The massage is performed with massage oil to improve blood circulation in the affected area. Gentle stroking is replaced by vibration, kneading and rubbing.

- Acquired and congenital clubfoot in children. symptoms. Photo.
- Is clubfoot unilateral or bilateral?
- Clubfoot in children: photo
- The main causes of clubfoot.
- symptoms of the disease.
- WHY EVERYBODY HAS A CLUB FOOT NOW.
- comment
- Classification of clubfoot in children
- Congenital clubfoot
- theories of origin
- With chisel and hammer
- A colleague might convert.
- Possible complications
- Symptoms of flat feet (in Ryazan)
- Prevention of flat feet in children
- How can the development of the disease be prevented?
- So what to do?
- prevention
Acquired and congenital clubfoot in children. symptoms. Photo.

Clubfoot – a defect that has become quite common in recent years, a deformity of the foot, a deviation of the foot from the longitudinal axis of the lower extremity. Children are unable to put their feet up or lean on them. There are several classifications for this musculoskeletal malformation: congenital and acquired clubfoot, unilateral or bilateral, typical or atypical. In this article you will learn what you can do to identify clubfoot in your child as early as possible, how to treat your child's clubfoot and what causes clubfoot.
Is clubfoot unilateral or bilateral?
It's simple: if a child has a deformity in one foot, it is unilateral clubfoot, if both lower limbs are affected, the doctor diagnoses bilateral clubfoot. In the latter case, the child's feet do not necessarily have to be symmetrically deformed, often the treatment of each foot requires an individual approach. The most common condition in children is unilateral clubfoot. Typically, the unhealthy foot is shorter and the shin is slightly thinner. Sometimes the healthy and unhealthy feet are not the same length, and shin length may need correction during adolescence.
Clubfoot in children: photo

 Clubfoot in children under one year old. Congenital clubfoot in newborns.
Clubfoot in children under one year old. Congenital clubfoot in newborns.
Congenital clubfoot can supposedly be detected before birth if the mother has an ultrasound scan performed at 16 weeks of pregnancy. The exact diagnosis is made by the doctor after birth by examining the baby. Clubfoot is diagnosed when the following symptoms are present:
- /wp-content/uploads/2016/12/koso.jpg' alt='Clubfoot' width='300″ height='480″ size-full wp-image-2312″ />The feet face each other. The outer edge of the foot is greatly lowered, and the inner edge, conversely, is raised upwards.
- Varus Deformity. The inner part of the foot is the main pressure point when the child tries to get to their feet.
- External rotation of the ankle bones.
- A complete twist of the foot is a severe form of clubfoot. The child's feet point upwards.
In addition to the four obvious symptoms, there are a number of other symptoms of clubfoot:

The main causes of clubfoot.
Depending on the cause of clubfoot, a distinction is made between congenital and acquired defects. The prerequisites for the development of the first type of pathology include:
- Severe poisoning during the first trimester of pregnancy, when the nerve endings are forming,
- Viral infections with a body temperature above 38 degrees,
- alcohol, uncontrolled medication, smoking, drugs,
- vitamin and micronutrient deficiencies,
- Excessive stress during pregnancy,
- multiple pregnancies.
Acquired clubfoot can occur as a result of rickets and bone dysplasia. Against the background of abnormal development of the ligaments and muscles, a lack of useful minerals, tumors and mental disorders. Also with excessive loads on the musculoskeletal system, high pressure on the lumbar muscles, wearing poor-quality footwear or severe injuries to the lower limbs.
Congenital spastic clubfoot in children develops against the background of pathological changes in the central and peripheral nervous system of the child. Causes of clubfoot are cerebral palsy, congenital short Achilles tendons, ligament and muscle weakness.
symptoms of the disease.
An experienced specialist can immediately tell if clubfoot is pronounced - the foot is turned in or out, the sole is flexed and the child's foot area looks underdeveloped.
Congenital clubfoot is characterized by fibrous atrophy, skin lesions, calluses, corns, and mucous membranes on the surface of the foot. Feet tire quickly when walking, and painful sensations appear when moving.
Symptoms of clubfoot in children with the acquired form:
- footprints on a flat surface parallel to the ground,
- toes turned in when walking,
- Difficult gait – when the child feels like they are brushing their feet on the floor,
- inward knees.
The most noticeable symptoms of clubfoot in a child are when the lower limbs are relaxed and dormant. Muscle tissue and ligaments cannot keep up with the growth of the skeletal system.
WHY EVERYBODY HAS A CLUB FOOT NOW.
Why do almost all girls (besides the pretty and high profile ones) have club feet all over their bodies? Why do girls get their bite corrected as children but don't work on correcting a loose clubfoot (which, by the way, is easier and cheaper to do)? I mean, that's ugly and not healthy.
UPD: Based on discussion in comments. A compelling argument as to why children (especially girls) should be weaned from clubfoot at a young age. If they later want to emulate the modern model pose of the clubfoot, they can do so, but they cannot do it again. If they can keep their legs straight (and preferably turned outwards), they may have club feet. But if they have club feet, they are permanent. Even teeth can be corrected in adulthood, but clubfeet will never be corrected.
comment
No, it's not always easier. I also have a club foot, it was inherited from my father. In order to have it corrected, my feet had to be fixed in a plaster cast, which my mother did not agree to. I only had clubfoot complex as a teenager, then I realized that it wasn't the most important thing. Now my son has a clubfoot too. I don't know if that's good or bad, but I'm not doing anything about it. His teeth, on the other hand – yes, I watch his teeth.
(I looked closely at the photos and realized it's a creepy photo! No, our family doesn't have it - one leg is straight and the other is turned slightly inward. And what you see in the photo is really ugly. But maybe they're normal? It's just that the photo was so unfortunate, so in that second there are these crooked legs)?
You know, if the other leg is turned in slightly, that's medically a 'slight relaxation'. Weak ligaments that don't keep the foot in the right position. Of course, the correct foot position must be practiced and maintained. Especially in girls. But nowadays the 'exaggerated clubfoot' is almost the most fashionable foot position. Sarah Jessica Parker, as far as I'm concerned, danced ballet seriously. She is a lumberjack.
All in all, it's a shame that parents seem to have lost sight of this simple and important topic over the last few decades.
Parents are not parents.
Besides, it's fashionable - this sentimental childishness. A woman in her fifties and standing - socks in - well, too bad.
I've lost count of clubfoot celebrities. By the way, neither Marlaire Dietrich, nor Marilyn Monroe, nor Greta Garbo, nor Audrey Hepburn, nor Brigitte Bardot, nor Sophia Loren had a club foot. They all kept their feet graceful and erect (not like ballet, of course).
Well, and it doesn't depend on age. If there is no exercise from the age of 6 to 12-13 years - then clubfoot persists to varying degrees.
The only point of view I have on this subject is the 'childish touch' I just mentioned, thanks for the wording. Excuse me if I mix things up, but those, um, pouty and pursed lips are all in one place. And by the way, it's not about fads. I noticed this trait in women about 15 years ago. That's when the ladies actually started to party. :)It's just that the image makers have allowed the herd to demonstrate it somehow, especially in recent years.
Classification of clubfoot in children
The pathology is classified according to the causes that led to the development of the disease, the angle of curvature, the number of affected bones and the severity of the defect. The typical form of clubfoot develops against the background of underdevelopment of the musculoskeletal complex and, as a rule, affects only the foot. With early diagnosis, this defect is easily corrected with massage, special exercises and other conservative methods that can be carried out under the supervision of a doctor or at home. Atypical clubfoot is much more serious: it is caused by abnormalities in the musculoskeletal system and requires more careful and long-term treatment. In this case, gymnastics and physiotherapy are used more as accompanying methods that can improve the child's condition.

Depending on the degree of curvature of the foot, a distinction is made between:
- Mild degree clubfoot that preserves ankle range of motion;
- Moderate degree with severe restriction of mobility;
- Severe grade with little or no joint mobility.
Congenital clubfoot
Clubfoot can appear before the baby is born. A competent diagnostician can detect it as early as the 16th week of pregnancy during a routine ultrasound examination and prepare the parents for this. There are usually several key symptoms that indicate an abnormally shaped foot:
- Lowering the outside and raising the inside of the foot;
- A foot deformity where the emphasis is on the outside of the foot;
- Underdevelopment of the foot, disproportionately small foot size;
- Lowering the toes while raising the heels;
- twisting of the bones of the lower limbs;
- transverse flexion of the sole in the infant;
- Twisting of the foot with the sole up (one of the most severe cases).
theories of origin

The earlier treatment for congenital clubfoot begins, the greater the chance of avoiding surgery.
The question of why clubfoot develops still worries scientists as there is no definitive answer. There are many theories that only try to lift the veil of mystery. The most common include:
The mechanical factors leading to the development of clubfoot include increased intrauterine pressure with too little or too much amniotic fluid, uterine tumors, a short umbilical cord and the presence of amniotenosis. Clubfoot is believed to develop due to the forced fetal position and limited range of motion caused by the above factors. In practice, the combination of clubfoot and the above factors is rare.
Some authors explain congenital clubfoot by delaying the development of the limbs at some stage of embryonic development. This occurs when the limb is in supination, adduction, and soleus flexion, which is physiological to the limb. This view is supported by the fact that the clubfoot limb is significantly impaired in growth and development after birth.
Proponents of the neuromuscular theory hold that the foot is firmly planted because of a muscular imbalance. According to them, the cause of this disorder is changes in the central and peripheral nervous system.
Gubanov attributes the development of clubfoot to the slow formation of ossification nuclei in the tarsal bones and insufficient blood supply due to a congenital vascular anomaly of the foot.
Congenital clubfoot manifests itself in different ways, which suggests that the causes that led to its formation are different in each case.
With chisel and hammer

This operation - or rather several operations in a row - drag on for hours. The orthopedist now looks like a bloodthirsty barmaley. Not only does he have to cut a lot – skin, tendons and muscles – but also cut off pieces of the fibula that is too wide. Otherwise the foot does not reach to the shin. The doctors exchange brief, factual remarks. But they look fierce: one doctor holds the child's leg while another chisels away the bone with a chisel and hammer, dropping large chunks into a jar. And then he puts a spoke in the drill, screws it into the live leg with a whirr, and cuts off the ends with wire cutters. And so four spokes in a row – along and across the foot. He jokes and encourages his tired colleagues. When the nurse hands Vavilov a pair of scissors with very thick blades, he bats his long eyelashes:
– 'This is from the plastic surgeon's kit'. – he replies, to everyone's amusement.
But the knobby foot, which seemed nondescript to me at first with a huge bump on the side like it had a second heel, looks fine after an hour. Except for the spokes sticking out of it and the blood slowly seeping out. And the doctors still have to sew everything up. And then they apply an Ilizarov clamp, which is also fixed in the bone tissue with spokes.
– Aren't you waiting for a breakthrough in orthopedic technology? – I then ask Vavilov. – Something fancier than spokes and Ilizarov clamps?
– No,' he replies. – I was at a conference in Tel Aviv in the spring: there is nothing new, in the good Russian centers everything is done the same way. The only possible breakthrough now would be to make expensive metalwork cheaper. That would change a lot of lives.
A colleague might convert.

There are already many orthopedic surgeons in Russia practicing modern methods of treatment, but they are practically impossible to find in district polyclinics.
– I don't have a nurse in the polyclinic, I don't have a cast room', explains Dr. Ekaterina Solovieva. - And even if I had one, I wouldn't use the Ponseti method - I don't have enough time and money for casts. I can only observe children with clubfoot; out of 13,000 children there are only two.
So the parents of clubfoot children have to spend money on braces once or twice a year, which from 10,000. RR cost, and after five years for a special stand where they have to stand for half an hour every day. And also for a doctor. After all, even in a good situation you need a professional to supervise you until you are 10 years old.
- Who do you have on your hands - the Daily Fury? – Vavilov asks the wrinkled forehead of a four and a half year old blonde. – Take off your socks: we have already seen them. But everyone's feet are different.
– Why is the left leg thinner? Muscular dystrophy? – The mother is worried.
– The oblique leg is always thinner because the muscles in the lower leg are shorter. Once you start pumping, the difference only becomes clearer: you can no longer lengthen the muscle.
– There was baby fat in the leg, which dissolved and became visible,' explains Vavilov. – If it is important to her, she will insert an implant. But that's something she'll decide for herself in her 20s, kids don't get surgery. Our job is to keep your leg flexible and pain-free. Therefore, please do not forget to wear an orthosis at night.
– Why is one foot shorter than the other? – My mother is worried.
– The foot will always be a little shorter,' answers Vavilov. – He will buy a pair of shoes, but the left foot will need to be laced more tightly.
– Just like now – the mother nods and seems to calm down.
The next four-year-old patient enters the office in semi-flexion and places her feet in a herringbone pattern:
Parents recall that six months ago Vavilov proposed the return of clubfoot. To strengthen his muscles, they take the boy to a hockey game. Vavilov watches the boy run, twist his feet and speak:
Possible complications
Despite the obvious signs of foot deformity in a child, sometimes there is negligence and inattention on the part of adults who do not turn to a specialist in time or do not follow his recommendations. As a result, the child is at risk of complications:
- It will start running later;
- The child often suffers foot injuries (sprains and strains);
- Muscle wasting occurs;
- thickening of the skin on the outside of the foot;
- develops flat feet (further information: How do children do gymnastics with flat feet?);
- problems with the knee joints;
- The axes of the legs become crooked;
- spinal deformities appear;
- venous congestion;
- Disability and mobility on crutches due to lack of treatment at a young age.
The video below shows the expert's comments and a series of massage exercises for this pathology.
She is a category 2 paediatrician, allergist-immunologist and BSMU graduate of the Federal Agency for Health and Social Development. Read more ,
Symptoms of flat feet (in Ryazan)
Flat feet are most commonly identified by a doctor using a plantograph. The feet are greased with a special solution, the person stands on a clean piece of paper and the orthopedist examines the imprint. This method works well for adults.
Mistakes can be made when using this method to diagnose flat feet in children.
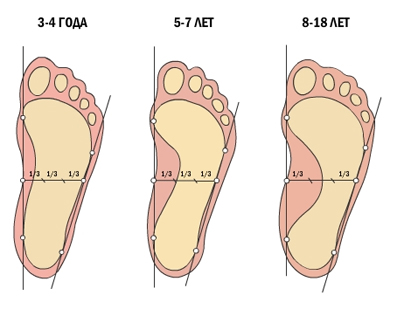
The illustration shows the standard. As can be seen, the younger the child (especially up to the age of 3-4 years), the more the footprint resembles a flat foot. Therefore, when diagnosing flat feet in children, a direct examination by an orthopedist is more often carried out.
X-rays are considered the most accurate way of detecting flat feet. Both feet are photographed under load in the anterior and lateral projection, with the patient standing. Based on the results, the orthopedist makes a diagnosis and determines the degree of flatfoot. This method should be used with juveniles to accurately determine the degree of flatfoot so that the juvenile's suitability for military service can be determined. The degree of flatfoot does not affect the treatment as the treatment is the same for all degrees.
Flat feet can only be corrected in childhood because the skeleton is still relatively flexible. This is why it is important to diagnose flat feet in children as early as possible. However, flat feet in children can only be detected by the age of 5 or 6 years. This is because the bones in children's feet are not yet strong enough and are mainly made up of cartilage. In addition, children's feet can appear flat because of the fat pad that protects the bony base. Children under the age of 5 should be checked annually by a pediatric orthopedist so flat feet are not overlooked. Diagnosis of flat feet in children over 6 years old can be made using a footprint, but for prevention it is better to visit the orthopedist periodically.
Prevention of flat feet in children
Prevention of flat feet in children begins in the first year of life. It includes the prevention and treatment of rickets and neurological disorders that can contribute to flat feet.
The child should have suitable footwear. Careless parents try to get rid of their child's imaginary flat feet. They make this diagnosis themselves, forgetting that when the child starts walking, the foot is still developing and looks like a flat foot. After the parents have made the diagnosis, they begin to treat this flat foot with special orthopedic shoes. This can affect the natural development of the child's feet. So if you suspect your child has flat feet, you should consult a doctor instead of fitting your child with special shoes.
It's important to walk barefoot on grass, sand, and other natural bumps. Studies by Indian doctors show that people who had a barefoot childhood are three times less likely to suffer from flat feet than people who have worn shoes since childhood. However, remember that it is not good for your child to walk barefoot on a perfectly smooth and hard surface.
For older children, you can play games that require great physical exertion. The children should do simple exercises such as B. walking on the heels, toes, outside and inside of the foot. Hop in place, lift heels (toes stay in place), crawl toes back and forth. Roll gymnastic sticks or tennis balls with a diameter of 2-3 cm with your feet, pick up small objects from the floor with your toes, climb ladders. All this promotes the development of foot muscles and improves blood circulation.
Any gymnastics shows the best results when combined with water applications. Swimming, for example, is a good way not only to stimulate skeletal muscle tone, but also to strengthen them.
How can the development of the disease be prevented?
The disease should be prevented even before conception. The most important measures are taking vitamins and the treatment of chronic diseases. This way you can pass as few diseases on to your baby as possible ⛹ . Do not forget that you should not consume toxic substances during pregnancy. Especially nicotine, alcohol or drugs. Try your best to protect your body from infection. It is worth taking care of a healthy diet.
To prevent the acquired form of the disease, some rules should be observed.
- Timely examinations by an orthopedist and neurologist.
- Give your child a daily massage and exercise.
- The use of so-called walking aids, which in no way help the child learn to walk, is strongly discouraged. This can lead to foot deformities.
- All sports always have a positive effect on the body. The most effective prevention of clubfoot is cycling or swimming.
- The cheapest way to prevent it is to get your child to walk on sand, pebbles, or grass.
So what to do?
The treatment of foot deformities is always complex and lengthy. The choice of treatment depends on the age, type and severity of the disease.
In order to eliminate clubfoot with classic treatment methods, the following measures are necessary:

- corrective massage – performed at mild degrees;
- the application of a soft bandage;
- PHYSICAL THERAPY;
- paraffin compresses in combination with massage treatments;
- plaster casts for correction;
- Plaster casts using the Ponceti method;
- use of orthoses, spica casts, orthopedic braces;
- wearing special orthopedic footwear;
- kinesitherapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Taking B vitamins and proserin.
If conservative therapies are ineffective, then surgery is performed by the method of Zatsepin or GA Ilizarov (over 4 years). Children are operated from the age of 8 months.
Using the video, any parent can learn how to massage a clubfoot in children:
prevention

As a prophylactic measure during pregnancy, with hereditary predisposition, drugs are prescribed for the normal development of the child's skeletal system.
At the first signs of the disease, a comprehensive examination should be carried out and all treatments aimed at correcting the pathology should be made.
clubfoot a serious condition that is progressive and can lead to permanent disability. Therefore, it is important not to delay treatment and consult an orthopedist in time.
Modern medicine has sufficient methods of correcting the defect and maintaining the correct shape of the feet.
Read more:- What is clubfoot?.
- baby splashing.
- Congenital clubfoot.
- Why does a child develop clubfoot?.
- Clubfoot in 7-year-old children.
- clubfoot.
- Clubfoot Treatment.
- 1 year old child with clubfoot.
