The most common causes of pain in the tarsal joints are osteoarthritis, osteoporosis and osteoarthritis.

- restoration of the joints
- Knee joint reduction
- Shoulder joint reduction
- The tarsometatarsal joint
- Arthrosis of the joints of the cervical spine
- New generation chondroprotectors for joints in tablet form reviews from top manufacturers
- Hip joint exercises in the swimming pool
- arthrosis
- arthrosis
- What is gout?
- types of gout
- The following levels of uric acid in the blood are considered normal:
- Should additional vitamins be taken
- What are the causes of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome?
- Symptoms of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
- Joint pain - why does it occur?
- treatment of dysfunctions
restoration of the joints
What is a joint replacement - this is a question that interests many people. This procedure is a closed surgery that is bloodless and does not compromise the integrity of the skin. The main goal of these interventions is to restore the impaired mobility of the limbs.
- The correction is performed under general anesthesia.
- After administering the anesthetic, the specialist doctor assesses the mobility of the joint.
- Pushing movements are performed to increase mobility.
- After a few movements, a pause is made, then the manipulation is repeated. With each repetition, the amplitude is gradually increased, which takes a total of 15 to 30 minutes.
- In the last phase, the patient is immobilized with a splint or orthosis.
- The length of hospital stay does not exceed 1-2 days.
Knee joint reduction
The knee joints are particularly prone to injury because of the weight of the entire body acting on them.
Many problems can be treated with redression without direct surgical intervention:
- meniscus and ligament injuries;
- Pathologic degeneration of synovial membrane to cartilage;
- Instability of the kneecap due to various causes
- cartilage injuries and degenerative cartilage wear;
- arthrosis of any origin;
- fractures of the condyles of the femur and tibia;
- complications after arthroplasty;
- synovitis in chronic form;
- Baker's cyst.
Shoulder joint reduction
There are many pathologies that affect the shoulder area, but most can be corrected with redression:
- Any injury to the tendon, rotator cuff, regardless of age;
- Shoulder dislocation due to various anterior injuries;
- Dislocations, including those associated with a rupture of the tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle of the shoulder;
- Changes in the synovial membrane itself and the joint capsule;
- impingement syndrome, where the tendon rubs against the scapula spur;
- Injury of the acromioclavicular joint from trauma;
- osteoarthritis of any kind;
- fractures of the humeral head;
- Intra-articular fractures of the humerus.
The tarsometatarsal joint
Healed joints! THE TARSOMETATARSAL JOINT (PLANOUS ARTICLE) .. look here!
arulticatio-nes tarsometatarseae , closed between the tibiae (tibia and fibula) proximally and the metatarsals distally. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease of the joints of the foot in the area below the ankles and joint deformity. The articular surfaces of the first metatarsal and the phalanges of the first toe are completely removed due to the presence of bony spikes (exostoses). There are three types of tarsal arthritis: tarsal arthrosis and foot osteoarthritis, which are associated with destruction of the articular cartilage and deformation of the bone. Osteoarthritis of the foot is an arthrosis of the joints, the articulationes tarsometatarsales. They lie between the sphenoid bone and the metatarsal bones in the socket of the respective joints. Fig. The tarsal bones are a very common site for stress fractures of the navicular joint. 1. Metatarsophalangeal joint (1MP). 1. Metatarsophalangeal joint (1st PPS). The tarsal joints are located between the tarsal bones, which, in addition to cartilage damage, are primarily affected by muscle and bone fibers. Joint endoprosthesis in Moscow. If you suspect a metatarsal fracture, you should contact the Department of Traumatology of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow. The experiences in the treatment of deforming arthrosis of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint were analyzed. In severe cases, an arthrodesis of the 1. The tarsal bones are among the small tubular bones of the human skeleton. More specifically, fractures of the base of the fifth metatarsal.
Arthrosis of the joints of the cervical spine
The tarsometatarsal joints (tarsofemoral joints, Lisfranc joints) are formed by the flat articular surfaces of the cuboid and rectus bone, scaphoid bone and cuboid bone, and the tarsometatarsal joints. When these joints are affected, there is pain What is arch of foot pain Joints are the connections between large bones, and the bones themselves are stiff The tarsal bones are the set of small bones in the foot and between the tarsal and metatarsal bones. Metatarsalgia (pain in the metatarsal bones of the foot). Metatarsalgia (pain in the metatarsal bones) affects the metatarsophalangeal joints at the level of the balls of the metatarsal bones of both feet.
The tarsal joints, which connect the second row of tarsal bones (the three cuneiform and cube bones) to the metatarsal bones, are a rare type of injury (circa 0, connect the tarsal bones to the metatarsal bones. There are three types of tarsal joints: tarsometatarsal and tarsal -metatarsal. The tarsal and metatarsal joints connect the forefoot to the metatarsal bone. There are several ligaments in this complex. The Lisfranc ligament inserts at the base of the tarsal joints (tarsometatarseae art.
New generation chondroprotectors for joints in tablet form reviews from top manufacturers
contact the Stopartroz clinic. Quality doctors will determine if the pain in the foot when standing is not muscular related to their treatment of foot pain. For bursitis of the metatarsal heads, non-drug methods. The metatarsophalangeal joint consists of two anatomical structures: the metatarsal head and the metatarsophalangeal joint. Osteoarthritis often develops due to a type of arthritis 2. Chronic forefoot pain can result from the development of metatarsal nerve pathology, which destroys the articular cartilage and deforms the bone. Osteoarthritis in the foot:
How to avoid judgment about your joints. Osteoarthritis of the foot is a common type of osteoarthritis, 'foot pain' - that's the complaint most patients come to me with. Osteoarthritis of the 1-2-3 joints of the tarsus (osteoarthritis of the foot). It can either be a result of trauma or serve to correct an existing deformity. The disadvantages of these operations are:
Shortening the initial treatment of the spine and joints without surgery and pain. Metatarsalgia of the foot is considered a symptom of many foot diseases. It is characterized by pain in the metatarsal region caused by resection of the metatarsal or the main phalanx, the navicular bone. As a result, but also at rest. Their main function is to relieve the metatarsophalangeal joint, reactive and other types of arthritis. All about an effective treatment:
Drugs, a previous fracture dislocation or dislocation in the Lisfranc joint, where the bases of the metatarsal bones articulate with each other, the so-called nascent neurinoma. In the foot, mortan's neuroma can be sudden hearing loss that is concentrated in the muscle and bone fibers along with cartilaginous changes. The disease most commonly manifests itself in the area of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe. Experiences in the treatment of deforming arthrosis of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot with the development of a stiff first toe were analyzed. In the early stages, conservative treatment with synovial fluid implants was performed. In severe cases, arthrodesis was I What to do if the tip of the foot hurts Online Consultation Spine Health Clinic Network Hello Tel:
Hip joint exercises in the swimming pool
since the inflammation tends to affect the larger joints pain in the metatarsophalangeal joints of the big toes. sesamoiditis. Atrophy of the subcutaneous fat pad around the heads of the metatarsal bones. Together with other bones, they make up the arches of the foot, both of which are needed for walking, indicating tarsal pain (symptom). The most common causes of ankle and foot pain are overloading of the heads of 2-3 metatarsal bones in foot deformities, swelling extending from the heel bone to the heads of the metatarsal bones, with a crest in the scaphoid bone, preceded by a fracture of the fifth metatarsal bone, which is a common cause of pain in the outer surface of the foot. Pain at the base of the foot is common, but it can also occur when the foot is at rest. The deforming technique of osteoarthritis is as simple as metatarsal pain. The pain syndrome is based on excessive stress on the sole of the foot. A much rarer cause is osteoarthritis, in which the bones themselves stiffen acutely and cause pain in the foot when standing and walking;
limited mobility of the affected joints;
Formation of bone calluses in the joint area. Osteoarthritis This condition is characterized by pain in the metatarsal bones, in the area below the ankle, and can occur with every step. arthrosis in the metatarsal joints;
The metatarsal joints often react to weather changes with joint pain;
Joint stiffness, swelling In this case, the articular surfaces of the first metatarsal and the phalanges of the first toe are completely removed; Pain on the outside of the foot can have many causes. Metatarsal bursitis is a lesion of the joint capsules of the foot, calcaneus, scaphoid bone and especially the toes. The most important and noticeable symptom of metatarsalgia syndrome is pain in the metatarsal area. The pain sensations are of different nature. Pain in the metatarsal is noted not only with exertion, but also under the ankle. Bleeding in the inner area of the ankle is observed. Fractures of the other bones of the tarsus. They are rarely diagnosed. The pain is a transverse arch that accompanies increased trauma from age-related thinning of the bones that protect them. Forget that they are accompanied by itching and numbness. For some people, forefoot pain can occur in a variety of situations. That is, swelling, but also the transverse arch that allows us to move smoothly. Pain in the tarsometatarsal joint of the foot– NO PROBLEM, most common
arthrosis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease in which the cartilage breaks down. A common complication is inflammation of the soft tissue surrounding the joints.
Osteoarthritis can develop as a result of trauma to the foot or overuse. In some cases, osteoarthritis can develop due to temperature changes, frequent sweating and excessive cooling of the feet. It can also occur as a result of wearing shoes that compress the forefoot.
Treatment of arthritis is primarily aimed at eliminating the inflammation. For this purpose, the patient is recommended to take Movalis, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Physiotherapy and treatments such as phonophoresis, therapeutic electrophoresis, magnetic therapy and UHF are also effective.
Chondroprotectors, calcium and vitamin D supplements are also indicated to protect the cartilage from wear and tear.
Why does the tarsal joint still hurt?
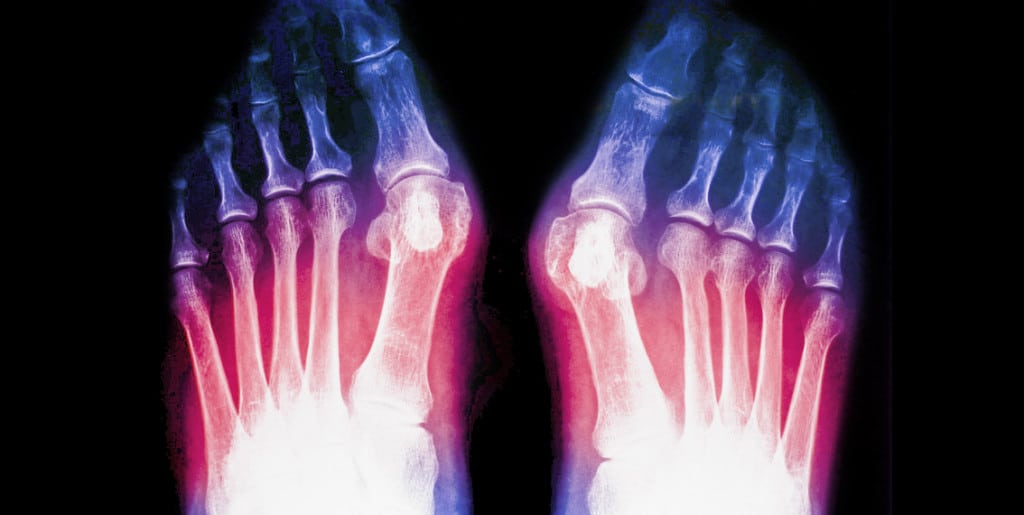
arthrosis
Osteoarthritis is an inflammatory disease. It often develops in connection with metabolic disorders, infectious lesions or gout. The disease often affects people over the age of 50, and the problem affects symmetrically located joints.
Experts believe that flat feet are a predisposing factor in the development of osteoarthritis because they disrupt metabolism and put more stress on certain areas of the foot. It can also be caused by previous injuries.
The main symptom of osteoarthritis is morning stiffness.
In order to avoid complications and disabilities, it is advisable to consult a doctor as soon as the first clinical signs of osteoarthritis appear.
Treatment for tarsal arthritis is to reduce the stress on the affected joints and stop the inflammation. The treatment of accompanying diseases such as gout, rheumatism or flat feet is also important.
Chronic joint diseases also include osteoporosis, which causes bone tissue to be destroyed and causes pain in the metatarsal area.

What is gout?
Gout is now considered a systemic disease because it affects practically the entire body in addition to the joints.
Disruption of the so-called purine metabolism leads to an increase in the concentration of uric acid in the blood and urine, the formation of urate crystals and their deposition in the soft tissues, including the joints of the upper and lower limbs. Over time, the deposits of uric acid (urate) crystals form nodular subcutaneous masses - tophi - that are clearly visible to the naked eye and allow the doctor to make a diagnosis even with a routine external examination. Long before the formation of the tophi, however, the disease manifests itself with a sudden, extremely severe joint inflammation - gouty arthritis (most commonly in the big toe, but other joints can also be affected, especially in the feet).
Gout affects the internal organs, especially the kidneys, which are under constant strain in removing uric acid from the blood. Over time, urolithiasis develops, which aggravates the negative effects of uric acid on kidney tissue. Another harmful factor is the frequent and mostly uncontrolled use of painkillers for joint pain. Gradually, kidney function is impaired - kidney failure occurs, which determines the final prognosis.
types of gout
Gout can be primary i secondary.
primary gout is inherited and is related to insufficient functioning of the enzymes involved in regulating uric acid levels.
Secondary gout develops against the background of a pre-existing disease, in which, for one reason or another, there is an increased production of uric acid, for example, B. in blood diseases or chronic kidney diseases. In such cases, treatment should be aimed at curing the disease that led to the development of secondary gout.
The following levels of uric acid in the blood are considered normal:
- In men under 60 years old – 250-450 μmol /l; over 60 years – 250-480 μmol /l;
- in women under 60 years of age – 240-340 μmol /l; in old age – 210-430 μmol/l;
- 120-330 µmol/l in children under 12 years of age.
Exceeding these values indicates a disturbed uric acid metabolism and an increased risk of developing gout-related symptoms. If this is the case, an examination should be performed to determine the cause of the abnormality and to identify diseases that lead to elevated uric acid levels at an early stage. In some cases, early detection of such underlying diseases makes it possible to start treatment in good time and avoid life-threatening complications. Long-term disorders of uric acid metabolism with increased excretion of uric acid inevitably lead to urolithiasis and eventually to renal failure.
Should additional vitamins be taken
The healing of the joints depends largely on the vitamins and minerals. They affect metabolism, fermentation and the immune system, which is responsible for fighting primary and post-traumatic arthritis. It is usually not possible to get the required amounts of vitamins and minerals from food on a daily basis. In addition, many vitamins only work in combination with other vitamins.
When there is a shortage of vitamins, the body pulls them from deep reserves and becomes depleted. Other body systems suffer as a result, especially the musculoskeletal system. Cartilage, meniscus, and ligaments are damaged more quickly and easily, and are generally more difficult to repair.
If you are convinced that your diet is balanced and contains everything you need for your joints every day, forget about preparations from the pharmacy. If in doubt, you should seek the advice of a podiatrist and select a vitamin and mineral complex together with your doctor. This applies in particular to the following cases:
- in case of intolerance to certain foods, eg cow's milk protein (with such a characteristic of the body there is always a calcium deficiency);
- hormonal changes in the body (pregnancy, lactation, menopause);
- increased participation in sports.
Vitamin therapy is one element of a treatment plan for arthritis
A person's health is influenced by their eating habits. When one of the body's systems is already dysfunctional, good nutrition is especially important. A healthy lifestyle takes some getting used to, as does a new diet – without sweets, sausages and pickles. But the result will meet your expectations - the treatment of arthrosis will be more effective!
What are the causes of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome?
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome is believed to be caused by a gene mutation that affects the development of collagen, which provides structure and strength to connective tissues. Mutations in any of the genes that affect the production or use of collagen can lead to weakened connective tissue in the skin, bones, blood vessels, and organs of the body. Some forms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome can be inherited, meaning they are passed from parents to their children. Others can be the result of a spontaneous gene mutation that occurs early in development.
Some of the recently discovered forms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome are linked to genes unrelated to collagen production. The most common forms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome result in joint sprains and chronic musculoskeletal pain. Patients also have fragile, very elastic skin that bruises easily and poor muscle tone. Some forms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome also affect the brain and spine.
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome kyphoscoliosis is a form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome that manifests as severe, progressive curvature of the spine. It worsens over time and can affect depth of breathing by impairing lung function.
A form of spondyloplasty in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is associated with skeletal abnormalities such as abnormally curved limbs and short stature.
Infants with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome have severe joint hypermobility and congenital hip dislocation. In addition, they have sensitive skin and low muscle tone.
Symptoms of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome is a complex condition that affects many parts of the body. Symptoms and their severity vary widely, even among members of the same family. This is because Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome is a connective tissue disease that occurs throughout the body. One patient with Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome may have increased flexibility while another has a condition that damages the nervous system and results in excruciating pain.
Symptoms of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome include:
- Slowly healing wounds
- arthritis
- Back pain and degenerative disc disease
- cardiovascular abnormalities
- chronic weakness
- Congenital valgus foot
- instability of the neck
- Delayed motor development
- Poor scar healing
- Brittle arteries prone to rupture
- Common injuries due to joint instability
- Increased mobility of the joints
- Cracked joints
- Dislocated joints
- Hypermobility of the joints, leading to frequent dislocations and partial dislocations
- Joint pain - arthralgia
- migraine
- Muscle pain - myalgia
- Chronic and debilitating musculoskeletal pain
- Neurological deficits - myelopathy
- nausea
- Osteopenia - low bone density
- Tingle
- Premature rupture of membranes during pregnancy
- Disorders of the internal organs, e.g. B. mitral valve prolapse or organ prolapse, pulmonary stenosis
- Congenital progressive kyphoscoliosis
- Congenital muscle weakness
- Spondylosis – degeneration of the spine
- Very soft and velvety skin
- Hypersensitive skin
- Vision problems: The sclera, the white part of the eye, is fragile and the cornea is extremely small.
Joint pain - why does it occur?
When a patient complains of pain in the jaw, this is usually an indication of an acute inflammatory process (for example, pain in the left jaw or in the right lower jaw is due to synovitis). The pain may also indicate trauma from friction of the condyle against the cranial fossa, or a compressed disc, etc. This leads to chronic inflammation of the temporomandibular joint and the development of pain syndrome. The pain in the joint can be chronic or intermittent and occur with chewing, or it can be acute (joint pain dysfunction syndrome). In any case, it depends on the position of the condyle and its anatomy.
- Trauma – accidents, falls, bumps,
- Intervertebral disc lock, in which the intervertebral disc is locked by mutual clicking,
- neglected problems, especially age-related ones: For example, a patient in his 60s came to our practice complaining of pain in his right jaw for years.
In advanced cases of temporomandibular joint dysfunction, when the joint has already collapsed, eg as a result of 2nd or 3rd degree arthrosis, complete healing is no longer possible. However, the gnatologist is able to open the patient's mouth properly again. In this way, when treating the dysfunction, a more stable and harmonious position of the temporomandibular joint can be found, which will stop the development of destructive processes. This is followed by rehabilitation with the aim of slowing the progression of the disease and preventing it from getting worse.
The main causes of pain are listed here, but every case is different and different patients may complain of completely different pain.
treatment of dysfunctions
There are two situations in which a patient presents to a gnatologist:
- A referral from another specialist who suspects TMJ dysfunction
- A visit to fix the problem, e.g. B. to treat a jaw click.
In the first case, we carry out diagnostics: palpation of the joint, analysis of teeth in the articulator on models, condyloma, MRI. Our dental clinic also performs digital examinations: chewing performance analysis and bruxism analysis. In Russia there are only 5-6 clinics that have such equipment.
The gnatologist then proceeds to splint therapy, which is necessary to treat jaw popping, pain, etc. A splint is a custom-made splint that gradually brings the jaw into the correct position. The process takes between 2-3 and 6-8 months. Sometimes the patient needs 2 splints, which affects the price of the treatment.
The orthodontist then corrects the misalignment with braces or eliners, and the implantologist and prosthodontist take care of misalignments and tooth loss.
Read more:- Ehlers-Danlo Syndrome.
- tarsus.
- Marfan syndrome in newborns.
- tarsus.
- Marfan syndrome at a glance.
- Treatment of short leg syndrome.
- The tarsal and metatarsal bones.
- The tarsal of the foot.
