Media registration certificate (Information Agency 'Public News Service') EL No. FS77-73623, issued on September 14, 2018 by the Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technologies and Mass Media (Roskomnadzor). Founder: Autonomous non-profit organization for the promotion of public information and education 'Media Holding 'Public News Service' (OGRN 1187700006328).
The opinion of the editorial team does not necessarily reflect the opinion of the authors.
The editorial team supports and shares the vaccination policy of the population.
- Causes and symptoms of synovitis of the ankle joint
- Causes of ankle tendonitis
- Indications for an ultrasound examination of the ankle joint
- How does the ultrasound examination of the ankle work?
- TREATMENT
- GRIGORENKO Andrey Alekseevich
- Tereshkin Vitaliy Vladimirovich
- Treatment and rehabilitation period:
- Symptoms of tendonitis
- Treatment of tendinitis and tendovaginitis
- SURGICAL TREATMENT
- possible side effects
- contraindications
- Stages of impingement formation
- Hip impingement symptoms
- In which age
- Where should learning take place?
- Documents
- Our advantages:
Causes and symptoms of synovitis of the ankle joint

Ankle tendovaginitis is an inflammation of the synovial membrane that covers the tendon responsible for movement of the foot. The inflammatory process can be acute or chronic and is accompanied by symptoms such as pain, swelling, limitation of limb mobility, etc.
The causes of ankle tendinitis are varied, most commonly due to injury or infection of the tendon sheaths. If the patient sees a doctor early, the disease is usually treated with medication.
The synovial membranes that surround the tendon sheaths of the foot may be located on the dorsal or plantar side of the foot. The consequences of untreated inflammation can be catastrophic, including complete loss of limb function. The patient may eventually become disabled. Therefore, a doctor should be consulted at the first signs of the disease.
Causes of ankle tendonitis
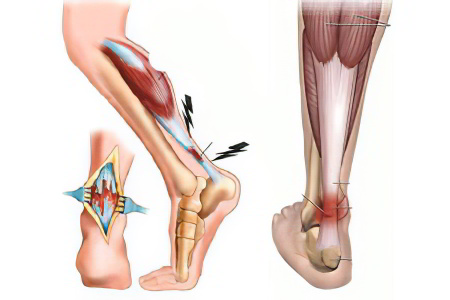
Ankle tendinitis can have the following causes:
- Microinjuries to the tendon sheaths of the foot. It occurs when there is significant overload or anatomical imbalance in the structures of the foot. Athletes, ice skaters, steppers and ballerinas are at risk of developing tendonitis.
- Flat feet can lead to the development of tenovaginitis of the foot. This also applies to congenital and acquired deformities of the lower limbs (heel foot, hollow foot, club foot, etc.).
Further risk factors for tenovaginitis can therefore include:
- Rickets;
- Poliomyelitis;
- Wearing high-heeled shoes;
- overweight;
- standing work;
- aging of the body;
- Inherited weakness of the ligamentous system;
- lack of physical activity.
- Presence of a nidus of purulent infection in the body. In this case, the pathogenic flora penetrates the tendon through the bloodstream or through direct contact with the tissue and begins to multiply in the synovial capsule. They constantly produce fluid, which provides a favorable environment for bacterial growth.
Pathologies such as:
- panarritis;
- Purulent arthritis.
- Injuries to the foot with penetration of infection;
- osteomyelitis;
- phlegmon;
- abscess, etc.
- Tendonitis of the foot can be caused by the following diseases: flu, gonorrhea, tuberculosis, brucellosis. In this case, the infectious agents enter the synovial sheath of the foot with the bloodstream.
- Rheumatic diseases are another risk factor for the development of synovitis of the foot. These include Bechterew's disease, systemic scleroderma, Reiter's syndrome, rheumatism and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Bone and soft tissue injuries to the foot are dangerous because pathogenic flora can invade the foot and cause inflammation. This can occur with deep burns, splinters in the foot, puncture wounds, cuts, fractures and tendon tears with compromised skin integrity.
- Particular attention should be paid to performing pedicures with non-sterile instruments, as this is the cause that often leads to the development of tendonitis in women. If the cuticle is cut with unsterile tools, the infection can get under the nail. Sweat and sebum accumulate where the skin meets the nail plate, providing a favorable environment for the growth of bacterial flora. As a result, pus forms in the toe, which can lead to the development of radiculitis of the foot.
Indications for an ultrasound examination of the ankle joint
Apart from obvious injuries, any complaints in the ankle joint can be a reason to make a diagnosis: pain of varying intensity and type, limitation of mobility. To understand what caused these symptoms, the doctor needs to know exactly the condition of the joint.
An examination is recommended in the following cases:
- for bruises, injuries, damage in this area;
- in the event of a misalignment;
- if degenerative processes such as arthrosis, arthritis are suspected;
- pain of varying intensity and nature;
- restriction of mobility of the joint;
- if the ankle is swollen, red and hot;
- before a surgical procedure;
- after surgery to determine the results and dynamics of recovery;
- In the presence of a heel spur;
- for foot deformities and flat feet.
Ankle problems are also associated with systemic diseases such as diabetes, musculoskeletal and spinal problems, and neurological disorders.
If the patient plays sports or dances - professionally or as an amateur - the pain may be caused by torn ligaments and tendons.
It is important to know that inflammatory processes are symptomless in the early stages. Since the therapy is particularly effective at this time, active, older people and people with joint strain should have a preventative ultrasound examination of the ankle joint carried out.
You do not need a doctor’s referral for the examination. You can do an ultrasound scan on your own and then contact a specialist.
How does the ultrasound examination of the ankle work?
During the diagnosis, which takes about 20 minutes, the patient sits or lies on a couch. First, socks, tights and pants must be removed to gain access to the joint.
A gel is applied to the skin in the examined area and the diagnostician uses a scanner to examine the condition of the ankle joint. During the procedure, the doctor asks the patient to change positions several times to see the joint in different projections' – anterior, medial, posterior and lateral approaches.
As a rule, in addition to the standard protocol, a blood flow Doppler examination is also carried out using a special attachment built into the ultrasound probe.
TREATMENT
GRIGORENKO
Andrey Alekseevich
25 years of experience Founder and head of the clinic.
Neurologist, Doctor of Osteopathy Europe (DOE), reabilotologist, orthopedist. Schedule an appointment
Tereshkin
Vitaliy Vladimirovich
More than 20 years of experience as an osteopath, chiropractor and rehabilitation doctor.
Specialist in restorative medicine, negative pressure therapy, medical stretching and remedial gymnastics. Schedule an appointment
Treatment and rehabilitation period:
- Restriction of any stress on the foot and complete immobilization of the foot.
- Medicines to relieve inflammation and pain (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Physiotherapy (ultrasound, UHF, microwave currents, magnetic therapy, UVB).
- Therapeutic exercises (simulator exercises) to strengthen the tendons.
- Correction of flat feet with orthoses and orthopedic shoes.

Symptoms of tendonitis
Symptoms of tendinitis They can appear immediately or develop gradually. It is characterized by a mild, aching or burning pain that can radiate to neighboring muscles, ligaments and bones.
You may also experience symptoms such as stiffness as movement is affected by the injury. Sometimes the joint can no longer be bent. There may also be swelling and pain around the injured tendon. Various noises may be heard when moving the joint.
The symptoms of tendinitis are varied and depend on the joint affected. People with patellar tendonitis have difficulty climbing and walking stairs. They also find it difficult to walk long distances. Patients with patellar tendonitis have difficulty grasping a door handle to open or close a door, and they also have difficulty eating because they are unable to properly hold a spoon, fork, or cup.
If symptoms such as redness, swelling, increased temperature or deformation occur in the joint area, it is worth seeing a doctor immediately. It is not uncommon for such symptoms to indicate chronic tendonitis. Chronic tendonitis is a source of constant pain that interferes with normal living (performing normal household activities). Consultation with a doctor is necessary to avoid irreversible changes when tendinitis damages the tendon.
Treatment of tendinitis and tendovaginitis
There is currently no clear methodology for this Treatment of tendinitis or tendovaginitis. The following measures are recommended.
- Quiet. The movement of the limb with the damaged tendon must be restricted. Different types of orthoses can be used for this purpose. Fixing the hand with an orthosis, for example, helps to significantly reduce the strain on the tendon.
- Application of cold. The injured area can be wrapped in an ice pack for 10-15 minutes daily. This significantly improves the effect of cold therapy. The exposure to cold reduces swelling and relieves pain.
- Painkillers. Commonly prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation (e.g., ibuprofen). However, inflammation is not necessarily the primary cause of tendinitis or tendovaginitis. However, painkillers help to relieve the pain. There are also ointments and gels with a pain-relieving agent that can be applied topically.
- Antibiotics. Indispensable if the process is infectious.
- Steroid injections into the affected area are recommended if other treatments have failed.
- Physical therapy. Has a good effect, reduces inflammation and stimulates regeneration.
- Autologous hemotherapy. In the past it was widely used in the treatment of these diseases (now it is rarely used).
- Shock wave therapy. The use of focused sound waves has a good effect as they stimulate reparative processes.
- Surgical treatment is rarely performed.
- Therapeutic gymnastics. Is only used after the pain sensations have subsided. Allows you to strengthen the muscles in the area of the damaged tendon.
The materials can only be used if they are provided with an active hyperlink to a permanent article page.
SURGICAL TREATMENT
There are two different surgical techniques available for the treatment of Achilles tendonitis: open and endoscopic.
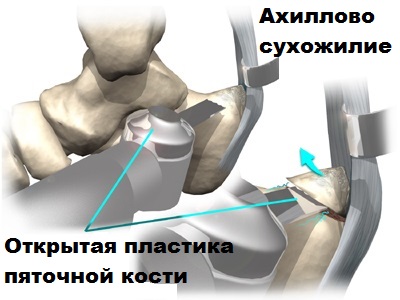
Open surgery is used less and less in this area and is often complicated, so we will not go into it in detail here.
Endoscopic surgery is preferred because of less pain, short recovery time after surgery, good cosmetic results and the possibility of a quick return to sports.
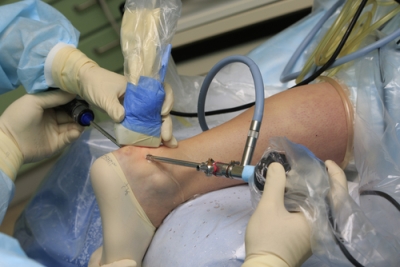
The operation is performed under the guidance of an arthroscope through several punctures in the skin in the Achilles area. The image from the arthroscope is transmitted via a video camera to a monitor on which the surgeon can see the inflamed capsule and the bony hypertrophy (osteophytes) of the heel bone. Osteophytes and inflamed tissue in the tendon area are removed using a special shaver device.
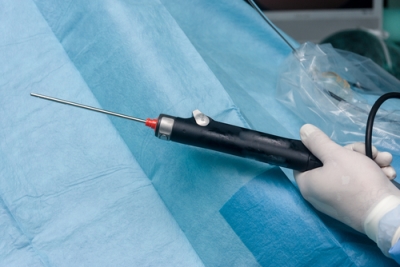
Cold plasma can also be used to more gently isolate and remove abnormal tissue in the Achilles tendon area. After the operation, the patient can immediately walk with almost full weight. After a few days, the patient begins exercises to restore mobility to the foot. The stitches are removed after two weeks.
Physiotherapeutic treatment accelerates rehabilitation.
In our opinion, arthroscopic surgery is a reasonable, minimally invasive alternative to open surgery. The extremely small skin incisions made during arthroscopy compared to open surgery prevent wound healing problems, unsightly scars and nerve damage.
possible side effects
When used correctly, the drug is well tolerated, but precautions must be observed. The following side effects may occur if instructions are not followed:
- Allergic reaction to the ingredients (manifested by rash, skin redness, severe itching, burning, increased local temperature;
- dizziness;
- General weakness, drowsiness, lethargy;
- Increased edema;
- Sharp drop in blood pressure (observed with prolonged use);
- Episodes of nausea.
If symptoms occur, see your doctor for further diagnosis. The specialist will select the drug with other active ingredients.
contraindications
Menovazin solution or ointment should not be used in the following cases:
- during pregnancy;
- while breastfeeding;
- in the childhood;
- skin injuries; Pustules at the application site;
- inflammatory diseases in the acute stage;
To prevent complications, doctors recommend testing for possible allergies before the first treatment.
Remember that Menovazin contains procaine hydrochloride and benzocaine. These active ingredients have a good pain-relieving effect, but often cause an allergic reaction, which can be complicated by anaphylactic shock or Quincke's edema.
Stages of impingement formation
The following stages are distinguished in medicine:
- First. Characteristic of people over 25 years old. Shown by swelling and bleeding.
- Second. The disease occurs in patients under 40 years of age. During this period, fibrosis and inflammation of the tendon occurs (inflammation in which changes in the structure of the tendon are noted).
- Third. The pathology is characteristic of older people. During special examinations, spurs and cracks in the cuff are identified.
Hip impingement symptoms

When the hip is impinged, the joint components press against each other during movement. The pathological process usually affects the femoral neck or the edge of the femoral head with the acetabulum.
Another name for hip impingement syndrome is femoral-acetabular conflict.
In a normal person, there is no femoral-acetabular conflict of the hip joint. However, in cases of deviations, when the femoral neck has a tuberosity or an acetabulum with irregular edges, pathological elements in the joint structure collide when moved.
Also read: Read hip x-ray
The nature of pain varies depending on the type of pathological process:
- In a pathological process in which the bone tissue on the neck of the femur is overgrown, pain sensations occur when the leg is moved axially (cam impingement).
- If the process is located on the edge of the acetabulum, the patient feels severe pain when moving the leg in flexion and extension as well as when it is pulled back, that is, with a greater range of motion (pinser impingement).
In which age
It is recommended to start learning ice skating at the age of 4-5. This is because children develop the ankle ligaments before this age and improper activities during this period can disrupt this process. Especially since the muscles of a three-year-old cannot withstand a lot of stress. Children as young as four or five years old have a better understanding of safety rules.
Older children are able to learn this simple art just as quickly as their younger peers, but the older they get, the more afraid they become of rollerblading. That's why the age of 4-5 years is optimal. If your child is afraid or doesn't want to learn at this age, you shouldn't force him, but wait for the moment when he is ready.
Where should learning take place?
It is recommended that you teach your child to roller skate on safe, flat surfaces. Suitable areas include: B. Roller skating parks, areas in parks and squares, a stadium, a sidewalk away from the street.
- At home, have your child roller skate on the floor for a while while holding on to the walls.
- Teach your child to stand confidently on roller skates. Ask your child to try standing with their heels offset and toes facing different directions, knees slightly bent, and torso leaning forward.
- Ask your child to try squatting on wheels with and without support.
Documents
Surgical and conservative treatment of acute trauma and chronic musculoskeletal diseases associated with professional and amateur sports
Minotraumatic (endoscopic) procedures on the shoulder, elbow, wrist, knee and ankle.
- If the meniscus of the knee joint is torn, it is stitched or resected;
- In case of tears of the anterior and posterior ligaments, as well as the collateral ligaments of the knee joint, plication is performed using both own tendons and artificial transplants;
- Patella dislocation is treated by medial collateral ligament (MPFL) repair and tibial tuberosity osteotomy;
- If the outer ligament group of the ankle is damaged, the ligament is sutured, and if the damage has existed for a long time, open or endoscopic surgery according to Brostrom is performed;
- Endoscopy of the anterior and posterior parts of the ankle joint is performed with correction of the identified pathology;
- In case of Achilles tendon pathology associated with Haglund deformity, correction of the deformity is performed with tendon refixation;
- In the event of an Achilles tendon rupture, a minimally invasive suture is performed via a mini-access;
- In case of sports injuries to the foot, the plantar plate of the metatarsophalangeal joints of the toes is sutured;
- Operations to correct complex foot deformities in hallux valgus with curvature of toes II-V;
- Operations are performed for Morton's neuromas;
- Habitual shoulder dislocation is treated both endoscopically and openly (Latarger operation). Depending on the indication and clinical situation, the rotator cuff suture can also be performed openly or endoscopically. For inflammation of the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii, tenodesis is most often performed;
- Elbow joint ligaments are repaired with tendon autografts (your own tissue). Endoscopy of the elbow joint with removal of foreign bodies is carried out, as is the treatment of synovial fold syndrome (plica syndrome) and joint stiffening;
- Experience in endoscopy of the wrist with restoration of the triangular fibrocartilage complex and good results in percutaneous osteosynthesis of scaphoid stress fractures;
- We have experience in the successful surgical and conservative treatment of chronic diseases such as Achilles tendonitis, subacromial impingement syndrome, epicondylitis, heel spur syndrome. Modern techniques to stimulate tissue healing, such as PRP (platelet-rich plasma) therapy, orthokine therapy, and hyaluronic acid injection, are widely used;
- We develop personalized exercise packages for post-surgery recovery.
Our advantages:
- Possibility of combined treatment: surgery and rehabilitation treatment
- Supervision of rehabilitation by a surgeon
- the patient can benefit from the proven recovery methods of the athletes of the Russian national team.
The Department of Sports Traumatology and Sports Medicine (OSTIS) turned one year old in June.
It was a challenging but very productive year.
We introduced new wrist, knee and elbow surgeries as well as sternoclavicular joint stabilization surgeries for chronic and acute traumatic instability. The department's employees were involved in the development of rehabilitation recommendations after operations on the joints of the upper and lower limbs. The recommendations have been published in paper form and are a continuation of a series of similar publications. We are currently conducting intensive research into the individualization of conservative and surgical treatment of illnesses and injuries to the musculoskeletal system in athletes.
We now have our own operating room and state-of-the-art rehabilitation equipment.
The doors of the department opened this year not only to the athletes of the elite national team, but also to patients who simply want high-quality treatment for their illness or injury.
Sports technology is of particular interest in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Here we often use our know-how in bioorthopedics, a new treatment area. In bioorthopedics, preparations made from the body's own tissue, such as fatty tissue or blood, are used to repair joints. We regularly use bioorthopedic techniques such as platelet-enriched plasma and mesenchymal stem cells to treat gonarthrosis, coxarthrosis and osteoarthritis of the ankle and wrist.
It's no secret that ligament injuries are very common in sports. For this reason, non-professional athletes often turn to us with injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament, posterior cruciate ligament, knee collateral ligament and ankle joint. We use our experience working with professional athletes to operate on and repair these types of injuries.
Read more:- tendons of the foot.
- ligaments and tendons of the foot.
- muscles and tendons of the foot.
- dislocation of the ankle.
- Treated subluxation of the ankle.
- Damaged ligaments of the ankle photo.
- Anterior Tibial Syndrome.
- ligaments of the ankle.
