tries to normalize heat exchange. The increased blood flow increases the risk of congestion and swelling in the legs;
- Sitting or standing for long periods of time. When the legs remain in the same position for a long time, blood stagnates in the legs, causing swelling. The worst thing is sitting with your legs crossed. Standing in one place for a long time doesn't help either. Swelling in the legs is typical for people with standing jobs - hairdressers, saleswomen, chefs;
- Uncomfortable footwear. When shoes impede blood circulation in the foot (high heel, narrow arch, tight straps), their presence causes swelling.
The 'female' causes of swollen feet include:

- Premenstrual syndrome. Before menstruation, the hormonal balance is disturbed - the relative estrogen increases, and the estrogen stores fluid in the body;
- Pregnant women. During pregnancy, the woman's body produces large amounts of progesterone, which reduces the tone of blood vessels. This contributes to blood congestion in the legs. The growing fetus can constrict large blood vessels, which is also the cause of swelling that becomes evident in late pregnancy. Swelling can also be a symptom of gestosis (late pregnancy).
Clinical manifestations of valgus and spinal ankle
The clinical picture of this pathology is unclear in the initial phase and does not reveal clear symptoms indicating a disease. As the ankle deformity progresses, there is a visible deviation of the ankle in different directions. This is visible to the naked eye. Unfortunately, at this stage of the deformity it is already very difficult to help the patient without surgery. That's why it's important to know the first typical symptoms that you should pay attention to.
So you or your loved ones should see an orthopedist as soon as possible if the following symptoms occur:
- The heels can no longer be pressed flat against each other when standing;
- When you look straight ahead, your shins appear to diverge or converge;
- The soles of shoes that are worn for a long period of time show noticeable signs of wear on the outer or inner edge;
- plantographic examination reveals abnormal foot position in the form of flat feet or club feet;
- Acute pain in the ankles and feet occurs with prolonged walking;
- Your foot often tips over in the ankle area;
- You have a feeling of instability and difficulty maintaining balance when walking.
An ankle deformity of the varus type is characterized by the heel tilting inward and the load when walking is distributed to the inside of the sole. This leads to deformation of all joints. The joint of the big toe is most affected. This type of curvature is common in women who are used to walking in high heels.
Ankle valgus deformity is often associated with clubfoot and is most commonly diagnosed in children under five years of age. It is a result of the abnormal formation of the foot and lower limbs during fetal development. These children often have hip dysplasia. You are overweight and have a hypersthenic body constitution. This is exacerbated by vitamin D deficiency and the development of rickets. As a result, they develop compensatory deformities of the tibia and femur. A so-called O-shaped deformity of the lower limbs occurs.
What are the risks of ankle deformity?
Now let's look at the risks of ankle deformity. Most often in childhood it leads to complete curvature of the lower limbs and the development of clubfoot, which is very difficult to correct in the future using conservative methods. The bones of the foot, their alignment, connecting joints, ligaments and tendons are actively formed before the age of five. Any deviation from the norm has negative consequences. The child begins to delay in physical development because he is unable to run and jump at the level of healthy peers. This leads to the accumulation of excess body weight, which can develop into full-blown obesity.
The metabolic disorders further exacerbate the pathological changes in the cartilage in the ankle joint. The length and flexibility of the tendons and ligaments are changed. The tendon-tendon apparatus is no longer able to fix the bone heads that form the joint capsule. This leads to numerous recurring strains and sprains.
In adults, deformities of the ankle joint damage nerve fibers and disrupt the blood supply to the soft tissues of the foot. This leads to pain and reduced endurance during physical activity. There is a risk of heel spurs forming.
An equally serious complication is the destruction of all large joints of the lower limbs. These include deforming gonarthrosis, coxarthrosis and arthrosis of the hip joint. The destruction of the intervertebral discs can also be accelerated by the increasing cushioning load that the ankle joints are also supposed to cushion.
Only by contacting an orthopedist in a timely manner and starting to correct an existing problem can the development of these dangerous complications and negative consequences be avoided.
Signs of thrombosis
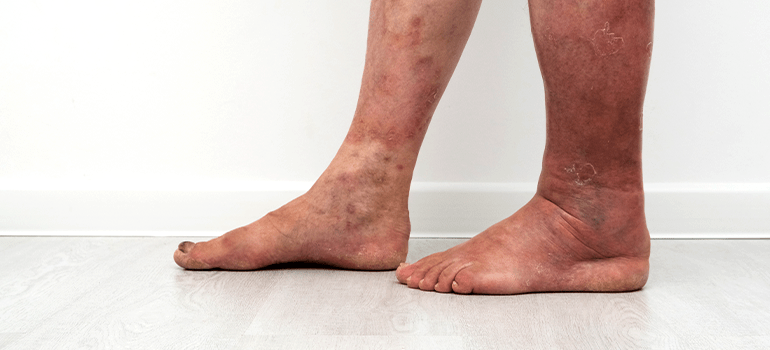
Of course, only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. However, even before a professional examination, there may be suspicion of thrombosis in the limbs and other parts of the body
- Swelling. The swelling usually occurs at the site of the embolism and gradually spreads to the entire limb. If the problem occurs in only one arm or leg, the clot may be localized there;
- Occurrence of cramps. Regular cramps may indicate a developing blood clot;
- Sudden pain in a limb;
- discoloration of the skin;
- A change in skin temperature at the site of the blood clot.
If you experience one or more of these symptoms, please contact your doctor. Never use self-medication: folk remedies and unreliable open source recipes do not bring relief and can only cause harm. Thrombosis is a dangerous condition that should only be treated by qualified professionals.
Diagnosis of thrombosis

It is not uncommon for the vessels in the leg to be the site of a thrombosis. The diagnosis of acute thrombosis can be made through anamnesis. A qualified doctor can diagnose a blood clot in the veins if you have the following symptoms
- a feeling of heaviness, a stabbing pain in the legs;
- usually only one of the patient's limbs is swollen;
- the skin over the blood clot is shiny and has an unhealthy blue color.
After taking the anamnesis, the doctor diagnoses the disease using laboratory and instrumental methods. Namely:
- He sends the patient for a blood test;
- orders a duplex ultrasound scan;
- The patient's entire venous system is examined with X-rays.
If the thrombosis is located directly in the patient's lower limbs, functional tests are ordered.
Modern medicine has taken advantage of innovative technologies and developments that make the diagnosis of various diseases much easier.
ACCOUNTING
GRIGORENKO
Andrei Alekseevich
Founder and director of the clinic.
Neurologist, Doctor of European Osteopathy (DOE), reabilotologist, orthopedist.
Tereshkin
Vitaly Vladimirovich
Osteopath, manual therapist, rehabilitation therapist.
Specialist in regenerative medicine, negative pressure therapy, medical stretching and remedial gymnastics.
SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT

| What is the difference between osteopathy and manual therapy? | Read the answer>> |
| Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Natus, provident harum non, voluptate place at quod! Nam aliquam maiores numquam, culpa asperiores at accusantium earum? Officia quas repellat, nam excepturi sapiente. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Possimus omnis modi nobis dicta repudiandae, quo fugiat, aperiam, mollitia expedita animi nihil explicabo incidunt eius laborum tempore quae? Doloribus dolores, voluptate! | |
| How is the fluid circulation in the tissues optimized? | Read the answer>> |
| Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Natus, provident harum non, voluptate place at quod! Nam aliquam maiores numquam, culpa asperiores at accusantium earum? Officia quas repellat, nam excepturi sapiente. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Possimus omnis modi nobis dicta repudiandae, quo fugiat, aperiam, mollitia expedita animi nihil explicabo incidunt eius laborum tempore quae? Doloribus dolores, voluptate! | |
Recovery after a fracture
During complete immobilization, the leg muscles atrophy due to the lack of active exercise, but physical activity should be increased gradually. For a quick recovery, semi-rigid models with a medium degree of immobilization are recommended. Adjustable orthoses are particularly effective: in the initial stages of recovery, when the stiffening ribs hold the limb in a safe position and the range of motion is limited, compression is gradually reduced, which is important for restoring muscle activity. Additional devices such as pneumatic chambers can be used to control the strength of compression, which is important for activating blood circulation in the injured area.
In the late stages of rehabilitation, when the bones have already grown together but final recovery is still some time away, effective flexible medium to light fixators such as the Orlett BAN-101 ankle brace are used.
Answer: 'I had a very difficult injury - fracture of the external and posterior ankle, tear of the deltoid ligament and complete posterior dislocation. This bandage helped me a lot during my rehabilitation. It holds the joint very well and there is no swelling, even under strain.
Ankle splint for sprains – what you need to know
An important aspect of sprains is immobilizing the joint. Elastic bandages are used for minor sprains. Due to the compression effect, they improve blood circulation and reduce swelling (e.g. Bauerfeind AchilloTrain Pro).
A moderate sprain requires more rigid immobilization, for which medium strength orthoses are suitable, which ensure preservation of the ligaments but limit active movement of the ankle. Semi-rigid and rigid fixators provide secure immobilization of the joint and allow the ligaments to fuse properly. The load on the pathological area is reduced and the swelling is less pronounced. The secure fit has a pain-relieving effect, which is also used in the rehabilitation of torn ligaments.
Experience report: 'I used the Bauerfeind AchilloTrain Pro ankle orthosis for ligament strains. It has a massaging effect when moving, the material does not wrinkle and the groove in the middle of the pad helps reduce tissue swelling. In addition, the model is comfortable to wear and can be worn with shoes.
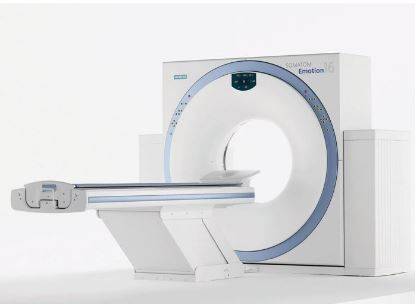
Computed tomography of the ankle, safety
The device used to perform the computer-aided analysis is called a CT scanner. It consists of several interconnected parts:
- X-ray tube – a direct radiation source that directs the rays through the thickness of the human body;
- Gentry frame – the frame that receives the backscatter of the processed signals. This is the mechanism inside that moves one or more X-ray tubes while examining the patient;
- Data conversion and analysis system – a set of devices that evaluate x-ray images and convert them into data about the condition of the examined body part;
- Mobile computer-assisted operating table (transporter) – the direct place where the patient is placed for examination. During the CT scan, the table moves the patient's body relative to the simulated information field that the device requires;
- the computer program used to transcribe the final analysis and release the data.
Obtaining information about the state of health or the presence of pathology in the ankle joint is based on the ability of various types of tissue to absorb and transmit a certain dose of X-rays, that is, a stream of particles with a high energy charge and frequency.
During the procedure, special sensors actively register the degree of reduction or increase in the number of particles as they pass through different environments in the human body. The highest absorption of radiofrequency energy is found in the bone tissues of the body, the lowest in organs with single or multiple air cavities.
This technique has been used for many decades and has proven to be extremely useful in diagnosing many diseases. Additionally, it is completely safe when used judiciously - a CT scan of the ankle is only performed when indicated and should not be done without reason.
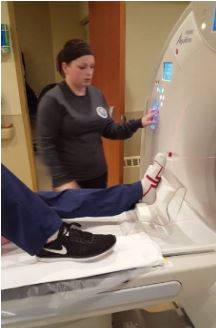
How a CT scan of the ankle is performed
After the paperwork is completed, the patient is invited into the CT room and lies down on the examination table. The ankle is fixed in a special holder to avoid motion artifacts, and the rest of the body is covered with a lead apron. Depending on the complexity of the case, the patient spends around 10-15 minutes in the practice. If vascular anomalies or tumors are suspected, an intravenous contrast agent is administered to clarify the diagnosis.
At our center, the captured images are post-processed to maximize data accuracy. As a result of the examination, all images are taken in the axial plane, and then, with the help of computer programs, horizontal and frontal projections are created so that the doctor can assess the structure of the ankle joint from all sides.
For a more precise CT scan of the ankle, it is better to use a multi-spiral CT scanner, such as the Siemens Somatom Emotion 16 in our Magnes center. This CT scanner is the best for CT examination of the ankle in terms of price-performance ratio and the quality of the images obtained.
Procedure for performing a CT scan of the ankle joint
In complicated cases, especially if cancer is suspected, a contrast agent may be used. The preparation is administered intravenously and allows a more precise analysis of the growth stage and location of metastases, as well as the assessment of blood vessels and the detection of circulatory disorders in the examined area due to atherosclerosis or thrombosis.
medication

Recovery from an ankle fracture also includes taking medication. At this point we would like to warn you: Never prescribe medication to yourself or a relative without consulting a specialist. Treatment is prescribed individually - the doctor takes into account all factors, including the presence of other diseases in the patient. Before starting rehabilitation after an ankle fracture (immediately after the injury), medical staff use strong painkillers (injections), such as: E.g.:
These are needed to relieve severe pain. Later, the patient should switch to milder tablets so as not to develop dependence on strong painkillers in ampoules.
Antibiotics are also prescribed in the first phase to prevent the patient from getting an infection. Non-steroidal drugs are:
These medications are needed to relieve swelling and inflammation. Also, the patient needs to take drugs that reduce congestion, improve blood circulation and normalize metabolic processes, such as Trental and Ascorutin. The blood's job is to transport the nutrients that the cells need to regenerate damaged tissue!
So-called chondroprotectors, such as Structum, are needed to repair the cartilage. The doctor will also prescribe vitamins and minerals (the same calcium needed for fusion), including B12 (cyanocobalamin), which has a blood-building effect.
Again, taking the right medications will only speed up the rehabilitation process, otherwise self-medication can significantly worsen the patient's condition! The doctor will take into account any contraindications such as: B. the possible presence of kidney or liver dysfunction, which may require more careful drug selection.
Nutritional recommendations

Here too, it's all science - it's not just the limb that suffers from the injury, but the whole body! It must be saturated with a range of nutrients, from minerals to amino acids, to reach the damaged area where the regeneration process takes place. An individual diet is put together for these patients, taking into account 'what you can do, what you have to do' and 'what you can't do'.
Although vitamins and minerals are prescribed for the injured person, the body's ability to absorb them naturally, that is, through food, should not be neglected. Here's what you can and should eat:
- Poultry – chicken and turkey are ideal;
- rabbit meat, which is often recommended for patients with bone fractures;
- fermented milk products;
- various nuts and seeds;
- berries and fruits, both fresh and dried;
- vegetable stews, salads; some vegetable oil can be added;
- fish, preferably freshwater;
- Oatmeal;
- green parsley, dill;
- clear soups – can be chicken, turkey or rabbit.
- Lightly toasted white bread.
Important: This is a sample list; Every person has their own diet that suits their needs. By the way, after such an injury, patients not only have to eat, but also drink plenty of fluids (this is a must for joints). What to drink:
- Mineral waters, slightly alkaline, are needed;
- sweet and sour snacks, juices;
- Milk snacks – tasty and useful (calcium);
- compotes.
Drink 2.5 liters of fluid on the day the plaster is removed! A decoction of rose hips and chamomile is often used as a folk remedy. What not to eat and drink:
period of rehabilitation
Once the cast is loosened, rehabilitation begins immediately. The aim of rehabilitation treatment is to fully regenerate tissue, restore nerve communication between the limb and brain, improve blood circulation and rebuild muscles lost during rest. How does rehabilitation work after an ankle fracture?
- In the first month, the doctor recommends light activity that focuses on the toes and knees. These exercises help restore joint mobility and gradually progress to more complex, compound exercises.
- The second phase includes more difficult exercises: jumping, fast walking, swimming, running. It lasts between 1.5 and 2 months, although these periods depend on the individual characteristics of the patient's body. For example, older people need much more time than children. Age is not the only limiting factor. It also depends on the complexity of the injury and chronic illnesses.
Important: Following doctor's recommendations is no less important. If these are followed, the positive prognosis is usually 100 %. Patients who do not adhere to the rest periods and special diet risk prolonged treatment and serious complications.
complications
A fragile mass is easily traumatized and can be difficult to repair. In addition, traumatization of the ankle joint represents an aggravating factor in therapy. It should be noted that compliance with medical recommendations, daily routine and diet can reduce the negative effects to zero, but unfortunately no one is immune from this. What are the possible complications?
- Formation of a false joint. A false joint is the formation of mobility in an area of bone where it should not be there. It is possible to eliminate this consequence through surgery.
- Development of arthritis, including purulent arthritis (if infected). This complication occurs more often after surgical interventions, but it can also occur with conservative treatment if rest and a balanced diet are not observed.
- Damage to the joint, e.g. B. Osteoarthritis. Partial, slight damage to the synovial membrane restricts the synthesis of synovial fluid. This leads to limited mobility of the joint, accompanied by painful sensations.
In some cases, damage to nerve structures can lead to loss of sensation and partial loss of innervation to the foot. Although these consequences are rare, they do occur.
There are many other complications, but they occur much less frequently than the variants described above.
Read more:- The hock in which the person is located.
- The bone where the ankle is located.
- The pubic ligament where it is located Photo.
- The Ligamentum Treitz, where it is located.
- The hock is the place where.
- dislocation of the ankle.
- The ankle bruise is where the picture is taken.
- The lateral ankle is.