Rule 2: Only your doctor can determine how these shoes should be worn.
- Everything you need to know about flat feet
- How do I know if I have a transverse flatfoot?
- How to choose the right orthopedic shoes?
- What orthopedic shoes should a child wear?
- Medical insoles
- How do orthoses and insoles help to get rid of the disease?
- Medical and prophylactic insoles
- Prevention of flat feet
- What shoes should I wear if I have flat feet?
- How orthopedic and therapeutic footwear can help with flat feet
- Differences between therapeutic orthopedic shoes for children and normal shoes
- Shoes with abnormal supination in the insole
- What are the problems associated with developing flat feet?
- Who must wear orthopedic shoes?
- Functions of orthopedic footwear
- Types of orthopedic footwear
- Orthopedic shoes for valgus deformities: advantages, types.
- What should be considered when choosing shoes?
- Difference between orthopedic and normal shoes
- principles of selection
Everything you need to know about flat feet
Flatfoot is a change in shape of the foot characterized by a prolapse of the arch of the foot and a loss of cushioning function. Clubfoot is a common musculoskeletal disorder. It is often not taken seriously, but can lead to spinal and joint problems.
There are three types of flat feet: longitudinal, transverse, and combined (both longitudinal and transverse) feet.
In longitudinal flatfoot, the longitudinal arch of the foot is flattened and most commonly occurs in childhood during the formation phase of the foot.
What is transverse flatfoot? Transverse flatfoot is characterized by flattening of the forefoot.
How do I know if I have a transverse flatfoot?
To determine if you suffer from flat feet, you need to be aware of the signs/symptoms of this condition, which are important to look out for:
- pain in the foot or lower leg that occurs mainly after or during exercise;
- tiredness in the feet and legs, even after moderate exertion;
- the foot is optically flattened;
- swelling in your feet or ankles;
- In some cases, there is a gait disturbance and a limp.
How to choose the right orthopedic shoes?
Signs of bad children's shoes: stiff sole, soft heel, no insole. Such shoes not only deform the foot, but also cause discomfort. A young child cannot always explain this to his parents, so he may be naughty, not eating, or not sleeping well.
- Put the child on a piece of thick paper.
- Trace the outline of the feet as accurately as possible.
- Cut out the template.
- Slip them into a shoe you liked at the store. If it is significantly longer, wider or narrower than the template, the model will not fit.
- Use the template to determine the correct shoe size and only then try it on.
- When trying them on, make sure that the shoes are neither too tight nor too loose; both extremes are unacceptable. Don't buy shoes that are too big.
What orthopedic shoes should a child wear?

Measurement at the ankle. From the beginning of walking until the age of 4, orthopedic shoes with a narrow ankle circumference should be worn. This distributes the load evenly, reduces foot fatigue and keeps it in the right position.
sock. In order to avoid twisting the toes, the socks of the orthopedic children's shoes should not be too tight. They should be closed to avoid injury.
sole. It must be light and flexible, but also stable and non-slip. Rubber-soled shoes are not recommended.
heel. Shoes with a stable heel are suitable for children aged 6-8 years. Trains the back muscles and promotes correct posture. The height of the heel should not be more than 1/14 of the length of the child's foot.
insole. It should be snug and have an insole that lifts the longitudinal arch of the foot. The insole should be made of a porous material so that the child's foot does not sweat.
Medical insoles

If your child's foot begins to deform, you should make an appointment with an orthopedist as soon as possible. Your doctor will write you a prescription, based on which the orthopedic laboratory will make custom-made, permanent insoles for you.
These orthopedic spinal insoles restore the correct anatomical position of the arch of the foot. They ensure that the load is evenly distributed by using previously unused muscles and ligaments.
The doctor checks the progress of the anatomy and function of the foot every three months. Therapeutic insoles must be worn for at least 6 months. This is strictly prohibited without medical advice.
tips. To treat and prevent flat feet, the child should regularly perform exercises for the musculoskeletal system.

St. Petersburg, 5 Olminskogo Street.
How do orthoses and insoles help to get rid of the disease?
The use of insoles and insoles is a way to correct flat feet at home, since these therapeutic and preventive products:

- They support the proper functioning of the musculoskeletal system;
- stimulate blood circulation;
- aid recovery from injury;
- reduce pain in the joints and muscles of the legs;
- prevent injuries during sports;
- Distribution of the burden of walking, especially important for the elderly, pregnant women and the overweight;
- Reducing the stress on ankle, hip and knee joints as well as the spine.
For the longitudinal type, orthoses allow:
- reduce the likelihood of swelling;
- prevent the formation of calluses and corns;
- to keep the foot in the right lumen;
- to put the foot in the right position;
- to reduce pain.
Medical and prophylactic insoles
Function and properties of prophylactic insoles
Prefabricated orthopedic insoles, which are available in pharmacies or specialist shops, support the arch of the foot. The arch of the foot can sag with heavy loads, pregnancy, weight gain, old age, or in people weakened by another medical condition. In order to prevent the development of flat feet in these cases, prophylactic support inserts are required.
These products are intended for people who have already been diagnosed with certain foot problems. These products are custom made after a thorough diagnosis by a doctor. The foot consists of 20 joints and 28 bones. When walking, this part of the foot has a pushing function and maintains balance. As a result of injuries, misdevelopments and other problems, the consistency of the functioning of the various parts of this complex system is disturbed. This leads to pain, adaptive responses, and can trigger pain responses throughout the body. The task of the orthoses in this case is not only to support the arch of the foot, but also to compensate for the pathology and prevent serious general disorders.
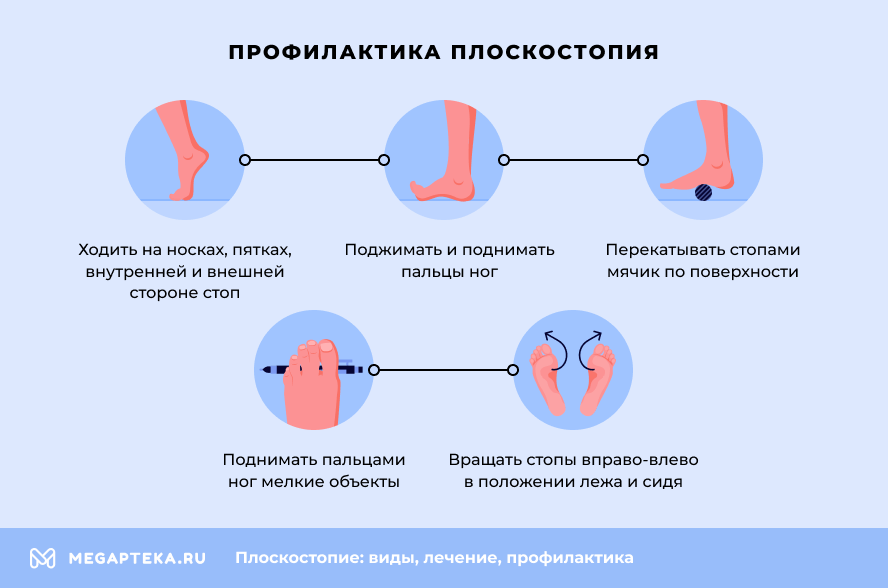
Prevention of flat feet
- Walk on your toes, on your heels, on the inside and outside of your foot, squeezing and lifting your toes during the exercise
- Use a ball to roll the soles of your feet on the surface.
- Practice lifting small objects with your toes.
- While lying down or sitting, rotate your feet to the right and left
To avoid the risk of illness, you should wear comfortable shoes, have regular medical examinations and monitor your weight.
What shoes should I wear if I have flat feet?
The effectiveness of the treatment depends on the type of flat foot insoles worn by the patient. An orthopedic insole is a special insole that corrects abnormalities in the anatomy of the foot. It supports the arch of the sole and reduces stress on the joints and spine.
These shoes have a wide toe box that keeps the toes in place so they aren't constricted. These shoes have a high, hard material heel and a soft interior without rough seams. They are equipped with buckles to comfortably attach the shoe to the foot. It is best if they are made of natural material.
It is important that they do not compress the foot and thereby impair blood circulation or pinch the foot. However, shoes should not be too loose either, otherwise the foot will sag and slip off, leading to deformation of the bones.
There are many types of insoles that can cover the entire length of the foot or take up 3/4 the size of the shoe. There are insoles in the heel or toe area. Supinators can help relieve the burning sensation in the foot.
How orthopedic and therapeutic footwear can help with flat feet
Orthopedic footwear can help with foot deformities until the child is twelve years old. At this point, the foot has completed its formation and flat feet cannot be completely eliminated afterwards.
The most important elements of orthopedic footwear - the high shin, the firm back, the specially shaped sole and the heel - keep the child's foot in an anatomically correct position, allowing it to develop without deformation.
The therapeutic footwear is not worn alone, but serves as a frame for an orthopedic insole, which is selected based on the diagnosis. This ensures the correct foot arch and corrects incorrect posture.
Differences between therapeutic orthopedic shoes for children and normal shoes
♦ high tibia – used to fix the ankle in the correct position during exercise;
rigid heel cuff - to support the heel in an anatomically correct position;
wide, stable heel cap – on the inside of the sole, the front part is additionally reinforced to keep the foot in the right position during movement.
♦ Polyurethane sole – forms the right foot roll;
When it comes to therapeutic shoes, not only is the foot fixation important, but also the wearing comfort. Children have a hard time wearing shoes that pinch, squeeze and pinch. That is why orthopedic and preventive shoes are made of natural calfskin. Calf leather is soft and comfortable for everyday wear. No chemicals are used in the manufacture of therapeutic shoes, which prevents allergies. In order to protect the child's delicate skin from abrasion, the shoes have only a few inner seams.
Shoes with abnormal supination in the insole
The insole maintains the physiologically natural position of the longitudinal arch of the foot. It helps the foot to fulfill its cushioning function.
If this part is poorly finished, its orientation and shape will not correspond to the anatomy of the foot. In this case, the joints and spine will not be protected from shock loads when walking.
Not only do flat feet 'like' stilettos, they also like flat surfaces, inferior materials and poor workmanship. To prevent the development of this condition, you should choose shoes with a relieved instep and a small heel, which accurately repeat the shape of the foot and are made of stretchy materials.
What are the problems associated with developing flat feet?

The unpleasant consequences of flat feet are not a problem with regular use of orthopedic footwear.
The correct arches of the feet are arched. They are important to reduce static and impact loads on the musculoskeletal system when standing and moving. With systematic overexertion, the connective tissue of the sole of the foot is stretched and the feet can no longer fully fulfill their function. The shock wave of movement is redistributed to the joints and spine.
Flat feet are first manifested by fatigue when walking, corns and systematic swelling and pain in the feet. Gradually, the development of the disease leads to more serious consequences, bringing measurable inconveniences in everyday life. Halux vargus, a foot deformity in the area of the big toe, complicates the choice of footwear and looks aesthetically unattractive. Heel spurs make walking a pain.
Who must wear orthopedic shoes?

The development of flat feet is stopped if orthopedic shoes are always worn.
Orthopedic shoes are very useful for everyone who lives in a big city. Modern lifestyle is one of the main causes of foot deformities. Constantly wearing shoes, a sedentary lifestyle, and slippery floors and pavements deprive the foot of the natural massage it receives in natural conditions: frequent walking barefoot on grass and rocky paths.
There are risk groups - people who are particularly prone to the emergence and development of flat feet:
♦ People forced to walk and stand for more than four hours a day;
Women who wear heels higher than 5 cm and those who wear uncomfortable shoes - narrow or wide;
Pregnant women: the effect of hormones on the connective tissue – the tissue becomes elastic and the soleus tendon in particular no longer supports the arch of the foot – the foot sags;
People who have suffered injuries to the lower limbs.
Functions of orthopedic footwear
With the right choice of orthopedic shoes and constant wearing of the model recommended by the doctor, the patient can see a reduction in discomfort when walking. High-quality products help stop pathological changes in the feet.
The effect of preventive and therapeutic shoes can vary depending on the model and the type of disease diagnosed in the patient. Products that are selected individually after medical advice from a podiatrist have the greatest effect.
Wearing orthopedic footwear all the time can provide positive results such as: e.g.:
- Elimination of foot discomfort, reducing the risk of flat feet and other diseases of the musculoskeletal and cardiovascular systems.
- Prevention of joint diseases and neuralgia.
- Formation of the correct foot arch in the child.
- Correction of lower limb deformities.
- Reducing the negative effects of arthritis and osteoarthritis.
- Decreased foot sensitivity in patients with diabetes.
- Speeding up rehabilitation after injuries or operations on the lower limbs.
Types of orthopedic footwear

Patients can choose adult and child orthopedic shoes for the treatment and prevention of various diseases. There are summer, winter and semi-seasonal versions, so patients can wear special therapeutic and preventive shoes all year round. Manufacturers produce different types, such as sneakers, athletic shoes, sandals, boots, and ankle boots.
Depending on the orthopedic effect they achieve, the models can be simple or complex.
Orthopedic shoes for valgus deformities: advantages, types.
Treatment of the disease depends on the degree of manifestation and the severity of the pain. In an advanced stage, the pathology can often only be corrected by surgical intervention - removal of the growth on the toe. In the early stages, the disease can be effectively treated with physical therapy, physiotherapy, and anti-inflammatory drugs. Painkillers are prescribed to relieve pain.
An important part of treating valgus deformity is wearing orthopedic shoes.
- They help spread the load on the foot, which improves muscle and ligament development. The stress on the stressed joints is reduced.
- The deformation of the joints is stopped.
- Distributes the load evenly over the entire musculoskeletal system.
- Forms a correct, beautiful gait and good posture.
When diagnosing a valgus foot deformity, orthopedic shoes are not a panacea that solves all problems. However, they are an important part of a comprehensive treatment concept that relieves symptoms and prevents the disease from progressing. Wearing special therapeutic shoes is recommended as a preventive measure to prevent the disease from recurring after a successful operation.
Orthopedic shoes are selected depending on the type and severity of the deformity. Their primary role is to maintain proper foot alignment and prevent flexion.
The times when orthopedic shoes attracted attention because of their ugly appearance are a thing of the past. Today they are not only comfortable, but also look good. Shops offer options for different seasons – summer, winter, mid-season. Manufacturers produce all types of orthopedic shoes: boots, ankle boots, sandals, sneakers. The therapeutic versions look very beautiful and visually do not differ from ordinary shoes.
When designing orthopedic shoes, not only the degree and form of the disease are taken into account, but also the gender and age of the patient. Men, women and children have different pathologies and different aspects need to be considered when correcting the deformity.
 What should be considered when choosing shoes?
What should be considered when choosing shoes?
An orthopedic pair is selected personally, because each foot has its own characteristics. The shoes adapt to the shape of the foot when worn. Parents should remember: Babies must not wear older children's shoes or their feet will develop the same abnormalities as their own.
When choosing a therapeutic version for children, pay attention.
- the quality of the materials. Shoes made of natural materials are made for the child. They are breathable and allow the foot to 'breathe';
- the quality of the seams. Carefully inspect the shoe, the quality of the seams, the inner surface - there should be no bulging seams, all parts are carefully sewn. This prevents chafing when worn;
- Adaptation to the anatomy of the foot. A doctor's recommendation on which details to pay attention to is helpful;
- the right size. A child should not buy oversized sneakers, which many parents do because children's feet grow quickly. He will not be comfortable in shoes that are too big, and his gait will be unsteady and unsteady. The shuffling habit persists after the foot has 'grown' into the shoe. A shoe that is too small compresses the foot and causes further curvature. Infant shoes should be chosen in the right size.
Pay attention to every part of the shoe. The inside of the shoe has a thick, wrinkle-resistant insole. The sole has a small heel to keep the foot in the right position and avoid flat feet. The sole itself is also important. It's better if it has rotated elements. Particular attention should be paid to winter shoes. Make sure that the sole is made of frost-resistant materials and does not slip.
The shoes are specially designed for a child with a deformed foot. The shoes are comfortable and support the foot well in the right position. A comfortable supinating insole, side rests and a high, rigid insole serve this purpose. Laces, Velcro fasteners and multi-level closures provide additional support.
Difference between orthopedic and normal shoes
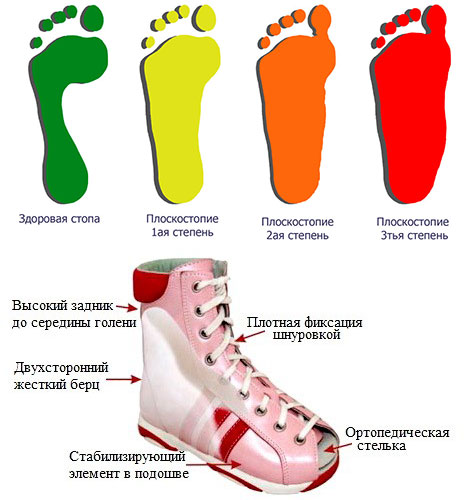
The main elements that characterize an orthopedic product are.
- the scope. Up to the age of 4 the shoe should fit snugly around the ankle;
- the high, hard cuff. This reliably fixes the ankle and supports the heel in the correct position;
- a wide toe box to avoid toe pinching. Preferably a closed toe so that the child cannot injure himself;
- Stable and wide Thomas heel (max. height 5-7 mm). For children from 5 years;
- flexible polyurethane sole, non-slip. The flexibility helps shape the correct transition of the foot. Rubber soles are not recommended by doctors;
- Orthopedic insole with foot support. The pressure of walking is distributed evenly across the foot, relieving specific parts of the foot. The insole should lie flat and not move;
- The convenience and comfort of the product. Natural calfskin, suede or nubuck leather is used for their manufacture. They let the foot breathe and don't sweat. No chemicals that can cause allergies are used in their manufacture. They are flexible and do not deform when worn.
principles of selection
To select the correct size of orthopedic prophylactic shoes, proceed as follows:
Try the product on your child. Loose or too tight shoes will not work. These models are not meant to be outgrown, they are meant to be fitted.
It is better to buy therapeutic shoes in specialist shops. They serve as frames for orthopedic insoles. The insoles and the way they are worn should be prescribed by the doctor.
Developmental disabilities can be corrected before the child is twelve years old. At this age, the foot has completed its formation and deformities can no longer be fully corrected.
The 'right' footwear helps to prevent the development of diseases, eliminate misalignments and keep your child's feet healthy.
- Catalog
- massage
- Care for the sick and the elderly
- For companies and professionals
- For sports and body shaping
- For home and family
- For prevention and care
- beauty
- Brands
- test and diagnostic devices
- baby products
- Information about the company
- Delivery & Payment
- Promotions
- For wholesale customers
- Contact
- credit
- credit overpayment
- Delivery to your home
- policy
The callback service is only available during store opening hours. If you leave a request outside of business hours, it will be processed at the beginning of the next business day.
We have over 2,500 products, don't waste your time searching, leave your phone number, our experts will help you!
We will send you an email with a link to activate your account.
Reviews from the online store TOPZDRAV:
- A
- Abakan
- Almetyevsk
- Anapa
- Angarsk
- Aprevka
- Arzamas
- Armavir
- Artyom
- Arkhangelsk
- Arkhipo-Osipovka
- Astrakhan
- Achinsk
- B
- Balakovo
- Balashikha
- Baranovichi
- barnaul
- Bataysk
- Belgorod
- Berdsk
- Berezniki
- Biysk
- Blagoveshchensk
- Bobruisk
- Borisov
- Bratsk
- Brest
- Bronnitzy
- Bryansk
- B
- Veliky Novgorod
- Vidnoye
- Vitebsk
- Vladivostok
- Vladikavkaz
- Vladimir
- Vlasikha
- Volgograd
- Volgodonsk
- Volzhsky
- Vologda
- Volokolamsk
- Voronezh
- Voskresensk
- Vsevolozhsk
- Vyborg
- Vyazma
- G
- Gatchina
- Gelendzhik
- Gomel
- Grodno
- Grozny
- D
- Deadovsk
- derbent
- Dzerzhinsk
- Dzerzhinsk
- Dimitrovgrad
- Dmitrov
- Dolgoprudny
- Domodedovo
- Dubna
- Dyatkovo
- E
- Eupatoria
- Egoryevsk
- Yekaterinburg
- Yelets
- Essentuki
- Ж
- Zhukovsky
- З
- Zaraisk
- Zvenigorod
- Zelenograd
- Zlatoust
- I
- Ivanovo
- Ivanovo
- Izhevsk
- Irkutsk
- Istria
- Й
- Joshkar-Ola
- K
- Kazan
- Kaliningrad
- Kaluga
- Kamensk-Uralsk
- Kamyshin
- Caspiysk
- kashira
- Kemerovo
- Kerch
- king sepp
- Kirov
- Kislovodsk
- clinical
- Kovrov
- Kozelsk
- Kolomna
- Kolpino
- Communarka
- Komsomolsk-on-Amur
- Kopeysk
- Korolev
- Kostroma
- Kotelniki
- Krasnoarmeisk
- Krasnogorsk
- Krasnodar
- Krasnoye Siovo
- Krasnoznamensk
- Krasnoyarsk
- Kronszstadt
- Kubinka
- Kudrovo
- kurgan
- Kurovskoe
- Kursk
- Kyzyl
- L
- Likino-Dulevo
- Lipetsk
- Lysyi Nos
- Lobnya
- Lomonosov
- Losino-Petrovsky
- Lugovichi
- Lytkarino
- Lubertsy
- Ludinovo
- M
- Magnitogorsk
- Majkop
- Malakhovka
- Maloyaroslavets
- Makhachkala
- miass
- Minsk
- Mogilev
- Moschaisk
- mono
- Moscow
- Murino
- Murmansk
- Murom
- Mytishchi
- N
- Naberezhnye Chelny
- Nazran
- nalchik
- Naro-Fominsk
- Nachschabino
- Nakhodka
- Nevinnomyssk
- Neftekamsk
- Nefteyugansk
- Nizhnevartovsk
- Nizhnekamsk
- Nizhny Novgorod
- Nizhny Tagil
- Novokuznetsk
- Novokuznetsk
- Novomoskovsk
- Novorossiysk
- Novosibirsk
- Novocherkassk
- Novocherkassk
- Novoshakhtinsk
- Novokuznetsk
- Noginsk
- Norilsk
- Noyabrsk
- O
- Obninsk
- Obukhovo
- Obukhovo
- Odintsovo
- ozery
- Oktyabrsky
- Omsk
- Orel
- Orenburg
- Orekhovo-Zuevo
- orsk
- p
- Pavlovsky Posad
- Penza
- Pervouralsk
- permian
- Peterhof
- Petrozavodsk
- Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
- Pinsk
- Podolsk
- Prokopyevsk
- Protvino
- Pskov
- Putilkovo
- Pushkin
- Pushkin
- Pushkin
- Pyatigorsk
- Р
- Ramenskoye
- Reutow
- Rostov-on-Don
- Roshal
- Rubtsovsk
- Rybinsk
- Ryazan
- C
- Salawat
- Samara
- St. Petersburg
- Saransk
- Saratov
- Sevastopol
- Severodvinsk
- Seversk
- Sergiev Posad
- Serpukhov
- Sertolovo
- Sestroretsk
- Simferopol
- Smolensk
- Solnechnogorsk
- Sosnovy Bor
- Sofrino
- Sochi
- Stavropol
- Stary Kupavna
- Stary Oskowo
- sterlitamac
- Strelna
- Stupino
- Surgut
- Syzran
- Syktyvkar
- t
- taganrog
- Tambov
- Tver
- Tikhvin
- Tolyatti
- Tomilino
- Tomsk
- Tosno
- Troitsk
- Tuapse
- Tula
- Tyumen
- U
- Ulan-Ude
- Ulyanovsk
- Ussuriysk
- Ufa
- f
- Fryazino
- Х
- Khabarovsk
- Khasavyurt
- Khimki
- Chotkovo
- c
- Cheboksary
- Chelyabinsk
- Cherepovets
- Cherkivsk
- Chernoglovka
- Chekhov
- Chita
- sh
- Shatura
- szachty
- Shushary
- Щ
- Shchelkovo
- E
- Electrogorsk
- electrostal
- electrougli
- Elista
- angels
- Ю
- Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk
- Yes
- Yakutsk
- Yaroslavl
- Orthotics for flat feet.
- Buy insoles for flat feet.
- Shoes for flat feet for women.
- Supinators for flat feet.
- What does the insole of a child's shoe look like?.
- flat feet (valgus foot).
- Orthopedic shoes for flat feet.
- flat feet.
