If the problem is ignored, it becomes chronic, limiting mobility and leading to chronic pain.
- First aid for a sprained ankle
- Can I take off my shoes?
- causes of injury
- symptoms of a sprain
- stages of recovery
- Methods of rehabilitation treatment
- What is rehabilitation like after sprains and dislocations?
- What is a fracture?
- Treatment of dislocations and fractures
- Prevention of sprains, joint and muscle strains
- 5 rules to protect against sprains
- Symptoms of an ankle sprain
- Anatomy' of the injury and most common injuries
- species
- symptoms
- Sprained ligaments: treatment
- How else can dislocations be treated?
First aid for a sprained ankle
Many people are familiar with the pain that occurs after a slip, twist or trip. A sprained ankle is painful and often unexpected. What is the first aid treatment like?
A tight bandage should be applied to the site of injury. An elastic bandage is best. This is the most effective way to deal with the situation. As a rule, a gauze bandage is used, which should be wrapped as much as possible. With an elastic bandage, two or three layers around the contour of the joint are sufficient to do the job. It is advisable to limit the movement of the injured person as much as possible. It is advisable to keep the injured area cold.
Can I take off my shoes?
If you have a serious injury, it is best not to take your shoes off because of the swelling, which will make it impossible to put them back on later.
Another important point: there is always pain. For such injuries, pain-relieving ointments or gels can be used.
If the injury was sustained during the day, the pain intensifies in the evening. To stay awake and rest, you can take some pain relievers from the medicine cabinet. However, only under the condition that the person concerned is familiar with the drug and knows for sure that he is not allergic to it.
causes of injury
Twisting of the ligaments in the ankle can be caused by
- lateral bending of the foot when walking or running;
- Falling or landing on your heels during a jump;
- twisting of the foot;
- twisting the foot on an uneven surface or stepping on the foot;
- twisting of the foot during sports.

These injuries are common in athletes during training. Ankle sprains in children and adolescents can be caused by flat feet or club feet. Adults with weak joints or limited coordination also suffer from this type of injury. The ankle can be dislocated simply by climbing or descending stairs, or by twisting the ankle. This often happens in women who like to wear high heels.
symptoms of a sprain
The main symptom of this injury is a sharp pain in the ankle. Swelling occurs immediately or after some time. There may also be reddening of the skin or a hematoma. The foot strike is painful and walking after the injury is difficult.
The symptoms of an ankle sprain depend on the extent of the injury. The more ligaments involved in the sprain, the greater the extent of the injury.
- With a mild sprain, the pain passes quickly and swelling can occur.
- A moderate sprain causes severe pain, swelling, and easy bruising.
- In severe cases, tendons and ligaments can also be torn.
In any case, a doctor's consultation is required to ensure there are no other injuries.
If the pain doesn't increase until the first 2 hours, there's a possibility of a more serious injury, such as a head injury. B. a torn ligament or a fracture. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.

stages of recovery
Restoring joint function begins with immobilization. Early treatment improves the patient's condition and prevents post-traumatic complications. The therapeutic measures to improve the regenerative capacity of the osteoarticular system are carried out in several stages:
- First phase.The first phase consists of a rest phase in which the injured area is firmly fixed. This is necessary to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. The specialist can prescribe medication to relieve symptoms, as well as physiotherapy treatments. Depending on the location of the injury, this can take up to 1.5 to 2 months.
- While second phase the restraining devices are removed. This phase lasts between 2 and 3 weeks. During this time you should only do little physical activity. There are specific exercises that can be performed for each anatomical area. Rehabilitation after a dislocated hip is much more difficult than with an injury to smaller joints. Therefore, it is better to do them under the guidance of a specialist. Soothing bandages should be applied regularly. The movements should be gentle and of low amplitude.
- The aim is phase three – Strengthening of the muscles and ligaments. This phase lasts 2 to 3 months. The therapeutic exercises in this phase include active movements to train the flexor and extensor muscles. A rotation of the joint is performed. Resistance and weight bearing exercises are performed under the supervision of a physical therapist. If there is a lack of exercise, the injured area is bandaged with an elastic bandage.
- Diploma, fourth phaselasts between six and twelve months. The aim of this phase is the complete restoration of function after the injury. A gradual increase in resilience through physical therapy is recommended.
Methods of rehabilitation treatment
Rehabilitation for dislocations includes a number of measures to restore function. All patients are subjected to the treatment procedures, regardless of the severity of the disease, the duration of immobilization, and the age group. Therapy is based on the following principles:
- therapeutic exercises – Therapeutic gymnastics is the most important method on the road to recovery. Regular exercises, starting with simple elements and gradually moving to more complex exercises.
- Massage of the injured area – Massages serve to improve blood circulation, reduce tissue edema and strengthen the musculoskeletal system of the upper limbs.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment – This physiotherapy accelerates cell regeneration and shortens the rehabilitation period.
- The use of supportive orthopedic.
What is rehabilitation like after sprains and dislocations?

Unfortunately, no one is immune to sprains and strains. Also, every body deals with these injuries differently. Therefore, a sprain, serious bruise or dislocation sometimes requires serious treatment and a long recovery process.
The rehabilitation process is designed individually for each patient. The severity of the injury, age and state of health must be taken into account. However, as a rule, doctors adhere to the following general scheme:
- Reduction of swelling and vascular changes that occur with prolonged immobility of the limb (or the whole body);
- increasing the tension and elasticity of muscle fibers (to prepare them for minimal physical exertion);
- gradual restoration of motor function (through massage, physiotherapy, mechanotherapy, physiotherapy, etc.).
- Strengthening the general condition of the body (through a healthy diet, a healthy lifestyle, adequate sleep).
What is a fracture?
Put simply, a fracture is an injury to a bone caused by mechanical damage. There are different types of fractures:
- Closed (the soft tissue is intact).
- Open (soft tissue is affected, bone fragments lie outside).
- Not displaced (bone fragments are not displaced).
- Shifted (bone fragments are shifted).
- Pathological (caused by a bone disease – cancer, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, etc.).
- You feel pain (which can be of different types).
- The limb is in an unnatural position.
- Mobility is impaired - you can only bend it a little, in the part where there is no joint.
- Bone splinters are visible in the wound (if the fracture is open).
- There is severe swelling at the site of the injury, which developed very quickly.
- Traces of blood are visible at the site of the injury and there is a hematoma.
- Pain increases when the limb is rotated about its axis, a symptom of axial overload.
Treatment of dislocations and fractures
Both types of injuries require proper assessment and an appropriate treatment plan. For this reason, trauma surgeons prescribe X-rays to assess the extent of the injury (rarely CT, MRI or ultrasound). Only after taking a picture of the injured area, taking the medical history and asking the patient about the treatment does the surgeon decide how to proceed.
In severe cases, a bone prosthesis may be indicated, in milder cases, a cast or bandage may be used. For mild sprains, the doctor may prescribe ointments to relieve pain. For bone sprains and fractures, doctors also often prescribe the following medicines:
On our website you can see all the medicines available in pharmacies in your city and their prices by entering the name of the medicine in the search box and doing a search.
Prevention of sprains, joint and muscle strains
In order to avoid sprains, it is important to be careful in sports and in everyday life. However, you should never protect yourself and your children from physical exertion. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises as part of an overall exercise program can help you avoid sprains and keep your joints strong and flexible. To prevent sprains, it is important to choose comfortable shoes, especially when exercising and when you are on your feet for most of the day. Shoes should be high heels, preferably with laces so they snugly enclose the ankles. Do not wear heels as they make it easier to twist your ankle. High-heeled shoes also promote this phenomenon.
If sprains are common during sports, you should wear special orthoses or protect the vulnerable joints with an elastic bandage. There are specific exercises that can strengthen the muscular corset and minimize the risk of dislocations.
5 rules to protect against sprains
- Warm up before exercising and warm up again afterwards.
- Don't exercise to the point of exhaustion - fatigue increases the risk of accidents.
- Avoid falls – Keeping stairs, hallways and the garden clean and sanding the paths around the house in winter is an excellent measure to prevent injuries.
- Try not to walk or run on uneven surfaces.
- Eat a healthy diet to strengthen your muscles, bones and joints.
Symptoms of an ankle sprain
Symptoms of an ankle sprain can range from mild to severe. Sometimes a minor injury doesn't cause noticeable changes in the ankle joint and movement is normal, but that doesn't mean there isn't a problem. Serious injuries may require hospital treatment. However, the symptoms should not be ignored to avoid numerous problems and repeated injuries. You should see an orthopedist or sports doctor as soon as possible.
Most ankle sprains are associated with ankle pain, which increases with walking as pressure on the injured ligament increases. Another symptom is swelling (oedema) or bruising, which is also common but not always present.
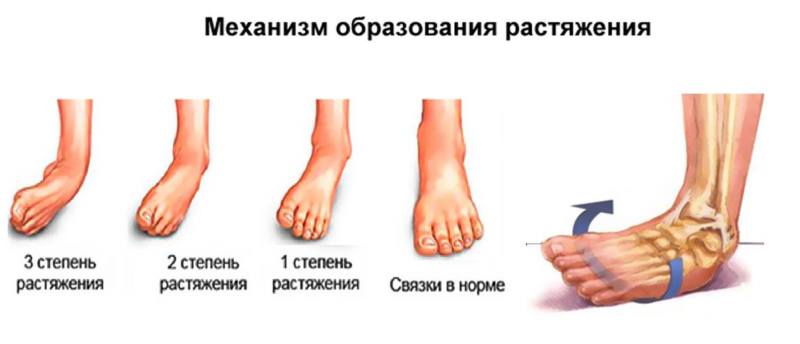
Ankle sprains are graded on a 3-point scale based on the degree of tissue damage. Treatment of the injury depends on the extent of the injury.
Anatomy' of the injury and most common injuries
The ankle joint consists of the articular surfaces formed by the distal ends of the tibia, fibula and talus. It also includes the joint capsule, which is reinforced by ligaments: on the medial side by the triangular ligament, on the lateral side by the anterior ambulatory and pectoral ligaments, the posterior and fibular ligaments, and the calcaneal ligament. The joint capsule holds the bones that make up the joint and provides the right environment for the joint to function by preventing adjacent tissue from penetrating between the bones and retaining synovial fluid. In an ankle sprain (commonly referred to as an ankle sprain), the ligaments of the joint become stretched or torn, damaging the joint capsule.
- The most common type of injury is a lateral twist that causes excessive ankle mobility. The sole of the foot is rotated inward, damaging the lateral ligaments of the ankle.
- On the other hand, dislocations of the ankle ligaments can be associated with fractures. The sole of the foot stretches outward, leading to an injury to the triangular ligament (at the inner ankle).
- The most common injury is to the anterior retaining ligament (ATFL), which is located in the lateral area of the ankle. The ATFL is also the main stabilizer of the ankle. Thus, as a rule, an important ligament is damaged and its injury may be underestimated. As the name suggests, this ligament attaches to the anterior border of the lateral ankle and runs anteriorly and medially.
- In severe injuries, the calcaneofibular ligament (CLL) can also be damaged. This ligament connects the heel bone to the fibula. This ligament is less damaged only in more severe injuries because it is naturally less strained, stronger and more flexible.
species
- First type - some fibers of the ankle ligament are torn, there is swelling and discomfort, but motor function is present.
- Second type - partial tear, the swelling covers the entire outer area; even at rest, the site of the tear is painful and motor functions are partially impaired, but generally preserved.
- The third type is completely ruptured, with acute persistent pain, severe swelling, and bleeding that spreads to both the external and epiphyseal portions.
Lateral, anterior (rarely), posterior, habitual dislocations and subluxations may be present.
symptoms
- Severe pain syndrome;
- inability to stand on foot;
- Specific clicking sound in the affected area;
- Progressive swelling all around;
- deformation of tissue;
- abnormal angle, limited active and passive mobility;
- localized temperature increase.
If the pain only occurs after the injury, a trauma surgeon or orthopedist should be consulted.
Sprained ligaments: treatment
The symptoms of a sprain determine the treatment of the injury: eliminating pain, reducing swelling, and improving mobility by treating the sprain.
In addition to their anti-inflammatory effects, nonsteroidal drugs (NSAIDs) have good pain-relieving effects in the treatment of sprains. Depending on the severity of the pain, they can be used externally (gels, ointments, creams) or internally (tablets, suppositories, powders, solutions for intramuscular injection) to treat sprains. The treatment duration for these sprains is usually 6-8 days. Such treatment is usually sufficient to reduce inflammation, but prolonged treatment can lead to undesirable side effects (ulceration and erosion of the gastric mucosa, liver and kidney dysfunction).
Swelling can be reduced by applying ice wrapped in a towel for 10-15 minutes every 3-4 hours. Elevating the injured limb is also recommended to reduce swelling in the first few days after injury.
If a large hematoma has formed, dislocation therapy may also include prescribing creams and ointments containing direct anticoagulants (drugs that reduce blood clotting). They help the hematoma subside faster, normalize microcirculation and prevent the formation of venous clots in the injured area. However, they should not be used if there is a tendency to bleed, the integrity of the skin is compromised, or there is a skin condition in the area of application.
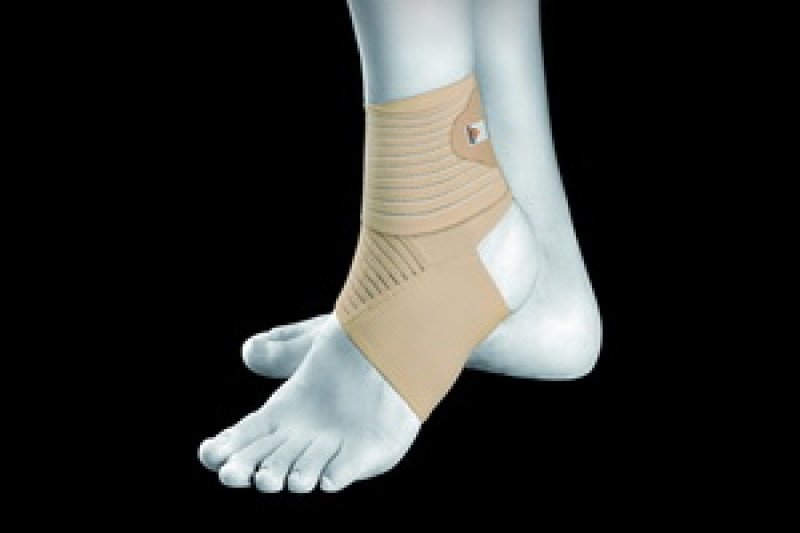
When treating a sprain, it's important to immobilize the joint where the ligament is torn. This is achieved by wearing a special device that fixes the joint in an anatomically correct position - an orthosis.

How else can dislocations be treated?
In recent years, sprains have been treated in the following ways Kinesiology taping – Attaching special adhesive fabric tapes to the injured area using a special technique. The positive effect of taping during stretching is to improve microcirculation and lymphatic flow in the injured area, correct the direction of movement in the joint, and reduce muscle hypertonicity.
The undoubted advantage of taping is that while the joint is stabilized, the ability to move it is preserved. At the same time, the procedure has disadvantages: taping is a rather expensive material, only a specialist who has undergone special training can impose it, taping treatment can not be performed in the presence of skin diseases at the site of application, deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities, severe kidneys -and cardiovascular diseases, complicated forms of diabetes are carried out.
Reconstructive treatments for dislocations are started after the acute symptoms and inflammation have subsided. They consist of special exercises therapeutic exercises.These exercises help muscles that were weakened during immobilization regain their original range of motion in the joint. It is important to remember that physical therapy should be supervised by a trainer as improper exercise can not only be harmful but can also lead to ligament stretching.
In addition, to speed up the recovery of motor activity after the inflammation subsides, it is advisable to use a therapeutic massage A course consisting of 8-10 sessions. In order to avoid undesirable consequences, the procedure should be performed by a specialist doctor with medical education and special training.
Separately, they want about the use of physical therapy speak for sprained ligaments. Physiotherapy is the perfect answer to the question of how to heal a sprain quickly. It helps reduce swelling and pain in sprains, accelerates hematoma healing, accelerates healing of damaged tissues, shortens immobilization time, and restores skeletal muscle tone, which accelerates sprain healing.
Read more:- How to distinguish a fracture from an ankle sprain.
- ankle sprain.
- Ankle ligament sprain.
- Photo of the ankle.
- Ankle ligament strain, ICD.
- ankle sprain.
- Ligament damage in the right ankle.
- Injury to the ligaments of the ankle.
