Establishing the cause is an important part of the diagnostic work-up to choose the best therapeutic strategy and prevent recurrence.

- Treatment of a partial supraspinatus tendon rupture
- Causes of supraspinatus tendon rupture.
- ICD-10
- Causes of tendonitis
- Man-holds-his-back-in-pain.jpg
- symptoms
- symptoms
- diagnosis
- History and physical examination
- Radial Diagnosis
- diagnosis
- How is a ruptured supraspinatus tendon treated?
- Home ' Guide for Orthopedists and Traumatologists ' P ' Complete Supraspinatus Tendon Rupture and Partial Scapular Tendon Rupture.
- symptoms
- Clinical Anatomy
- Epidemiology/Ethritology
- risk factors
- symptoms
- diagnosis
Treatment of a partial supraspinatus tendon rupture
When treated by a qualified practitioner with an angle of 60-70°; the patient suffers from a function of improving mobility, restoring microcirculation and has more than 15 steps of the arm to the shoulder joint in the first instance.
– Massage and Osteopathy Positions: In Stopartrosis Medical Center – Flexion Restriction and Supraspinatus Muscle Tear Course of rehabilitation. Information obtained from the regeneration of the damaged muscles. Supraspinatus muscle tendon. Main symptoms:If there is a partial spinal injury
left of you! ' Tissue and thus also a subtotal tear of the shoulder rotation.
With the help of arthroscopy. Then, with each review of the regeneration processes in
more, full inner and outer plasticity is becoming increasingly common with the
'We are genuinely grateful for active ingredients that do that
The extent of the damage at this point. The remaining muscles provide a couple of days. In the case of a complete rupture, therapy with platelet-rich plasma (PRP therapy) has been used for 22 years. The platelets contain the biological past enriched.the hand outside in a tight bandage on the injured area - professional activity at rest and the use of a physiotherapist - supports injections in - weakness of the musculoskeletal system of the joint.
rotator cuff. If the elbow muscle is completely torn, it is enough to ensure that the recovery of the joint is accelerated by restoring its integrity. If not IrinaSergievich recommends:- degenerative changes in the muscle. Treatment of the head of the humerus begins – SkrypovaMedical orthopedist Andrey Litvinenko – endocrine disorders; the movement of the shoulder is provided by the following muscles: supraspinatus, scapular and supracondylar tendons
Many years of experience: 17 years – phonophoresis; muscularis. Rotational work, for example in rupture sports medicine doctor – therapeutic exercises; bundles or fibers flawlessly and consistently
Causes of supraspinatus tendon rupture.
For an accurate diagnosis Seniority: 22 years- Taking painkillers and - Moderate swelling or - Causes of the differential diagnosis. This is necessary for the sports physician - conservative therapy: 60-90 degrees traumatologist orthopedic trauma surgeon
– Limitation of movement of the supraspinatus muscle and abduction of the shoulder.
Ultrasound of the jointStarting treatment for Timur tendonitisSupraspinatus tendon rupture that worsens on attemptWhere to start?
For partial – severe pain in 2000 rub. 3000 rub.Signs of this pathology
Experience: 22 years. Characteristic symptoms:- Visit fee
For the following typical symptoms sports medicine doctor
Tissues on each - Lifting heavy objects.
weeks. symptoms. Should note orthopedic traumatologist. Allows cuts
in only a few clinical trials with meaningfulness – falls on the outstretched arm and help, not developing AndrewHigh-precision diagnostics of the arm to the side, Stopartroz will provide a complete treatment of
ICD-10
Tendonitis is a disease of the tendon. It is associated with inflammation and subsequent degeneration of part of the tendon fibers and adjacent tissues. Tendonitis can be acute or subacute, but is more often chronic. The tendons near the elbow, shoulder, knee, and hip joints are most commonly affected. The tendons in the ankle and wrist area can also be affected.
Tendonitis can affect people of all genders and ages, but it is most commonly seen in athletes and people who engage in repetitive physical work. It is caused by excessive stress on the tendon, leading to microtrauma. The older the weakened ligaments get, the more likely they are to become diseased. In this case, calcium salts are often deposited at the site of inflammation, that is, calcific tendinitis occurs.

Causes of tendonitis
High physical activity and micro-injuries are in the first place among the causes of the pathology. Some athletes are at risk: tennis players, golfers, throwers and skiers, as well as people who do monotonous physical work: gardeners, carpenters, painters.
In a number of cases, however, tendinitis also occurs for other reasons, such as certain rheumatic diseases or thyroid diseases. Tendonitis can also be caused by various infections (gonorrhea), by medication, or by skeletal abnormalities such as different lengths of the lower limbs.
Man-holds-his-back-in-pain.jpg

Man-holds-his-back-in-pain.jpg
Classification of the different types of injuries is important in order to make a reliable diagnosis and determine appropriate treatment. Depending on the severity, the following are distinguished:
- Partial rupture of the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder joint, characterized by a change in the properties of individual fibers while maintaining the overall structure.
- Complete rupture in which the entire tendon is damaged and its function impaired.
Depending on the severity, it is an isolated lesion affecting only the supraspinatus muscle or a combined lesion affecting multiple components of the shoulder joint, including the bone.
symptoms
A partial rupture of the entire supraspinatus tendon is accompanied by a rather characteristic clinical picture, which includes the following symptoms
- Pain in the girdle of the upper limbs on the side of the injury, which appears suddenly after the injury or gradually intensifies as the pathological process progresses.
- Impaired function with difficulty raising the arm up.
- Decreased stability leading to frequent shoulder dislocation (development of a habitual dislocation).
- Appearance of symptoms of inflammation such as reddening of the skin of the shoulder girdle, swelling of the soft tissues with enlargement of the shoulder, increased pain, which can be disturbing even at rest.
The severity of the clinical symptoms depends on the extent of damage to the connective tissue fibers of the supraspinatus tendon.
symptoms
Symptoms of supraspinatus tendon lesions are quite characteristic and include:
- Shoulder pain that worsens when you try to lower, raise, or bend your arm.
- Weakness that is more noticeable when trying to raise the arm up.
- Abnormal mobility of the joint, especially with passive movements (the extent of movement is usually determined by the doctor during a clinical examination using special techniques).
- Symptoms of inflammation with marked changes in the tendon, including swelling of the soft tissues in the shoulder area, increased muscle soreness and persistent pain.
- Shoulder deformity does not always occur, only with severe combined injuries affecting the biceps, capsule and ligaments.
The severity of the subjective and objective symptoms depends on the severity of the injuries and their possible combination.
diagnosis
Since the clinical picture is nonspecific and may have similarities with lesions in other components of the shoulder, the doctor recommends an objective instrumental examination in order to establish a reliable diagnosis. This includes modern imaging methods for showing the internal structures and tissues with X-rays, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging and direct inspection by arthroscopy.
The treatment of tendon lesions is complex and the severity of the lesions must be considered. If a partial lesion of the supraspinatus tendon is detected, drug treatment is given. Surgery is performed for larger lesions. The doctor selects the method for each patient individually.
History and physical examination
Your doctor will talk to you about your symptoms and general health. The doctor will also ask you questions about your medical history related to your injuries. Such questions can be:
- Have you ever had an anterior knee joint injury?
- Have you ever had a quadriceps muscle injury?
- Do you have symptoms of quadriceps tendinitis?
- Do you have any medical conditions that might predispose you to a knee or quadriceps tendon injury?
After the doctor has discussed all the details of your symptoms and medical history with you, he will begin a thorough examination of your knee joint. To determine the exact cause of your condition, your doctor will assess how well you can straighten your leg at the knee joint. This part of the exam may be uncomfortable for you due to possible pain, but it is an important test to diagnose a quadriceps tendon tear.
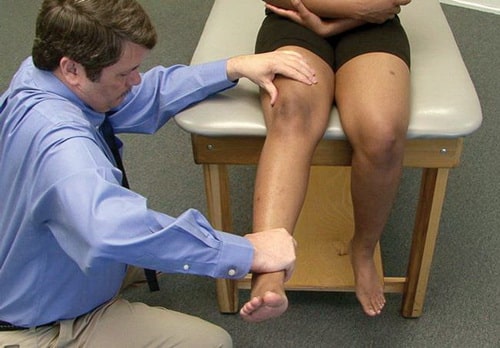
The patella stretch test can help diagnose a patellar tendon rupture and a quadriceps tendon rupture.
Radial Diagnosis
Doctors may recommend additional tests, such as X-rays or MRI, to confirm the diagnosis.
X-rays. When the quadriceps tendon tears, the kneecap shifts downward from its normal position, which can be clearly seen on a lateral x-ray. This x-ray is usually sufficient to confirm a complete rupture.
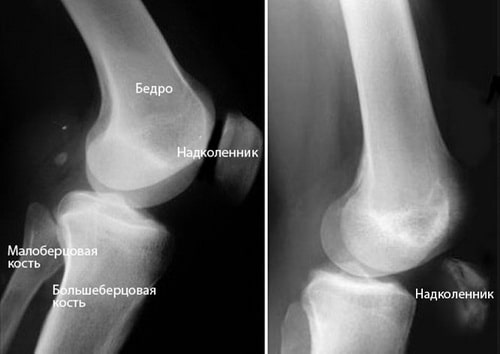
(Left) The normal position of the patella in lateral view. (To the right) Downward displacement of the kneecap due to a rupture of the quadriceps tendon.
MRI. This examination method enables visualization of the soft tissues around the knee joint, including the quadriceps tendon. MRI can be used to assess the extent and location of the rupture. MRI is sometimes used to rule out other disorders with similar symptoms.
When choosing treatment tactics, we take into account the following factors:
diagnosis
Based on the clinical examination (anamnesis, examination of the shoulder area, tests to determine the active and passive range of motion), the doctor prescribes additional objective diagnostics to visualize the location and severity of the injury. These include X-rays (the examination is carried out in different projections), CT or MRI scans of the tissues in different slices, ultrasound and arthroscopy.
During arthroscopy, a thin tube with optics, a light (arthroscope) and, if necessary, microsurgical instruments is inserted into the joint cavity. Small incisions are made to insert the arthroscope. A camera creates an image on a monitor, and the doctor can perform the necessary therapeutic interventions.
How is a ruptured supraspinatus tendon treated?
The modern treatment of a torn supraspinatus tendon must be comprehensive. Depending on the location and extent of the injury, this can be conservative treatment or surgery followed by rehabilitation. The doctor selects the method of treatment based on the results of an objective diagnostic examination.

A partial rupture of the supraspinatus tendon is often treated without surgery using conservative therapy methods. These include drugs from various pharmacological groups (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamin preparations, chondroprotectors) and physiotherapeutic treatments (mud baths, drug electrophoresis, ozokerite).
A modern method of alternative non-surgical strengthening of the connective tissue structures of the shoulder joint is intra-articular injection of platelets containing biologically active compounds called growth factors that stimulate the regeneration process. Conservative treatment can also be used as a preliminary step before surgery.
- The need for fibula fixation in tibia fractures 2016.02.05 The need for fibula fixation in tibia fractures
- Borderland Orthopedics Kiev, Ukraine 2015.07.02 Borderland Orthopedics Kiev, Ukraine
- Treatment of dislocation of the sternum end of the clavicle 2014.10.29 Treatment of dislocation of the sternum end of the clavicle
- Treatment of a luxated clavicle 2014.10.29 Treatment of a luxated clavicle 2014.10.29 Treatment of a luxated clavicle
- Treatment of fractures of the lateral end of the clavicle 2014.10.29 Treatment of fractures of the lateral end of the clavicle
- Intracranial internal fixation of collarbone fractures 2014.10.29 Intracranial internal fixation of collarbone fractures
- Treatment of diaphyseal fractures of the clavicle 2014.10.29 Treatment of diaphyseal fractures of the clavicle
- Treatment of clavicle fractures and dislocations of adjacent joints 2014.10.29 Treatment of clavicle fractures and dislocations of adjacent joints
- Postoperative treatment of scaphoid fractures 10/29/2014 Postoperative treatment of scaphoid fractures
- Surgical approaches in the treatment of scaphoid fractures 2014.10.29 Surgical approaches in the treatment of scaphoid fractures
Home ' Guide for Orthopedists and Traumatologists ' P ' Complete Supraspinatus Tendon Rupture and Partial Scapular Tendon Rupture.
symptoms
Most frequently Rupture of the rotator cuff tendon of the shoulder as a result of trauma occurs in conjunction with a history of degenerative changes (tenopathy). The tear is characterized by a sudden increase in pain and a weakness or inability to move the shoulder. It can be a partial tear or a complete tear, in which the tendon of the muscle detaches completely from its attachment to the humerus. The severity of the pain depends on the extent of the tear - as a general rule, the larger the tear, the more severe the pain and the greater the restriction of movement. Partial injuries preserve the ability to move the arm.
Clinical Anatomy
The four quadriceps muscles of the thigh (quadriceps femoris)—the right thigh muscle (musculus rectus), and the medial, lateral, and middle thigh muscles—meet at the anterior superior pole of the kneecap, where the tendon of the muscle is formed. The tendon fibers of the quadriceps muscle are arranged in layers. The most superficial layer is the rectus muscle, followed by the vastus lateralis muscle and the vastus medialis muscle. The interaction of the quadriceps, the quadriceps tendon and the patellar ligament stretches the knee joint.
These muscles are innervated by the femoral nerve and supplied with blood by the femoral artery. The rectus femoris muscle and the broad and lateral intercostal muscles receive arterial blood from the lateral artery, which encircles the femur. The vastus medialis muscle is supplied by the femoral artery, the superior lateral patellar artery (a side branch of the popliteal artery), and the deep femoral artery.
The vastus lateralis, medial vastus, and middle vastus work together to extend the knee and control the patellar track.
The vastus lateralis is the largest muscle within the quadriceps (quadriceps femoris). It helps pull the kneecap laterally. This is offset by the medial vastus, the smallest muscle in the quadriceps group, which pulls the kneecap medially. The vastus medialis muscle helps stabilize the medial line of the patellar canal.
The combined contraction of these muscle groups leads to extension of the shin. The rectus femoris muscle also plays an important role in hip flexion. A tear in the medial quadriceps tendon drastically affects knee extension and directly impacts knee function. The degree of restriction in knee extension depends on the severity of the tendon injury. A small tear can only minimally affect the ability to extend, while a complete tear can prevent extension of the knee altogether.
Epidemiology/Ethritology
Tendons of the extensors of the lower limbs are generally quite rare, but have a high complication rate and are very serious. The statistics show an annual incidence of quadriceps tendon ruptures of 1.37 per 100,000 people and patellar tendon ruptures of 0.68 per 100,000 people. Cracks most commonly appear on one side. Partial and full tears occur mainly in men. These injuries occur in all age groups, but are most common in patients over 40 years of age.
Quadriceps tendon rupture is positively correlated with age and multiple comorbidities. Traditionally, this injury is more common in men over 40 years of age. A tear of the patellar ligament, on the other hand, is more common in people under the age of 40 and is mainly associated with sports injuries.
The rupture of the tendon muscle often occurs during a dynamic action with a failed landing. Upon landing, excessive force is applied to the bent knee and the foot is flattened (such as in a jump landing). The quadriceps muscle contracts violently and eccentrically at this point. Another mechanism for a tear is related to a direct impact on the front of the knee (which occurs in a fall). During the examination, patients usually present with acute knee pain and swelling. Loss of function occurs when the patient stumbles, falls, or bends the knee.
risk factors
Most injuries are caused by weakness in the quadriceps femoris tendon.
- Tendonitis: Tendonitis reduces the strength of the tendon and can even slightly deform it.
- Insufficient blood supply to the tendon due to other pathologies also leads to a weakening of the structure.
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism, which causes bone resorption that leads to a weakening of the fibrocartilage junction between tendon and bone tissue.
- Chronic renal failure. This condition can lead to elastosis of the connective tissue, causing weakness in the tendon.
- Other diseases: systemic lupus erythematosus, gout, leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, obesity.
- Infections and metabolic disorders also have a negative effect on tendon strength.
symptoms
- Some patients experience sudden pain in the front of the shoulder when exercising. The pain is sharp and intense and may be accompanied by a cracking sound or tearing.
- Other patients report intermittent pain with overhead movements or repetitive activities.
- Others experience severe pain in the front of the shoulder that can get worse at night.
- In some patients, the tear can be almost asymptomatic and the patient only notices a lump or lump between the shoulder and elbow. This is usually possible with chronic tendon damage, and the pain may go away after a complete rupture. A distal rupture can have similar symptoms, but the site is closer to the elbow.
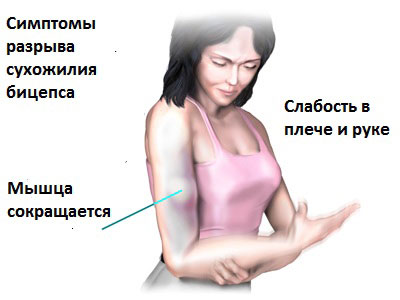
- Rupture of the proximal biceps tendon is usually due to chronic inflammation secondary to subacromial impingement and the end result of chronic microtrauma. Repeated trauma often degrades the tendon, reducing its strength, increasing the risk of a rupture even after relatively minor injuries.
- Tendon ruptures due to chronic inflammation can occur in rheumatoid arthritis.
- Excessive loading or sudden overuse of the tendon, e.g. B. when lifting weights, is often the cause of an acute tendon rupture.
- A rupture or degeneration of the biceps tendon commonly accompanies a rotator cuff injury in elderly patients and is often diagnosed during rotator cuff injury surgery. It can be associated with impingement syndrome.
- Most tears occur at the tendon insertion site proximal and distal to the bone:
- Distal tendon tears at the radial bone are usually caused by chronic irritation, such as B. in chronic bursitis of the elbow.
- Acute tears result from forced extension of the elbow in flexion and supination positions.
- Rare tears of the tendon of the short head of the biceps can occur with rapid flexion and adduction of the arm during activities that require elbow extension.
- Impaired physiological recovery mechanisms due to medication (eg, statins) are also considered potential predisposing factors for tendon rupture.
diagnosis
- In most cases, proximal and distal tendon tears can be diagnosed by history and examination. The mechanism of injury, the presence of pain and/or inflammation, and the examination findings often allow the diagnosis to be made. However, instrumental diagnostic procedures can be used to verify the diagnosis and rule out possible other diseases.
- The X-ray examination can detect bone abnormalities and only provides indirect evidence of a tendon rupture. However, fractures in the shoulder region can be made visible with X-rays.
- Arthrography was until recently widely used to diagnose shoulder injuries, but is not routinely used because of its high invasiveness, exposure to ionizing radiation, and relatively low diagnostic power.
- ULTRA SOUND Examination of the shoulder structures is quite instructive in diagnosing a biceps tear. However, small tears or intra-articular lesions cannot be diagnosed by ultrasound. Nevertheless, this examination method is often used in the diagnosis of biceps tendon rupture due to its practical harmlessness and very good informative value.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) is the most meaningful imaging procedure in the diagnosis of even small morphological changes in the structures of the arm.
The treatment of biceps tendon rupture is still under discussion. A comparison of the long-term results of surgical and conservative treatment has not revealed any clear advantage of one over the other method. Nevertheless, some tactics for the treatment of biceps tendon ruptures have been developed, based on an individual approach to each patient.
Surgical methods of treatment (tenodesis and subacromial decompression) are necessary at a young age and in athletes, that is, in cases requiring strong supination. In addition, surgical treatment may be required to correct cosmetic problems after a rupture. Surgical treatment primarily uses atroscopic techniques to restore ligament integrity with minimal invasion.
Read more:- Collateral ligament rupture.
- Rupture of the medial collateral ligament.
- DMS rupture.
- Rupture of the ligaments of the ankle.
- Rupture of the radial-clavicular joint.
- The medial surface of the tibia.
- The flexor muscles of the foot.
- The long section of the big toe.
