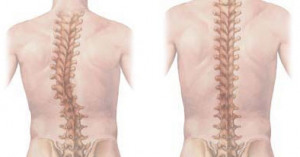
'During exertion, muscle tension can occur in this area, which manifests itself as discomfort, pain and restricted movement in the cervical spine,' explains Yulia Hazime, neurologist at the MEDSI Premium Unit Clinical Diagnostic Center Krasnaya Presnya. – explains Yulia Hazime, a neurologist in the MEDSI Premium Unit of the Clinical and Diagnostic Center in Krasnaya Presnya. - Tight neck muscles can cause pain, along with a moderate, nagging headache that usually lasts for some time after the contraction. If the muscles of the shoulder girdle and neck are systematically overworked, such attacks can recur.

- Why do headaches occur after exercise?
- 1. Pain that occurs in response to intense exertion
- 2. Pain associated with chronic diseases
- Why does the head hurt after exercise?
- What are the causes?
- How to prevent.
- signs
- Pain treatment at the Dr. Ignatiev Clinic (Kyiv)
- What to do while running to stop the pain
- What you can do to avoid side pain while jogging
- What accompanying symptoms can accompany the pain?
- Back pain when walking, running or jumping
- The main symptoms are: ↑
- How to relieve pain
- cause of the pain
- Inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract
- Diseases of the urinary tract
- Second step: start with the right diet
- Step Three: Prepare your back and joints
Why do headaches occur after exercise?
This painful feeling can occur after endurance training as well as after strength training. And sometimes even after a yoga class. How does this happen? And what should I do if I get a headache after a workout?
Doctors distinguish two types of post-exercise headaches.
1. Pain that occurs in response to intense exertion
These are called primary headaches and can occur even in perfectly healthy people.
'Primary headaches are usually harmless, have nothing to do with a disease and can be treated simply by taking medication or changing the intensity of physical activity' - comments Fedor Mikhnevich, general practitioner at the GMS clinic.
Such headaches are often felt as throbbing and occur during or after intense exercise. The pain is usually bilateral - for example a 'throbbing' feeling in the temples after a hard run.
'The most common occurrences of this symptom are after intense running, cardio or plyometric exercise (which are exercises that simultaneously increase muscle strength and general endurance while burning maximum fat),' explains Greg Zheja. – says Gregory Zheja, a doctor of physiotherapy and sports medicine at the SportMedica clinic.
2. Pain associated with chronic diseases
'They are caused by health problems: related to the brain (hemorrhage, tumor) or outside the brain (e.g. arterial disease of the heart). Secondary headaches may require urgent medical attention' – notes Fedor Mikhnevich.
Secondary headaches can resemble a primary headache but are often accompanied by other symptoms: vomiting, loss of consciousness, double vision, excessive neck muscle tension.
Read more:'Primary headaches can occur within five minutes of starting exercise but do not last very long. Secondary headaches will plague you for at least a day, sometimes even several days, after exercise'. – comments Fedor Mikhnevich.
Why does the head hurt after exercise?
Primary headaches after exercise can occur for a variety of reasons. Let's look at the most important of them.
'There are several possible causes: increased pressure in the body from the absorption of a load (can occur in connection with a reaction to increased air pressure), vasospasm of the blood vessels (along with the cerebral vessels), various limitations in the mobility of the cervical spine (compression of the ducts and bundles of the nervous system). Headaches have little to do with the type of exercise itself, as they can occur with different types of exercise — cardio, strength training, and even functional training, says Ruslan Panov, professional instructor for the X-Fit network in Russia.
What are the causes?
Eating the wrong meal before a run, running too fast, breathing incorrectly, and so on can affect mood. Let's find out what happens to your body when you feel an uncomfortable twinge in your side. Exercising increases blood flow in the body, but unless the body is prepared for a fast run with a warm-up routine, blood can spread unevenly and overwhelm the liver (right side) and spleen (left side). When these blood-filled organs press against their own coverings, the nerve endings create painful sensations. These are not dangerous, but very uncomfortable.
If you suddenly feel that your organs are 'offended' while jogging, do the following.
- Slow down. You probably ran too fast to begin with - give your body time to warm up and get into running mode;
- Take a deep breath. Frequent breathing doesn't help stabilize your heartbeat, so relax, breathe in slowly - breathe out slowly, think of nice things;
- Synchronize your breathing and your steps. For example, breathe in for four steps and breathe out for the same amount of time. As you increase the tempo, your breathing will speed up, but it won't get out of rhythm;
- Relief of the painful side. As you exhale, your abdominal and diaphragm muscles relax. So if you step on the painful side with your foot while exhaling, you hit the painful spot even harder. For example, try exhaling when you touch the ground with your left foot if your right side hurts;
- Gentle massage Massage the side that is spasming: Gently press on the side and massage in a circular motion to increase blood flow to internal organs;
- If these methods don't work, switch from jogging to stepping.If that doesn't help, walk around, stand and stretch your obliques and abs with slow right-to-left movements and breathe.
How to prevent.
Prepare ahead of time for your run: think about what you will eat for your last meal before the run. Avoid fatty, heavy foods and give preference to protein and light vegetable salads; do not drink too much, but rather take water with you to training.
After eating, give your stomach time to digest, at least 40 minutes, and then you can walk. Read more about what to eat before, during and after a race:
Warm up before you start! Dynamic stretches, joint rotations, squats, lunges, hip raises, laps—take 10 minutes to make your workout comfortable and pain-free.
Start the run slowly, letting your body transition smoothly from a slow pace to a fast pace. Pay attention to your posture and the speed and depth of your breathing. If you're running with headphones on and find yourself rushing to the music, leave your favorite tunes for another activity. It is better to listen to your body and work with it, then running will bring you only pleasure and benefits.
If you exercise regularly, your body will develop and you will not have pain in your side. However, when it doesn't, it's a sure sign that it's time to see a doctor. Pain can indicate chronic diseases such as hepatitis, gallstones, pancreatitis and others.
signs
Pain syndrome can occur both with walking and other movements, and with running. In the latter case, it occurs only when running and during heavy physical exertion. In general, the pain begins when walking. It is not a severe and unbearable pain, but rather a feeling of discomfort and discomfort in the lower back. Later, the pain becomes almost unbearable and can accompany the patient for a long time. In most cases, patients present to the specialist with severe pain, which indicates a chronic stage of osteochondrosis, which most often leads to this type of pain.
However, in order to receive the right treatment in a timely manner, it is important not only to immediately consult a doctor, but also to make a differentiated diagnosis. This will exclude possible diseases and determine the cause of the pain syndrome. This can not only be an osteochondrosis or a strain, but also a pinched nerve root and more.
Pain treatment at the Dr. Ignatiev Clinic (Kyiv)
The main goal of treatment is to eliminate the cause of pain, that is, the disease or inflammatory process. Doctors also treat the pain syndrome itself. This is done both with conservative methods of manual therapy and physiotherapy, and with drugs in advanced stages of the disease. Before starting treatment, an MRI or ultrasound scan, if necessary, and a number of other tests should be performed. In this way, the treatment regimen can be adjusted.
If you are suffering from this type of pain, you should contact the clinic of Dr. Contact Ignatiev, where qualified specialists can help you to solve the problem in a short time.
What to do while running to stop the pain
It is difficult to control side pain while running. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends some actions that may help, but each case is different, so effectiveness cannot be guaranteed.
- Slow down, but don't stop.
- Begin with deep breathing, inhaling on two steps and exhaling on a third step. This will relax your muscles and allow the symptoms to subside.
- Stop and do some stretching exercises - bend sideways or forward.
- Walk gently in one step and then stop. Then lean forward slightly – the tense internal organs and the diaphragm will relax.
What you can do to avoid side pain while jogging
There are a few things you can do to prevent side pain.
- Always warm up before you run. This warms up the muscles and prepares the body for the workout, both physically and mentally.
- Don't rush the start, even if it's a competition. When exercising, start out at a slow pace and gradually increase the speed.
- Pumping up the cortical muscles is a good way. If you can strengthen your back muscles and abs, you'll feel more stable during running and other activities, and you'll be less likely to experience pain.
- Maybe you should see a trainer and work on your running technique. Researchers have pointed out that errors in technology, such as B. a high step frequency or steps that are too long, can lead to side pain.
- Don't eat before a workout. The last meal should be 2-3 hours before training.
What accompanying symptoms can accompany the pain?
Recreational runners often suffer not only from lower back pain, but also from associated symptoms if they have not exercised enough. They all signal inflammatory processes in the body and disturbed blood circulation.
The most common injuries in runners
There are also cases when during training the Transverse processes of the lumbar spine of the lumbar spine tear and begin to compress the nerve endings. However, this is an isolated case that only shows that you don't really understand running and your own body.
Headaches are caused by poor blood circulation in the shoulders and neck. This happens especially when the shoulders are not moving while running and are quite high. To avoid this, just keep them relaxed by moving them freely. And if you feel uncomfortable in your shoulders, try twisting your arms and shaking them.
An increase in general body temperature tells us that an active inflammatory process is underway in one of the body's systems. This can be the lower back, but also a muscle strain or a ligament injury.
Pain in the thoracic and cervical spine is usually caused by flat feet and poor posture.. You need running shoe inserts, good cushioning in your running shoes and proper back posture - you should be looking straight ahead, not at the sidewalk, your head should be tilted up and your shoulders should remain straight.
Back pain when walking, running or jumping
back pain – Back pain is a symptom of dystrophic changes in the muscles and ligaments of the back or spine that are severely restricted by a spinal nerve. Chiropractors treat this pain.
The specialists of the Dr.Ignatiev Clinic in Kiev can offer you qualified help in the treatment of back pain. A consultation appointment is only possible by appointment.
Back pain when walking, running or jumping occurs in 40-80 % of the population. For people in sedentary jobs, attention drops twofold after 42 minutes of listening.
The main symptoms are: ↑
- weakness in the legs;
- impairment of plantar flexion of the leg;
- bladder and bowel dysfunction;
- urinary and fecal incontinence;
- muscle cramps;
- Headache;
- pain in the extremities;
- arm weakness;
- numbness.
To determine the cause of back pain, the doctor conducts a differential diagnosis for such diseases as herniated disc, myogenic pain, fibular canal rupture, facet arthropathy, torn fibrous ring.
Treatment of back pain when walking, running, jumping in the clinic of Dr. Ignatyev (Kyiv)
- Articulation, mobilization techniques. The osteopath performs oscillating rhythmic movements on the limbs or joints of the spine at the limit of physiological possibilities. The muscles around the joints slowly relax, tension is released, the periarticular muscles open, and the joints return to their normal position.
- Muscle Energy Techniques - the mechanics of post-isometric muscle relaxation. It is performed by combining phases of relaxation and contraction in the muscles surrounding the blocked joint. The osteopath acts on the secondary system and internal muscle regulation. This relaxes the muscles and pulls the joints into the correct position. The therapist guides the limbs and torso into a specific position, relaxing the necessary muscle groups and maintaining the position. Then the patient tries to perform a movement - to raise the leg or twist the trunk. The practitioner gently applies resistance while maintaining the body position. After 3-5 seconds in this position, the patient's back or limb muscles are physiologically fatigued. He/she is asked to relax. After waiting a few more seconds for the muscle fibers to relax, the practitioner gently increases the amplitude of the movement. This stretches the relaxed muscles and releases the remaining tension. The joint returns to its normal position. The treatment is carried out three times;
- The general osteopathic techniques are circular, flowing movements performed on the peripheral joints of the body. They relax the transverse periarticular fascial attachments and normalize the musculo-nervous reflex functions. The function of the body's own receptors is restored. Common osteopathic approaches include traction, stretching, and vibration techniques;
- Bioresonance integration.
How to relieve pain
There are general recommendations that do not promise 100% effectiveness, but can reduce pain symptoms:
- Avoid eating large amounts, especially fatty foods, before exercising.
- Take deep breaths while exercising.
- Get a subcostal massage.
- If there is pain on the right side, stopping may help.
- In the case of pain in the left side, it is advisable not to stop completely, but to proceed gradually.
- Practice in correct posture, without hunching or hyperextension.
For some, these techniques help, for others, the symptom returns with enviable regularity. There is no foolproof method because the mechanism of abdominal pain in athletes is unclear.
cause of the pain
The simplest causes of pain can be:
- poor warm-up;
- shallow breathing;
- liver disease, gallbladder disease, which can be triggered by exertion;
- osteochondrosis.
However, the true causes of pain in healthy athletes are still unknown.
The theory was that blood flow in the liver is probably impaired, blood stagnates, and the liver stretches its own capsule, causing right-sided pain. On the other hand, if the pain occurs on the left side, it is assumed that it is due to a stretching of the spleen. Blood supply to parts of the diaphragm has also been considered abnormal, causing ischemic pain. Another putative mechanism is stretching of the subdiaphragmatic ligaments from running and other concussive stresses.
Recent studies have shown that all of these theories are not true. In one study, it was found that such pain occurs not only in runners, but also in swimmers (without concussion) and cyclists (although they sit and there is no lack of oxygen in the tissues). One assumption so far is excessive irritation of the nerve endings in the peritoneum. This is the case when the tissue in the abdominal cavity rubs heavily during intense physical activity.
There is also a connection between the consumption of hypertonic drinks and the occurrence of pain. Symptoms were less common in athletes who consumed isotonic or hypotonic fluids.
In addition, an association with facet joint dysfunction and excessive flexion of the lumbar spine has been identified. One possible pain mechanism is related to compression or irritation of the nerve roots that supply the affected abdominal areas.
The cause of the pain and the way to combat it are still unclear. If the pain is severe and increasing, a doctor should be consulted to rule out other problems. Only then can it be assumed that this pain is related to a strain.
Inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract
Pain in the right side can be caused by a number of inflammatory processes in the digestive tract. 'For example appendicitis, diverticulitis, colitis, gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer,' says Bulat Yunusov.
Most often, these diagnoses are expressed by excruciating, moderate pain that gradually increases in intensity. With appendicitis, pain may increase when walking, coughing, or changing body positions, and decrease at rest. In addition, there is an increase in temperature, nausea and vomiting.
Peptic ulcer pain worsens after eating greasy, spicy, or fried foods, drinking alcohol, or strenuous exercise. Other symptoms can include heartburn, nausea, and vomiting.
With colitis (inflammatory bowel disease), the pain can be excruciating or aching. Diarrhea, fever, general weakness, headache and mucus in the stool can also accompany the disease.
Diverticulitis (bulging of the intestinal walls) is manifested by severe pain to the right of the navel, fever and diarrhea (blood and mucus).
Inflammatory bowel disease (inflammation of the lining of the stomach and small intestine) can be accompanied by pain in the right side, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, etc.
With pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), the pain comes on suddenly and is constant and intense. Sometimes they 'stick' to the left side or get worse after eating heavy, greasy or spicy foods.
Diseases of the urinary tract
It is not uncommon for right side pain to be caused by the urinary organs. 'These include urolithiasis and pyelonephritis,' says Bulat Yunusov.
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of the kidneys that can cause pain in the right side, weakness, nausea, vomiting, increased heart rate, dry mouth, and fever.
The pain in the side with urolithiasis can be constant or wavy, dull or stabbing, and may be present only at rest or worsen with walking. It depends on the location of the stone, but sometimes the pain is first felt in the lower back (known as renal colic) and then 'sets down' in the right side.
Second step: start with the right diet
If the body lacks vitamins and minerals, the joints and spine cannot develop their full potential. A lack of calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D can lead to osteoporosis and broken bones. When running, it is also important to pay attention to a balanced ratio of the necessary nutrients - proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Excess of the latter leads to obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases - and is a contraindication to running.
If you put a lot of strain on your joints and back while running, the nutrient imbalance can prove fatal. You can prevent the development of complications if you compose your diet correctly:
- Limit animal fats and quickly absorbable carbohydrates.
- Include sources of vitamin D, calcium and phosphorus - milk and dairy products, vegetables and greens (carrots, spinach, broccoli), legumes, sea fish.
- Stay hydrated: Drink at least 1.5 liters of fluids per day.
Step Three: Prepare your back and joints
Many people go running unprepared - and immediately put a strain on their joints. When running, the knees suffer first - they get injured and the risk of arthrosis increases. The lumbar spine is affected - back pain is inevitable after such a run. If you've been sitting in an office chair for a year and then suddenly decide to go jogging, don't be surprised if your joints hurt badly again the next morning.
Start each morning with a simple exercise to stretch your hamstrings and lower legs and prepare your joints and back for the challenge. Here are three simple exercises:
Preparing for a marathon requires special attention. You can't just run a long distance - your body may not be able to cope with the increased stress. That's how it's done. says about it from Vadim Yangirov, a marathon runner:
You have to prepare for every race. There are a few rules that I recommend you follow. First, make a schedule and work out your pace through daily practice. Your body and mind have to adapt to long-distance running.
And of course, don't forget to replenish your fluids and recharge your batteries during your workout and run. There is now a lot of material on this topic, develop your individual training program, do not make sudden jumps and take care of yourself!
Applied kinesiology is a biofeedback tool for the body.
- Which muscles hurt after running?.
- muscle work while running.
- Muscles congest when running.
- Why do feet hurt after running?.
- Why do your calves hurt when you run?.
- The calf is constipated when running.
- Acute pain in the calf muscle when running.
- Why the legs hurt below the knees after running.