It is important to know that subluxations can occur both in completely healthy people and in patients with osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis, which cause weakening of the ligaments around the patellar joint.
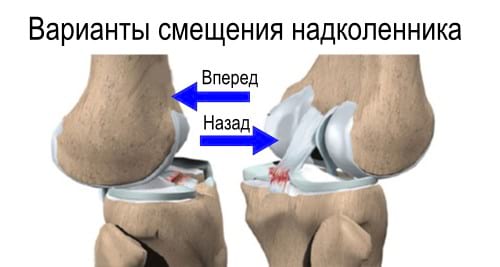
- Kneecap dislocation
- The reasons.
- Causes of hip subluxation
- How to recognize a hip subluxation (signs and symptoms)?
- Symptoms of vertebral subluxation
- Diagnosis of vertebral subluxation
- diagnosis
- Surgery for temporomandibular joint subluxation
- What are the risks?
- Diagnostic features.
- Symptoms of a dislocated kneecap
- Diagnosis of a dislocated kneecap
- Treatment of a dislocated kneecap
- Rehabilitation after a kneecap dislocation in the city of Naberezhnye Chelny
- Treatment of jaw joint problems
- Advantages of our clinic
- Possible complications
- Conclusions
- Related:
Kneecap dislocation
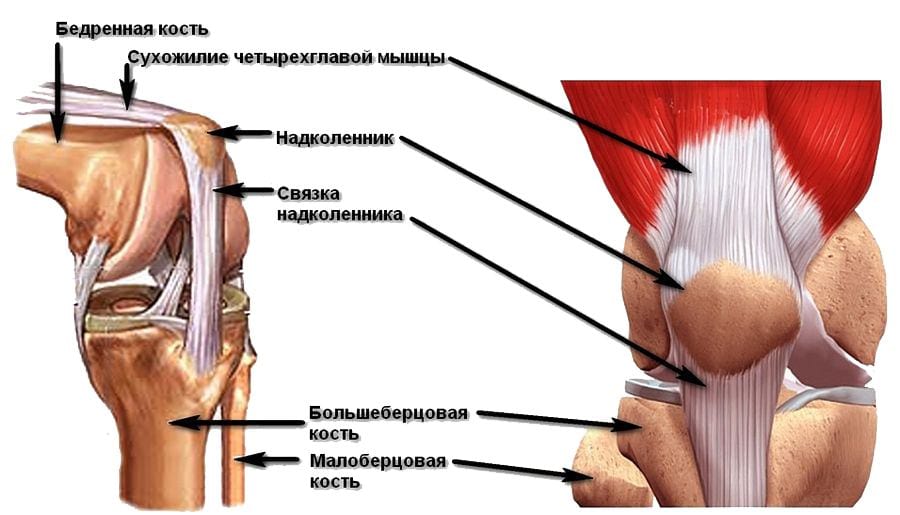
The patella is a large sesamoid bone (about the thickness of a tendon) located at the front of the knee joint. It is also known as the kneecap. It is covered with cartilage tissue on the inside, which faces the joint cavity. The tendons of the muscles and ligaments above the knee are attached to it, and the ligament that connects it to the thigh bone runs inwards from it. Its main function is protective (it surrounds the joint structures from the front) and stabilizing (it prevents the shinbone and femur from moving against each other).
A dislocated kneecap is a relatively common injury caused by a fall on the knee or an impact and is usually associated with anatomical peculiarities. It usually occurs on the outer (lateral) side. The patellar ligament may be torn and the cartilage structure may be compromised. The factors that predispose the patient to the pathology often remain unnoticed until the accident occurs and are not noticed. Injuries usually occur at a young age, mostly in women. This is due to the nature of the knee joint. People with pre-existing valgus deformities of the lower limbs (x-shaped) or connective tissue dysplasia are more susceptible to dislocations.
The reasons.
People who lead an active lifestyle, play sports and engage in strenuous physical exertion are at greatest risk of injury. The most common mechanisms are a fall on the knee, a side blow to the joint area and a sudden extension of the lower limbs.
Unique causes of this type of injury include:
- Tear of the meniscus.
- Abnormal development of the kneecap.
- Weak ligaments and muscles in this area.
- Prolonged dislocation of the kneecap.
- dysplasia.
- Arthrosis of the articulating part of the knee.
- Valgus-like deformities.
- previous trauma.
- Bleeding in the joint cavity.
Causes of hip subluxation
In early infancy, hip dysplasia most commonly causes subluxation of the femoral head. However, one should not think that if this injury does not occur in childhood, one will be sufficiently protected from it in adulthood. Quite the opposite. If you developed congenital or acquired cartilage dysplasia of the hip joint in infancy, you are at risk of various pathological changes in this bone joint.
First of all, it is important to understand that dysplasia does not go away. The thinning of the synovial cartilage layer in the affected areas persists throughout life. The alignment of the feet is abnormal, the femoral heads are not physiologically aligned in the acetabulum, and compensatory twisting and rotation of the pelvis often occurs.
All of these anomalies are not noticeable because they are not externally noticeable. Therefore, doctors do not pay attention to the existing risk factors during medical examinations.
Coxarthrosis hip subluxation often occurs in old age because not only the articular cartilage but also the bone tissue is destroyed. The degree of fixation decreases and deformation of the ligaments and tendons occurs.
Other possible causes of hip subluxation include:
- Excessive body weight, which puts increased pressure on the articular surfaces, displacing them against each other;
- abnormal alignment of the foot in the form of flat feet and clubfoot;
- Valgus or varus curvature of the tibia, thigh;
- deformities of the femoral neck;
- heavy physical work with constant strain on the muscles of the back and lower limbs;
- Deformed arthrosis of the knee joint;
- spinal curvature and poor posture;
- osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine, in which the patient has to spend a long time in an unnatural forced position;
- dystrophy or atrophy of muscle fibers;
- Scarring of ligament and tendon fibers after sprains and tears;
- hip joint arthroplasty; hip replacement surgery;
- stretching of the joint capsule;
- Fractures and breaks of the femoral head, femoral neck or acetabulum.
How to recognize a hip subluxation (signs and symptoms)?
The first symptoms of a hip subluxation are stiffness, limitation of movement, and pain that occurs with certain movements. For example, a characteristic symptom of a hip subluxation can be the inability to sit upright without support from other objects. The person is unable to pull the leg backwards relative to the torso. It may also not be possible to move the leg to the side. Any limitation in mobility is a symptom of a hip subluxation.
It can be difficult to distinguish the clinical signs of hip subluxation caused by trauma. The characteristic symptoms of a sprain or tear of ligament and tendon fibers, a bone fracture, etc. come to the fore. However, it is important to know that any trauma can affect the joint capsule. What is characteristic of a traumatic etiology is that the subluxation is almost always not fixed. It is an unstable condition that is very difficult to diagnose. However, an unstable position of the femoral head is very dangerous.
Here's how to diagnose a hip subluxation at home:
- Sit on a chair with your knees spread. If you feel like something is bothering you, see your doctor;
- Squat down, if this is not possible, you need help;
- Lie on your back and bring your bent knees to your chest; if you can do this, there is no subluxation in that plane.
This is only part of the diagnostic functional tests. You can have the others carried out together with your orthopedist during your first free visit to our chiropractic clinic.
We strongly recommend that you consult an orthopedist if you notice periodic cracking noises in the hip joint, tension in the surrounding muscles, rapid fatigue of the legs, inability to perform certain movements, stiffness and mobility that cause pain.
Symptoms of vertebral subluxation
The clinical picture can vary depending on the cause of the dislocation. A cervical subluxation presents with the following symptoms
- Sharp, stabbing pain in the neck making movement difficult;
- The patient is forced to keep his head tilted to the side or forward;
- The pain increases when the affected area is touched;
- Swelling and swelling can be felt in the area of vertebral displacement;
- The patient feels dizzy and has difficulty concentrating on anything;
- Tingling in the hands and 'goosebumps' on the body;
- Loss of strength in the upper limbs, and the patient is unable to hold an object or perform simple movements for a long period of time.
Spinal subluxations do not always cause immediate acute pain, so the condition can be old and neglected. If the diagnosis is not made in time, the situation worsens. The pathology does not resolve spontaneously, but the patient's condition worsens day by day.
- Neck pain syndrome occurs and worsens with prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position (sleeping on a high pillow or rapid movements are also risk factors);
- Physical strain or compression of the neck and back of the head muscles causes headaches limited to the forehead or back of the head;
- sideways movement of the neck is impaired;
- Autonomic dysfunction, reduced visual and hearing acuity, tinnitus, dizziness.
These symptoms do not go away with a change in posture. They can only decrease in intensity. If the thoracic vertebrae are subluxated as a result of the injury, discomfort and pain will occur in the abdomen, sternum or ribs.
If two lumbar vertebrae are dislocated, pain of varying intensity occurs in the lower back and sacrum area. The symptoms worsen with movement and are accompanied by abdominal and kidney pain. The lower limbs are also affected and there is numbness and tingling.
Diagnosis of vertebral subluxation
In almost all cases there are noticeable symptoms that make it impossible to confuse it with other diseases. In rare cases, the doctor has difficulty recognizing the condition during examination and mistakes a simple bruise for a dislocation or compression fracture. He then orders an examination using special equipment. The patient is sent for an X-ray, and the images are taken in two projections - straight and lateral.
It is important to diagnose the subluxation in a timely manner and initiate comprehensive treatment. Otherwise, the functioning of all organs and systems will be disrupted. At first the damage may not be that serious, but over time the situation gets worse. The musculoskeletal system, the cardiovascular system and the nervous system are attacked. The misalignment of the two vertebrae in relation to each other often leads to intestinal disorders and gastrointestinal dysfunction.
This pathology often occurs in childhood. Such disorders lead to the development of the following problems
- delayed physical development;
- cramps in the upper and lower limbs;
- attention and memory disorders;
- chronic fatigue, rapid fatigue;
- vision problems, nearsightedness or strabismus;
- Osteochondrosis, scoliosis and flat feet.
These abnormalities significantly affect the quality of life of young and adult patients. Timely treatment relieves pain and restores freedom of movement.
diagnosis
Traumatologists and oral surgeons, less often dentists, are responsible for diagnosing the pathology. The lesion is usually diagnosed through examination and questioning of the patient.
To clarify the diagnosis and exclude the dislocation and accompanying injuries and fractures, an x-ray is recommended to clarify the clinical picture. If the specialist still has doubts about the extent of the dislocation, a computer tomography or magnetic resonance imaging can also be ordered.

Surgery for temporomandibular joint subluxation
In most cases, the injury can be repaired conservatively. Recurrent subluxations of the temporomandibular joint are treated surgically. The procedures can be carried out openly or endoscopically. For example, the height of articular cartilage is increased by splitting it and inserting a Teflon implant into the gap. There is a method of deepening the socket that involves changing the position of the disc from horizontal to vertical. In some methods, part of the capsule is removed or reinforced with a strip of collagenous connective tissue. The exact type of operation is decided by the surgeon after a thorough examination of the patient and taking into account the characteristics of each individual patient.
Take advantage of this unique opportunity and arrange a free consultation for your planned procedure. Find out more here.

What are the risks?
A subluxation can cause serious disorders that negatively affect the body's future functionality. The musculoskeletal system, nervous system and circulatory system are primarily affected. A subluxation can also disrupt the digestive system and cause intestinal distress. Therefore, signs of a pathological condition should not be ignored, but the smallest symptoms should be paid attention to. Childhood pathology can lead to the development of the following complications
- Cramps;
- Impaired memory, inability to concentrate;
- increased fatigue;
- developmental delays;
- eye abnormalities such as myopia or strabismus;
- flat feet;
- Development of osteochondrosis, scoliosis and other spinal diseases.

Most of the disorders mentioned above are preventable; the most important thing is timely detection of a subluxation and its timely treatment.
Diagnostic features.
To determine the cause of the pathological condition, the patient must undergo a diagnostic examination, which usually begins with an initial examination and taking an anamnesis. The neurologist then carries out a palpation examination of the affected area.

However, since these measures are not always enough to make an accurate diagnosis, the child may be prescribed several radiological examinations, including oral x-rays, oblique x-rays (used to examine all articular processes) and spondylography, a common diagnostic method for subluxations, in which the condition of the Intervertebral discs and joints are assessed. Based on the results of these measures, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment.

Symptoms of a dislocated kneecap
Symptoms of a dislocated kneecap include pain at the front of the knee joint, an unstable kneecap, and a painful clicking sound when the knee joint moves - this occurs when the kneecap does not reset properly.
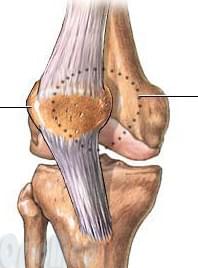
Outward displacement of the kneecap
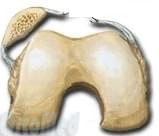
One cause of a kneecap dislocation is an injury to the internal anchoring of the kneecap.
Synovitis is an excessive buildup of fluid in the knee joint. During the examination, the doctor will question the patient and examine the leg. The doctor conducts special tests to determine the inclination of the kneecap - pressure on the kneecap from the outside can increase pain; increased pain when pressure is applied to the kneecap tilt.
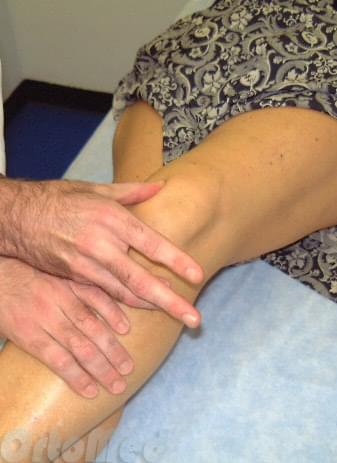
Examination of the leg if patellar instability is suspected
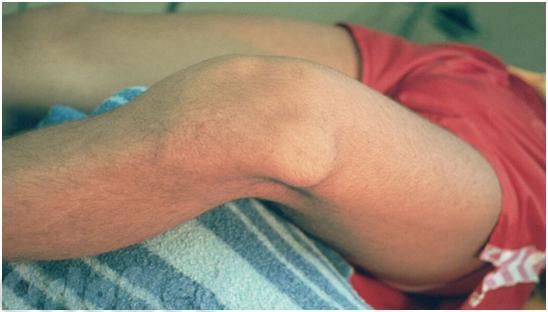
Diagnosis of a dislocated kneecap
To clarify the diagnosis X-rays, MRI or CT scans can be performed to clarify the diagnosis. X-rays are taken in straight, lateral and axial projections as well as in 20g or 45g flexion. A CT scan allows for a more accurate assessment of the patellar luxation. In addition, the position of the tibial tuberosity can be determined on the CT scan. The most important indicator is the TT-TG index. This is the distance between the tibial tuberosity and the femoral sulcus in an axial view - a distance of more than 15 mm is in most cases an indication of a patellar subluxation.
Treatment for a patellar luxation can be conservative or surgical. Conservative treatment consists of exercise, taping and the use of special orthoses.
Treatment of a dislocated kneecap
To confirm a dislocated kneecap, diagnostic procedures such as x-rays, CT scans and MRI scans are used. They are used to assess the condition of the kneecap, the bony and cartilaginous structures of the joint, and the bones of the thigh and shinbone. The method of treatment is determined only after a thorough examination.
In most cases, the dislocated kneecap is treated conservatively. First it is straightened again. All manipulations are carried out by a traumatologist or orthopedist under local anesthesia. After anesthesia, the specialist bends the injured leg at the hip joint to relax the tendons of the quadriceps muscle on the thigh. He then carefully straightens the knee joint and moves the kneecap in the right direction. An x-ray will check the correctness of this measure.
After a sprain, a plaster cast should be applied. In some cases, a special orthopedic bandage may be used. Immobilization of the knee joint takes between 4 and 6 weeks. The patient is prescribed painkillers or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,
Long-term recurring kneecap dislocations and acute traumatic dislocations may require surgery. After surgery, a knee cast is required for 4 to 8 weeks (depending on the cause and type of surgical treatment). Rehabilitation of the joint begins immediately after immobilization and continues for at least a month after the injury until full mobility is restored. Unfortunately, the operation does not always have a lasting effect - in 15-40 % cases it worsens.
Rehabilitation after a kneecap dislocation in the city of Naberezhnye Chelny
Rehabilitation after a kneecap dislocation or stabilization surgery is possible at the Center for Restorative Medicine in Naberezhny Chelny. Experienced physiotherapists and physiotherapists examine each case of dislocation individually. After analyzing the X-ray images, a rehabilitation program is developed. This includes:
The main goal of rehabilitation treatment is to normalize the motor function of the knee joint.
Among physiotherapeutic methods, UHF therapy, magnetic therapy and laser therapy are the most effective, as they help restore blood circulation and cartilage integrity. Hydrotherapy is possible immediately after removing the cast. Full recovery of knee joint function and return to active work is possible 4 to 6 months after the injury.
Manual therapeutic massage sessions improve local blood circulation, nourish cartilage tissue and restore physiological muscle tone to the injured limb. Massage is important for strengthening the muscles of the upper and lower legs, restoring correct biomechanics of gait and proper loading of the limbs. You can read more about massage techniques used in rehabilitation after a patellar dislocation here.
Physiotherapy sessions at the center are led by a rehabilitation therapist. The patient is trained to carry out the therapeutic exercises independently in the future. Physical therapy is essential for maintaining joint stability and proper tendon and muscle function. You can find out more about the physiotherapy program here.
The Restorative Medicine Center has the most modern equipment that allows patients to return to their normal lives, exercise regularly and regain full mobility. Find out about all treatment options here.
You can find out about the costs of the services offered at the clinic on this page. After any injury, proper rehabilitation is essential. Attempts to improve well-being alone often lead to irreversible complications. Call: +7 (8552) 78-09-35, +7 (953) 482-66-62 to get the necessary information and make an appointment with a specialist.
Treatment of jaw joint problems
Treatment of temporomandibular joint subluxation can be divided into therapeutic, occlusal and surgical treatment.
- Therapeutic treatment is used in the early stages of temporomandibular joint dysfunction to relax the masticatory muscles and normalize the function of the articular disc.
TMJ exercises are an example of a non-surgical treatment aimed at improving muscle strength and joint coordination. Most often, the exercises are performed with the help of a mirror 2-3 times a day for 20-30 minutes. This strengthens the tension of the muscle fibers and helps the joint to 'right itself'. However, orthodontic exercises have a moderate effect on the ability to prevent recurrent subluxations, so this treatment can be used as an adjunct to medical therapy. In addition to stretching and strengthening exercises for the jaw muscles, physical therapy treatments using heat, ice, electricity and ultraviolet light can also be used.
Other non-surgical methods include:
- Fixation of the premaxilla with orthopedic devices;
- Prolotherapy – injection of sclerotic or proliferative solutions;
- Botulinum toxin injections into the masseter and pterygoid muscles.
- Occlusion therapy includes custom-made mouthguards and braces in the form of removable and non-removable systems. With these systems, the chewing muscles are brought back into the correct position during treatment. This treatment can last between three months and 1.5 years. Occlusion treatment is more effective than drug therapy, but is more time-consuming and expensive.
If the symptom of mandibular subluxation is accompanied by pain, your doctor may recommend drug treatment to be used in conjunction with occlusion treatment. The most important medications may include:
- Painkillers prescribed by the doctor. They can have a local or large-scale effect;
- Tricyclic antidepressants – these are all types of antidepressants that act as analgesics in microdoses and also combat bruxism and insomnia due to severe pain;
- Myorelaxants – this type of medication also reduces pain syndrome caused by muscle spasms.
Advantages of our clinic
Oleg Konnikov's Gnathology Clinic specializes in the treatment of temporomandibular joint dysfunction. We can help you with:
- Facilitating chewing and improving chewing in general;
- correct swallowing and speech problems;
- minimizing excessive wear and fractures of teeth;
- ensure correct occlusion;
- Correction of facial irregularities;
- improve the ability of the lips to close completely;
- to relieve pain caused by temporomandibular joint disorders and other jaw problems;
- correction of facial injuries or congenital defects;
- Relief from obstructive sleep apnea.
Our experienced physicians are able to determine the exact cause of temporal lobe disorders and use modern conceptual treatment techniques to relieve symptoms and restore healthy function to the lower temporal lobes.
Possible complications
A subluxation is not as dangerous as the complications of an untreated long-term injury or foot drop disorder. Seeking professional help prematurely, inappropriate action by the trauma surgeon or not following medical recommendations for treatment and rehabilitation can lead to the following consequences
- inflammation of soft tissues;
- habitual contortion;
- Impaired blood circulation in the limbs;
- Muscular dystrophy;
- Arthritis, arthrosis and chronic hemarthrosis of the foot.
The most serious complication that can occur after an injury is partial or complete immobilization of the limbs. Most often, these disorders occur in older people whose joints are no longer able to fully regenerate due to wear and tear, even if they have fully followed medical protocols.
Conclusions
Any type of foot injury, including a subluxation, is always associated with interference with normal activities, lengthy treatment and rehabilitation. However, the earlier the disorder is noticed, the more effective the treatment and the more likely it is that mobility of the limb can be fully restored. But even if everything went well, you should not forget that the damaged joint will never be resilient again. That's why it's important to choose comfortable shoes with non-slip soles and to be careful when exercising.
Related:
Read more:- outward rotation of the leg.
- Treated subluxation of the ankle.
- dislocation of the foot.
- The lateral dislocation is.
- Subluxation of the ankle.
- X-ray foot subluxation.
- Dislocation of a bone in a joint.
- This is what a dislocated leg looks like.
