Phase 4 symptoms Characterized by the development of deep necrosis. The toes are affected. An infection with anaerobic or putrefactive bacteria, with moist gangrene and heavy mucus is typical.
- Trenchfoot: What is it and how is it treated?
- Etiology of trench foot syndrome.
- What is and what are the features of the vertical pile driver?
- causes and symptoms
- Treatment of the vertical ramus using the Dobbs method
- Treatment of the ram in Yaroslavl
- rehabilitation
- Anatomical structure
- Anatomy of the heel bone
- species
- symptoms
- Advantages of modern implantation technology:
- How can external signs indicate an indication for surgery?
- indications
- Advantages of ankle arthroeresis
- Injuries to the pelvic bone
- What are the symptoms of a fracture?
- Treatment
- Surgery: tenotomy and longitudinal displacement
Trenchfoot: What is it and how is it treated?
'Moat Foot' (from English, trench foot)) – or 'submerged foot syndrome' – is a form of cold injury or frostbite that occurs with prolonged exposure to temperatures above freezing and repeated contact with moisture. In trench foot, the distal parts of the foot (toes) are injured, and it differs from classic frostbite in that the lesions are much less severe (necrosis, development of gangrene).
The term was widely used during World War I, when soldiers in the armies of France, England and Germany began to suffer from this cold-related ailment.
During trench warfare, soldiers spent long periods of time in flooded trenches, often for several days, without being able to dry their boots. At the same time, the soldiers complained of pain in their feet, numbness and slight tingling.
Etiology of trench foot syndrome.
The main etiological factors for its development are:
- Moisture and its constant or prolonged contact with the skin of the foot. Moisture is the main etiological factor that significantly affects the heat-insulating function of shoes;
- Low but not below zero temperatures. The syndrome most commonly occurs at temperatures between +2 degrees Celsius and +10 degrees Celsius. Cases have become known in which the following symptoms, among others, have developed. 'Moat Foot' at temperatures between +12 and +14 degrees.
- Lack of mobility. If there is insufficient mobility, blood flow to the tissue decreases and the skin barrier decreases, which leads to an increased sensation of cold.
What is and what are the features of the vertical pile driver?
The vertical ramus is a deformity of the flat foot.
It is characterized by abnormal alignment of the bones in the foot, with the talus bones leaning forward and the scaphoid bones tilting outward.
The condition is best diagnosed when the foot is standing and putting weight on it. The heel is in a valgus position that is directed inward. The longitudinal arch is indeterminate, there is some abduction of the distal part of the foot and a medial protrusion of the talar head visible from the front (X-shaped appearance).
The mobility of the ankle joint is normal, but abnormal pronation and supination of the foot are noted. If the condition is not neglected, the feet will have normal arch height and bone alignment at rest and without stress.
The disease causes bone deformities and secondary joint changes in the muscles and ligaments of the foot, particularly in the ankle joint.
Pain when walking is characteristic and is caused by a misalignment of the bones under stress, by the pressure of a deviated heel bone on the ankle joint, by overstretching of the ligaments and by the effect of displaced bones on the supporting nerve. When the head of the carpal bone descends, the nerve is damaged, resulting in neuropathy or reflex muscle spasm.

causes and symptoms
Depending on the cause, a distinction is made between the following forms.
- Congenital PVDS (flat ankle deformity) or club foot.
- Neurogenic PVDS caused by cerebral palsy or other pathologies.
- Secondary statics.
Congenital bilateral vertical ramus (or unilateral ramus) is diagnosed in newborns; in half of the cases it is an independent disease caused by anomalies in the formation of the skeletal system or the ligamentous apparatus. In the other half it is accompanied by severe malformations of various kinds.
A common cause is static stress. In some cases, a flattened foot (flat foot) can be the cause of a flat foot deformity. As a result of unbalanced static forces caused by weakened muscles and ligaments, the talus shifts and the lower leg muscles lose tension, resulting in a valgus position of the foot.
In children, the development of the foot is influenced by muscle tension in the first year of life and later by stress. When the child begins to walk, there is a lack of muscular coordination to evenly distribute the load on the foot, resulting in foot deformity. Flat feet are the norm in children under 3 years old.
The valgus deviation and support on the inside of the foot should alert the parents and doctor (orthopedist).
The absence of any symptoms in children is characteristic.
In adults there are two forms of the disease with different causes. The first variant (late form) does not occur for a long time and is painless. It is characterized by a gradual increase in the inward deviation of the feet. Causes are:
- overweight;
- Reduced strength of the ligamentous apparatus;
- standing work;
- Loss of muscle strength due to illness or age.
The second type develops due to structural and functional abnormalities caused by untreated flat feet at a young age, rheumatic polyarthritis.
Treatment of the vertical ramus using the Dobbs method
Treatment should begin immediately after diagnosis. Childhood is the most appropriate age for effective treatment. Children's tissue is more flexible than that of adults, so the talus can be repaired without major surgery.
The treatment process includes the following steps:
- Plastering. This is done to fix the foot in a healthy position. The orthopedist makes several projections (usually 5-6) from the toes to the thigh, bending the child's legs to 90 ° at the knees.

- Minimal surgical intervention. The ankle bone is fixed in a healthy position with a Kirschner wire, then the Achilles tendon is severed with a puncture and the foot is placed in a cast in the metatarsal position.
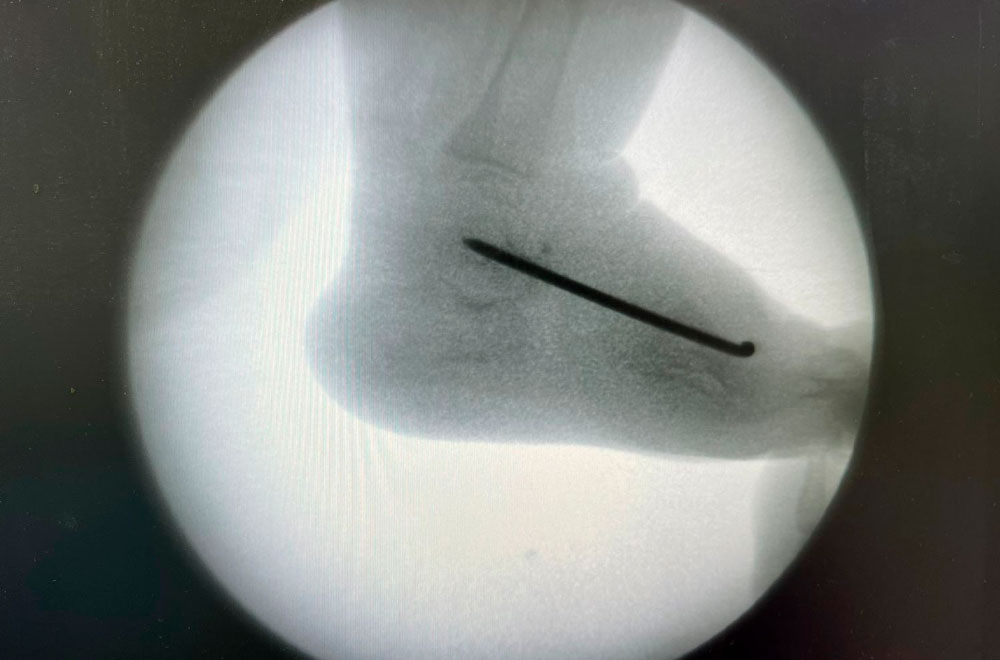
- The wire is removed under local anesthesia. The splint is removed after eight weeks. At the same time, a new plaster cast is applied, not only on the thigh but also on the knee joint.
- An orthosis is also put on. The plaster cast is removed after 4 weeks. The child is equipped with special orthopedic shoes - orthoses. Wearing these shoes will increase the effect and prevent the clubfoot from recurring. During the first three months, the child must wear the shoes 23 hours a day, after which the doctor will adjust the wearing time according to the orthosis protocol.

The importance of parental supervision in the final stages of treatment of vertical rams
Treatment of the ram in Yaroslavl
In Yaroslavl, treatment of this disease is carried out by the Konstant clinic. The treatment measures are carried out at your own expense and with funds from the Rusfond Charitable Fund.
The clinic's doctors are the leading pediatric orthopedists Dr. M. Vavilov – President of the Russian Ponseti Association – and Dr. M. Gromov. These are specialists with great experience who quickly find access to the children and their parents.
Patients from other cities can receive advice via Skype or email. In order for the orthopedist to make a diagnosis, an email must be sent to [email protected]:
- A photo of the feet from the front and from the side, bent backwards as far as possible.
- X-ray images in the same positions.
- A video of the child walking upright and backwards.

Maxim Vavilov 
Gromov Ilya Valeryevich 
Yuri Valeryevich Ryabkin
If you have any questions about your treatment, you can always contact the coordinator of the Russian Ponseti Association:
Yuri Ryabkin
Email: [email protected]
tel. +7 (800) 700-04-29
WhatsApp +7 (960) 539-86-91
rehabilitation
After the destruction of the plate, the patient needs a long period of rehabilitation and recovery. The plaster cast must be worn for at least 3 weeks. The duration depends on many factors - the severity of the disease and the extent of the fracture. No pressure should be placed on the injured foot while wearing the cast.
The use of crutches or a cane is recommended when walking. The patient receives physiotherapy treatments that include:
All treatments are carried out on an outpatient basis. Physiotherapy treatment is recommended after application of the patch and continued after its removal. In addition to the main treatment, diuretics, calcium, vitamin and mineral complexes should be prescribed.
It is strictly forbidden to choose the medicines yourself. The doctor will always take allergies and comorbidities into account.
After removing the cast, you should move carefully. Forced immobilization of the foot leads to a weakening of the ligaments. The immobilized muscles should be exercised carefully.
Anatomical structure
The talus bone, which is surrounded by ligaments and tendons and surrounded by the articular surfaces of other neighboring joints, is characterized by an asymmetrically complex structure.
Anatomy of the heel bone
The bony meniscus of the ankle consists of:
- the head, which is slightly flattened at the front;
- the body with a large articular plane on the top (the block) and medial and lateral planes on the sides;
- the neck, which is completely covered by cartilage;
- the posterior process.
The bony head is connected to the navicular bone by the navicular surface of the same name. The body of the ramus is wrapped around the ankles of the tibia. There are two cusps on the joint (lateral, medial).
Important: In some individuals, especially ballet dancers, there is a bony triangular formation that replaces the lateral tubercle. It is possible that it developed as a result of the heavy, regular stress during the jumping portions of ballet performances.
The cartilage that covers the articular surfaces of the ramus is the largest compared to the other bones of the human body. The wide front part of the ramus gives the ankle a stable footing. The lower articular surface ensures firm contact with the heel bone. The ramus is also called the carpal bone because the heel bone underneath supports it.
species
There are the following forms of valgus deformity:
- Congenital – the disorder develops prenatally, with a change in the position of the talus of the carpal bone. This anomaly is called 'vertical ram' or 'tilt foot' and is quite difficult to correct;
- Acquired – is the result of tendon and ligament defects in children. It develops with the child's first independent steps (up to the age of 10-14 months).
Normally, the alignment of the feet should be strictly parallel and maintained with each step. The severity of the pathology is different and depends on the degree of deviation:
The larger the angle, the longer the therapy must last.
The consequences of this pathology can be flat feet, osteochondrosis, arthrosis, scoliosis and, in rare cases, shortened limbs.
symptoms
The foot has a supporting function. If there is insufficient muscle tone in the legs, deformation of the knee and pelvic joints as well as poor posture when walking and if left untreated can occur.
The symptoms of the disease appear when the child takes his first independent steps:
The gait becomes unsteady, clumsy, wobbly, pain and fatigue occur. The soles of the feet wear unevenly, especially on the inside. With normal development, the clumsiness and insecurity disappear as the ability to walk is acquired, otherwise the symptoms only worsen.
Advantages of modern implantation technology:
- Reducing pain and fatigue in the feet and legs
- Low risk of infectious complications
- No immobilization (walking on crutches) is required; the bone or cartilage is removed
- No drilling of the bone required for insertion
- No bone cement is required for fixation
- The implant can be removed again if necessary.



How can external signs indicate an indication for surgery?
If the condition of your feet does not improve with age and in addition to conservative treatment, you should consult an orthopedist. The doctor will recommend surgery to correct the flat feet. Correction will help you lead a more active life, improve your quality of life and avoid more complicated surgeries in the future.
The implants do not need to be removed. However, some patients may experience persistent pain, which may be a reason for implant removal.
indications
Flat feet alone are an indication for surgery. If there is only slight pronation of the foot and there are no symptoms, conservative treatment methods can be used.
This includes special exercises, orthopedic shoes and special insoles.
Indications for tibial arthroaeresis include the following symptoms
- pain syndrome and swelling of the foot;
- Gait disorder, severe clubfoot, foot weakness;
- Difficulty choosing shoes, rapid wear and tear;
- severely reduced quality of life;
- problems in the professional area;
- lack of effect of conservative treatment.
Advantages of ankle arthroeresis
Arthroaeresis of the subtalar joint has some advantages over other methods of treating flat feet:
- It is highly effective;
- There are practically no infectious complications;
- Stable results;
- She is completely safe;
- It does not require immobilization of the limb, allowing the patient to move independently;
- completely eliminates clubfoot;
- does not require bone cement to fix the implant;
- has good patient feedback.
Injuries to the pelvic bone
Because this bone is the most massive of all the bones in the foot, injuries to this bone can cause serious damage to the musculoskeletal system. Statistics show that fractures of this bone result in lifelong disabilities in a large number of people. Although such injuries are quite rare, they are very serious. Since the talus bones have a special location and are nourished by specially located vessels, the treatment of fractures requires a number of special measures and a long rehabilitation period.
Causes of damage to the ankle bone are:
- Traffic accidents;
- Falls from heights with unsuccessful landing;
- Sports injuries (jumping, running, etc.);
- direct shocks to the ankle bone (mechanical shocks).
There are different types of impact injuries depending on the type of impact. For example, a fracture of the talar neck, the most vulnerable part of the talus, occurs when the foot is excessively flexed. This type of injury is more common in athletes.
A comminuted fracture occurs when the foot is subjected to high stress or falls from a height and the bone is crushed.
A transverse process injury occurs when the foot is subjected to severe flexion and the outward rotation of the foot causes a fracture of the main part of the foot (the block).
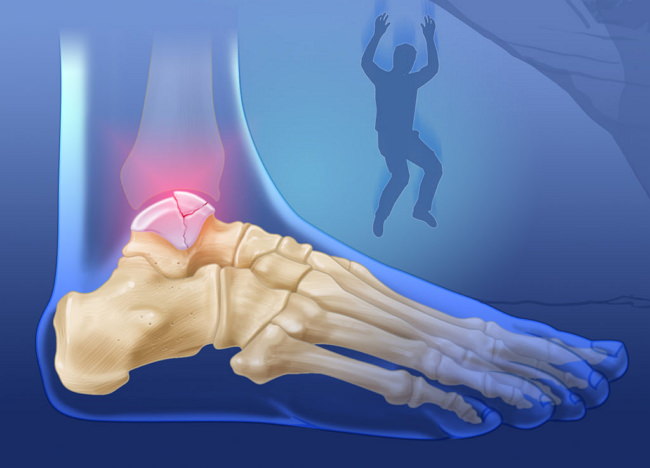
A rupture of this anatomical region results in a loss of its integrity. This causes the damaged limb to become completely immobile and unable to function.
What are the symptoms of a fracture?
The symptoms of bone fractures become noticeable immediately. They appear immediately after the injury. Swelling and pain are the main symptoms. In this case, the swelling is in the back of the sole of the foot, making it enlarged. The foot swells so much that it becomes twice the size of a healthy foot.
Depending on the location of the injury, the pain can occur in both the front and back of the foot. Severe pain occurs when trying to move the big toe. And trying to lean on the injured foot makes it completely impossible to function. Therefore, with this type of injury, it is impossible not only to walk but also to stand on the injured leg.
There is also a type of displaced fracture. In this case, the main symptom is deformity of the foot and loss of function of the ankle joint. This means that not only the foot but also the ankle is affected. A fracture of the marginal bone leads to a mild pain syndrome and moderate impairment of the motor function of the foot.
Treatment
Treatment of VFD begins with manual manipulation and massage in the first few days after birth. The triangular, fibula and patellofemoral ligaments are stretched in three planes by mobilizing the ankle joint. The duration of stretching each structure is half a minute. The daily chiropractic session lasts 15-20 minutes. The dressing is changed after 2 weeks. The total duration of the immobilization treatment is 6-8 weeks. If treatment with short casts is not successful after 6-8 weeks, the patient is treated with stepped knee grip casts, in which reduction is performed at the talofemoral joint. After applying the fresh cast, the foot is pulled longitudinally to extend the joints, followed by inversion and flexion of the foot. The total duration of the cast immobilization is 4-6 months. The reduction of the talocrural joint is controlled by lateral radiographs. After the cast is removed, the child is provided with a supination orthosis or orthopedic shoes with reinforced supination. For severe forms of curvature, transarticular fixation is performed through a window in a plaster cast. The spokes are inserted through the ankle joint under anesthesia for 5 weeks. Transarticular fixation of the foot can prevent recurrence of the deformity. Surgical treatment of VFD is used when conservative treatment is ineffective and when a 3-month cast does not reduce the hip angle to less than 50°. Surgical techniques depend on the patient's age. In children under 3 years of age, soft tissue unloading and reduction of the dislocation is performed. In children over 3 years of age, arthrodesis is performed if the hip angle is greater than 50°.
Release occurs before the age of 1 year. Incision on the hindfoot. Capsulotomy of the scaphoid and calcaneal-cube joints, release of the talocrural and intercostal ligaments. Posterior longitudinal section. Lengthening the Achilles tendon. Performing a posterior capsulotomy of the ankle and knee joints. Reduction of ankle dislocation. A plaster cast is applied.
Surgery: tenotomy and longitudinal displacement
Severing the tendon of the long extensor muscle and the third fibula. Reduce the dislocation at the talo-phalangeal joint and fix it transarticularly with spokes. A percutaneous dissection of the Achilles tendon is performed. A plaster cast is applied.
Cincinnati transverse section from the anteromedial side of the ankle at the ankle-clavicular joint to the anterolateral side at the distal aspect of the tarsal sinus. Rear relief of the ankle joint, bilateral relief of the ankle joint. Lengthening of the tendons of the long fibula, the third fibula, the long finger extensor 1. Relocation of the attachment point of the tendon of the tibialis anterior muscle to the talus. Percutaneous division of the Achilles tendon. Reposition of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe, transarticular fixation of the joint with a spoke. Plaster immobilization with knee joint transplant. The splint is removed after 8 weeks.
Read more:- Photograph of the periosteal foot.
- On half-bent legs.
- muscles in the legs.
- What to wear with short legs.
- dislocation of the ankle.
- The ankle bruise is where the picture is taken.
- Structure of the human ankle.
- The hock is the place where.
