Example of a treatment plan for a valgus foot deformity:
Insoles for flat feet

Plantar foot deformity – It is one of the most common problems of the musculoskeletal system and occurs in both children and adults. It looks like a curvature of the ankle and is often accompanied by a crooked big toe and a bony 'hump' at the base. This foot condition can be easily corrected, especially in children. However, if not treated properly, it can lead to serious health problems, including curvature of the spine. Wearing orthotics is an essential part of treating this condition. This article will discuss the question of which orthoses should be worn for clubfoot deformity and how to choose orthoses for patients with this diagnosis.
Club foot, or simply valgus deformity.hallux valgus) is a common disease that leads to a reduction in the height of the foot and a curvature of its central axis. As already mentioned, in patients with this condition, the ankles are inclined towards each other. As a result, the arches of the feet are tilted inward and the legs look like an X. Therefore, this problem is also called plantar flexion X'. Now it's about what causes valgus foot deformity, how to recognize it and how to treat it correctly.
How can I recognize flat feet?
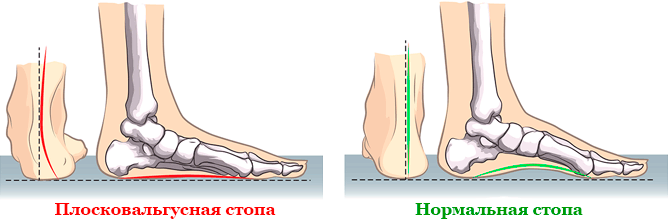
Recognizing flat foot problems in adults You can recognize them by external signs. Let's take a closer look at the most important of them.
- Tiredness when walking. In the early stages, a person may notice that they tire quickly when walking and experience pain in their joints. Calluses and dry calluses can also form on the foot, especially at the base of the 1st foot.
- Deformation of the big toe and a bony 'hump'. The big toe leans to one side and a bump appears at its base on the inside of the foot. The thumb is followed by the other toes, which are pressed in.
- Problems with footwear. As the disease progresses, pain increases, familiar shoes become tight, and it is difficult to find a comfortable pair. Sometimes the big toe can become ingrown, which also hinders normal walking.
- Bursitis. Calluses and soft tissues become inflamed and painful. The result can be a bunion, initially acute and then chronic.
- Deformation of the hindfoot. If you look at the injured foot from behind, you can see a type of club foot.
Benefits of orthoses
An orthopedic foot insole is an essential part of treating clubfoot. It is important that the type, degree of hardness and other parameters of the insoles are determined by the doctor. Wearing incorrect insoles will not improve the patient's condition, but may even worsen it. The best results are achieved with insoles that are made according to the individual characteristics of the foot.

The job of insoles is to keep the foot in the correct position and distribute the load evenly across the entire foot. Orthoses form a corset using special foot supports and other additional elements. In this way, they restore the correct position of the joints, redistribute the pressure on the feet and prevent the further development of deformities and possible complications of the disease.
Regular use of orthopedic insoles coupled with following all podiatrist recommendations will help effectively correct valgus deformity in children and adults. The best results are achieved when the condition is detected at an early stage, particularly in children under 7 years of age, when the foot is still forming and the cartilage is still flexible.
Please note that patients who have undergone foot surgery will need new insoles as the parameters of the foot change after surgery.
side effects.
Drowsiness (especially at the beginning of treatment), nausea, dry mouth and throat, dizziness, restlessness, headache, swelling, skin rash, muscle cramps, disturbances in external breathing.
Enhances the effects of anti-anxiety and sleep-inducing medications.
When taken at the same time as ethanol, psychomotor reactions are slowed.
Tricyclic antidepressants and m-cholinoblockers increase the risk of increased intraocular pressure.
MAO inhibitors potentiate anticholinergic and CNS depressant effects.
overdose
Symptoms: CNS depression and somnolence (mainly in adults), CNS agitation and m-choline blocking effects (mainly in children), including agitation, ataxia, tachycardia, hallucinations, tonic-clonic seizures, mydriasis, dry mouth, flushing, urinary retention and fever; Drop in blood pressure, collapse.
Treatment: Administration of activated charcoal, saline laxatives, medications to support cardiac and respiratory function (analeptics should not be used).
Read more:- Massage for flat feet.
- flat feet.
- Orthotics for flat feet.
- Buy insoles for flat feet.
- flatfoot μb.
- The shoe inserts are.
- Bandaging the flat foot.
- flat feet (valgus foot).
