The procedure is contraindicated in epilepsy, pregnancy, fever and the presence of a pacemaker.
- muscles of the foot
- Back flexor muscles (dorsiflexors)
- Muscles of the little finger
- The adductor muscle of the little finger (musculus abductor digiti minini)
- Short finger flexor (Musculus flexor digiti minimi brevis)
- Muscles of the metatarsal
- Short finger flexor (musculus flexor digitorum brevis)
- Quadriceps muscle (musculus quadratus plantae)
- Human Quadriceps Muscle Anatomy Information:
- Which doctors do you go to to have your quadratus lumbar muscle checked?
- Sex-dependent myotonia with leg muscle wasting
- Diagnosis of muscular atrophy of the legs, thighs and lower legs
- diagnosis
- Treatment
- removal of blood
- plaster cast
- Oral medications
- Topical preparations
- Treatment with shock wave therapy
- Metatarsal-soleus muscle group
- Quadriceps soleus muscle –>.
- function
- Tell your friends about Wikiwand!
- Suggest a photo for the cover
- Many thanks for your help!
- Muscular squat in strength training
- Loading exercises for the quadriceps of the back
- Basic exercises for the thigh muscles
- Isolation exercises for the quadriceps of the thigh
- Read more
- Immunodietology - not for everyone, but for you
- The first cold in a child: what to prepare for?
muscles of the foot
The human foot does an enormous amount of work every day and is constantly involved in movement and statics. The muscles of the foot are involved in both simple and complex coordination tasks. All this is due to the coordinated work of the muscle complex of the hindfoot and the soles of the lower limbs.
The muscles of the foot can be divided into two broad categories:
- the hindfoot muscles, which include the short extensor muscles of the toes, the intercondylar muscles of the back, and the short extensor muscles of the painful toe;
- the soleus muscle. These include the muscles of the big toe (adductor, flexor and adductor), the little toe (adductor, short toe, opposite toe), the metatarsal muscles (short toe flexor, quadriceps soleus, cochlea, interdorsiflexor, intermetatarsal soleus).
Back flexor muscles (dorsiflexors)
The short extensor muscle, Latin extensor digitorum brevis, is a flat muscle. It lies directly on the back of the foot. It begins at the front of the heel bone and attaches to its upper and side surfaces.
Towards the toes, the muscle gradually develops into four narrow tendons, which are connected in the distal area to the extensor tendons of the toes. These attach to the base of finger phalanges 2-5 and are tightly wrapped with fascia. Its main function is to carry out the movements of all fingers except the thumb and sometimes the little finger, since it is not connected to the tendon of the little finger in all people.
In addition, due to the short extensor, it is possible to pull the fingers back slightly to the side. Blood supply comes from the anterior tibial artery, which supplies the muscle, and innervation comes from the deep oculomotor nerve.
The short extensor muscle of the thumb is also one of the dorsiflexors of the foot and is known in Latin as extensor hallucis brevis. This muscle is directed inwards from the short toe extensor. Like the extensor digitorum brevis, it attaches to the heel bone in its upper and front part.
The extensor muscle ends anteriorly in a tendon. It attaches proximally to the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. In the distal area, the edges of the tendon meet the edges of the extensor tendon of the thumb. It is an integral part of the dorsal fascia.
SPRINGS. The main function of this foot is to extend the big toe. The blood supply comes from the lateral tarsal artery, and the innervation comes from the deep branch of the oculomotor nerve.
The interosseus muscle completes the anatomical formation of the hindfoot corset. The dorsal interosseous muscles are four muscle bundles that are tightly arranged in the spaces between the bones that form the back surface of the foot. These muscles arise from the metatarsals and are attached to the proximal phalanges of the toes except the thumb and little finger. The first muscle pulls the second toe, causing it to flex medially, while the first, second, and third muscles move the toes laterally.
Muscles of the little finger
The adductor muscle of the little finger (musculus abductor digiti minini)
If you have a thumb adductor, you must also have a little finger adductor, right?
Of course there is such a muscle in our body. And it's easy to remember - it's the opposite of the thumb inverter muscle.
When the thumb grip muscle occupies the most medial position, the little finger grip muscle occupies the most lateral position on the foot - makes sense, right?
If we remove the skin, subcutaneous fat and plantar aponeurosis, we can clearly see the little finger retractor muscle on the lateral side (that is, the little finger side):
By the way, this muscle forms a 'V' with the already known adductor muscle of the big toe (highlighted in yellow):
Let's go back to our little finger adductor muscle and get to know its basic parameters.
Start: Lateral and medial processes of the calcaneal tuberosity
Adduction: Lateral part of the proximal phalanx of the little finger
Short finger flexor (Musculus flexor digiti minimi brevis)
We continue the analogy with the muscles of the thumb, which we have already prepared. As you remember, there is also a short flexor muscle on the thumb. It is located slightly inward, i.e. a little further to the side than the adductor muscle.
The same applies to the little finger. We also have the short flexor muscle of the little finger - you will see it clearly if you slightly flex the abductor of the little finger. The short flexor muscle lies underneath, as a second layer so to speak, and a little further medially.
By the way, I hope you haven't forgotten why this muscle is called that. The flexor because it is located on the inner (conditionally posterior) surface of the foot, and the short because the belly of the muscle is on the foot itself, and not on the shin.
Muscles of the metatarsal
And so we come to the last muscle group of the foot, a little further to the left. That wasn't so hard, was it? The short flexor and intertoe muscles are on the outside, and the thumb and little finger muscles are on the inside. Now let's find out what is between the muscles of the thumb and little toe.
Short finger flexor (musculus flexor digitorum brevis)
This is also a relatively simple muscle. It is large and superficial and is located directly under the soleus tendon. We already have a short thumb flexor and a short little finger flexor. How can we handle this situation without the short flexor of the other fingers?
Let's take the familiar board and mark the short finger flexor on it:
In this muscle, which is certainly very easy to teach, there is a detail that confuses many students. Since the flexors of the thumb and little finger are already controlled by separate muscles, many people make the mistake during tests and exams of claiming that the short finger flexor is attached to 2-4 fingers. This is of course wrong. If you look at the photo I attached above, you will see that the short finger flexor is attached to all fingers except the thumb.
Begin: Anterior part of the soleus surface of the calcaneus, plantar aponeurosis;
Approach: Middle phalanges of 2-5 toes. Each tendon of the muscle is divided into two limbs that wrap around the respective toe on the lateral and medial sides. The long flexor tendons of the fingers run between these branches;
Quadriceps muscle (musculus quadratus plantae)
If you remove the short finger flexor tendon you just examined, you can see the quadratus plantae muscle. This muscle lies as a second layer under the tendon. In fact, it's not particularly square, but looks more like a quadriceps.
Human Quadriceps Muscle Anatomy Information:
M. quadratus lumborum, quadriceps lumborum muscle.The quadratus lumborum muscle is a muscle lamella of the quadriceps that lies in front of the erector spinae muscle and is separated from it by the deep fascial lamina thoracolumbaris. It begins at the iliac crest and lig. The iliolumbar, runs to the 12th rib and to the transverse processes of the 1st to 4th lumbar vertebrae.

Features. When contracted unilaterally, the quadratus lumborum muscle, together with the other abdominal muscles and the erector spinae muscle, tilts the spine and the trunk to the side. With bilateral tonic contraction, it tilts the spine upright together with the other abdominal muscles. By pulling the 12th rib downward, it can also act as an exhalation muscle. (Inn. Th12, L1-4. Lumbar plexus).
Which doctors do you go to to have your quadratus lumbar muscle checked?
Is there anything that worries you? Would you like to learn more about the quadriceps muscle of the shoulder or do you need an examination? You can make an appointment with dr. – Clinic Eurolaboratory is always there for you! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary care and diagnose the problem. You can also doctor at home. clinic Eurolaboratory is open for you 24 hours a day.
How to contact the clinic:
Phone number of our clinic in Kiev: (+38 044) 206-20-00 (multi-channel). The clinic secretariat will find a suitable day and time for you to visit the doctor. Click here for our coordinates and directions. Further details on all of the clinic's services can be found on the clinic's homepage.
If you have been examined before Be sure to bring the results with you to your doctor's office. If you have not yet done any examinations, we will carry out the necessary work in our clinic or with our colleagues in other clinics.
It is important that you take a very close look at your general health. There are many diseases that do not initially make themselves felt in our body, but unfortunately are treated too late. To do this, it is simply necessary to be examined several times a year Get a medical check-up several times a yearYour doctor should not only know how to prevent a serious illness, but also how to keep your body and organism as a whole healthy.
If you have questions to ask your doctor, you can find the answers to your questions in our online consultation area. Self Care Tips. If you are interested in reviews of clinics and doctors, you can find information on the forum. You can also register on the physician portal Eurocoolto stay up to date with the latest Quadriceps lumbaris news and information automatically sent to your mailbox.
Sex-dependent myotonia with leg muscle wasting
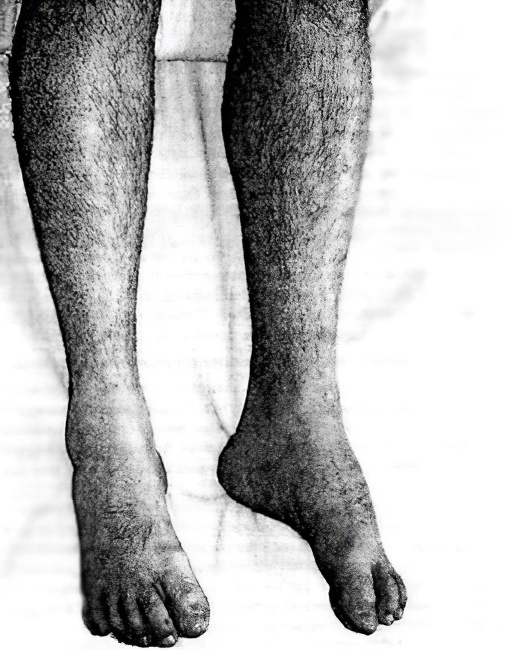
Pseudohypertrophic Duchenne myotonia is one of the most common forms of sex-linked myotonia. It only occurs in boys. The first symptoms appear in the first five years of life. Characteristic symptoms include muscle wasting of the legs and pelvic girdle. Pseudohypertrophy develops early, especially in the calf muscles; the deltoid muscles are less commonly affected. There is also atrophy of the end muscles, a retraction of the tendons, especially the Achilles tendon, and a loss of reflexes, which is particularly noticeable when checking the knee reflexes. The child has difficulty climbing stairs, keeping his hands on his hips while walking, cannot jump, and has difficulty rising from the floor. Weakness gradually develops, the muscles of the shoulder girdle atrophy and after a while the child is no longer able to stand up. Later symptoms of the disease include contractures caused by tendon retraction and the development of a horse's foot.
Generally, children with this congenital genetic defect do not survive until age 14.
The pathology is also accompanied by changes in the heart muscle, the brain is damaged, and the child is stunted. Weakness in the respiratory muscles leads to poor ventilation of the lungs, which contributes to the development of pneumonia. The course of pneumonia is complicated by weakness of the heart muscle, which is the most common cause of death in patients. The Duchenne form is characterized by the pleiotropic effect of a pathological gene.
In the mid-20th century, Becker described a mild variant of myopathy that is sex-linked and bears his name. The first symptoms of the disease appear after the age of 20. First, pseudohypertrophy of the calf muscles is noticeable. Atrophy of the leg muscles develops slowly and gradually affects the muscles of the pelvic girdle and thighs. In this form, intelligence is preserved. These variants of the disease are characterized by damage to different genes located at two loci on the X sex chromosome, which are gene copies. The two forms of the disease do not occur at the same time in the same family.
Diagnosis of muscular atrophy of the legs, thighs and lower legs
In order to diagnose muscle atrophy, a thorough anamnesis is required, which also includes questions about hereditary and chronic diseases. A detailed blood test with mandatory determination of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, blood sugar and liver function tests is recommended. Electromyography and sometimes nerve cell biopsy and nerve conduction studies are mandatory. If there is a history of chronic illnesses or infectious diseases, additional examinations are carried out if necessary.
When choosing treatment, primary attention is paid to the cause of the disease. The age of the patient, the extent and severity of the disease are taken into account. Drug treatment can inhibit the process or even bring about some improvement. The prescription of physiotherapy, massage, electrotherapy and gymnastics play an important role. Blood transfusions are also often used to treat muscle loss. If all recommendations are followed, patients can live an almost normal life for a long time.
diagnosis
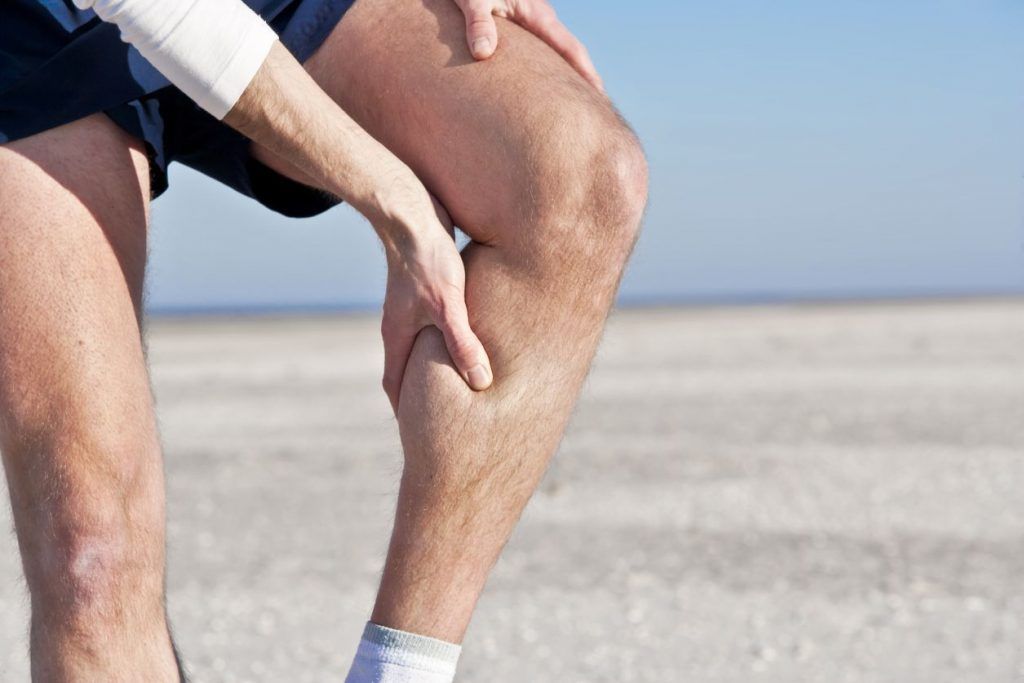

The injured patient is examined by a trauma surgeon. The doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis using functional tests and palpation. The doctor will then refer the injured person for further diagnostics. The most common methods are the following:
After the examination, the doctor will draw up a treatment and rehabilitation plan. He prescribes ointments and medications, selects treatments and provides information about when and how training can be resumed. For severe tears, trauma surgeons recommend an ultrasound or MRI scan on the 12th to 15th day of treatment to determine how quickly the damaged areas will recover.
Treatment
For the first 24 hours, the patient should rest and apply ice packs to the injured limb. The cold reduces swelling, prevents bruising and relieves muscle pain. Massages and heat treatments are prohibited, as they only worsen the patient's condition and delay recovery.
A cold pack can be supplemented with magnetic therapy. Magnetic therapy improves blood flow to damaged tissue, relieves discomfort and swelling, stimulates regeneration and relieves inflammation.
removal of blood
If a hematoma has formed near the site of injury, a needle is inserted into the subcutaneous tissue and the blood is sucked out. On the second day, stagnant blood will also be suctioned out to reduce the risk of blood clots.
plaster cast
Large wounds must be covered with a plaster cast. It immobilizes the injured limb and protects the soft tissues from stress. The muscle fibers need rest to recover quickly. This is particularly true for transverse cracks.
Oral medications
Painkillers and muscle relaxants help relieve the symptoms of a muscle tear. The first group of drugs dulls pain. Myorelaxants relieve spasms and relax muscles, speeding up their recovery. The drugs of the second group are not prescribed for heart and kidney failure, glaucoma and serious injuries.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also contraindicated in patients with muscle fiber tears. They do not accelerate the regeneration of soft tissue and impair liver function and metabolic processes in the body.
Topical preparations
Topical painkillers are supplemented with ointments or gels. These can have an anesthetic, anti-inflammatory or warming effect. The ointments should be rubbed in gently 2-3 times a day. Topical ointments relieve swelling, redness, and puffiness.
Treatment with shock wave therapy
Patients with micro-injuries and strains that do not require surgery are treated with shockwave therapy.
Metatarsal-soleus muscle group
Short toe flexors lies beneath the soleus aponeurosis. On the lateral side it borders the little toe extensor muscle and on the medial side it borders the big toe extensor muscle. Below the short toe flexor are the quadriceps soleus muscle and the tendons of the long toe flexor. This muscle attaches to the front of the calcaneal tubercle on its soleus surface and to the soleus aponeurosis. Four tendons arise from the flat belly of this muscle and attach to the middle phalanges of the II-V toes. Each tendon divides into two bundles at the level of the basal phalanx. The long flexor tendon of the fingers passes through the gap between them. Some of the bundles of short flexor tendons are woven directly into the fibrous sheaths of the fingers. The specific relationship between the short digital flexor tendon and the long digital flexor tendon in the foot is similar to the relationship between the superficial and deep digital flexor tendons in the hand. This muscle flexes 2-5 toes; it is involved in strengthening the longitudinal arch of the foot.
Quadratus soleus muscle (Adductor flexors) has two heads, a lateral and a medial head. The lateral head arises on the outside of the inferior surface of the calcaneus and on the lateral edge of the longitudinal ligament. The medial head arises on the medial side of the same surface of the calcaneus and on the medial edge of the longitudinal ligament. The two heads unite to form a single flat muscle, which attaches at the level of the metatarsus (soleus) on the lateral side to the flexor tendons of the long toes, which are directed at 2-4 toes. This muscle is involved in flexing the toes, providing traction to the long flexor fingers in a straight line.
Worm muscles – Four small fusiform muscles. The three lateral muscles arise from the opposite surfaces of the long flexor tendons of the fingers, the medial muscle arises from the medial side of the adjacent long flexor tendons of the fingers. Each psoas muscle merges into a thin tendon that attaches medially to the proximal phalanx of the corresponding finger (II-V). Part of the tendon bundle of the vermis muscle flexes the proximal phalanx and extends to the dorsum of the fingers, where it interlocks with the tendons of the long flexor muscle of the fingers. The muscle flexes the proximal phalanges and extends the middle and distal phalanges of fingers 2-5, pulling them towards the big toe.
Quadriceps soleus muscle –>.
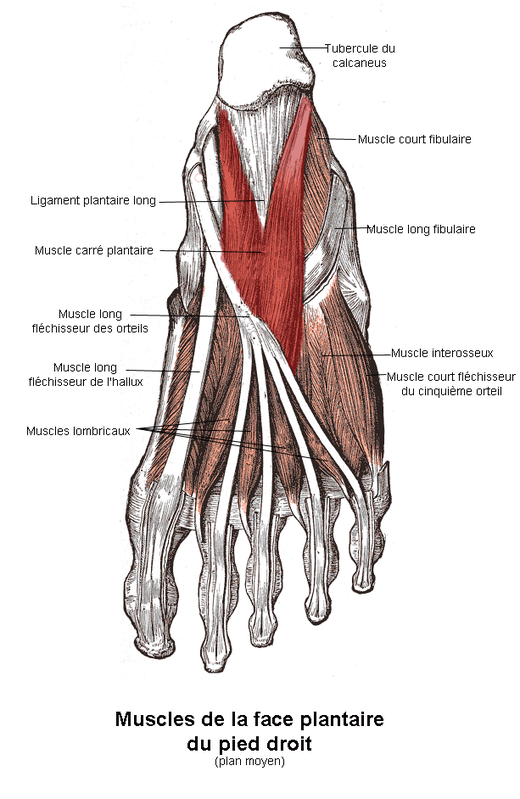
Quadriceps soleus muscle (quadriceps) (Latin: Musculus quadratus plantae) is a muscle of the plantar system.
It is quadriceps-shaped and lies under the short toe flexor (M. flexor digitorum brevis) [1].
It begins on the inferior and medial surface of the posterior aspect of the calcaneus with two separate heads that join to form a common abdomen. The muscle tapers slightly towards the front and attaches to the outer edge of the flexor tendon of the long toe, where it divides into individual tendons [1] .
function
This bundle of muscles regulates the activity of the long flexor tendon of the fingers by attaching its attachment directly to the muscles [2] .
- ↑ 12Р. D Sinelnikov, JR Sinelnikov. Muscles of the foot // Atlas of human anatomy. – 2-е. – M. Medycyna, 1996 – Т. 1. – C. 316-317. – 344 s. – 10,000 copies. – ISBN 5-225-02721-0.
- ↑M. G. Prieses, NK Lysenkov, VI Bushkovich. Muscles of the foot // Human anatomy. – 11th ed. – SPb. Hippocrates, 1998. – C. 218. – 704 s. – ISBN 5-8232-0192-3.
> > This page is based on a Wikipedia article written by the co-authors (read/edit).
The text is available under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms and conditions may apply.
Images, videos and sound are available under the respective licenses.
Tell your friends about Wikiwand!
Suggest a photo for the cover
Would you like to suggest this image as the cover image for this article?
Many thanks for your help!
Your contribution, along with other users' contributions, will influence the choice of cover photo.
This browser is not supported by Wikiwand 🙁
Wikiwand requires a browser with modern features to give you the best reading experience.
Download and use one of the browsers listed below:
The extension you are using may be preventing Wikiwand articles from loading properly.
If you use the following HTTPS Everywhere or do not have access to Wikiwand articles, you should switch to HTTPS (https://www.wikiwand.com).
The extension you are using may be preventing Wikiwand articles from loading correctly.
If you have one Ad blockerIf you use it, it may accidentally block our content. To view this page, you must temporarily disable your ad blocker.
Please click the 'Downloads' icon in the Safari toolbar, open the first file in the list,
then click to install.
Muscular squat in strength training
By combining the recommendations of many other athletes as well as our own training experiences, we have a our own strength training program
designed for men that will make your back and lower back exceptionally strong. Among the exercises that are great for the quadriceps muscles, we have highlighted the following:
– Leg raises in prone position; – Upper body lift in prone position; – Leg and arm curls; – Plank with bent arms; – Plank with straight arms.
Below we will go into the technique and special features of each of the exercises presented. Remember that maximal training at home can only be successful if you follow all the correct recommendations for training with your own body weight, that is, alternating loads and rests, a sensible diet and the correct selection of exercises and the correct technique of execution. To prevent the muscles from adapting to the load placed on them, it is recommended to perform at least 3 exercises per muscle group during a training session and then use alternating exercises.
Loading exercises for the quadriceps of the back
Sloth suggests. the most effective exercises
which will help you improve your fitness and strengthen the quadriceps of the lower back.
– is a relatively simple exercise that, due to its effectiveness, is suitable for both beginners and experienced athletes who want to train the quadriceps muscle of the lower back. Essentially, this is the same exercise as the reverse lunge.
To get to the starting position, secure the exercise area with a special fitness mat or other suitable floor covering and then lie on the floor with your stomach facing down. The arms should either be extended to the sides or bent at the elbows and placed near the chin. Keep your legs straight and shoulder-width apart. Tighten your abdominal muscles and try to keep your lower back tight.
To do this posture exercise, lift your legs to their maximum height with an exhale. Your pool should be slightly away from the surface. Raise and lower your feet until your hips touch the floor. After relaxing the quadriceps muscle for a few seconds, move on to the next exercise. When doing this back strengthening exercise, make sure to keep your chest and shoulders on the floor; it is important not to round your back. Also try not to raise the torso and legs with your arms, and after lowering, do not relax the legs so that they do not touch the floor - the amplitude should be short. At the same time, the slower the exercise is performed, the more effective it is. If you want to train the glutes, you should increase the amplitude. Increase the amplitude by placing a support under the pelvis - lying on a bench or stool is no problem as long as the hip bones can rest directly on the corners of the riser used.
– It is also a simple and basic lower back exercise that simultaneously promotes strengthening of the quadriceps muscles of the back. To take the starting position, lie on your stomach and remember to lie on the floor in the form of a special mat or equivalent support. The arms should be straight and extended to the sides. With an exhalation and contracting the quadriceps muscles, lift the upper half of your body as much as possible, pulling your shoulders away from the floor. Then return to the starting position and lower your chest and shoulders back to the floor.
Basic exercises for the thigh muscles
The basic exercises for the thigh muscles should be the core exercises of the multi-gym. With their help, you will improve your overall strength and increase the volume of your core muscle fibers.
Weighted squats are ideal as a basic exercise to target all four quadriceps muscle bundles. A barbell of any design should be used in the gym. Barbell squats not only strengthen the quadriceps muscles of the thighs, but also work the glutes, abdominal muscles, and lumbar muscles.
The barbell should be placed on the rear flexion sides to increase the effectiveness of this component. The back must remain straight both when raising and lowering the dumbbell. The squat should be performed with your feet wide apart. At the peak of tension, you should fixate yourself in a static position and then slowly return to the starting position.
The Gakk trainer is a powerful device for training the quadriceps muscles of the thighs and the glutes. Because your back is pressed against the support as you lower and raise your upper body, there is no harmful strain on your back.
One of the main advantages of this exercise for the thigh muscles is that the center of gravity can be shifted independently. This is possible by changing the position of the feet. The further the foot is, the greater the effect on the inside of the thighs.
To ensure that the exercise works all the quadriceps muscle bundles at the same time and does not transfer the load to the joints, do not flex and extend the leg all the way down. This keeps the muscles under constant tension.
It is an effective core exercise that helps work the entire quadriceps muscle without putting strain on the spine. In addition, the longitudinal muscles of the lower legs are activated, which can rarely be trained without isolated stress. Make sure that your knees are not fully extended when lifting the platform, otherwise all the stress will be transferred to the joints and not the muscles. It is recommended to lower the platform until your knees touch your chest.
Isolation exercises for the quadriceps of the thigh
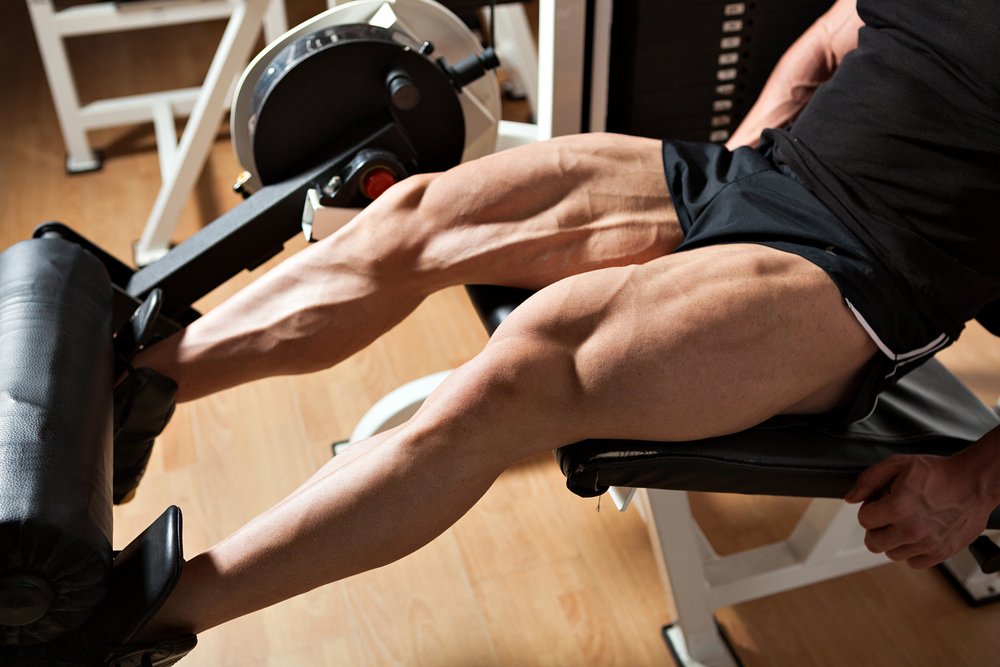

Isolation exercises allow you to actively target the target muscles. It is particularly effective to combine them with a series of core exercises. It is sufficient if there are 1-2 isolated loads for every 4-5 core loads.
For a thorough training of only the rectus and lateral quadriceps muscles, which provide aesthetic hip relief, you can turn to the hamstrings in the trainer. To avoid shifting the load on the knee joints, it is better to use medium weights without moving to heavy weights. The movements should be performed slowly, and to build volume, a low number of repetitions and a moderate number of sets should be performed (for example, 5-6 sets of 8-10 repetitions). Hold the handles of the machine tightly so that the body is in a static position during fitness training.
The single-leg platform press shifts the center of gravity so that the entire weight of the work engages the muscles of just one leg, rather than being distributed over two limbs at once. In this way, the entire quadriceps muscle is used. This exercise is particularly commonly used by professional athletes for the ultimate thigh resurfacing.
Read more

Immunodietology - not for everyone, but for you

The first cold in a child: what to prepare for?
What are the characteristics of respiratory viral infections in infants? Who is hospitalized?

- The pronator is in anatomy.
- The long section of the big toe.
- The flexor muscles of the foot.
- Pronator - what does that mean?.
- Tibialis posterior muscle.
- Exercises for the triceps tibialis muscle.
- Longitudinal soleus muscle.
- The muscles that move the foot.
