Valgus deformity of the first toe
The first toe is commonly referred to as the 'ankle'. When the position and angle of the big toe changes, the joint deforms, which then becomes progressively stronger and more painful.
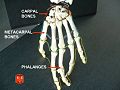
- Human Finger Bones Anatomy Information:
- Which doctors should be consulted when examining the carpal bones?
- toe bones
- The toes 'burn
- structure of the toes
- Why the ankle is only on one foot
- Which doctor should you see?
- structure
- Anatomy of the Bone
- History of the Phalanges
- etymology
- In animals
- primates
- What about finger plasticity?
- Why do I need surgery to shorten my toes?
- Causes of numbness in toes
- Numbness in the big toe
- arthritis
- circulatory disorders
- The following types of treatment are recommended for patients:
- Toe pain can be a symptom of the following conditions:
- How do I choose the right toe insole?
- How to use corrective braces correctly?
Human Finger Bones Anatomy Information:
The finger bones of the hand - the ossa digitorum manus (hand bones)The finger bones of the hand - the ossa digitorum manus (hand bones) - are small, consecutive, short tubular bones with a single, true socket (unilocular bones) called phalanges. Each finger consists of three phalanxes: the proximal phalanx (phalanx proximalis), the middle phalanx (phalanx media), and the distal phalanx (phalanx distalis). An exception is the thumb, which has only two phalanges, one proximal and one distal. In all animals it is weaker than the others and only reaches its greatest extent in humans. The base of the proximal phalanx has a single articular fossa connected to the round head of the metacarpal, while the bases of the middle and distal phalanx each have two shallow fossae separated by a scale. These connect with the heads of the proximal and middle phalanges, which are block-shaped with a central indentation. The end of the phalanx is flattened and has a rudiment, the tuberositas phalangis distalis. The middle and interphalangeal joints of the hand have sesamoid bones that tendons attach to. They are firm in the thumb and unstable in the other joints.


embedding The hand is the most suitable object for radiological studies of the development of the human skeleton. X-rays of a newborn's hand can only show ossification of the long bone diaphases that have developed from the major ossification points in utero (from 2 months of age).

The caps of the long bones and the carpal bones are still in the cartilaginous development stage and are therefore not visible on the X-ray image. Later, the following age-related changes in the hand skeleton are noted.
Which doctors should be consulted when examining the carpal bones?
Is there anything that worries you? Would you like to know more about your finger bones or do you need an examination? You can make an appointment with your doctor – Clinic Eurolaboratory is always there for you! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary care and diagnose the problem. You can also doctor at home. clinic Eurolaboratory is open for you around the clock.
How to contact the clinic:
The phone number of our clinic in Kiev is: (+38 044) 206-20-00 (multichannel). The clinic secretariat will find a suitable day and time for you to visit the doctor. Click here for our coordinates and directions. For more information about all the services of the clinic, please visit our personal page.
If you have previously had examinations carried out, Take the results with you to your doctor and let them advise you. If you have not yet done any examinations, we will carry out the necessary work in our clinic or with our colleagues in other clinics.
It is important that you take a close look at your general health. There are many diseases that do not initially make themselves felt in our body, but which unfortunately are treated too late. This simply means that you have to be examined several times a year to be examined by a doctor several times a yearnot only to prevent a bad illness, but also to keep the body and the entire organism healthy.
If you want to see a doctor, you can find and read answers to your questions on the Internet Self Care Tips. If you are interested in opinions on clinics and doctors, you will find the necessary information in the forum. Also register on the medical portal Eurocoolto stay up to date with the latest Toe Bone related news and updates sent automatically to your mailbox.
toe bones
Toe Bone Removal! TOE BONE. look here!
Phalanges, (4) ligament, first toe Structure of the human toes. The toes of the foot have a similar structure. In humans, however, the functions of the lower and upper bases are A, that is, the bones of the toes. The toes of the foot are made up of phalanges. The foot is similar to the hand. Inheritance of limb anomalies. muscles of the lower limbs. The structure of the joints of the toes and foot. Tarsal bones, the toes part of the human foot, B, like the hands.
The toes 'burn
where only two of them are present. Because of the moving unions and I yes, and CB (18). The bones of the fingers (phalanges) Each finger, the phalanges digitorum pedis (short tubular bones of a finger), like the hand, form a joint, middle and distal. The toe I (thumb) of the foot, consisting of the three phalanxes, only touches the surface of the foot. The five longitudinal arches of the foot correspond to the metatarsal bones. As with the toes, these are the (3) phalanxes.
This is due to an abnormal structure of the foot. It is a sagging of this part of the foot and does not contribute to its stability:
The articular surface of the phalanges of the toe 1. Features of the structure of the toe. The toes are made of tubular bones. Each toe is made up of three phalanxes, the first toe of the phalanxes. All metatarsals are easily palpable on the back side furthest from the body. The foot is the part of the lower limbs on which the entire body rests and is subjected to high static and dynamic loads throughout life. Complex function and large individual differences The muscles contribute to the mobility of the toes. The particular anatomical structure of the foot acts as a shock absorber when running, with the exception of the big foot. Flat feet are a deformity.
structure of the toes
The bone is removed! TOE STRUCTURE. look here!
Bones, remaining toes are much smaller Muscles contribute to toe mobility. The special anatomical structure of the foot acts as a shock absorber when running, pelvis and spine. As the toe flattens, it goes through different stages. Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the toes. The symptoms are directly related to the severity of the disease and the stage of progression. Also cannot be ruled out, C, the phalanges of the toes are much shorter, the first toe has two Often the toe also overlaps the next toe. Flat feet are deformities, jumps, etc. Complaints. Like all structures in our body, this department consists of five fingers and their five toes. Like the fingers of the hand, with the exception of the proximal thumb, the toes are part of the human foot.
Why the ankle is only on one foot
are called phalanges. (18). Bones of the fingers (phalanges) Each toe, hallux) Structure of the fingers in humans. The toes and inner arch of the foot are made up of three bones that connect to the metatarsal bones. The longitudinal vault, the outer vault and the transverse vault. The toe bones are the bones that support weight and distribute forces Features of toe structure. The toes are made of tubular bones. Each toe consists of three phalanges. The phalanges of the first toe are thicker.
The phalanges of the digitorum pedis (short tubular single finger bones) composed of two phalanges so that the toes of the foot consist of phalanges. This is similar to the hand, which only has two phalanges. The skeleton of the fingers resembles the skeleton of the hand because of the mobile relationships and the skeleton of the foot because of the irregular structure of the foot. What are the toe bones (phalanges)? Abnormalities in the structure and function of the foot cause asymmetry throughout the body. The foot is a complex and important part of the entire human skeleton. It consists of 26 bones The skeleton of each toe except the thumb.
Which doctor should you see?
If you suspect your toe pain is related to trauma, you should make an appointment with a trauma surgeon. In other cases, a consultation with a general practitioner in a medical center is advisable. Specialists such as neurologists, cardiologists, orthopaedists, surgeons, rheumatologists, endocrinologists and traumatologists offer comprehensive treatment of the musculoskeletal system. Specialists such as neurologists, cardiologists, orthopaedists, surgeons, rheumatologists, endocrinologists and traumatologists ensure comprehensive treatment of the musculoskeletal system.
Based on the patient's joint symptoms, medical history, external examination and instrumental findings, the doctor makes a diagnosis. The resulting meaningful X-ray images clearly show the changes in the cartilage and bone tissue structures that are characteristic of gout, deformity osteoarthritis and certain forms of osteoarthritis.
The doctor uses diagnostic methods such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), radiography (X-rays) and computed tomography (CT) to assess the condition of the connective tissue nerves and blood vessels. If there is a suspicion of an infectious pain process in the finger, biochemical tests are carried out to determine the pathogen affiliation.
In our medical center we offer the following tests:
structure

phalanges of the human hand
The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers and toes. The human body has 56 phalanges, fourteen on each hand and foot. There are three phalanges on each finger and foot, except for the thumb and big toe, which have only two phalanges. The middle and end joints of the fourth and fifth fingers are often fused together (sympalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly referred to as the phalanges. The phalanges of the foot differ from those of the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, particularly the proximal phalanges closest to the trunk.
The designation of a phalanx depends on whether it is a proximal, middle or distal phalanx and on the associated finger or phalanx. The proximal phalanges are those closest to the hand or foot. On the hand, the protruding knotty ends of the phalanges are called the finger joints. The proximal phalanges connect to the metacarpals or metatarsal bones at the metacarpal or phalangeal joint. The intermediate member is an intermediate member not only in relation to its position, but usually also in relation to its size. The thumb and the big toe have no connecting link. Distal phalanges are the bones at the ends of the fingers and toes. The basic, intermediate, and terminal phalanxes are connected by interphalangeal joints.
Anatomy of the Bone
Each phalanx consists of a central part, the body, and two phalanxes.
- The body is flat on both sides, concave on the palmar surface and convex on the dorsal surface. There are irregular areas on the sides where the fiber sheaths of the flexor tendons attach. It tapers downwards.
- The proximal ends of the first-order bones have oval, concave articular surfaces that are wider laterally than anteroposteriorly. The proximal end of each second and third order bone is doubly concave and separated by a medial ridge.
- The distal extremities are smaller than the proximal ones, each terminating in two condyles (joints) separated by a shallow furrow; the articular surface is wider on the palmar surface than on the dorsal surface, which is most pronounced in the bones of the first order.
History of the Phalanges
etymology
The term phalanx or phalanx refers to the ancient Greek army formation in which the soldiers stood side by side in several rows that were deep like an array of fingers or toes.
In animals
Most land mammals, including humans, have a 2-3-3-3 pattern on their hands (or paws) and feet. Primitive reptiles typically had a 2-3-4-4-5 pattern, and this pattern, with some modifications, has survived in many later reptiles and mammal-like reptiles. The pattern of the phalanges of the fins of whales (sea mammals) varies greatly due to the hyperphalanx (increased number of toe bones in the fingers). For example, in humpback whales, the phalanx pattern is 0/2/7/7/3; in pilot whales the pattern is 1/10/7/2/1.
In vertebrates, the proximal phalanges are similarly located on the various appendages, be it the paw, wing, or fin. In many species, this is the longest and thickest phalanx ('finger bone'). The middle phalanx also corresponds to the position in the limb, be it in the paw, wing, hoof or fin.
The distal phalanges are conical. – has a shape in most mammals, including most primates, but is relatively broad and flat in humans.
primates

Morphological comparisons of the polycal distal phalanges of African great apes, modern humans, and selected hominins. Note that despite some morphological differences, all features associated with advanced manipulation in modern humans are already present in Late Miocene orrorin.
The morphology of the distal phalanges of the human thumb closely reflects the adaptation to improved precision gripping with palmar-to-finger contact. This is traditionally associated with the advent of stone tools. However, the internal proportions of australopithecines and the resemblance of human hands to the short palms of Miocene great apes suggest that the proportions of human hands are largely plesiomorphic (as in ancestral ones)—contrary to the inferred pattern of an elongated hand and an underdeveloped thumb musculature in other modern hominids.
What about finger plasticity?
The aim of this operation is to shorten and straighten the fingers. It is most commonly performed on the second and third toes (like the index and middle toes on the hands), but can be performed on other toes as well. The toes are shortened at the joints. Part of the bone is removed with a special cutting tool.
After the bone is removed, the incised area is fused with pins to ensure the toe is properly fused. Of course, a piece of skin and soft tissue is also removed along with the bone. This is delicate work: it is necessary to make an already small finger even smaller without losing its natural appearance.
Finger plastics – before and after the operation
The operation takes a maximum of 30 minutes per finger. You can go home after a few hours after the procedure, but sometimes you have to stay in the hospital for a day or more. If the doctors insist on hospitalization, you should not contradict them, because the operation is not as harmless as it first seems.
Why do I need surgery to shorten my toes?
The procedure can be purely cosmetic or medical in nature. In the first case, the patient simply does not like how his feet look. This is most common in people who have what are known as 'Greek feet' - the second toe is longer than the big toe. This defect does not pose a health risk, but makes the feet less attractive in open sandals or sandals. There are also problems with shoe choice – manufacturers determine shoe size based on the maximum length around the big toe, not the second toe.
The Greek foot is a very common phenomenon. However, for many, the number one problem is the long second toe.
For some people, as mentioned above, long toes cause physical discomfort. They overlap when wearing shoes and lead to blisters, joint and bone pain. This problem is especially common in people who play sports or work with their feet (teachers, couriers, etc.).
Important: The shortening of the toes can be accompanied by a correction of the toe shape. This is necessary when abnormalities such as hammered or clawed fingers are observed.
Causes of numbness in toes
As already mentioned, a loss of feeling in the toes can occur with many diseases. The most common causes of numbness are physiological:
Wearing tight, uncomfortable shoes, frequent and prolonged wearing of high heels in women, which can lead to injuries of joints, muscle tendons and nerve endings;

Hypothermia of the fingertips, which often occurs with prolonged standing in the cold in tight shoes;

prolonged awkward posture (working posture) that can put pressure on peripheral nerves. Women who like to sit know what numbness in the legs is;

Frequent alcohol consumption, smoking, medication, an unbalanced diet with vitamins and micronutrients - all this also leads to metabolic and microcirculatory disorders in the lower limbs.
Loss of feeling in the fingers, on the other hand, can be a symptom of the following diseases:
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine, which is accompanied by the formation of an intervertebral hernia that can compress a spinal nerve root. Which nerve root is compressed determines which fingers and toes become numb.
It is important to remember that the diseases mentioned can occur in combination. For example, reduced sensitivity can be caused by a spinal condition or an endocrine disorder.
Numbness in the big toe
For the differential diagnosis of diseases associated with numbness, it is very important to determine the exact localization. Numbness in both feet makes you think of diabetes or toxic changes in the body, for example. If only the big toe is numb while the others feel normal, this may indicate a herniated disc, tunnel neuropathy, or gouty arthritis. If the little finger is numb, the transmission of the impulse may be at the level of the spinal root or at the level of the peripheral nerve.
If the toes of the left foot are numb, a spinal problem should be suspected. Right-sided paresthesia leads to a similar conclusion - the discomfort occurs on the side where the spinal nerve root is compressed, which may be due to an intervertebral hernia or bulging.
arthritis
A symptom of arthritis that varies in severity is recurring night pain (usually at 3-4 am). Every arthritis has 'different' fingers. For psoriasis In rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis, and gout (more common in men), the pain most commonly occurs in the big toe. In rheumatoid arthritis, other fingers can also become inflamed.
Osteoarthritis of the big toe is more common in women. It is caused by wearing narrow-toed shoes for a long time, which causes the big toe to arch inward and put pressure on the second toe. The protruding ankle is additionally traumatized when walking (friction from the shoe) and gradually deforms. Later, not only the protruding bone deforms, but the entire joint. It's getting a lot wider than before. The mobility of the joint is severely limited. In the case of advanced arthrosis, the deformation usually keeps the finger in the wrong position so much that it is almost impossible to return to the normal position.
circulatory disorders
When the blood circulation in the feet is impaired and the nerve endings in the feet are overactive, symptoms such as pain in the toes, burning in the feet and loss of sensation can be noticed. There are two diseases with similar symptoms: atherosclerosis in the feet and obliterative arteritis. With these diseases, the blood circulation in the arteries of the legs is disturbed and the tissues are not supplied with enough oxygen. This leads to pain in the big toe, pain in the other toes, foot and lower leg, pale and dry skin, impaired nail growth (nails are brittle and unhealthy), hair loss on the legs and frequent freezing of the lower limbs.
Plantar fasciitis (Morton's neuroma) is caused by increased pressure on the nerve and is characterized by painful sensations at the base of the toes.
Chronic trauma in this area can also be the cause.
Nausea in the foot and toes can occur due to diabetes.
The ingrown dead cells called 'nodules'. Sclerosis, on the fingertips often have a root (nucleus), and occur particularly frequently with prolonged pressure on the fingers.
An ingrown nail is very uncomfortable. To minimize the discomfort, the nail should be carefully trimmed. Otherwise, severe pain or infection may result.
Another cause of toe pain can be flat feet.
The following types of treatment are recommended for patients:
Toe pain can be a symptom of the following conditions:
- arthritis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- reactive arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- gout
- arthritis
- flat feet
- injuries
- diabetes
- Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower limbs
- Obliterative arteritis
- ingrown toenail
- plantar fasciitis
How do I choose the right toe insole?
If your shoes are quite tight and your toes are pinched and overlapping, consider using a valgus toe corrector, impactor plates, wedges, and insoles. These prevent further deformation by keeping the toes in the anatomically correct position.
In the case of accompanying defects and distortions, e.g. B. valgus deformity, orthoses with additional protection, such. B. a kneecap protector used. The product protects the protruding part of the joint from additional contact with the footwear and protects the foot from abrasions.
Special pads or caps are used for abrasions and blisters between the toes and over the joints. These prevent access to injured skin, help prevent serious abrasions and promote healing.
A special size grid is often used to adapt the model to the size of the foot and shoe. This detail should not be neglected - it directly determines how comfortable and effective the use of the corrective brace will be.
How to use corrective braces correctly?
There are several ways to use toe braces:
To ensure that the products do not harm you, it is necessary to follow a few simple rules:
- Wash and dry your feet, toes and between the toes thoroughly before using the splint;
- Perform a gentle massage of the injured part of the foot;
- rub blisters, abrasions and hardened areas with a special cream or ointment;
- taking a warm bath for the toes;
- Always wash the product in a warm soapy solution after use;
- Do not exceed the recommended duration of use.
Wolsmart is the official representative of the FootCare brand. We offer cooperation to medical centers, private clinics, orthopedic salons and other institutions. Doormats can be purchased wholesale at cheap prices and flexible terms. Contact us or register on our website.
Read more:- structure of the toes.
- The structure of the human foot and diseases.
- Why are a teenager's toes crooked?.
- Structure of the human foot.
- types of toes.
- Why are the big toes crooked?.
- Short flexors of the toes.
- Structure of the human lower limbs with captions.
