It is well known that boys mature emotionally later than girls. Therefore, parents should give them time and space to feel comfortable and learn to control their own behavior.

- Aneurysmal Bone Cysts (AAC): Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
- The distinctions include. primary и secondary AKC.
- On macroscopic examination, AKC
- Contraindications, side effects
- How often can Milgamma be injected?
- Puberty in adolescents - hormonal changes
- Puberty in teenagers - physical changes
- chickenpox
- rubella
- Precautions and advice from experts
- Effective analogues
 Aneurysmal Bone Cysts (AAC): Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
Aneurysmal Bone Cysts (AAC): Causes, Symptoms, Treatment

An aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) – is a locally destructive, benign bone tumor lesion consisting of numerous blood-filled cystic cavities.
Acc – is one of the most common variants of primary bone lesions in children and adolescents. On the basis of reproducible clinical parameters (age, location of the mass in the bone, pattern of bone lesions and type of periosteal reaction), this neoplasm does not present any diagnostic difficulties, with the exception of its solid variant.
The incidence of ACC in the general population is 0.14 per 100,000 population. ACC account for between 1 % [2] and 9.1 % [3] of all bone tumors. ACC was first published in 1942 by HL Jaffe et al. described [4].
The etiology and pathogenesis of this neoplasm are not fully understood.
There are several theories on the development of ACC, considering the influence of various predisposing factors (local vascular, traumatic and genetic factors).
The distinctions include. primary i secondary AKC.
A primary ACC is an ACC that has no evidence of another neoplasm; a secondary ACC is merely part of another bone tumor (eg, secondary ACC in giant cell tumor, osteoblastoma, etc.). The primary ACC accounts for 50-70 % of the cases, the secondary ACC accounts for 30-50 %.
ACC can occur at any age but is more common in children and adolescents (up to 80 %) and slightly less common in children under 5 years of age. Some authors report that women are slightly overweight with a ratio of 1:1.3 [2].
Although any skeletal bone can be affected, AKC is more commonly (50-60 % of cases) found in the metaphysical region of the long bones (femur, tibia, and humerus). The posterior vertebral elements (20-30 %), the small bones of the hands and feet (7, 8), and the flat bones of the skeleton (pelvis, scapula) are commonly affected. Rarely, ACC has been reported in the bones of the skull and jaws. There are isolated reports of AKC in soft tissue (extraskeletal localization) (9).
On macroscopic examination, AKC
On gross examination, AKC presents as a multilobular mass with a blood-filled cavity. The edges of the mass are relatively clear. In some areas, the mass can disrupt the cortical layer of bone and extend beyond the normal anatomical limits. Occasionally, solid sections must be taken in their entirety for histological examination to potentially detect another tumor and rule out secondary ACC. In rare cases, the lytic component can predominate, and its predominance over the cystic component poses a major diagnostic challenge.
There are two histological variants of ACC: classically cystic (about 95 % of cases) and solid (5 %), depending on whether one or the other component predominates (2).

On histological examination, the tumor is well demarcated and consists of cystic cavities filled with red blood cells. The walls of these cavities do not contain endothelial cells. The septa are composed of mature connective tissue formed from elongated fibroblast-like cells.
mitotic activity may be minimal to moderate, but no abnormal mitotic figures are found. Foci of reactive osteogenesis are observed in the form of immature globules of thick fibrous bone of irregular shape. In one third of the cases, structures with irregular mineralization, the so-called 'reactive' structures, are encountered. 'blue bone'.

This finding is not necessarily specific to ACC as it occurs in other tumors as well.
In almost all cases, deposits of hemosiderin and small clusters of hemosiderophages (better seen on iron pearls stain) and focal hemorrhage can be found. With a history of pathological fracture, foci of necrosis can be detected.
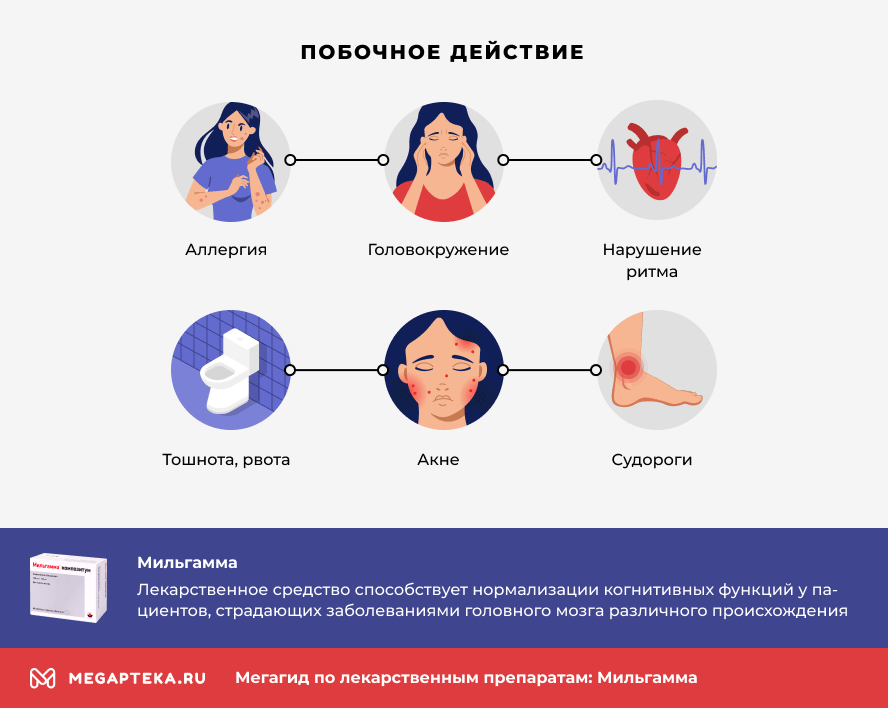
Contraindications, side effects
The drug is not recommended for children, pregnant and lactating women, patients with hypersensitivity to the components of the drug and patients with congestive heart failure.
- Allergic reactions (rash on the skin and mucous membranes, shortness of breath, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock);
- dizziness, rarely disorientation;
- arrhythmia, fast or slow heartbeat;
- nausea, vomiting;
- Increased sweating, skin pruritus, urticaria, acne;
- convulsions.
Sometimes irritation occurs at the injection site. If side effects occur, tell your doctor.
How often can Milgamma be injected?
Two milliliters of the drug are injected daily for ten days to quickly stop the pain syndrome. Once the pain has subsided and the condition is mild, patients are given oral medication or injections of the drug solution at two to three-day intervals for two to three weeks.
Neurologists prescribe the drug Milgamma in combination with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and central muscle relaxants. Which is Better - Milgamma Injections or Milgamma Tablets? These are the two forms of the drug that doctors prescribe one after the other. Patients are first given Milgamma injections and then tablets. With a mild disease, treatment is carried out with the tablet form of the drug.
Puberty in adolescents - hormonal changes
Hormones are highly specialized chemicals that are carried around the body in the blood. They transmit specific messages to cells, tissues and organs.
The endocrine system, responsible for the production and regulation of hormones present in the body from birth, activates the glands involved in male sexual development:
- The hypothalamus is the brain structure that produces gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), a neurohormone that regulates the function of the pituitary gland. It is associated with the onset of puberty. Its main function is to regulate growth, development and testicular function.
- Pituitary Gland – Responsible for secreting growth hormone and regulates the thyroid gland.
- Thyroid – secretes the hormone thyroxine, which regulates growth and development.
- Adrenal cortex – secretes androgens – hormones that control sexual organ development and puberty, as well as cortisol, which affects body growth.
- The gonads (testes) – are responsible for the secretion of androgens (testosterone) and the production of male germ cells (spermatogenesis).
In young men, testosterone release and spermatogenesis are not observed until puberty. It only takes place during puberty.
The first surge in hormone levels in young men occurs between the ages of 6 and 9 and is known as adrenarche. Two years later, the increased release of gonadal hormones begins. This happens a little later in boys than in girls.
Young males also develop primary and secondary sex characteristics between the ages of 9 and 15 (average age 12).
Puberty in teenagers - physical changes
Adolescent growth during puberty is associated with a number of physical changes. Puberty brings with it one of the fastest and most significant accelerations in male body growth since infancy.
In young males, height and weight increase rapidly at age 11, peak at age 13.5, and end at age 17.
Changes that occur in young men during puberty
They measure 28cm on average (10cm per year) and are taller than girls at the end of their growth spurt.
They gain an average of 9 kg per year up to the age of 14 and weigh more than girls on average by the end of puberty
The fat on your arms and legs decreases and you gain muscle mass. By the end of puberty, they have 1.5 times more muscle and bone tissue than girls. The ratio of fat to muscle at the end of puberty is 3:1
Arms, legs and feet grow faster, then the torso, shoulders broaden in relation to the hips
chickenpox
Chickenpox is caused by the chickenpox virus. It's usually a childhood disease (although it can be much more dangerous if you catch it at an older age). Anyone who has had chickenpox is immune to it for life.
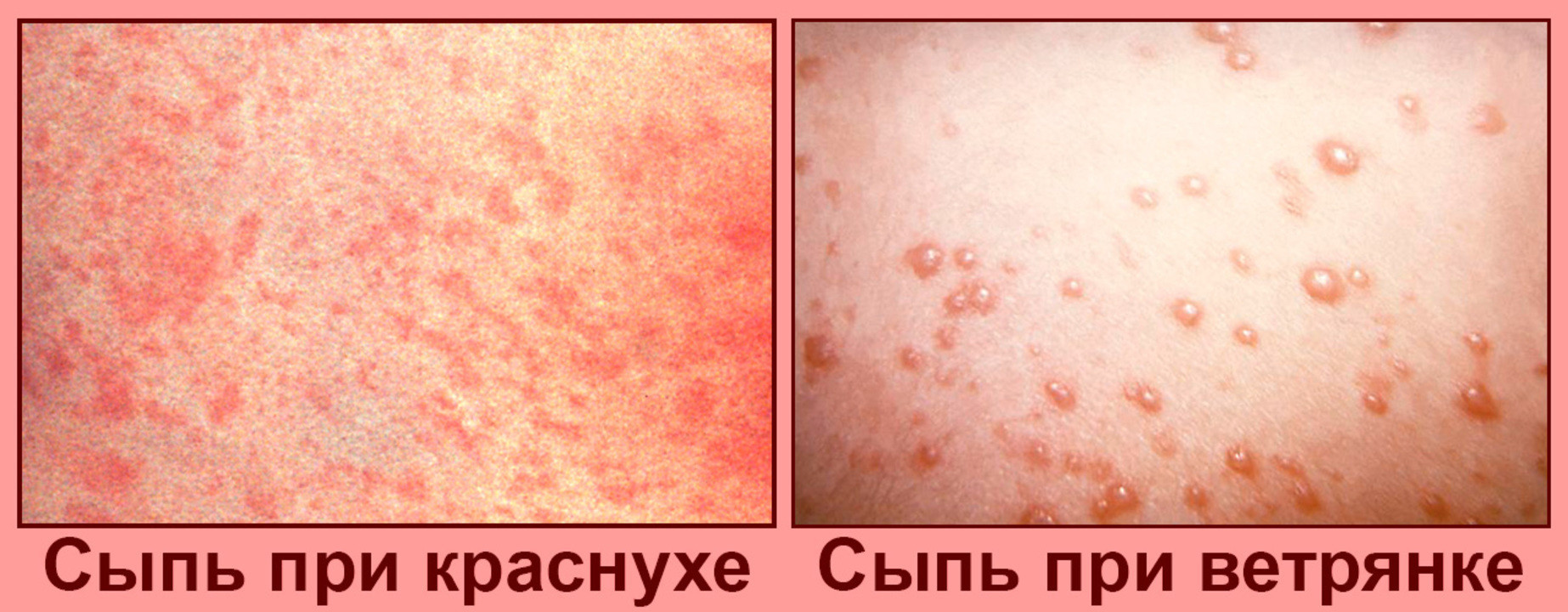
The incubation period lasts from 7 to 21 days, after which a rash appears: red or pink bumps that crust over for 14 days and then disappear. The rash is accompanied by a headache and fever.
Treatment is limited to applying topical ointments and isolating the patient from others. Warm baths are also recommended.
Chickenpox is particularly dangerous for pregnant women. There is an increased risk of babies being born with the following abnormalities:
rubella
A disease that most commonly affects children between the ages of 5 and 9 years. In addition to fever and skin rash, there is an enlargement of the lymph nodes. Rubella is a mild infection that goes away within a week without treatment.
The rash is a pink or red patch that appears on the face and gradually spreads to other parts of the body.
The disease can be dangerous for pregnant women as it can lead to chronic fetal rubella, increasing the risk of miscarriage or physical abnormalities after child birth.
Precautions and advice from experts
When used correctly, the drug does not affect the speed of reactions. During treatment, the patient can drive a car or operate machines that require increased concentration without restriction.
The medicine should only be used externally. It contains alcohol and other components that can lead to serious complications when used internally. Menovazin must not be used to make tinctures or to drink when you have a mouth cough.
When rubbed in externally, the ingredients do not penetrate into the bloodstream. The product does not react with various drugs that can also be used to treat a cold or neuralgia.
Effective analogues
With sciatica, myalgia and other painful conditions, the doctor can choose a drug with a similar composition. Menovazin can be replaced with the following products:
- Apisartron – available as an ointment, contains bee products, warms muscles, relieves pain after injuries, exercises;
- Voltaren Emulsion – effective in inflammation of the joints, muscles, sprains or bruises, relieves discomfort and stiffness in rheumatism;
- Iricar is a herbal medicine for topical use, safe for many chronic diseases, prescribed to treat inflammatory skin conditions, to relieve itching after insect bites.
There are many indications for which Menovazin is used. Affordable and effective, it reduces muscle swelling and restores blood circulation after injury. When combined with other therapies, it reduces pain and restores the ability to actively move without restriction or stiffness.
Read more:- At what age do girls' legs grow?.
- Girls feet 13 years old.
- The largest bone in the skeleton of the human foot.
- Photo of a teenager's leg.
- Legs in adolescent boys.
- Anatomy of the pelvic bones.
- Outer malleolus of the right tibia.
- Growth zones of the foot bones.
