Reconstructive surgery is used to treat old ligament tears that result in instability of the ankle joint. The ligaments are surgically repaired and the ligament is then stabilized with an Ilizarov brace. If the injury is less than five months old, surgery is often performed using arthroscopy. Older tears, on the other hand, require open reconstruction.
- Closed ankle injuries
- Short description
- Clinic automation: fast and cheap!
- classification
- Description of ankle ligament injuries
- First aid for sprained ankle ligaments
- Treatment
- Conclusions
- Symptoms of a fracture
- Treatment
- Symptoms of an ankle sprain
- causes
- causes
- Which doctor should I see?
- Our specialists
- Prices for Services
- Conclusions
- Symptoms of a dislocated leg
- causes
- Which doctor should I see?
- Our specialists
- Prices
- Arthroplasty and arthrodesis
- clinical picture
- symptoms, course
- diagnosis
Closed ankle injuries
ICD categories: Other superficial ankle and foot injuries (S90.8), Multiple superficial ankle and foot injuries (S90.7), Superficial ankle and foot injuries, unspecified (S90.9), Ligament tears of the ankle and foot (S93. 2), strain and strain of the ankle (S93.4), injury to another muscle and tendon of the ankle and foot (S96.8), injury to multiple muscles and tendons of the ankle and foot (S96. 7), injury to unspecified muscles and tendons of the ankle and foot (S96.9), injury to own muscles and tendons of the ankle and foot (S96.2), ankle contusion (S90.0)
Short description
Closed ankle injuries – Injury to structures of the ankle joint without skin injury [1].
Patient category: Adults with closed ankle injuries.
Users of the protocol: Orthopedic traumatologists, surgeons, general practitioners, emergency doctors, paramedics.
Class I – the usefulness and effectiveness of the diagnostic method or treatment measure has been proven and/or generally accepted
Class III - the available evidence or general consensus suggests that the treatment is not useful/effective and may even be harmful in some cases
B - Results from a single randomized clinical trial or large non-randomized trials
C – General expert opinion and/or results from small studies, retrospective studies, registries.

Clinic automation: fast and cheap!
– 800 RUB / 5,500 KZT / 27 BYN – 1 order per month

classification
II. DIAGNOSTIC AND THERAPEUTIC METHODS, APPROACHES AND PROCEDURES
MRI of the ankle joint (indications: torn, dislocated and damaged ankle ligaments).
Minimum list of examinations to be carried out at the time of referral for a planned hospitalization: A planned hospitalization will not be carried out.
1. Magnetic resonance imaging of the ankle joint (indications: torn, dislocated and damaged ankle ligaments)
1 Collection of complaints and anamnesis, physical examination.
Complaints: Pain in the ankle, impairment of the motor function of the ankle.
Medical history: Presence of trauma with a direct (fall on foot) or indirect (acute rotation of the tibia while the foot is standing) mechanism of injury.
– X-ray of the ankle joint in two projections: no bony pathology, but secondary signs of soft tissue damage: expansion of the joint space, expansion of the syndesmosis.
– MRI: There are signs of damage to the ligaments of the capsule and tendon.
Description of ankle ligament injuries

Ankle ligament injuries are one of the most common injuries suffered by modern humans. In 12 % cases they are caused by tears, lacerations and dislocations in the ankle area. Sprains or subluxations of the ligaments in this area can also lead to damage.
Injuries to the ligaments around the ankle joint most commonly occur in cold weather when a person is crossing icy surfaces. They can also be caused by crossing uneven terrain or jumping from a height.
First aid for sprained ankle ligaments
An ankle ligament sprain can sometimes be attributed to injuries that occur when the foot is twisted. However, in this case it is incorrect to speak of a sprain because there is a bruise and swelling. At the time of the injury there was a tear in the ligamentous area. In contrast, in a sprain, the integrity of some fibers is compromised, but the functional properties remain unchanged.
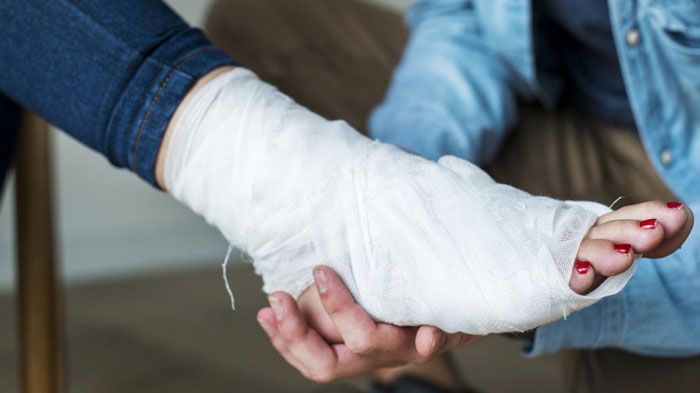
If signs of injury are found in the ankle area, the affected person should be treated urgently. The first step is to minimize stress on the ankle joint. This will prevent further deterioration of the ligaments and tendons. The following measures should also be applied to the affected person:
- Apply a cold compress. This prevents swelling and bruising in the surrounding tissues. The patient will notice a loss of sensation in the affected area, which will help eliminate the pain. In addition, using a cold compress immediately after the injury shortens the duration of the healing process. The bandage should be applied to the painful area for 20 minutes;
- Applying an elastic bandage. A bandage should be applied to immobilize the injured joint. Experts advise against a tight bandage as it can lead to loss of feeling in the fingers and swelling. However, such a bandage prevents future injuries;
- Elevate the leg. The injured limb should be placed on a pillow or chair (sitting position). This can relieve ankle pain and reduce swelling in the surrounding tissue.
Treatment
On admission, anesthesia of the fracture site was performed with 0.5 %iger novocaine solution (40.0 ml). Single-stage closed manual reduction of the medial malleolus fracture and foot subluxation was attempted. The patient was then admitted to a special ward for further treatment.
After examination and resolution of soft tissue swelling, the patient underwent surgery on the fourth day after injury. Under spinal anesthesia, an open reduction of the right medial malleolus fracture was performed with spokes and a wire tension loop, and the distal interdigital syndesmosis was fixed with a tension loop to which metal plates were attached.
The early postoperative period went without complications. On the third postoperative day, the limb was immobilized with a plaster cast from the lower third of the right thigh to the metatarsophalangeal joints. The patient was mobilized with forearm crutches without putting any weight on the right lower extremity. He was discharged to the outpatient clinic under the supervision of the district trauma center.
- Walking on crutches without putting weight on the right lower limb for 6-8 weeks after surgery.
- Plaster immobilization of the right lower extremity for 6-8 weeks.
- X-ray of the right ankle 4, 8 and 12 weeks after surgery.
- Gradual rehabilitation treatment after removal of the plaster cast.
Conclusions
The specialist dealing with this injury must be aware of the peculiarities of its diagnosis and treatment.
1 There are 100 % indications for surgical treatment for this injury. Conservative treatment with a plaster cast is doomed to failure and carries the risk of further complications:
- secondary displacement of the fragments;
- Consolidation of a medial malleolar fracture with displacement (fracture fusion and bone marrow formation);
- Outward subluxation of the foot;
- Stiffening of the ankle joint.
- This leads to early development of deforming osteoarthritis of the right ankle.
(2) The presence of an isolated medial malleolar fracture on the radiographs of the ankle obliges the doctor to examine the tibia along its entire length to detect a fracture of the fibula in its upper third.
3. To assess the distal syndesmosis injury in ankle fractures, an X-ray of both ankles should be taken in Mortis projection for comparison with the healthy limb.
5. Ankle fractures of the Weber C / Maisonneuve type are always 100%ige syndesmosis fractures.
(6) Immobilization of the distal intercondylar syndesmosis with a self-locking sling allows the correct positioning of the fibula in relation to the tibia and prevents surgical re-interventions.
(7) Plaster immobilization of the limb in the postoperative period is mandatory due to damage to the soft tissues of the tibia.
Symptoms of a fracture
- difficulty walking;
- inability to support oneself on the leg;
- Strong pain;
- swelling at the site of injury;
- In the event of a sprain, it is possible to lean on the leg.
The doctor examines the injury and orders an x-ray in two projections. If this measure proves to be inadequate, a CT scan will be ordered.
Once the fracture is closed, a splint is applied and painkillers are given. For an open hernia, a tourniquet and aseptic bandage are applied. It is forbidden to straighten the bone yourself. This work is carried out by a trauma surgeon.
Treatment
An ankle fracture is treated by straightening the joint and restoring its function. If this is not done, the injury can lead to osteoarthritis.
If the injury is not thoroughly repaired, full recovery is impossible and the patient suffers constant, excruciating pain. A severe dislocation and lack of skilled care result in disability.
- Conservative – manual repositioning of the bone. If necessary, a cast is applied to retract the limb with further correction.
- Surgical, with osteosynthesis – pins and metal connections are attached to the damaged bones. The patient wears a plaster cast for up to 1.5 months.
After the treatment, the patient has a long recovery period ahead of him.
Symptoms of an ankle sprain
Unfortunately, people who have suffered an injury do not seek help immediately. This is because the symptoms only become noticeable after a few hours. In addition to the visible changes in the shape of the joint, the symptoms also include
- Pain when moving or feeling the joint;
- bruising;
- Local or general increase in temperature;
- swelling.
The severity of the injury is divided into three levels. In mild sprains, the ligaments are only slightly damaged and the symptoms are unnoticeable. In the second degree of injury, the lesions are more extensive and there is severe pain with movement. The most severe form is where the ligaments are completely torn. Movement is then impossible.
causes
Many people mistakenly believe that an ankle injury can only be caused by sports or heavy exertion. Of course, these situations are the most common, but ankle sprains are also not uncommon in the home environment. This pathology is caused by:
Women who prefer high-heeled shoes often suffer from this pathology. The risk of a sprain also increases with age: as we age, the ligaments lose their elasticity and can no longer fulfill their function properly.
causes
Athletes, but also people with a sedentary lifestyle, often suffer from the symptoms of an ankle sprain. The risk increases with:
- overweight;
- high physical activity at work;
- lifting and carrying heavy weights;
- Congenital anomalies of the foot;
- wearing ill-fitting footwear.
A ligament strain is caused by instability of the joint. The structure of the joint changes due to inflammation and osteoarthritis. The second most common cause after sports injuries is weakening of the ligaments:
The second most common cause after sports injuries is weakening of the ligaments due to hypodynamics. A sedentary lifestyle leads to a loss of tissue tension, so a short jog or even a sudden movement can cause a tear.
Which doctor should I see?
A sprained ankle should be treated by an experienced doctor. If you notice discomfort, pain, temperature changes or skin tension in the area of the joint, you should consult a doctor:
Our specialists
The prices stated on this page are not a public offer. Please call us at 8 (495) 255-37-37 to clarify the cost of services and make an appointment with a doctor.
Prices for Services
In order to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy, the doctor must obtain an objective picture of the disease. He:
Conclusions
The doctors in our clinic recommend that you see a doctor in any case, even if your leg is only slightly swollen or hurts a little when twisted. Even small complaints can indicate a larger problem. If a bump or bruise forms after a leg sprain, it is an internal injury that requires treatment. If you miss a sprain or fracture, your ankle may become unstable and the pain is likely to become chronic.
What should you do if you dislocate your foot and the traumatologist confirms the injury? Firstly, you should follow his advice carefully and secondly, put as little strain as possible on the injured limb in the first few days after the injury (or, best of all, avoid it altogether). The success of rehabilitation depends on the type of injury and the individual characteristics of the body, as well as the mentality of the injured person. Remember that treating the spine and joints is time-consuming and you need to take responsibility for your own health.
Symptoms of a dislocated leg
The clinical picture of a dislocated leg is almost always the same and can only differ in the severity of the symptoms. The main symptom is severe and excruciating pain. It occurs at the moment of dislocation and increases with the slightest movement of the leg. A change in shape of the joint can be observed visually. Any attempt to touch the damaged area is accompanied by painful sensations. Other symptomatic features include:
- Swelling, swelling:
- skin changes, bruising;
- impairment of motor function;
- increase in body temperature;
- Numbness, paralysis of the limbs.
A dislocation compromises the integrity of the joint, and the displacement puts pressure on nearby blood vessels and nerve endings. If this condition is not treated in time, it can lead to paralysis of the leg. However, this is not the only consequence of a dislocation. Complications are possible:
The above symptoms are characteristic of an acquired dislocation, but in rare cases it is congenital. In such cases, the child should be diagnosed with this condition. Symptoms such as gait abnormalities, asymmetry of the buttock folds, and visible shortening of one leg warrant medical consultation.
causes
The causes of an acquired dislocation can be divided into traumatic and pathological causes. The latter includes diseases or conditions that caused the dislocation. These can include arthritis, joint inflammation, sprains or fractures. Traumatic causes are considered to be:
Most injuries that result in a sprain occur at home, during sports, and at work. Some professions are at risk, as are people who play contact sports, for example:
Most sprains occur from a fall or impact, so there is an increased risk of injury when skiing or ice skating. To prevent injuries, it is important to follow safety rules and use all necessary tools to protect your joints in the event of a fall.
Which doctor should I see?
If you experience severe pain in a lower leg joint after an injury that increases when you try to take a step, you should go to a medical facility as soon as possible. It could be a dislocated ankle. Your doctor will give you comprehensive advice:
Our specialists
The prices stated on the website are not a public offer. Please call 8 (495) 255-37-37 for costs and office hours.
Prices
Each of these specialists is able to diagnose a sprain and prescribe treatment as they specialize in a range of bone, muscle and joint injuries and conditions. When you see your doctor, you should tell them how your injury occurred and what symptoms bother you most. To complete the picture, he or she may ask you some additional questions:
Arthroplasty and arthrodesis
Most ankle surgeries are performed when severe post-traumatic osteoporosis is associated with severe pain and limited ankle mobility.
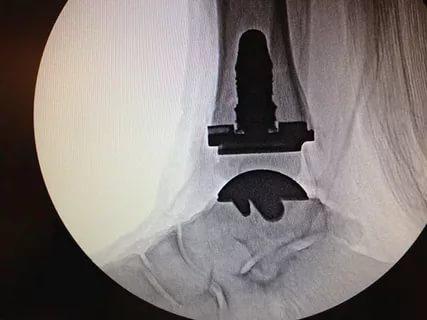
For younger patients, arthroplasty is more likely to be an option, in which the joint is replaced with an artificial joint prosthesis. This operation can restore full function of the ankle joint. If arthroplasty is not possible (old age, severe comorbidities), the patient undergoes arthrodesis - immobilization of the joint. This operation is performed as a last resort.
- Torn ligaments and fractures of the ankle joint are common at young ages. They are difficult to treat and often lead to disability.
- Fresh injuries are much easier to treat. The sooner a person receives medical care, the greater the chance that the function of the joint can be restored.
- Various methods are used to treat injuries, from conservative treatment to surgery.
- The choice of treatment depends on a number of factors. The severity and age of the injury, the instability of the ankle, the degree of post-traumatic osteoporosis, etc. all play a role.
- Surgery is the most radical method of treatment. It is usually carried out when the function of the joint cannot be restored with other means.
clinical picture
symptoms, course
A patient with a complete acute dislocation of the kneecap almost always notices the appearance of the deformity and complains about it when seeing a doctor.
Occasionally, the kneecap becomes dislocated when attempting to move the knee joint alone or with someone else's help. When taking an anamnesis, the patient may say that he has dislocated his knee, when in reality it is a dislocation of the kneecap. A kneecap sprain can occur from physical activity, direct trauma, or normal movement of the knee joint.
During the initial examination of the patient, deformities and swelling in the knee joint area are noticeable, and the clinical examination can be difficult. Consequently, the clinical diagnosis of accompanying knee joint injuries, such as. B. a cruciate ligament tear or meniscus tear, difficult. The restriction of movement of the knee joint during a patellar luxation is caused by pain and swelling of the soft tissues in this area.
When examining the knee joint, the doctor must assess the condition of the medial condyle and the ligaments that hold the kneecap in the upright position of the lower limb, check the health of the cruciate ligaments, and examine the articular protrusion on the talus for pain. Palpation of the knee joint reveals pain in the medial aspect of the patella, and the patient is distressed when attempting to move the patella outward. There is also swelling in the medial aspect of the joint near the inner part of the quadriceps muscle of the thigh (VMO).
Flexion and extension of the knee joint may be limited due to pain, but if slight flexion of the knee is possible, lateral displacement of the patella may be noticeable compared to the contralateral, intact knee joint. The lateral part of the knee joint is often painful to feel. The doctor must also check and assess the full range of motion of the joint. In elderly patients with patellar dislocation, rupture of the quadriceps tendon proximal to the patella may occur, resulting in significant limitation of active extension of the lower extremity and soft tissue loss in this area that is difficult to detect in the presence of a hematoma. The patient should be instructed to move the extended leg forward and if this is not possible, active extension should be checked. If possible, the patient should also be examined in a standing position to determine lower limb alignment and assess varus or valgus deformity [11].
diagnosis
Diagnosis of the disease or condition (group of diseases or conditions), medical indications and contraindications to diagnostic methods
2) Medical history examination (direct or indirect trauma to the knee joint, sudden flexion of the knee joint at home, during a fall, while dancing or during sports activities)
3) Instrumental examination (X-ray, MRI, CT, ultrasound).
Dislocation of the kneecap usually occurs spontaneously. In 80 % of patients, the kneecap may dislocate spontaneously or unilaterally; the remaining patients require specialist treatment (conservative or surgical treatment). Patients with a kneecap dislocation experience severe pain, deformation of the knee joint due to the displacement of the kneecap, limitation of movement of the joint, and impairment of the supporting system of the lower extremity.
Patients with a spontaneous dislocation may complain of pain in the anterior region of the knee joint, swelling of the knee joint, and a limitation in range of motion [12].
The diagnosis of patellar luxation is made based on the symptoms, the anamnesis and the clinical examination. Various clinical tests (Fairbanks test, Bassett test) have been described to assess kneecap instability [13, 14]. Physical examination is of great importance in the diagnosis of patellar luxation, but there is currently no evidence to support the use of a specific test. Further research is needed to confirm the applicability of testing in assessing patellofemoral joint instability [15].
comment. The Fairbanks test (Moving Patellar Apprehension Test) is performed in a supinated position with the patient flexing the knee joint to 20°. The inner edge of the kneecap is felt and an attempt is made to move the kneecap laterally. The patient reflexively tenses the quadriceps to prevent the kneecap from dislocating.
Read more:- Subluxation of the ankle.
- Inward subluxation of the foot.
- How do you treat a sprained ankle?.
- dislocation of the ankle.
- The lateral dislocation is.
- Dislocation of a bone in a joint.
- Ankle ligament strain, ICD.
- This is what a dislocated leg looks like.
