The multidisciplinary health center Health Energy invites you to examine your body and eliminate possible problems. We offer:
- dizziness
- General information
- trembling of the legs. Risks related to leg tremors
- Complications caused by limb tremors
- treatment of leg tremor
- types of ataxia
- symptoms of ataxia
- Osteopathy – a painless method of treating gait disorders in children
- Symptoms of ataxia in humans
- Treatment of ataxia in a person
- diagnosis
- Current treatments.
- causes
- symptoms
- administration of medication
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Anatomy of the hip joint
- Why do we hear hip pops?
- conclusion
- sources for information.
- Related articles:
dizziness
Dizziness is not an independent disease, but a symptom that can develop as a result of various pathologies. During an attack of dizziness, the affected person feels disoriented in space and can twist or turn the body around other objects. It is a very common condition that requires medical attention, especially if the attacks are more frequent.

General information
The sense of balance and position in space is created through the interaction of several systems:
- The visual system;
- The vestibular system (perceives position in space);
- the proprioceptive system (responsible for perceiving the relative position of different parts of the body and their movements).
These signals are processed by the central nervous system. Dizziness can occur when one of these departments isn't working properly. Often, a doctor can guess the cause of this condition based on the dizziness and accompanying symptoms.
When they think of dizziness, many people think of dizziness, light-headedness, and pronounced balance disorders, such as dizziness. B. Unsteady and unsteady walking. In themselves, these symptoms have nothing to do with dizziness, but often the mechanisms and causes are the same.
trembling of the legs. Risks related to leg tremors

As mentioned earlier, leg tremors are usually not dangerous, but in some cases, it can be a signal that should be investigated.
Tremors are common in highly anxious people who suffer from nervousness. In addition to tremors, it usually manifests itself through mechanical actions (finger plucking, tics, increased instability in stressful situations). A neurosis can lead to chronic tremor attacks. This condition is also difficult to diagnose and therefore difficult to treat because it does not affect the symptom (tremor) but the cause (nerves).
Another dangerous cause can be neuropathy (damage to the nerves in the limbs). This is accompanied by tingling and numbness in the fingers.
Dementia is also manifested by tremors in the legs and sometimes other limbs.
Complications caused by limb tremors
Even the first symptoms must not go unchecked. A neglected limb tremor can cause the following complications:
1) On the brain. The most common is impairment of the social adjustment function. This is accompanied by underachievement, absent-mindedness and weakness. Emotional disturbances and the like can occur. Other brain complications include speech disorders.
2) Inability to perform simple functions. Impaired motor functions make it difficult to perform the most common activities of daily living.
Therefore, if you notice the first symptoms of a leg tremor, you should immediately consult a qualified doctor. Never let even minor symptoms go unnoticed, as the consequences can be fatal.
treatment of leg tremor
If you are sure that your leg tremors are of a mild nature, you can resort to folk home remedies. Tea infusions and calming tinctures are good for nervous disorders. Otherwise, it is necessary to visit a psychologist and take drugs that act on the central nervous system.
It is possible to take anticonvulsants, but there are always contraindications and side effects (decreased ability to concentrate and weakness, so one should not drive a car or work in particularly difficult conditions). Be careful and consult a good medical specialist first.
With severe tremor that affects motor skills, surgical methods are used. Chiropractic therapy can be used: massage and orthopedic techniques.
There is a specific treatment with physical exercises for the necessary muscle areas of the body. Exposing certain nerve impulses from the muscles can help isolate the tremor in the legs.
types of ataxia
The impairment can be static, when a person has trouble with balance when standing, or dynamic, when there is incoordination with any type of movement.
What types of movement disorders are distinguished? Ataxia can be:
- cerebellar – is the result of damage to the cerebellar structures;
- vestibular - indicates a dysfunction of the balance apparatus;
- sensory - results from damage to the peripheral nervous system, the spinal cord;
- Cortical – occurs when there is damage to the cerebral cortex and frontal lobes.
In order to correctly diagnose the type of ataxia, the triggers and the disease are identified. Treatment is then prescribed.
symptoms of ataxia
The easiest way to spot incoordination is when a person is in motion. Gait is impaired, arm movements are slack, legs are spread, and there is a clear staggering when walking. Speaking can also be affected. Speech is slowed and words are stretched. When articulating, the syllables are separated.
- loss of consistency of movements;
- Dizziness;
- tinnitus and head noise;
- neurological abnormalities - hallucinations, inability to concentrate, delirium;
- nausea, vomiting;
- impairment of the sense of smell, changes in facial expressions;
- Tachycardia, dyspnea as a result of low physical activity.
Chronic heart failure develops as a complication of ataxia. The affected person becomes susceptible to infectious diseases.
Osteopathy – a painless method of treating gait disorders in children
Osteopathy addresses gait disorders comprehensively, taking into account the balance of all body systems, including those mentioned above. An osteopath can balance the ankles (foot – shin – hip – pelvis) and correct birth injuries that are often the cause of gait disorders. Early correction can prevent or reduce the risk of skeletal deformities as the child grows.
We recommend that you see an osteopath if your child shows the above gait abnormalities after the age of 1.5 years.

Osteopathic doctor, orthopedic surgeon. Specialty: Problems of the musculoskeletal system in children, headaches, neuroses in children, treatment of stuttering.
Symptoms of ataxia in humans
In sensory ataxia Limb impairment – may affect both arms and legs at the same time, or one leg or one arm. As the sufferer loses musculoskeletal sensitivity, when walking, his legs bend sharply in the pelvis and knees, and the gait becomes a stomping gait (sharp, powerful steps with the foot hitting the ground). There is a feeling of walking on a mattress or cotton wool, which causes people with ataxia to constantly stare at the floor. With severe impairments, standing or walking is almost impossible.
In the cerebellar form. the affected person cannot stand upright with outstretched arms, but immediately falls to the side or forwards/backwards. When walking, he staggers, trips his legs, and cannot walk in a straight line. All movements are staggered, awkward and slow, and visual control has failed to improve gait and balance. Speech suffers - it is slow, jerky, stretched and chanted (like Mayakovsky's poetry). Handwriting is impaired - it is uneven, very coarse and unclear. Muscle tone suffers, muscles weaken and tendon reflexes are altered.
vestibular shape manifests itself in dizzy spells – one has the feeling that all objects are rotating in the same direction. Turning the head increases dizziness, leading to a wobbly gait and falls. The affected person tries not to turn their head. Nystagmus also occurs - the eyes appear to 'swim' and nausea and vomiting occur.

cortical ataxia Unsteady gait, especially when turning and leaning sideways. If the cerebral cortex is severely damaged, the person affected can hardly stand or walk. Visual control does not improve the situation. In addition, grasping reflexes, mental problems and odor disorders occur.
Treatment of ataxia in a person
If a person finds problems with gait, clumsiness and other disorders, it is necessary to consult a neurologist and exclude the development of ataxia. With early diagnosis, the problem can be controlled and measures can be taken to make life easier.
diagnosis
In order to diagnose ataxia, it is important to have a detailed discussion with the patient, describing all the complaints and symptoms, when they started and how they have changed. In addition, a number of tests should be carried out:
- EEG - to detect abnormal waves of brain activity;
- Biochemical blood tests - to detect abnormalities in amino acid metabolism that can damage the nervous system;
- MRI or CT scan of the brain to detect possible injuries, vascular lesions, tumors or cysts;
- Electromyography – to determine muscle status and areas of muscle damage.
Genetic counseling and molecular genetic testing are essential to identify hereditary forms of ataxia.

Current treatments.
– Among the methods of treatment, according to neurologist Svetlana Ryazantseva, primarily include drug therapy to improve blood circulation, correction of hormonal balance and vitamin therapy. In addition, there is physiotherapy, stabilization training and therapeutic physical training aimed specifically at the formation of feedback (if one part of the brain is damaged, it is possible for this function to be taken over by another part of the brain, a type of mirror neuron formation).
causes
Gait imbalances are caused by the wrong arrangement of muscles performing the same or opposite functions: flexors-extensors, adductors-adductors, etc. They tense and relax in the wrong order, which prevents correct movement of the limbs.
On the other hand, the nerve fibers are damaged. This is often due to damage to the central nervous system (CNS). The motor coordination area is located in the cerebellum. If some of the cells in this area die, there will be a loss of balance and an unstable gait.
Movement instability can be caused by damage to the vestibular apparatus. This is located in the inner ear and is responsible for maintaining balance. Damage to any part of the vestibular apparatus or its pathways causes the brain to produce incorrect information about the body's position in space. This leads to a shaky gait.
symptoms
When balance and coordination problems while walking are caused by the cerebellum, it's called 'cerebellar ataxia'. Depending on how it occurs, it is divided into different types:
- Static Locomotive – problems moving and keeping the body in an upright position;
- Dynamic – Poor coordination between arms and legs.
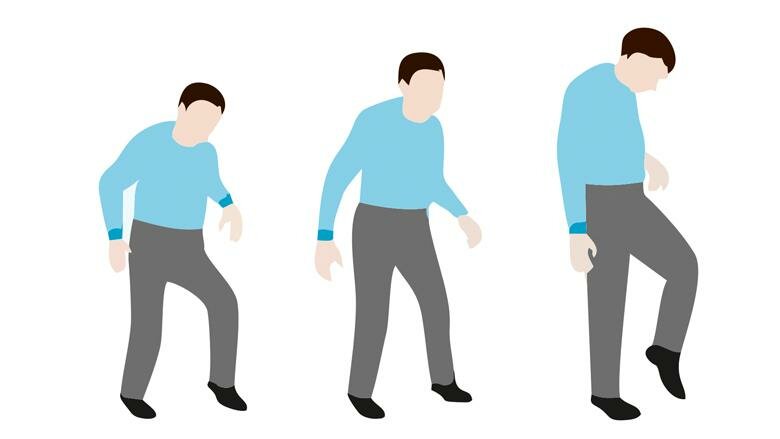
If the balance organ is damaged, vestibular ataxia develops. The most characteristic is the appearance of symptoms when accelerating, bending and twisting the body.
The characteristics of all types of ataxia are similar, but they appear in different situations.
- Dizziness;
- inertia of movement;
- slow movement;
- asynchronous muscle work;
- inability to quickly change direction of movement;
- trembling of the limbs when approaching a target;
- illegible large handwriting;
- muscular hypotension;
- slowed or slurred speech;
- problems walking.
In severe cases, the person loses the ability to stand or sit.
administration of medication
Dizziness and unsteady gait can occur as a side effect of some medications, including:
- antidepressants;
- tranquilizers;
- Painkillers
- sleeping pills;
- antiarrhythmics;
- muscle relaxants;
- anticonvulsants;
- chemotherapy drugs.

Orthostatic hypotension
Everyone knows the dizziness that sometimes occurs when we stand up abruptly from a sitting or lying position. This phenomenon is called orthostatic hypotension - when we stand up abruptly, the blood from the lower part of the body does not have time to reach the heart, resulting in a sudden drop in blood pressure and reduced blood flow to the brain.
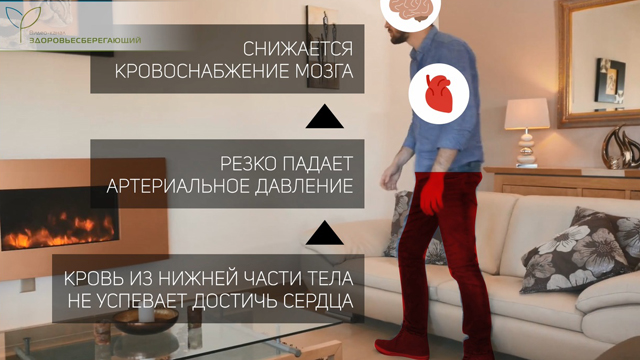
In a healthy person, this is relatively rare, but if this dizziness occurs regularly, it can indicate the following diseases:
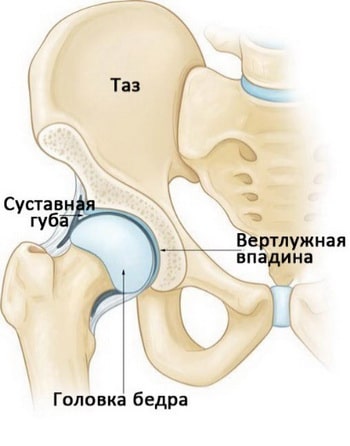
Anatomy of the hip joint
The hip joint, which consists of the femoral head (femoral head) and the hip socket (acetabulum), is spherical in shape. The acetabulum is surrounded by a cartilaginous-fibrous mass that gives stability to the joint (labrum acetabularis).
Ligaments run along the outside of the joint and hold the hard (bony) parts of the joint together. Tendons run across the ligaments, connecting the muscles of the pelvis, buttocks, and thigh to the bone. This anatomical arrangement ensures that all types of everyday movements can be performed.
In addition, there are several bursae around the hip joint that provide lubricity and cushioning and contain a special fluid.
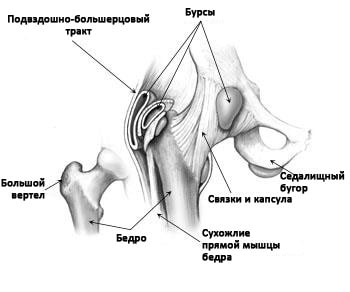
The figure shows the anatomy of the hip joint, consisting of bones, tendons and bursae.
Why do we hear hip pops?
The occurrence of cracking noises in certain areas of the hip, which can often also be felt physically, can be observed where the muscle tissue and tendons are as close as possible to the bone.
outer articular surface
Very often the popping is heard on the external articular surface of the hip, where the tract of the iliac spine overlies the posterior aspect of the greater trochanter, which is under constant tension.
Ventral Articular Surface
The femoral extensor tendon running along the anterior joint surface can also cause an audible popping sound. This is because the tendon moves relative to the femoral head during flexion movements and vice versa during extension movements.
Posterior surface of the thigh (gluteal area)
The rattling noise in this anatomical area is caused by the biceps femoris tendon attaching to the ischium.
Articular cartilage injuries
Injuries to any type of cartilage surrounding the hip socket can not only cause a popping sound, but can also lead to pain and joint blockage.
Injuries to the joint cartilage or the joint lip can also cause cracking noises.
conclusion
Atactic gait and gait incoordination are symptoms that can indicate the presence of multiple sclerosis, malignant growths in the brain and spinal cord, intoxication with alcohol and other toxic substances, stroke or pre-stroke and many other serious pathologies.
Ataxia is a group of acquired and inherited diseases that cause degeneration of the central nervous system. Atactic gait, dysarthria, tremors of the eyeballs/upper and lower extremities, numbness and tingling in the fingers, and complete loss of balance are common in people with ataxia.
Important: See a doctor as soon as symptoms of ataxia appear for an effective diagnosis and treatment that improves quality of life or eliminates the underlying disease.
sources for information.
- Akbar U, Ashizawa T, Ataxia. Neuroscience Clinics, 2015, pp. 225-248.
- Zhang K, Zhou S, Li Y, Yang S, Abbasi K Clinical diagnosis of sensory ataxia and cerebellar ataxia. Front Hum Neurosci', 2021, pp. 56-121.
- National Ataxia Foundation, 'What is Ataxia?'.
- Ashizawa, T., Xia, G., 'Ataxia: continuing education in neuroscience', 2016, pp. 1208-1226.
- Silva RN, Vallortigara J, Greenfield J, 'Diagnosis and treatment of progressive ataxia in adults. Practical Neurology', 2019, pp. 196-207.
- Johns Hopkins, 'Medical Health Library. Ataxia.'
- Pirker V., Katzenshlager R., 'Gait Disorders in Adults and the Elderly: A Clinical Guide.' Wiener Wedge Wochenschr, 2017, pp. 81-95.
- Bonney H, de Silva R, Giunti P 'Management of the ataxias: towards best clinical practice'. Ataxia UK, 2016.
- Jayadev S, Bird TD, 'Hereditary ataxias: an overview'. Genet Med 2013, pp. 673-683.
Related articles:
Read more:- Why people tiptoe.
- Girls feet 13 years old.
- A wobbly gait means.
- Legs in adolescent boys.
- Spastic gait is.
- Causes of tiptoe walking in babies.
- Unsteady gait in the elderly.
- Pain in short fibula when walking.
