However, an enlarged foot arch does not always have to lead to the consequences mentioned above. In some cases, a very high arch can occur even in completely healthy people. In these cases, foot shape is usually hereditary, a familial trait, and does not lead to dysfunction and secondary deformity. In these cases, the change in foot shape is considered normal and does not require treatment.

- Varus foot deformity
- Causes of varus deformities
- Possible complications and prevention
- Causes of varus deformity
- How does he make himself felt?
- Surgical treatment of pes cavus.
- Two stages of disease development
- Surgical treatment of hammer toe deformity as part of pes cavus.
- Prevention of varus deformity
- Prevention of foot deformities
- Prevention of clubfoot deformities in children
- Treatment of varus deformities of the foot in children by massage.
- types of deformity
- Tips for choosing
- How to wear them correctly
Varus foot deformity
A varus foot deformity is an O-shape of the lower leg. In this deformity, the medial portion of the tibia tilts outward, and the entire deformity is viewed at an inward angle. With this deformity, the knee joints develop unevenly, with the outer condyles of the thigh increasing in size and the inner condyles decreasing. This deformity leads to compression of the menisci and enlargement of the joint spaces on the outside and inside.
In the varus deformity of the foot, the tibia is arched outwards.In severe cases, the thigh is external and the tibia internal. The feet then become flat-footed (forefoot and heel are tilted inward, resulting in a valgus foot). If you suffer from a varus foot deformity, you may not be able to fully straighten your knee. If this deformity is not treated, it causes serious orthopedic problems (e.g. gait changes, severe leg fatigue, foot swelling, other bony deformities of the feet, spinal problems).
The varus foot deformity can be congenital or developed in childhood. It can also occur due to a bone disease, a metabolic disorder, or another condition that causes a disruption in the strength of the skeletal system. Under these conditions, any congenital deformity can only worsen and the depth of the arch of the foot can only increase. In adolescents, varus foot deformities can be caused by vitamin D deficiencyVitamin D deficiency, calcium deficiency and a lack of sunlight.
Causes of varus deformities
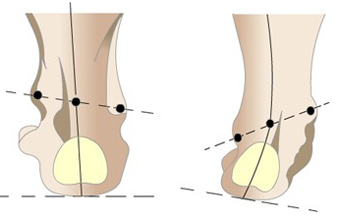
The main causes of varus foot deformities are:
- A weakened body;
- Recent diseases;
- metabolic diseases;
- Rickets;
- diseases of the skeletal system;
- Endocrine disorders (thyroid disease, diabetes);
- genetic predisposition;
- foot injuries;
- wearing unsuitable and uncomfortable footwear;
- Incorrect distribution of the load on the foot.
The varus deformity of the foot develops quite slowly. The first The first sign that a varus foot deformity is developing is discomfort from wearing uncomfortable footwear.Difficulty choosing footwear and pain in foot after standing or moving. The forefoot is then deformed, the toes are curved and bunched, which significantly affects the blood circulation and innervation of the foot area.
Possible complications and prevention
When the foot bones are misaligned, it leads to fatigue, decreased physical activity, frequent falls, and injuries. Femoral neck fractures at a young age occur in patients with varus deformity.
There is an increased risk of degenerative changes in the joints. In the second stage of curvature, pain begins, redistributing the load on the spine and fingers. As a result, blood circulation and innervation are impaired, muscle and ligament atrophy occurs.
Prevention consists in normalizing nutrition and leading an active lifestyle. Gymnastics courses, massages and the right shoes are also recommended.
Causes of varus deformity
- calcium and vitamin D deficiency;
- Rickets;
- metabolic disorders;
- endocrine disorders;
- flat feet;
- Musculoskeletal disorders;
- infectious inflammatory processes;
- overweight;
- inactive lifestyle;
- genetic predisposition;
- Trauma;
- Use of poor quality or narrow footwear.
Like the valgus, the condition develops gradually. With timely treatment, the development of complications can be prevented.The condition develops gradually, so with timely treatment, it is possible to prevent the development of complications and diseases of the spine.
How does he make himself felt?
A hollow foot can not only be recognized visually. There are a number of symptoms that indicate this anomaly:
- calluses on big toe or base of little finger that hurt;
- pain in the arch of the foot;
- dislocated ligaments;
- ankle pain;
- tiredness when walking;
- familiar shoes become uncomfortable.
Symptoms can vary depending on the cause. After polio, for example, there is unilateral paralysis and a poor balance of the foot. There are no deformities and muscle tone is reduced. After cerebral lesions, on the other hand, there is increased muscle tone, increased tendon reflexes and spasticity.
Surgical treatment of pes cavus.
The primary goal of surgical treatment is to eliminate pain and improve movement and gait function with a variety of possible procedures, including tendon transposition, tendon grafting, corrective osteotomy, and in some cases, arthrodesis.
Surgery is done only when the deformity causes pain, muscle weakness, and contractures, and disrupts the normal biomechanics of gait. If we find a patient with a pes cavus who has no symptoms, there is no reason to rush into surgery.

Two stages of disease development
The foot deformity develops gradually. Experts distinguish two stages of this process.
The first stage is characterized by morphological changes in the soft tissues. If the foot curves due to deformation of the muscles, ligaments and skin, these changes are easy to correct.
It is enough to put pressure on the head of the first metatarsal.
In young children, pes cavus is difficult to recognize, since the clinical picture of the disease is not very pronounced.
However, if no appropriate measures are taken, the deformity will go into a stable phase. This is associated with serious health consequences.
Surgical treatment of hammer toe deformity as part of pes cavus.
The weakening of dorsiflexion of the foot is compensated by overuse of the toe extensors, eventually leading to a hammer toe or claw toe deformity.
If this deformity causes discomfort and makes fitting shoes difficult, Johnson's surgery is indicated.
The extensor tendon is transplanted to the lower third of the metatarsal bone and the toe is fixed in an extended position with a spoke. With this procedure, the patient can continue to use the extensor tendon to lengthen the foot and correct toe deformity.
Prevention of varus deformity
For the prevention of pathology, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Choose quality and comfortable shoesChoose quality shoes, preferably leather. If you have musculoskeletal disorders, flat feet or other ailments, your orthopedist should advise you to choose a new pair of shoes, sandals or boots. Wear only orthopedic footwear.
- Strengthen your immune systemVitamin, mineral, vitamin and mineral deficiencies should be avoided. Vitamin and mineral deficiencies lead to many health problems. Most important for the prevention of orthopedic diseases are calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D.
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Smoking, drinking alcohol, working and resting should be avoided. Excessive exercise combined with an unhealthy diet and lifestyle leads to metabolic disorders.
- Avoid sedentary activities and exercise regularly.. Physical activity not only reduces the risk of varus deformities, but also prevents obesity.
- Pay attention to the position of your feet when walking and standing.
- Avoid injuring your anklesAvoid sports that can lead to injury.
A varus deformity of the foot is easier to treat in the early stages when the knee, hip and spine are not yet affected. At the first symptoms, it is worth visiting an orthopedist. In advanced cases, only surgery can help.
Prevention of foot deformities
Knowing what is varus and what is valgus, it is easy to guess that the preventive measures are the same in both cases.
- Diet should be adequate and contain the right amount of minerals and vitamins.
- The supply of vitamin D is necessary.
- Constant support of the immune system.
- Physical movement.
- swimming and cycling.
- A good range of shoes to suit the size and fullness of the feet.
Foot soaks just before bedtime are a great way to relax and reduce stress.
Prevention of clubfoot deformities in children
Preventing clubfoot in children is similar to preventing deformity in adults. However, there are some rules that apply to childhood. For example, it is forbidden to put babies on their feet very early and to use a walker for this purpose. This can lead to negative consequences, which are expressed in diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Children should choose appropriate footwear and wear low-heeled shoes (at least 5 mm).
The most important thing is to observe the child and if there are any abnormalities, immediately consult the doctor.
Specialist area: surgery Specialist area: traumatology and orthopedics (specialist training) Experience – more than 10 years. State Department of Medicine and Preventive Medicine, Moscow. Responsibilities: 'Treatment of trauma patients and orthopedic patients in the trauma center.
Treatment of varus deformities of the foot in children by massage.
Treatment of varus foot deformity in children should be started as early as possible, before foot curvature develops. In the early stages of varus foot deformity, massage can correct muscle tension in the lower leg and arch of the foot. In most cases, however, a comprehensive approach is required.
An experienced podiatrist will examine the foot and develop a customized exercise program. They are designed to strengthen certain muscles, encouraging the child to place their foot in the correct position.
In severe cases, special footwear is indicated to prevent twisting of the foot. Osteopathy, physical therapy and many other treatments can also be used to speed up the healing process.
In our chiropractic clinic you can arrange a free initial appointment with an orthopedist. The doctor will examine your child and prescribe an effective treatment.
Doctor of Medicine, Chief Physician
types of deformity
As the disease develops, the foot changes, with the arch flattening and the sole turning inward. The main support is on the outside (little toe, heel), the big toe may not even touch the ground when walking. The position of the foot in which the toe is always up and the outer edge is always down is called isosceles. Classification of the disease:
Distinguish the types of this disorder by the cause of the disorder:
| type (name) | Caused |
| Static | Bad posture |
| Structurally | Vertical talus (part of the foot skeleton, between the tibia and heel bone) |
| compensatory | Shortening of the Achilles tendon, malposition of the ankle and/or hip joint, tibial plateau deformity. |
| paralyzing | Poliomyelitis, encephalitis, cerebral palsy |
| Spastic | muscle cramps |
| rickety | Rickets in childhood |
| hypercorrection | Abnormal treatment of clubfoot in infancy or other musculoskeletal disorders |
| traumatic | Strain, sprain, dislocation, fracture |
If the defect is congenital, the cause may be:
- heredity, genetic predisposition;
- an abnormal development of the fetus in the womb due to hypoxia, stress, diseases (viruses, infections), poisoning, poor nutrition or trauma;
- Premature birth (joint dysplasia).
An acquired disease can result from factors such as:
- Trauma;
- Diseases (rickets, cerebral palsy, polio, diabetes)
- Disorders of the endocrine system and nervous system;
- avitaminosis;
- mineral deficiencies;
- disorders of metabolism;
- poor absorption of calcium;
- weakened immune system;
- hormonal imbalances;
- chronic bone injuries;
- prolonged wearing of unsuitable footwear;
- overweight;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- Excessive physical activity at a young age (when the child starts sports early, is interested in choreography and the loads exceed physical endurance);
- Increased muscle tone.
External influences are particularly dangerous for small children, whose cartilage has not yet been completely replaced by bone.
In infants, a varus foot deformity can be detected with regular medical exams. Older children and adults should be examined, have blood tests, and see a specialist. The exact cause of the disorder and its extent are determined by X-rays.
The external varus position of the feet seems to be the same in all age groups. A worrying sign is when the soles of the shoes are worn on the outside. If the bare foot is placed on a flat surface, the imprint will not be correct: incomplete, narrow, with no separation between the heel and toes.
Tips for choosing
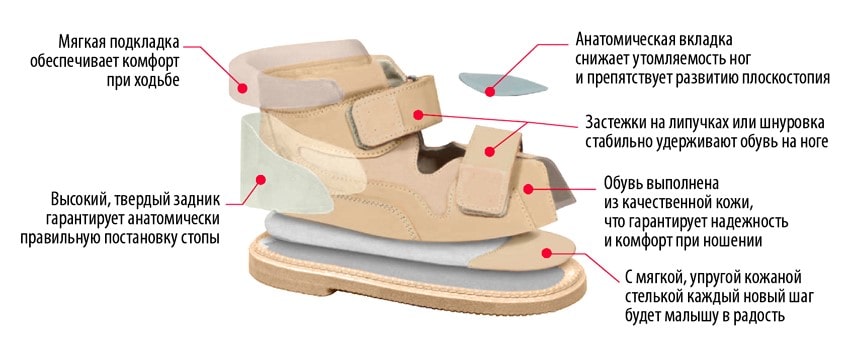
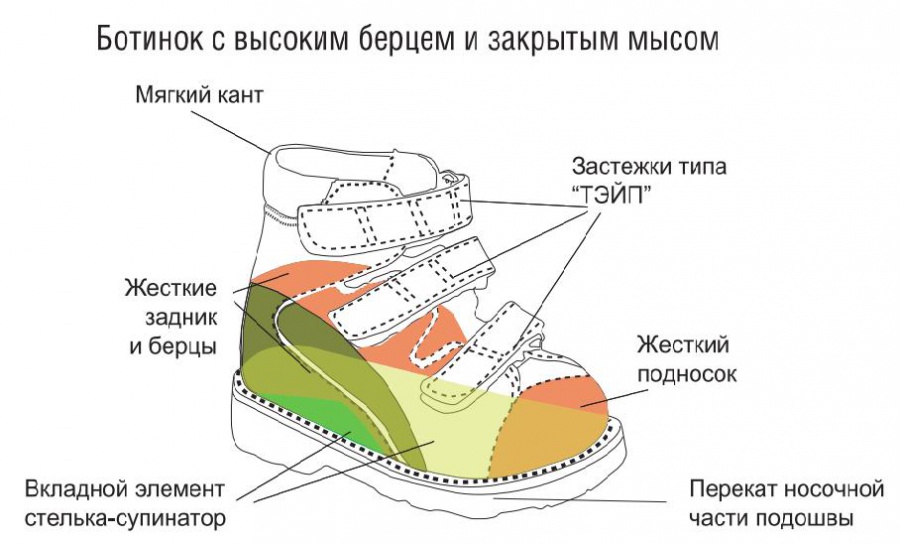
Once you understand what non-slip shoes are and get acquainted with their characteristics, you can proceed to choosing this attribute for your wardrobe. Today's market offers a wide range of orthopedic shoes, sandals and heeled sandals of various colors and designs. However, the appearance of the product in this case plays a minor role. When choosing orthopedic shoes, the following points should be considered in particular:
- the presence of rigid shins that hold the foot in a strictly upright position;
- Higher shoes should be preferred to increase the therapeutic effect;
- the soles of the shoes should be stable, flexible and non-slip;
- the closures (Velcro, laces) are adjustable lengthwise to better support the foot without 'fluttering';
- the heel has a groove that keeps the heel in a stable position;
- heel height of at least 0.5 cm;
- removable insole;
- the toe of the shoe has a lateral shift of 8-10 degrees to correct varus deformity;
- the toe box is wide and does not pinch the toes.
Non-slip shoes are not designed to grow with your child.. Their size should be adjusted according to the length of children's feet. In order not to make a wrong choice, children's shoes should be bought by parents together with the child. It should also be remembered that only genuine leather products should be preferred. The effectiveness of treatment depends on making the right choice and taking into account all the doctor's recommendations.
When buying shoes, pay attention to their weight. Shoes or sandals should always be light so that the child's feet are not put under additional strain.
How to wear them correctly
Only after the child has been examined, clubfoot has been diagnosed and the doctor has been consulted can the child start wearing anti-slip shoes. The use of such an orthopedic device is a prerequisite for recovery. As a rule, these therapeutic measures are prescribed for the entire period of foot formation and growth. They help bring the lower part of the foot into the right physiological position and normalize the biomechanics of the joints.
It's important to remember that corrective shoes should be worn in the preschool years, when bones are forming and ligaments are particularly flexible. It is best to only wear them outdoors, but for a long time, i.e. not once a week. Slippers or socks are allowed at home. Don't decide for yourself whether you want to remove an orthopedic bandage; only a specialist can decide when to stop treatment.
Antivarus shoes are often used as an adjunct to basic therapy, including therapeutic massage and physiotherapy treatments to correct the shape of the foot. However, in mild forms of the disease and in the absence of serious musculoskeletal changes, it is sometimes possible to improve the situation with corrective splints alone. Therefore, the most important thing in this regard is the correct approach to treatment and the timeliness of the necessary actions, which are the key to a successful recovery.
Read more:- Icb varus foot deformity.
- Foot.
- Shoes for valgus deformities in children.
- Child with Komarovsky clubfoot.
- What does the insole of a child's shoe look like?.
- Do orthopedic shoes help children?.
- The shoe inserts are.
- orthopedic shoes.

