Treatment is not subject to seasonal restrictions. It can already be carried out in summer.
- How to regain your voice and heal your vocal cords
- How the voice is made
- Symptoms of a wrist sprain
- How are wrist ligament strains treated?
- Symptoms of a sprain or tear
- Possible complications
- Indications for surgical intervention
- Contraindications for surgery
- Signs and symptoms of cruciate ligament injury
- extent of cruciate ligament damage
- How is the injury manifested?
- The essence of the diagnostic procedure
- symptoms
- diagnosis
- Functions of the periodontal ligament
- Diseases of the periodontal ligament
- Which devices are used for the SMAS lifting?
- At what age can I have an ultrasonic face lift?
- How often can I have a SMAS-Lift treatment?
- How long does the treatment last?
How to regain your voice and heal your vocal cords


Our voice is our most important means of communication. We use it to transmit information to others and to comment on various topics. For some people, the voice is an integral part of their job and a way of making money (e.g. for singers or speakers). However, our voice is not always loud and clear. Like any other human organ or system, our vocal tract can fail.
A condition in which the voice droops and becomes hoarse is called dysphonia. A temporary loss of voice is called aphonia.
A missing or hanging voice is a real problem, especially in speaking professions.
So why is this problem occurring? What treatment can eliminate it quickly and effectively? What preventive measures can help to avoid aphonia in the future? Find answers to these and other questions in our new article.
How the voice is made
To understand why your voice is a problem, you need to understand the mechanism of the voice. The vocal cords, located in the larynx, play a central role in the voice. They are made up of muscles and connective tissue. There is a space between the strings - the vocal cord gap. When a person is silent, this gap is wide open, while when speaking or shouting it narrows. A sound is produced when a current of air from the lungs travels down the throat, causing the vocal cords to vibrate and flutter. The straps must be taut and closed when the air flows through them. Logically, if a person's voice falls or rises, it means that the vocal cords are not close together. In this case, a person can only whisper: the whispering is caused by the rubbing of the air flow on the walls of the larynx.
Vocal cord problems are most commonly associated with infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract, but you would be surprised to know that diseases of the throat are just the tip of the iceberg.
Symptoms of a wrist sprain
A sprain damages blood vessels, connective tissue or nerve fibers. This process is accompanied by:
There are three stages in the development of a wrist sprain:
- slight degree of injury - micro tear of the ligament - moderate pain, no swelling;
- moderate - partial tear - pain is clearly noticeable, mobility is restricted, swelling and bleeding are present;
- severe - torn ligaments - extensive swelling and hematoma, severe and acute pain, inability to move.

How are wrist ligament strains treated?
The treatment process depends on the extent of the injury. The injured limb is treated with painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. This is usually a long-term process. It is important not only to relieve pain, but also to create conditions for the regeneration of damaged tissues.
For a wrist sprain where more than half of the fibers are intact, treatment is conservative and a bandage is applied for 2-3 weeks. After this period, the patient is recommended to wear an elastic splint or orthosis.

Protection against injury and the restoration of mobility and function is provided by taping, ie immobilization of the hand with tape, and surgical treatment of a complete tear by suturing the tapes.
Physiotherapy also helps with rehabilitation:
Rehabilitation can begin the day after the injury by moving the hand and massaging it with warming medication.
Treatment that is started in good time ensures that no more complaints occur in the future.
Symptoms of a sprain or tear
The symptoms of a ligament injury in the elbow appear immediately after the injury, but become progressively worse over time. When a sprain or strain occurs, symptoms such as
- pain when moving the elbow or when in contact with the injured area;
- swelling and slight swelling in the injured area;
- Discoloration of the skin, bruising
- characteristic cracking noises in the injured elbow;
- limited mobility of the joint.
Doctors distinguish three types of injuries with the following characteristic symptoms:
- Inflammation of the medial epicondyle - accompanied by pain in the inner part of the elbow. The pain increases when bending the wrist. It is also known as 'golfer's elbow'.
- Epicondylitis - the pain occurs only with active movement of the elbow. The pain syndrome intensifies when squeezing the hand. Epicondylitis does not manifest itself externally. The usual term is 'tennis elbow'.
- Medial epicondylitis is characterized by pain on the inside of the elbow joint and swelling. The pain subsides with rest, but the discomfort returns when physical activity resumes. Another name for it is 'baseballer's elbow'.
At the first suspicion of tissue damage, a doctor should be consulted immediately for diagnosis, since the loss of time and inadequate treatment can lead to irreversible consequences.
Possible complications
Without diagnosis or self-treatment, even minor injuries to the elbow joint can lead to the following consequences
- Osteoarthritis – damage to articular cartilage;
- nerve damage in the forearm or shoulder;
- Permanent restriction of mobility, etc.
Any complications make it difficult to treat the underlying damage, and the effects of the above diseases are long-lasting. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to see a doctor at the first symptoms that indicate ligament damage in the elbow joint.
Indications for surgical intervention
Arthroscopic ACL reconstruction of the knee joint is not performed immediately after the incident to avoid complications. Surgery is usually not planned until the inflammation and swelling have subsided. During this period, competent conservative medical care and immobilization of the limb are organized.
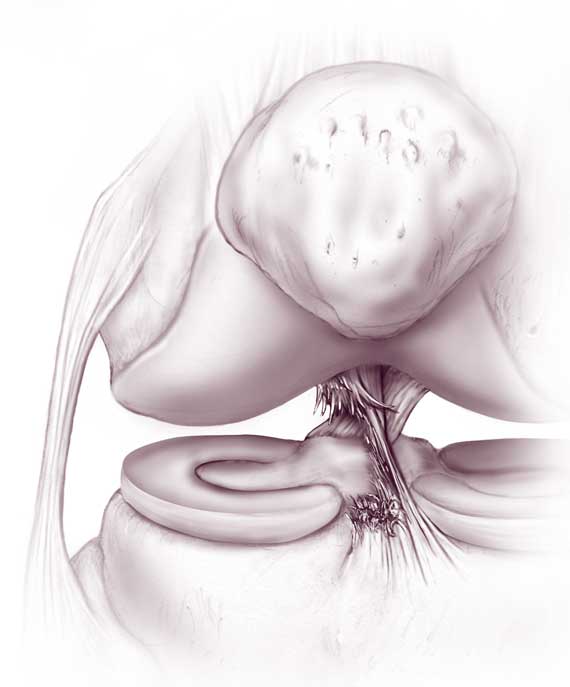
If I have problems over a period of time, do I need to undergo knee ACL reconstruction? There are certain factors that clearly speak in favor of arthroscopic plastic surgery, e.g. B.
- Rupture of the transverse ligament along the entire width line;
- absolute separation of the fibers from the point of attachment to the bone;
- Partial damage with pronounced knee instability;
- unsuccessful plication of a damaged ACL that failed to stabilize the knee joint due to an abnormal graft;
- chronically repetitive sprains and strains;
- Ineffective conservative treatment.
Important: Once again, it is worth remembering that reconstructive surgery is not performed immediately after the injury, but this does not mean that the injured person does not need the help of a trauma surgeon. In order not to aggravate the problem, you should be examined immediately, seek qualified specialist advice and act immediately! Exceptionally, immediate surgery can be performed both in the case of an extensive combined injury (rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament in combination with bone, meniscus and other ligament damage) and in athletes who want to quickly return to professional sports.
Contraindications for surgery
Although ACL reconstruction is one of the most popular procedures due to its high effectiveness and minimal invasiveness, it is not suitable for everyone. Fortunately, there are not many contraindications:
- Pronounced contractures of the joint;
- local skin infections, inflammation, purulent abscesses, ulcers;
- Severe abnormalities of the heart, respiratory system, veins and blood vessels in the legs;
- Any chronic illness that has worsened;
- Allergy to the drugs used for anesthesia.
If autologous tendon transplantation of the quadriceps femoris or patellar ligaments is proposed and the patient has problems with the musculotendinous components of the flexor-extensor system, this procedure cannot be performed. However, he may be offered one of two alternatives: an allograft or a Legamis implant. Of course, this only applies if the clinic offers such services.
Signs and symptoms of cruciate ligament injury
The first symptoms of a cruciate ligament injury appear immediately after exposure to the traumatic event. It is a stabbing pain that forces you to stop putting weight on the injured leg. Other signs of an anterior cruciate ligament injury include:
- The injured joint is swollen;
- Bruises and hematomas appear on the skin surface;
- accumulation of blood in the joint, making the knee feel stiff from the inside;
- the kneecap is ballasted (moves up and down freely);
- Crunches and crepitations occur when attempting to palpate the joint;
- Severely dislocated knees can appear unstable due to excessive blood pooling in the joint cavity.
The clinical symptoms of cruciate ligament injuries increase in the first 3-5 days and then gradually subside. If a therapeutic puncture of the joint is performed and the blood is removed, improvement may occur the day after the medical manipulation. If this does not happen, the symptoms of an anterior cruciate ligament injury indicate developing hemarthrosis. In this disease, the synovial membrane of the cartilage inside the knee can deform due to the buildup of decaying red blood cells. Autogenous inflammation occurs to eliminate the remains of the decaying blood. This process can take two to three weeks. During this time, the cartilage in the joint is destroyed. The clinical picture of secondary post-traumatic osteoarthritis can occur.
extent of cruciate ligament damage
The anterior cruciate ligament is damaged in three different degrees:
- The first is characterized by a small intramedullary tear in which the mobility of the tibia is not significantly reduced;
- The second is a partial rupture of the ligamentous fiber with complete immobilization and inability to flex and straighten the leg at the knee;
- The third form is complete rupture with joint instability, inability to walk with support of the injured limb, rapid accumulation of blood in the joint capsule and development of hemarthrosis.
Cruciate ligament injuries can be diagnosed using MRI and ultrasound. The initial treatment is performed by a trauma surgeon. Rehabilitation is performed by an orthopedist or chiropractor.
How is the injury manifested?
Unlike dislocations of the muscle tissue of the hip, hip ligament injuries are immediate and acute. Characteristic symptoms include:
- a sharp, throbbing, often stabbing pain in the ligament area (felt from the inside of the thigh);
- There may be numbness or tingling in the thigh;
- Swelling and redness of the skin around the hip joint may occur after 5 to 20 minutes if there is no response;
- restriction of mobility;
- persistent feeling of pressure on the ligaments.
The essence of the diagnostic procedure
As with dislocations of any other part of the body, hip injury can range in severity from mild to particularly severe (when part of the bone is detached). Determining the extent of the injury is the first task in hip diagnosis. For this purpose, the accident surgeon carries out the following examinations:
- an objective examination with palpation, percussion and functional tests;
- a history of the conditions under which the symptoms of the sprain occurred;
- arthroscopy.
X-rays may be required to check the integrity of the bony structures. If there is a suspicion of ligament inflammation, an ultrasound examination is recommended. A clinical analysis of the synovial fluid in the hip joint will be required as an additional examination.
symptoms

- Pain and soreness on the inside of the elbow, especially when trying to throw a ball
- Clicking or popping of the crook, or discomfort from injury
- Swelling and bruising (after 24 hours) at the site of injury on the inside of the forearm in the area of the elbow and above if there is a tear.
- Inability to throw with full power, loss of ball control
- Stiffness in the elbow, inability to straighten the elbow
- Nausea or tingling in your fingers
- impairment of hand function, e.g. B. when gripping and fine movements.
diagnosis
Pain on the medial side of the elbow, pain just above the ulnar collateral ligament, and specific functional tests that reflect loading on the ligament can help diagnose a ligament injury. Specific physical tests include the valgus loading test, which involves applying force to the elbow and testing range of motion. This is possibly the most sensitive functional test.
MRI is the best way to visualize the soft tissues of the elbow joint. Small tears in the lower (innermost) part of the ligament are particularly easy to see when contrast is administered (injected into the elbow), since such injuries are not visible without contrast.
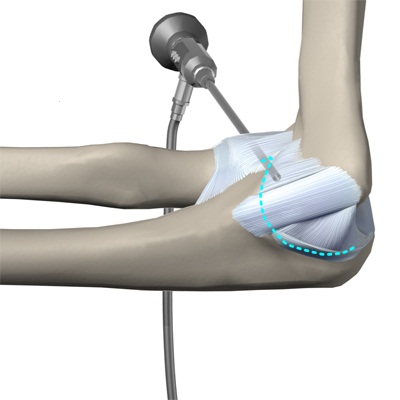
A minor injury can heal spontaneously.
Conservative treatment is indicated for most patients who manage to return to normal activity. Conservative treatment includes taking NSAID pain relievers (ibuprofen, aspirin), applying cold compresses to the injured area, immobilizing the elbow, wearing a splint, and physical therapy. Surgical treatment is usually only necessary in a small number of people with a torn ligament or when there is persistent pain, arm dysfunction, or a risk of a ligament tear. Most of these patients are baseball players.
The 'Tommy John' operation.
Surgical reconstruction (repairing the ligament using other tissues) is required in patients with an acute torn ligament, in whom conservative treatment is ineffective, and who wish to continue playing baseball. This operation is known as the Tommy John operation and is named after the player whose career was shaped by the tape's reconstruction by Dr. Frank Job could be saved.
The ligament can be reconstructed using a variety of soft tissue grafts harvested from the patient, but the most commonly used is the palmar forearm muscle tendon. This is because this tendon has similar biomechanical properties to the original ligament and since its absence is of no consequence, it is an ideal ligament replacement. Some patients do not have the original palmar muscle tendon and therefore require alternative grafts for reconstruction, such as lower limb extensor tendons.
Functions of the periodontal ligament
With its various components, the ligament has several important functions.
- It is both supportive and shock absorbing. The collagen fibers must hold the tooth firmly in the acetabulum, evenly distributing chewing forces and controlling pressure. This is achieved through the elasticity and resilience of the fibers. When the human bites, they stretch and the tooth pushes deeper into the floor of the hip socket. And when the pressure is off, the fibers contract again, returning the tooth to its original position.
- Barrier. The band prevents dangerous substances and microorganisms from penetrating the root of the tooth. Macrophages and mast cells are responsible for this task.
- trophic. An extensive network of blood and lymph vessels supplies the cementum with nutrients.
- receptive and reflective. Nerves and receptors perceive mechanical stimuli and reflexively regulate the chewing process: They send impulses that cause the chewing muscles to contract.
- plastic. Includes regeneration of tissues lost through physiological or pathological processes. Fibroblasts, osteoblasts and cementoblasts help in this process [1].
Diseases of the periodontal ligament
The periodontal ligament can become inflamed, caused by trauma (such as biting a very hard object), pathogens, or drugs used in dental procedures that have entered the periodontium through the root canal.
- Acute apical or apical periodontitis. The periodontal damage results in an intense tissue reaction that is usually confined to the periodontal ligament. An inflammatory process begins, which is accompanied by constant and increasing pain. Pus accumulates near the root tip and is difficult to drain. If left untreated, the process worsens and often leads to serious complications.
- Chronic apical periodontitis (apical granuloma). It can follow the acute form, when pus leaks through the root canal of the tooth. It is also often an independent disease caused by pulp necrosis.
Chronic periodontitis, as a rule, proceeds asymptomatically and is detected during an X-ray examination or under acute conditions.
Kozlov VI, dentist and surgeon of the highest category [3].
The periodontal ligament plays an important role in the gum tissue complex. It is able to hold teeth under chewing pressure without loosening and falling out. In order to maintain a complete set of teeth for years, periodontal problems should be recognized immediately by a dentist.
List of sources:
- Sakharuk N. A., Volkova M. N. Parodontalerkrankungen: Klinik, Diagnose, Prävention und Behandlung: ein pädagogischer und methodischer Leitfaden. Vitebsk: VSMU, 2014 // URL: https://elib.vsmu.by/bitstream/123/6947/1/Sakharuk-NA_Bolezni%20periodonta%20klinika%20diagnostika%20profilaktika%20i%20lechenie_2014.pdf (Zugriff am 10.12.2020).
- Samusev RP, Dmitrienko SV, Krayushkin AI Fundamentals of clinical dental morphology. M.: Publishing House 'ONYX 21st century': Mir i Obrazovanie, 2002 // URL: https://iknigi.net/avtor-rudolf-samusev/21113-osnovy-klinicheskoy-morfologii-zubov-uchebnoe-posobie-rudolf- samusev/read/page-17.html (accessed on December 10, 2020).
- Specialist article on periodontitis by the dentist and surgeon Kozlov VI // URL: https://probolezny.ru/periodontit/ (accessed 12/10/2020).
- Borovsky EV. Therapeutic Dentistry: Text-book for Medical University Students. Moscow: Medical Information Agency, 2003. // URL: https://www.booksmed.com/stomatologiya/153-terapevticheskaya-stomatologiya-borovskij.html (accessed on December 10, 2020).
Which devices are used for the SMAS lifting?
Special products with HIFU are used for the treatment. These can be used to treat specific areas of the face and body with high-intensity ultrasound. The devices differ in wavelength and power, as well as in a number of technical parameters.
Doublo, Ultraformer and Ulthera are some of the best devices currently available for SMAS lifting. In our clinic we use the Ultraformer III, a new generation device that 'delivers' focused micro and macro ultrasound to a specific depth into the dermis layers. This treatment shrinks the collagen and elastin fibers and further regenerates the layer.
This device can be called a full-fledged alternative to surgery, as it can treat a wide range of aging problems on the face and body. The device comes with a large number of multi-cartridges, so that the depth of tissue irradiation can be selected (from 1.5 to 13 mm). This is necessary to avoid overexposure of sensitive areas of the face and to achieve the desired effect in areas with deep SMAS deposits.
Another important benefit of the device is security at all times. The effectiveness of the device with HIFU does not depend on sun exposure, the technique can be performed at any time and on any skin phototype. So if you are looking for the best solution for SMAS lifting, we recommend the Ultraformer III.
At what age can I have an ultrasonic face lift?
With this question, everything is individual. The procedure is most often recommended for patients over 40, since it is at this age that skin changes are most noticeable and the effect is most effective.
But here, too, everything is an individual matter. It is not uncommon for patients aged 30-35 to require a SMAS lift. For example, if there are pronounced wrinkles and tissue wasting.
From the age of 55-60, the method also gives good results and can be combined with other rejuvenation methods if necessary. In rare cases, the SMAS lifting can even be carried out at the age of 25-30 years. But before that, a consultation with a specialist is necessary. It is possible that the cosmetologist can suggest another method to correct existing problems.
How often can I have a SMAS-Lift treatment?
It is important to know that the effect of the treatment does not appear immediately - on average it takes 3-4 months before the final result is visible. It lasts 18-24 months, less often the effect is visible up to 3 years.
How long do I have to wait before having a CMAS lift? The treatment should be repeated 2-3 years after the first treatment. There is no point in doing the procedure earlier, as there will be no additional effect.
Often patients believe that CMAS lifting is harmful to the body, so the procedure allows only a limited number of repetitions. In fact, when asked how often a CMAS lift should be performed, many experts give a figure of 2-3 treatments. In reality, however, there is no fixed limit and the number of lifts is individual.
How long does the treatment last?
The technique provides long-lasting results for several years. As mentioned earlier, no one can give an exact number - a lot depends on individual skin characteristics, type of aging, lifestyle, etc. As a rule, the result of an SMAS lift lasts 2-3 years, in rare cases up to 5 years. The procedure should be carried out only after the effect has completely disappeared, so as not to damage the subcutaneous fat layer.
Read more:- is liquorice.
- The pubic ligament where it is located Photo.
- Ankle ligament strain, ICD.
- Treatment of torn ligaments in the ankle.
- Anatomy of the syndesmosis.
- Photo of an ankle fracture.
- Damaged ligaments of the ankle photo.
- Photo: Outer malleolus fracture.
