Diagnosis in our clinic always begins with a comprehensive visual examination. The traumatologist examines the condition of the knee joint and asks the patient when the injury occurred and what symptoms are associated with it. This is followed by a comprehensive instrumental examination. This examination is carried out using modern, specialized equipment, which is very accurate and makes it possible to assess the condition of all internal structures and make an informed decision about further treatment.
Knee injuries in children
Adults are familiar with injuries to the meniscus, where the anterior cruciate ligament is located. If your knee suddenly hurts after running, jumping or skiing, you are right to assume that it is a meniscus injury.
Nowadays, a healthy lifestyle is fashionable and many sports activities such as snowboarding, freeskiing, inline skating and skating have become available to us. We adults actively encourage our children to attend sports clubs and participate in sports such as rhythmic and artistic gymnastics, fencing, football, hockey, basketball, volleyball, athletic dance and more. And that's great!!! But, as always, there is the proverbial 'but'! Where there is sport, there are also injuries - an undeniable fact.
In recent years, the number of children with various knee injuries has increased. Let's talk about the most complex knee injuries in children.
The reason for the discussion was not only the injury itself as the subject of the examination, but above all the question of treatment. Today, medical care is much more accessible and medical facilities are equipped with modern equipment. You will agree that a CT or MRI scan is not a big deal these days. It is also not difficult to assess the clinical picture and suspect a problem. And here we come to the most important question: where should the treatment be carried out, how should the treatment be carried out?
The treatment of knee injuries in children and adults is completely different. The main difference is that the child is still growing and developing and that damaged joint structures behave differently in children than in adults. It must always be remembered that a child is not a small adult, but is still growing and living. It is our task to choose the best and most appropriate treatment method that minimizes the negative consequences on the child's future life and allows him to continue his active life, including sports and leisure activities.
Oversaturation of medical devices is not a cure. Experience is the most important thing! In the GI Gorky National Research Center for Children's Traumatology and Orthopedics. The Turner Medical Center of the Russian Ministry of Health has accumulated extensive experience in the treatment of knee injuries and has developed unique rehabilitation and treatment methods.
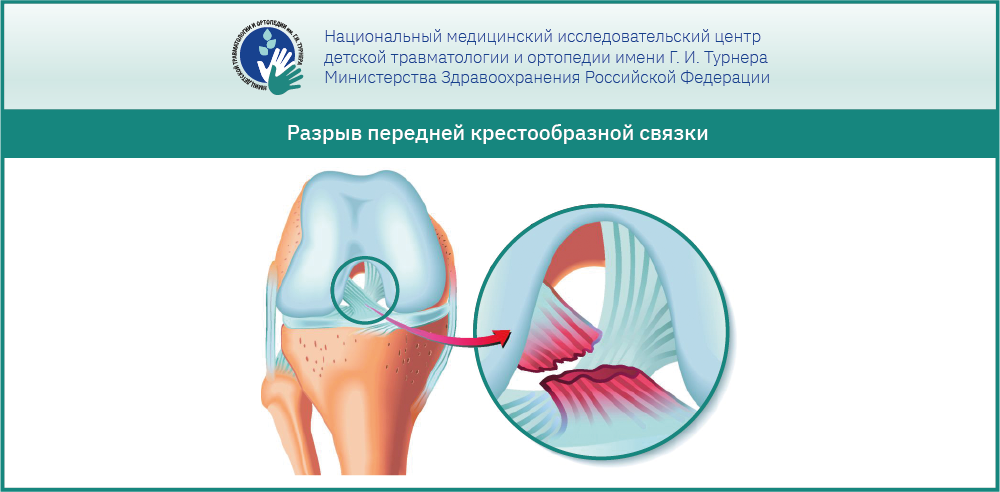
Partial anterior cruciate ligament injury, anterior cruciate ligament tear
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury – This is one of the most serious knee injuries in children. The anterior cruciate ligament is one of the most important stabilizers of the knee joint.
The main complaint of patients with a torn ACL is instability of the knee joint, that is, the feeling that the bones in the knee joint are 'sliding' against each other. Pain on strain and a blockage of the joint can also occur, especially if other joint structures (meniscus, cartilage) are also damaged.
Symptoms of a rupture of the collateral ligaments of the knee joint
Several types of injuries can be distinguished. Each has its own symptoms.
Injury to the external collateral ligament of the joint
The outer ligament is injured less frequently than the inner ligament. The injury usually occurs due to excessive inward flexion of the shinbone. The tear is usually complete and may be accompanied by a burst fracture of the fibula head.
The main symptoms of the injury are:
The severity of symptoms depends on the extent of the injury. With a complete tear, there is excessive mobility (laxity) of the joint.
Injury to the internal collateral ligament of the joint
This injury is more common. It is usually diagnosed as an incomplete tear. This injury is caused by too much outward traction on the shinbone. It is often associated with an injury to the joint capsule or a tear of the medial meniscus.
The main symptoms of an incomplete tear are:
With an incomplete tear, there is excessive mobility.
Causes of a tear in the collateral ligaments of the knee joint
The main causes of a collateral ligament tear include:
- Walking in a squat position (including high heels). The injury usually occurs when a person simply trips on an uneven surface.
- Excessive outward flexion of the lower leg. This injury usually occurs during sports and other physical activities.
- Sudden physical overexertion. This leads to significant tension in the connective tissue.
- Violent shocks. The injury can occur as a result of a fall from a height or a car accident.
- Wear and tear of the articular surface. The injury is caused by degenerative changes in the joint.
Important: Any type of injury requires immediate medical attention.
Injuries to the knee joint can lead to various complications.
With a partial tear, the patient may endure pain but suffer from severe swelling. If treatment is not initiated immediately, a pronounced inflammatory process will develop that can become purulent. Active movement of the joint provokes a complete rupture of the tendon.
If the joint ruptures completely, motor function is restricted. The patient can then no longer walk normally. The injury often leads to the development of dangerous pathologies of the joint, leading to complete immobilization of the limb.
Read more:- Rupture of the ankle.
- Femoral collateral ligament.
- tibial ligaments.
- Thigh tendon rupture.
- Collateral ligament rupture.
- Rupture of the medial collateral ligament.
- How much does meniscus replacement surgery cost?.
- Which muscles of the anterior tibial group do you know?.
