Transverse and longitudinal flatfoot is the main cause of forefoot deformity.
It is usually caused by tight, uncomfortable shoes with high heels.

- Pronation and supination of the foot
- Excessive supination occurs when the weight of the body is on the outside of the foot while walking or running. When the opposite is true and the person shifts their body weight from the heel to the forefoot primarily on the inside of the foot, it is called overpronation.
- Inappropriate footwear
- How the foot works when running
- What is pronation?
- Insoles and trainers for flat feet
- Insoles for runners with hyperpronation
- Causes of hyperpronation of the foot
- Testing the pronation of the foot
- poor
- rotation
- Exercises to correct pronation
- 1. Stretching the feet
- 2 – turns in a circle
- 3 Walking on tiptoes
- 4: Heel walk
- 5. Lift your toes
- Selection of the trainer
- Features when choosing a trainer
- What to do if you suffer from hyperpronation?
- Short and sweet
- Supination – Pronation: Running speed and fatigue
- The importance of the tibialis posterior muscle in the development of hyperpronation
- What diseases can impaired supination lead to?
- Treatment of pronation and flat foot deformities
- How to prevent impairments
- Choosing the right running shoes depending on your pronation
Pronation and supination of the foot
Supination and pronation are the most important phases of a healthy step. They are essentially a universal damping mechanism created by nature adapted to bipedal (two-legged) movement.
pronation. As the foot hits the ground, the arch of the foot becomes flatter and thus absorbs the force of the impact. The effect of the vault in this phase is similar to a car spring.
supination. With the shift in the center of gravity, the muscles of the foot and shin begin to work harder, as if they were turning on'. Supination has the opposite phases to pronation, namely the return of the tibia to its normal plane of movement; the foot no longer overpronates on its inside and its support shifts towards the metatarsal bone (ie forward); and supination itself tenses the muscles and ligaments of the arch of the foot and restores flexion. While pronation aims to soften the foot and bring it into a correct position, supination contributes to the active phase of push-off.
Excessive supination occurs when the weight of the body is on the outside of the foot while walking or running. When the opposite is true and the person shifts their body weight from the heel to the forefoot primarily on the inside of the foot, it is called overpronation.
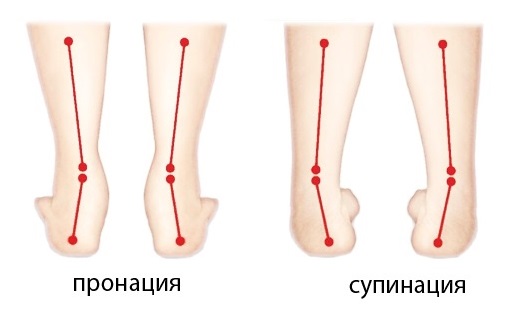
Excessive supination (insufficient extension) and excessive pronation (excessive overpronation) can cause alignment problems and pain in the feet, knees, hips, and back.
Some facts about supination and pronation:
- Too much supination can cause problems such as pain and soreness.
- Most people with excessive supination have structural problems in their feet.
- Ways to treat or prevent excessive supination include wearing the right shoes.
Inappropriate footwear
Good footwear supports the arch and soft tissues of the foot, which protect the foot from injury. This is especially true when walking on hard, level surfaces.
Incorrect footwear -- like stiff or tight shoes -- can lead to supination and other foot problems. Wearing shoes that are worn or that do not support the arch of the foot also causes supination.
When the body is not properly aligned, certain parts of the body have to work harder to maintain posture and balance. Likewise, poor posture during exercise can cause certain muscles and bones to overcompensate, resulting in supination.
How the foot works when running
The mechanics of the foot when running are completely different from the mechanics of walking, where the heel touches the ground; When running, the foot touches the ground with the ball of the foot and only then rolls onto the heel. At this point the Achilles tendon, the plantar fascia, the ligaments, our entire foot and the ankle have a spring function, this work significantly reduces the energy expenditure when running, this principle is used in nature not only by humans, but also by 'running' animals such as Used for dogs and horses.

What is pronation?
Pronation is part of the human running mechanism, a phase that concerns the moment of positioning, the moment of contact of the foot with the ground, a phase that allows both to minimize energy expenditure and to provide the musculoskeletal system with the highest level of protection and safety of the running process.
What are the mechanics of the pronation process?
When the foot hits a surface, the arch of the foot, which relieves any resulting tension, becomes flat, essentially acting like a car spring.
Insoles and trainers for flat feet
Improper ankle alignment can cause pain in the knees and back, periosteum, and Achilles tendon. Insoles and shoe inserts for flat feet are designed to support the body with natural cushioning problems. Roughly speaking, insoles and shoe inserts for hyperpronation are crutches for runners. They don't heal, but they help prevent more serious injuries.
To correct abnormalities, you should perform special exercises to strengthen your feet.

Insoles for runners with hyperpronation
If you don't want to change your favorite running shoes, consider getting insoles that are tailored to your foot. It is better to order custom-made insoles. Don't forget to tell your doctor that you want to use them for running.

In some cases, foot abnormalities can only be corrected through surgery. Consult an orthopedic surgeon to determine the extent of the abnormality and choose treatment.
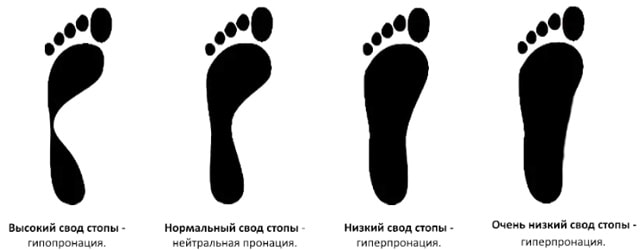
Causes of hyperpronation of the foot
The main causes of foot hyperpronation are plantar feet and weakness of the lower leg muscles, particularly the anterior and posterior tibialis. In most cases, these heel bone anomalies occur in childhood and should be corrected by the age of 12-14 with physical therapy, appropriate footwear, and insoles. After that it is much more difficult to correct.
By using special shoes or custom-made insoles, the foot can often be brought back into a neutral pronation position and overloading the musculoskeletal system when running and jumping can be avoided. However, the use of these products must be combined with regular physiotherapy and massage of the foot and lower leg muscles.
Normal pronation is up to 5 degrees when standing and up to 15 degrees when landing while running. To determine the degree of pronation when running, specialized shoe stores and clinics use special video or photo fixation devices.
Testing the pronation of the foot
At home, the degree of pronation can be determined by examining the axis of the heel and tibia at the ankle from behind while the foot is at rest and supported while running, and calculating the angle between the two to determine the degree of pronation Appreciate pronation.
You can also do a 'wet test': stand on a piece of cardboard or paper with wet feet and trace with a felt-tip pen. However, you should be aware that such results are only approximate, which is why it is better to seek professional help.
poor
Pronation and supination are two types of movement that also affect the shoulder. It differs in biomechanics from other parts of the body and depends entirely on the structure of the shoulder joint, which is one of the most complex in its biomechanics. It is performed by moving the shoulders inward (pronation) and backward (supination). The pronators and supinators of the shoulder girdle have the task of maintaining the posture and straightness of the upper back and are also opposites (antagonists) in their biomechanics.

The following muscles work during pronation (inward rotation) of the shoulder: the pectoralis major muscle, the major circularis muscle, the dorsalis broadis muscle and the subclavius muscle.
Supination (outward rotation of the shoulder) involves the subscapularis and great circular muscles.
rotation
Rotation is another type of movement and means 'turning'. It occurs not only in the limbs of the human body, but also in some of its components, such as: B. the vertebrae. Pronation and supination can be considered partial rotation. The range of motion of the upper and lower limbs is very different, which must be taken into account. Each rotation serves to stabilize a part of the body during movement.
The rotator muscles (pronators and supinators) are small and do not deserve attention in the context of general muscle mass building. However, athletes need to talk about them, and the coach needs to convey to beginners the importance of antagonists in building body composition.
Exercises to correct pronation
There is often an imbalance between pronation and supination, but it is possible to correct this misalignment. Excessive inward tilting of the feet is caused by weakness in the gluteus maximus, the muscles that stabilize the thighs, shins, and ankles. It is therefore advisable to strengthen the legs to correct this problem.
1. Stretching the feet
Sit down, extend your legs, and place your hands on the floor next to your glutes. Lift your feet apart, hold them for a moment, then pull them towards you. Do the same movements with your toes. Perform 15-20 reps and repeat in 2 sets.
2 – turns in a circle
Sit up, stretch your legs. Bring feet together and then twist to one side and vice versa. Move slowly and maintain maximum amplitude. Perform 10-15 twists to one side, then 10-15 twists to the other side, repeat in two sets.
3 Walking on tiptoes
Stand upright, place your hands on your waist and feet shoulder-width apart. Stand on your tiptoes and walk until you feel tired. It is possible to take about 15 to 20 steps on tiptoes, repeated in 2 sets.
4: Heel walk
Stand upright, place your hands on your waist and feet shoulder-width apart. Stand on your heels and walk until you feel tired. You can do about 15-20 steps on your toes, repeat in 2 sets.
5. Lift your toes
Take a classic stance and place your feet close together. Start lifting your heels off the floor, stand on your toes, hold for a second and return to the starting position. Perform 15-20 reps and repeat the exercise in 2 sets.
Not only the feet need to be strengthened, but also the glutes, quadriceps and biceps muscles of the thighs and the calf muscles. Gradually, pronation and supination balance each other out, but it is not always possible to completely eliminate the imbalance. Therefore, it is also advisable to choose the right footwear for your type of pronation.
Read on to find a selection of exercises:
Selection of the trainer
Professional runners carefully select their equipment, including shoes. Do the same for amateurs to protect your feet and ankles from injury. When choosing running shoes, pay attention to pronation to distribute the load from the toes to the heel.
Why should you pay attention to pronation when choosing running shoes? Running puts enormous strain on the musculoskeletal system. If your feet cannot keep up while running, the pressure increases many times over. The choice of shoes can help improve redistribution and thus reduce the risk of injury. Manufacturers today produce running shoes for athletes that take into account all types of pronation. They offer optimal support for the foot, cushioning and the necessary rigidity.
Features when choosing a trainer
When choosing a sneaker, one should first consider pronation, that is, the anatomical structure of the foot. This aligns the angle to the central axis and improves movement control, cushioning and stability when pushing off and landing. Instep height, heel type and sole thickness are taken into account.
- For people with hyperpronation. Insole in the midsole and sometimes into the heel area. Additional cushioning. Special projection on the inside, ie the longitudinal arch. Provides stability, foot support and protection from tipping over.
- For people with hypopronation. Strong cushioning in the midsole area to absorb shock loads. Flexibility of the shoe. Cushioning in the heel area and outsole.
- For people with neutral pronation. Adaptation to the foot. Many models fit here, but for people with neutral pronation it is better to choose models with cushioning.
Choosing the right shoe helps stabilize pronation. The result is cushioning that restores natural movement, comfort and protection. It is recommended to buy shoes after trying them on to make sure they fit perfectly and take into account the structure of your foot.

What to do if you suffer from hyperpronation?
The main cause of hyperpronation is weakness in the muscles that stabilize the foot and thigh. These can and should be strengthened to improve the situation. We already have a selection of simple exercises to strengthen the feet, ankles and calf muscles. We'll be creating a list of exercises for hyperpronators soon, but for now just a few.
To strengthen the muscles that stabilize the foot:
- Place a weight of 800 to 1500 g (for a tall person) on the front of the foot in the area of the toes and metatarsals. The easiest way is to use a hand weight. Lift the foot and move it to both sides in a full amplitude circular motion.
- An exercise you can do during transport: Stand on one leg with the other slightly raised and balance as you move.
To strengthen the gluteus muscles: squats, lunges, deadlifts, step-up lifts and more.
To strengthen the glute medius: pulley or weighted leg raises, leg lifts and adductions.
Trainer with protection against hyperpronation
These trainers are recommended for people who have hyperpronation but not severe flat feet.
The fact is that arch support and overpronation protection have different functions in a sneaker. Support shoes are designed for people with flat feet. They have a special protuberance (reinforcement) in the area of the longitudinal arch.
Hyperpronation protection shoes, in addition to arch support, have a built-in wedge in the heel area that makes the inside of the heel firmer and often higher.

Choosing an anti-hyperpronation trainer should be done in a store that has a video about treadmills. Without this, adjustment is hardly possible and there is a risk that the correction will be too strong. In this way, trainers can cause hypopronation of the foot and the knees will be stressed by impact rather than torsion. This means that one model is required for 15 degrees of hyperpronation and another for 10 degrees of hyperpronation.
Short and sweet
Pronation is a normal, natural mechanism that uses the work of the foot to help absorb the impact of landing and protect our knees, hips and lower back from injury.
In normal (neutral) pronation, the ankle tilts inward 5-7 degrees upon landing, up to a maximum of 8 degrees.
The deviation can occur in both directions. If there is insufficient pronation (hypopronation), the ankle remains flat or tilts outwards (0 degrees or negative angle) - the impact load is poorly compensated. With excessive pronation (hyperpronation), the roll is too great (8-15 degrees) - this causes twisting and can affect the knee joint, ankles and overlying areas.
Hypopronation is rare, 70 % of runners have some degree of hyperpronation. Correction is required in 20-30 % cases: when the angle is more than 10 degrees or the person walks long distances.
The three main causes of hyperpronation are: longitudinal flatfoot, weak foot-stabilizing muscles, weak thigh-stabilizing muscles.
Pronation is what happens in movement, flatfoot is what happens in static. Flat feet are often accompanied by hyperpronation, but not always. Strong stabilizing muscles can compensate for a flat foot and bring the foot into neutral pronation. By the same logic, a person cannot have flat feet but can have hyperpronation.
The most accurate method for diagnosing hyperpronation is a video treadmill test (gait analysis) that measures the angles.
You can also check for hyperpronation yourself by recording your run from behind or looking at the wear and tear on your running shoes. However, these are only approximate methods.
What to do if you hyperpronate: Strengthen the muscles that stabilize the foot, the gluteus maximus and gluteus medius. If you have excessive pronation without severe flat feet – choose running shoes with hyperpronation protection. If there are severe flat feet – use individual insoles.
Choose anti-hyperpronation shoes from a store that has a treadmill film to prevent overcorrection.
Supination – Pronation: Running speed and fatigue

Excessive supination during ground contact greatly reduces damping and produces excessive amplitude, negatively affecting gait and running performance.
Overpronation is also unacceptable as the sole stretches and becomes flatter and more flexible.
Pronation provides two main mechanisms: cushioning and pressure relief upon contact with hard surfaces and compensation on uneven ground.
If the cushioning process is too slow, the sole does not have time to react in time and gain sufficient rigidity, which significantly reduces cushioning and contributes to cumulative fatigue and thus reduces endurance.
Excessive so-called hyperpronation has a negative effect on gait and running performance and is also harmful to health.
The importance of the tibialis posterior muscle in the development of hyperpronation
The tibialis posterior muscle is the main responsible for pronation and provides the necessary elevation of the arch of the foot in all phases of walking or running.
The ligaments of this muscle run under the foot and connect and support the bones.
At the beginning of the stance phase, the tibialis posterior stretches, slowing down the dynamics and duration of shock absorption.
Because it raises the arch of the foot, the push-off is much stronger.
When the tibialis posterior tendon is tense, it relaxes.
The result of a weakened muscle is a significant reduction in performance when walking, running and jumping. The tibialis posterioris is the most important mechanism for ensuring a soft landing or a powerful push-off.
What diseases can impaired supination lead to?

Increased supination and especially hyperpronation leads to chronic pain in the legs and lower back as well as regular injuries.
Cervical spine problems, headaches and bite problems can be the result of the foot flattening due to the increased load.
The deviation of the knee joint from the central axis of the body can cause the kneecap to move outward, causing abrasion of its cartilage.
Treatment of pronation and flat foot deformities

The first step in treating pronation deformity is to relieve the patient of the pain caused by various physical activities and prevent the condition from getting worse. For this purpose, the doctor will prescribe customized orthopedic insoles and shoes.
If there is severe pain after a day on the feet and swelling, baths and foot massages can improve the condition.
Exercise therapy also plays an important role in the treatment of pronation disorders. Regular exercise strengthens the muscles and ligaments that are involved in maintaining the arch of the foot in the correct position.
How to prevent impairments

No matter what type of foot pronation disorder is present, it is not life-threatening. However, that doesn't mean the problem should be ignored because the consequences can be quite devastating.
Modern medicine offers special computer-based tests to find out what caused the pronation disorder.
To avoid the occurrence of these disorders, it is enough to carefully select footwear. – They should be neither too loose nor too tight, and you should get supinating shoes (especially for children's shoes). It is best to use orthotics to reduce the strain of standing for long periods of time.
Choosing the right running shoes depending on your pronation

When choosing running shoes, you should first determine the distances you want to run and then determine your pronation type.
- Normal pronation – In this case, you should choose running shoes from the category 'Support'. Because with normal pronation, the natural cushioning of the human being works well and the foot does not need any additional support.
- people with flat feet, should pay attention to shoes in the 'Control' class. These prevent excessive 'twisting' of the foot and ensure adequate control of excessive pronation. Not wearing these shoes can lead to various running injuries.
- hyperpronators, People with high arches should choose running shoes with neutral cushioning that allow them to take full advantage of the cushioning benefits. This class of running shoes is called 'Neutral'.
The treatment of pronation disorders does not take long and does not require complicated procedures. However, you do not have to allow your foot health to deteriorate to the point of requiring qualified orthopedic treatment.
Follow the advice in this article, pay attention to the quality of the shoes you buy and there will be no problems. My ladies!!! High heels have a negative impact on the health of your feet. This should not be forgotten.
Read more:- How to determine the type of pronation.
- What is pronation and supination?.
- pronation and supination.
- Sneakers with hyperpronation.
- What is a neutral pronation?.
- Pronation and supination in anatomy.
- hip pronation.
- Excessive pronation of the foot.
