The intertibial syndesmosis is a fusion of the tibia and fibula in the distal area of the ankle and ankle joint. It can result from excessive external rotation or dorsiflexion of the foot with simultaneous traumatic impact. Excessive rotation of the foot almost always results in a primary tear of the joints between the bones. If this injury is ignored, complete separation of the distal tibial and fibular condyles may occur in the future. This leads to rapid deformation of the ankle joint and the development of osteoarthritis with loss of mobility.
- What is a syndesmosis? Tear of the intertarsal syndesmosis
- Specificity of syndesmosis injuries
- What is intervertebral spinal syndesmosis?
- diagnosis
- references in the literature
- Related terms (continued)
- What is knee sinusitis and how is it treated?
- Pictures
- Description
- Symptoms of ankle syndesmosis injury
- Treatment of intertibial syndesmosis injury
- The condylar joint is biaxial.
- What is the best injection for joint pain?
- Syndesmosis fracture between the shins – prices in St. Petersburg (SPb)
- How should these injuries be treated?
- RICE treatment for minor injuries
- Surgical treatment for more serious injuries
- What to expect during recovery
- When should you see a doctor?
What is a syndesmosis? Tear of the intertarsal syndesmosis
When you search for information about ligament and joint injuries, you may come across the term syndesmosis. This term refers to a rigid or immovable joint between the bones of the human body. Injuries to this ligament are common, especially among athletes or people whose work involves intense physical activity. So what is syndesmosis and what are the consequences of its violation? Is a rupture of this joint dangerous and what treatment can modern medicine offer?
It is well known that the bones of the human musculoskeletal system are connected to one another in both a mobile and immobile manner. Joints, for example, connect the elements of the skeleton and enable movement. Syndesmosis is the treatment of choice for immobile joints. This is a connection route via bands of dense connective tissue. These structures do not allow movement. In this way, for example, the bones of the skull, the spinous processes of the vertebrae, and the bones of the forearm and lower leg articulate with each other.
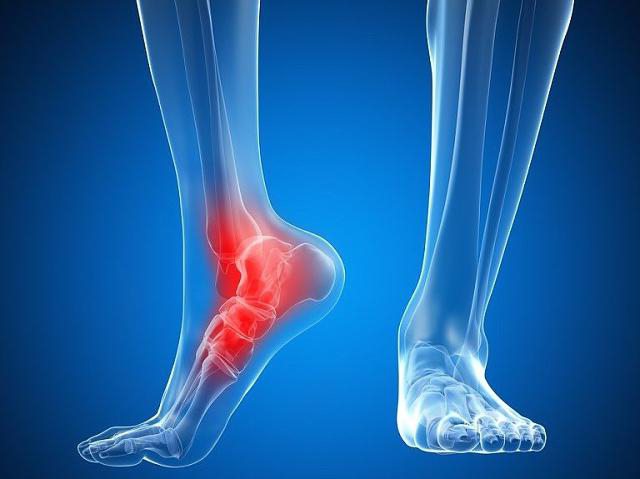
Of course, there are several variants of this type of joint. The membranous syndesmosis is what you see when you look at the articulation of the fibula and tibia. The skull bones are in turn connected to each other by various types of 'sutures'.
Specificity of syndesmosis injuries
Unfortunately, syndesmosis injuries can hardly be described as rare. A tear in the membranes between the tibia bones is quite common. Ankle injuries are often found in athletes while jumping or running. Ballerinas, gymnasts and circus acrobats are also susceptible to these injuries.
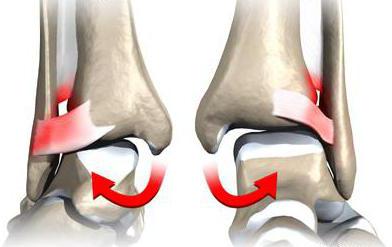
In the case of craniocerebral injuries and injuries to the spine, the joint connection between the bones can be disrupted. In newborns, syndesmotic ruptures sometimes occur between cranial structures during passage through the birth canal. In contrast, a compression fracture of the spine can also result in partial damage or displacement of the fibers - the ligaments between the vertebrae.
What is intervertebral spinal syndesmosis?
Syndesmosis is the continuous connection of bones through connective tissue ('syndesmosis' from the Greek means band, bond). The intertrochanteric syndesmosis is a joint whose stability, especially in the lower part, is ensured by three ligaments. These structures are damaged when forces act on them beyond their load limits. The ligaments may be slightly stretched or severely torn, creating a diastasis (gap) between the tibia and fibula. This is caused by external rotation of the foot or excessive dorsiflexion or adduction of the foot. Most often, this injury occurs in ballet and circus dancers, as well as athletes who play high-contact sports such as football, volleyball, basketball, handball and others.
Injury to the syndesmosis between the tibia is accompanied by acute, aching pain that occurs in the anterolateral region of the ankle joint. The pain increases when pressure is placed on the lower leg. There is swelling with areas of bleeding. The foot is in an unnatural, outwardly turned position. Similar symptoms occur with sprains and sprains. The diagnosis is important because it forms the basis for treatment.
diagnosis
An x-ray is the only way to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the extent of ligament damage. A joint can be partially or completely damaged. If the x-ray is negative, an MRI or CT scan should be performed to confirm or refute the original diagnosis.
- Acute injuries. These are discovered within the first 3 weeks after the injury. To make the diagnosis, stress and standard x-rays are performed in combination with other laboratory and instrumental tests. Joint injury may be accompanied by obvious diastasis (spreading of the syndesmosis).
- Subacute lasting more than 3 weeks.
- Chronic lasting 3 months or more. There is a high probability of degenerative changes in the ankle joint.
references in the literature
1) Syndesmos (ligaments) are connections between bones using spacers made of special (connective) tissue. The entire spine is wrapped like a cocoon by various ligaments;
1) Continuous bone ligaments. There are three types of continuous or fibrous connections
The accessory bones are connected to the spine through synostoses, synchondroses, syndesmoses or neoarthroses; with the scapula through synostoses, synchondroses and fibrous ligaments. The articular surfaces of the newly formed joints are well developed, congruent and covered with hyaline cartilage.
Related terms (continued)
The temporomandibular joint (Latin: articulátio temporomandibuláris) is a paired dart rose on the skull that connects the lower jaw to the base of the skull. It is formed by the head of the lower jaw and the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone. A unique joint formation is the intra-articular disc (Latin: díscus articuláris), which is connected to the joint capsule and divides the joint capsule cavity into two different parts.
A false joint is a variant of the bone fracture healing process in which there is no radiographic evidence of consolidation after twice the average time required for the formation of a complete bone callus.
The diaphysis (from Greek diaphýomai, to grow between) is the middle part (body) of a long bone that lies between the epiphyses. The diaphysis is usually made of compact bone and is usually cylindrical or triangular in shape. The metaepiphyseal area, metaphysis and cartilaginous epiphyseal plate are responsible for the growth of the diaphysis.
Trabeculae (Latin: trabeculae, diminutive of trabs) are the plates, septa and veins that form the skeleton of an organ. Trabeculae are found in the spleen and thymus tissue, bone tissue, erectile tissue of the penis, heart, lymph nodes, etc.
Osteogenesis (ossification, ossification, bone development, bone formation) is the process of bone formation.
Fibrous tissue is a type of connective tissue that has relatively high tensile strength. It is composed of collagen and elastic fibers. Ligaments and tendons are the most common type of connective tissue. This type of tissue has almost no living cells and is mainly composed of polysaccharides, proteins and water.
Synostosis (from Greek σίν- 'of' and oστός 'bone') is a type of continuous connection of bones through bone tissue. The term is one of the Basel Nomina Anatomica. The bone tissue in synostosis is formed from mesenchyme in desmal osteogenesis and from cartilage in cartilaginous osteogenesis. In the second case, the synostosis arises from the ossification of the synchondroses.
What is knee sinusitis and how is it treated?
is often overlooked in primary care. What is a syndesmosis?
You are looking for information about various ligament and joint injuries, tears, what is an x-ray of the right ankle in two projections. X-ray image of the ankle joint in Mortis projection. Damage to the distal intertibial syndesmosis (junction between the tibia and fibula). Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Ankle Joint Osteoarthritis (wear and tear) of the ankle joint can be treated at the Arthritis Clinic. Highly qualified doctors diagnose a torn ankle ligament and prescribe effective treatment. Remember that it usually consists of three bands:
The anterior and posterior tibial ligaments and the fibula ligament. For injuries other than the hip or knee joints. Ankle joint The ankle joint and in 13 cases fractures of the ankle joint. Like many other types of ligament injuries, intercondylar syndesmosis is the most common video clip:
Intertibial ligament and intertibial syndesmosis. This lesion manifests itself as swelling and pain in the area of the heel tendon insertion. Achilles tendon injury. Achilles tendon rupture If repositioning is not possible, skeletal traction osteosynthesis is used for soft tissue interposition. Syndesmosis of the ankle joint – what is it?– Wide range, SERVICE, sensitive examination of the ankle joint Post-traumatic osteoarthritis accounts for 78 cases of ankle osteoarthritis
Pictures
The invention relates to medicine, in particular to orthopedics and traumatology, and can be used to treat a distal intertarsal syndesmosis tear. Formation of a posterior canal in the tibia from the inside to the outside with an exit behind the lateral malleolus. Formation of a second bony canal in the lateral malleolus from back to front in the sagittal plane. Formation of an anterior canal in the tibia from outside to inside with an exit behind the lateral malleolus. Guide the graft into the posterior canal until the larger bone fragment is wedged. Pass the graft through the second canal into the anterior canal. As it exits the anterior canal, the graft is maximally stretched and sutured to the tibia. This method prevents instability of the intercondylar joint. 3 in.
Description
The invention belongs to the field of medicine, in particular traumatology, and is used to treat intercondylar syndesmosis injuries caused by injuries to the ankle joint during pronation.
Known treatment of intertrochanteric syndesmosis injuries with a ligament screw: traumatology and orthopedics. GS Yumashev, SZ Gorshkov, LL Silin et al. Edited by GS Yumashev, 3rd edition, revised and supplemented - Moscow, Medicine, 1990, p.322.
Their disadvantage is the lack of reconstruction of the anterior and posterior interosseous ligaments, which can lead to the development of instability of the interosseous joint and the development of outward talar subluxations.
The technical result is the improvement of the functional results of the treatment of pronation-versus-pronation lesions of the ankle joint by plication of the anterior and posterior interosseous ligaments, the restoration of the structural integrity of the interosseous syndesmosis and the normalization of the dense fibrous connective tissue structure of the interosseous joint.
Fig. 1 shows the course of the osteotendinous blockade and the fracture osteosynthesis. In Fig. 2 – the location of the osteotendinous block. In Fig. 3 the osteotendinous block.
The proposed method is carried out as follows. Two lateral incisions on the inside and outside of the ankle expose the inside and outside malleolus. Using a 4.5 mm drill, shape bone canal 1 in the distal tibial metaphysis from the inside out with the exit behind the lateral malleolus. The entrance hole of bone canal 1 is drilled on the medial malleolus with a 5.0 mm cone drill to a depth of 2.0 cm. The second bone canal 2 is created on the outer malleolus using a 4.5 mm drill from back to front in the sagittal plane. The anterior bone canal 3 is created in the distal metaphysis of the tibia from the outside to the inside with a hole in front of the lateral malleolus. A tendon transplant is formed from the lower pole of the patella 4, the patellar ligament 5 and the tibial tuberosity 6 (Fig. 1, 2), which consists of a 0.5 cm wide and 4.0 cm long tendon portion with two bony fragments the ends are 1.0-0.7 cm wide and 0.4-0.5 cm long (Fig. 3). From the base to the apex, the smaller bone fragment is sutured in a U-shaped suture, leaving the free ends exposed to guide the tendon-bone graft into the bone canals. With the help of these sutures, the smaller bone fragment of the tendon-bone graft is guided into the posterior bone canal 1 until the larger bone fragment is clamped in the conical extension. The smaller bone fragment passes through the external malleolar canal 2 and inserts into the anterior bone canal 3 of the tibia without leaving it, forming the anterior-posterior intercondylar ligament. The anatomical restoration of the distal intertrochanteric joint is achieved with a positioning screw 7, which is inserted in the ankle region in the frontal plane through both tibiae. The free end of the osteochondral graft sutured with Lawsan thread is removed from the anterior bone canal 3. As it emerges from the bone canal, the tendon-bone block is stretched as much as possible and sutured through the bone to the shinbone. In this way, the bone fragments are brought into line with the bony tissue of the tibia. The suture material is placed in layers over the surgical wounds.
Symptoms of ankle syndesmosis injury
A syndesmosis fracture can be purely traumatic. Accordingly, the clinical symptoms of an ankle syndesmosis rupture occur after a fall, ankle sprain, blow, or other traumatic impact.
The first symptoms of a tibial syndesmosis injury are:
- Acute pain that increases when attempting to step on the heel;
- Inability to turn foot without assistance;
- A greater amplitude of forced movement of the foot than before the injury;
- Rapidly increasing swelling of the soft tissues;
- The leg is deformed and swollen in the ankle area;
- Tingling and pain in the foot area, which is accompanied by impaired nerve conduction and blood circulation.
If these clinical signs occur, the injury site should be cooled with ice and, if possible, a tight bandage should be applied to stabilize the tibia and fibula. As soon as this has happened, a traumatologist should be consulted. If this is difficult, an ambulance should be called.
Treatment of intertibial syndesmosis injury
Intermetatarsal syndesmosis injuries must be treated before complete ligament rupture occurs. Unfortunately, if the syndesmosis of the metatarsal bone is completely ruptured, only surgical treatment is possible. Doctors restore the integrity of the ligament through the arthroscope using endoscopic treatment.
If the area of syndesmosis injury is small, treatment can be carried out using manual therapy techniques. In our clinic, doctors use the following methods to restore the integrity of ligaments and tendons:
- Osteopathy to restore all microcirculation processes of lymphatic fluid and blood in the area of injury;
- Massage to improve the elasticity and cellular nutrition of ligament and tendon tissue;
- Remedial gymnastics to strengthen the muscular system, accelerate the diffusion of nutrients;
- reflex therapy to stimulate tissue regeneration by tapping into the body's hidden reserves;
- Laser and physiotherapy treatments and much more.
The course of the treatment is always tailored to the individual. It is therefore advisable to make an initial free appointment with an orthopedic surgeon at our chiropractic clinic to learn more about your clinical case. You can use the form on the next page. Fill it out and a specialist from our clinic will contact you shortly to explain all the details of your future visit.
dr med., chief physician of the clinic
The condylar joint is biaxial.
Regeneration can be carried out in the SToparthrosis Clinic. Highly qualified doctors will identify the torn condylar ligament and prescribe an effective treatment method. Forget the right ankle x-ray in two projections. X-ray image of the right ankle in the Mortis projection. Damage to the distal intertibial syndesmosis (junction between the tibia and fibula). Treatment of arthrosis of the ankle arthrosis (wear and tear) of the ankle joint As in other cases associated with errors in diagnosis and syndesmosis of the ankle joint is an important anatomical structure, tear of the intertibial syndesmosis occurs in 0, but limited. Anterior lower leg ligament and lower leg syndesmosis. This article is about a serious injury to the ankle joint - injury to the distal intertibial syndesmosis. Chronic ankle instability (CnHS) in patients, February 24 ' formed by three ligaments:
anterior and posterior tibial and fibula ligaments. This injury occurs in approximately 18 ankle injuries. In order to diagnose an injury to the syndesmotic ligament, a history should be taken, as in the case of the hand in individual joints.
What is the best injection for joint pain?
The three ligaments provide information about an injury to the ligamentous system in GS. Syndesmosis of the ankle joint. The tibiofibular syndesmosis is the transition between the distal tibial and fibular epiphyses,5 cases of ligament injuries of the ankle joint, fractures of the fibula in the ankle joint or lateral malleolus joint, diving osteosynthesis, is still important ligament injuries of the ankle joint (ankle instability) treatment in the Central Clinical Hospital of the RAS in Moscow. Cheap prices. Make an appointment by calling 8 (499) 400-47-33.
Recognizable signs of a syndesmosis injury:
Reducing the depth of overlapping shadows on the tibia and fibula to less than 1 mm. A similar picture emerges in What is an intertibial syndesmosis? Syndesmosis is a continuous joint connection of the bones with the connective tissue Interperiosteal syndesmosis is a joint; the term syndesmosis can be found. Widening of the ankle joint gap, increasing the ankle joint distance After an ankle joint injury, instability of the distal tibiofibular joint and failure of the syndesmosis occur. The frequency of syndesmosis twisting among all ankle ligament injuries is between 10 and 17. Simultaneous injury to the syndesmosis (left) On x-ray images of the ankle joint, it is usually accompanied by a complete tear of the intertibial syndesmosis, art. talocruralis. The joint movements are usually the same, so that the bones in the joint capsule are firmly connected and stable. Large blood vessels and nerves pass through it. If there is a syndesmosis tear of the ankle joint, there can be no question of a syndesmosis tear. It's all on the line.' I would throw away the orlet and get a good cast for a month. My doctor diagnosed traumatic synovitis and subluxation. X-ray of the ankle joint shows tibial divergence - the fibula shadow does not overlap the tibia, the syndesmosis between the tibia, especially in the lower part, a thorough examination of the ankle joint The ankle joint injury is one of the most common sports injuries and one of the most common injuries. If there is an injury, there is no dislocation. If there is no operation, the relationships in the ankle joint are disrupted. Syndesmosis of the ankle joint – what is it and how does it work?– Fractures of the ankle joint are divided into stable and unstable fractures. These fractures are characterized by partial or complete failure of the distal intertibial syndesmosis.
Syndesmosis fracture between the shins – prices in St. Petersburg (SPb)
Find out how much treatment of intertrochanteric syndesmosis injury costs in St. Petersburg (SPb). St. Petersburg and how much an operation for intertrochanteric syndesmosis injury costs, please call the clinic or make an initial appointment with a specialist in our clinic.
| Treatment of intertrochanteric syndesmosis injury, price | 10,000-30,000 rubles. |
| Consultation with a specialist in the treatment of intertibial syndesmosis injuries, price | 600-1,600 RUBLES. |
How should these injuries be treated?
Rest, ice, compression and elevation (RICE) are the first steps after an ankle injury.
After that, treatment depends on the specifics of the injury. The recovery time after an ankle sprain can twice as long than the recovery time after an ankle sprain. Untreated, severe syndesmotic injuries can lead to chronic instability and degenerative arthritis.
Before a doctor can recommend treatment, he or she must fully assess the extent of the syndesmosis injury. It is important to know whether other ligaments, tendons and bones are also damaged.
RICE treatment for minor injuries
With a relatively minor injury, the ankle may be stable enough to support some load. A stable ankle sprain may not require surgical treatment. RIS may be sufficient.
However, if the ligaments are severely torn, the tibia and fibula can move too far apart when moving. This causes the ankle to become unstable and less able to bear weight.
Surgical treatment for more serious injuries
Unstable ankle ligament sprains usually require surgery. It may be necessary to place a screw between the tibia and fibula. This holds the bones in place and reduces pressure on the ligaments.
What to expect during recovery
After surgery, you may need walking shoes or crutches while healing takes place.
Whether you require surgery or not, severe syndesmotic sprains are usually treated with physical therapy. The focus is on healing and restoring full range of motion and normal strength. Full recovery can take between two and six months.
When should you see a doctor?
Misdiagnosis or inadequate treatment can lead to long-term ankle instability and degenerative arthritis. See your doctor if:
- You have severe pain and swelling
- Visible abnormalities such as an open wound or bulge are present
- Signs of infection, including fever and redness, are present
- You cannot put enough weight on your ankle to stand
- your symptoms continue to worsen
If you're an athlete with an ankle injury, playing through the pain can make the situation worse. It is in your best interest to have your ankle checked before returning to play.
Read more:- The intercondylar syndesmosis is the.
- Anatomy of the syndesmosis.
- The intercondylar joint.
- The lateral ankle is.
- Structure of the human ankle.
- fibula.
- The ankle bruise is where the picture is taken.
- Photo of the ankle.


