The treatment of hyperkeratosis on the feet is carried out by medically trained podiatrists. The treatment regimen has been developed over many years and involves several steps: softening the rough skin of the feet, removing the hard horny layer and then plumping up the skin.
Hyperkeratosis on the feet
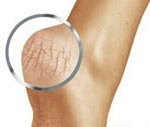
foot hyperkeratosis – This is excessive keratinization and thickening of the epidermis on the plantar surface. Hyperkeratosis on the feet is characterized by thickened and dry skin, scaly skin, painful cracking and bleeding of the skin. The diagnosis of hyperkeratosis is based on the external examination of the foot by a dermatologist, podiatrist or podiatrist, the results of a skin biopsy and subsequent histological examination of the material. Treatment of foot hyperkeratosis is comprehensive: foot baths, foot scrubs, medical pedicures, special cosmetic preparations, etc. are effective.
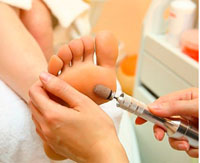



General information.
Hyperkeratosis of the feet (hard stratum corneum, abbreviated GSR) is an abnormal hypertrophy of the stratum corneum, reaching a thickness of one centimeter or more. Complications of hyperkeratosis can manifest as small cavities (hemorrhages), soft (between the toes, nails) and hard (tarsus) calluses and ulcers caused by increased pressure on the feet. Hemangiomas and calluses are not generally harmful to health, but they represent a cosmetic defect and cause discomfort when walking. They must be removed with special treatments. Foot ulcers are common in diabetics and require treatment of the underlying condition in addition to cosmetic measures.
Often cracks in the stratum corneum of the foot appear against the background of hardening of the stratum corneum, which can cause significant discomfort. However, their development is not always directly related to hyperkeratosis; it can also be a result of poor foot care.

Tinea pedis symptoms (signs)
Fungal infections not only affect the skin of the feet, but also the spaces between the toes and the nails. If the first symptoms are ignored, the infection can spread to other areas of the body. The severity of the disease depends on the type of fungus, the degree of damage and the size of the affected area of skin. Spontaneous epidermophytosis can be recognized by a change in the skin structure on the feet:
The skin begins in the interdigital folds, where the areas are in close contact with each other. The parasite gradually spreads to the soles of the feet, the back and sides of the feet, and the nails. As the disease progresses, the following symptoms appear
- dryness and thickening of the skin;
- formation of furrows;
- thickened calluses;
- cracking of the skin;
- peeling of the skin in the form of plaques;
- white spots and streaks.
The cracks get deeper and deeper. Painful sensations join the unbearable itching. In a chronic course, the symptoms are suppressed, which means that the affected person does not see a doctor for a long time and triggers the disease.
cause
The infection is caused by different types of molds or yeast-like microorganisms: dermatophytes, candida, trichophyrotron red, trichophyrotron interdigitalee. The clinical picture of the disease depends on the type of parasite. Infection occurs through direct contact with the fungus, which lives in a warm and humid environment that favors its multiplication. The transmission routes are:
- baths, saunas, swimming pools;
- baths, showers, floor mats;
- shared towels;
- personal care products;
- Wet socks or shoes.
The list also includes sports clubs and places of infection within the family. Triggers include:
- Poor personal hygiene;
- environmental degradation;
- unhealthy lifestyle;
- Frequent use of antibiotics;
- hormonal disorders;
- overweight;
- high age.
Occupations such as miners, athletes, metalworkers, military personnel and service personnel who work in saunas, spas and swimming pools are at risk. Foot diseases (including those caused by diabetes) and injuries such as corns and calluses, cuts and lacerations, valgus deformities, and osteoarthritis increase the likelihood of infection.
Which doctor should I see?
If left untreated, tinea pedis can lead to a number of complications, including allergies and bacterial infections. Only a doctor can diagnose and identify the characteristic symptoms of tinea pedis. Doctors who deal with this disease include:
Our specialists
Read more:- The sole in the heel area has sunk in, what can you do about it?.
- What are photos in photography.
- Treatment of a broken heel bone.
- hole in the heel.
- Why amputate legs for diabetes?.
- Why are the big toes crooked?.
- scabies.
- Mortar for soles.
