In addition, there are chronic diseases that drag on for years and significantly impair the body's ability to heal quickly.

- Damage to the growth zone
- causes
- Other possible causes of growth plate injuries
- What diseases can an MRI scan of the ankle reveal?
- When is an MRI scan of the ankle recommended?
- Fracture of the femoral neck
- fracture of the hand
- Effectiveness of taping in ankle fractures
- Taping of the ankle after a fracture
- Causes and treatment of fractures of the ankle
- Rehabilitation in the post-traumatic period
- Peculiarities of thigh fractures
- Rehabilitation after surgical treatment
- Treatment at the Energy Health Clinic
- Benefits of the clinic
Damage to the growth zone
The growth zone, also known as the epiphyseal plate or physis, is the area of growing tissue at the end of the long bones of children and adolescents. Every long bone has at least two growth plates: one at each end. The growth plate determines the future length and shape of the mature bone. When growth is complete at the end of puberty, the growth plate is dissolved and the area is replaced with hard bone tissue.
Children and young people suffer from damage to the plates. The plates are the weakest area of the growing skeleton, weaker than the adjacent ligaments and tendons that connect bones to other bones and muscles. In a growing child, severe joint injuries damage the growth plates rather than the ligaments responsible for joint stability. Injuries that can cause dislocations in adults can damage growth plates in children.
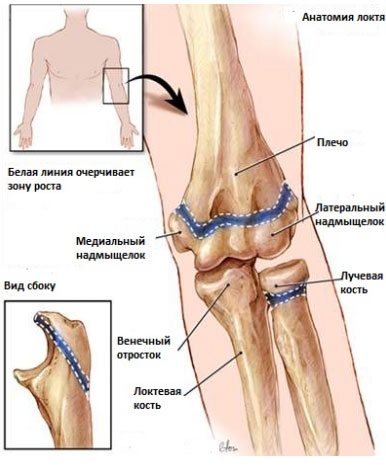
Growth plate injuries occur along with fractures. They account for 15 percent of all pediatric fractures. They occur twice as often in boys as in girls and are most common in 14- to 16-year-old boys and 11 to 13-year-old girls. In the older age group, fractures occur less frequently in girls because the musculoskeletal system matures earlier in girls than in boys. As a result, bone formation is completed earlier in girls and the growth plates are replaced by dense bone tissue. About half of all growth plate injuries occur in the lower forearm (radius) or elbow. These injuries are also common in the lower leg (tibia and fibula). They can also appear in the thigh or in the ankle and foot.
causes
Although growth plate injuries are usually caused by acute trauma (fall or blow to the limb), the damage can also result from chronic injury resulting from excessive and frequent loading. Such growth plate injuries can occur, for example, in athletes: gymnasts, track and field athletes, baseball players.
Some studies of childhood injuries indicate that growth plate injuries are caused by falls on the playground or from a chair. Sports such as football, track and field and gymnastics are responsible for a third of all injuries. Other physical activities such as bicycling, sledding, skiing, and in-line skating are responsible for a fifth of all growth plate fractures. Injuries related to driving, motorcycling, and similar traffic accidents account for only a small percentage of growth plate fractures.
If your child is in pain after acute trauma or exertion and the pain persists or is relieved with a change in physical activity, or if local pain occurs, you should see your doctor. In no case should a child move in pain. Children who play sports often feel a certain discomfort when they have to perform new movements. In some cases, the occurrence of certain complaints is quite predictable; nevertheless, every complaint of a child deserves attention, since some injuries, if not treated properly, can lead to irreversible changes and interfere with the normal bone growth of the injured limb.
Although most growth plate injuries are related to gaming and sporting injuries, there can be other causes of growth plate injuries (such as a bone infection) that can interfere with normal bone growth and development.
Other possible causes of growth plate injuries
Overuse in children can lead to bone injuries, especially in young children whose bones are just beginning to grow.
What diseases can an MRI scan of the ankle reveal?
However, the most accurate diagnostic method is the MRI scan. It can reveal changes in tissue structure of less than 1 mm in size. Therefore, any pathology will be visible on an MRI scan much earlier than with other methods of investigation. This is a great advantage for treatment because the earlier it starts, the more effective it is. Sometimes surgical treatment can be avoided at an early stage. In cases where tumors are discovered, the chances of recovery are much higher and the techniques are gentler, with fewer surgical interventions.
For this reason, MRI is widely used in orthopedics and traumatology, as well as in oncology. This is what an MRI scan of the ankle looks like:
- Inflammatory diseases – arthritis, synovitis, bursitis, tendonitis, synovitis, fasciitis, vasculitis.
- Benign and malignant soft tissue and bone tumors – osteosarcoma, chondroma, sarcoma, hemangioma, fibroma, osteosarcoma, presence of metastases, stage of the disease.
- Diabetic foot syndrome - depth of tissue damage, presence of necrotic lesions in soft tissues and bones.
- Traumatic injuries of the ankle, ankle and toes.
- Foreign objects in the area, including the joint cavity, unless they are made of metal.
- A valgus deformity of the foot, grade.
- Osteoarthritis due to age-related changes, due to chronic inflammation, after trauma. Sometimes a heel spur develops, ankle impingement syndrome – the bones of the talus and tibia growing together, pinching other tissue between them. Podagra most commonly affects the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe.
When is an MRI scan of the ankle recommended?
An MRI is performed in the following cases:
- Condition after an ankle injury to determine the presence and type of ligament damage (sprains, tears), muscle damage (contusions, erosions, necrosis), tendons, vessels (soft tissue effusions), bones, joints (dislocations, subluxations, intra-articular fractures). A fracture is usually clearly visible on the X-ray, but the associated damage to the surrounding tissue is only visible on the MRI.
- If the area around the joint is swollen, the skin is red, hot and painful at rest or when moving, this indicates an inflammation. An MRI scan shows how severe the inflammatory changes are and which tissues are affected. This has a direct impact on treatment and choice of medication. The joints become inflamed in rheumatic diseases, metabolic disorders (gout), allergic and infectious arthritis.
- In degenerative-dystrophic processes, the affected person complains of pain in the foot, ankle, crunching in the joint, stuttering, restricted movement. The pain is most noticeable at the beginning of the movement and then gradually subsides as the person 'walks'. An MRI shows how badly the cartilage is damaged and whether there are changes in the bone tissue under the cartilage layer. First, the cartilage thins, narrowing the gap between the joint ends of the bone. Then small pockets of cartilage can be seen, gradually enlarging. In return, the bone density at the edge of the cartilage increases. Resorption foci in the bone can be identified, exostoses - bone outgrowths that injure the neighboring tissue.
- If a mass is visible in the joint area, it may be painful, or there may be no pain on palpation. MRI can differentiate between cysts and tumors and determine their exact location and size. Based on the data on the type of blood supply, the borders of the tumor and the condition of the surrounding tissues, it is possible to assess whether the tumor is benign or malignant. A contrast medium is often used for clarification. This migrates through the blood vessels to the tumor and accumulates there. The tumor can thus be displayed in more detail.
- Anomalies are detected immediately after birth. Severe abnormalities require surgical intervention so that the person can stand and walk properly in the future.
- The pain can persist long after the injury. An MRI scan can help pinpoint the exact cause. When a nerve or vessel is pinched between bone or swollen tissue, the person feels pain, numbness, difficulty moving the leg, and the foot may be swollen, pale, cold, or bluish.
Fracture of the femoral neck
A femoral neck fracture in old age is one of the most serious and painful injuries requiring long-term treatment. It is more common in women because their bone tissue is more prone to osteoporosis. Notable symptoms of this fracture include the shooting pain that occurs when attempting to lean on the broken bone and the inability to move the leg. A hematoma may not form because the bleeding is minimal. A femoral neck fracture in the elderly is treated immediately as it is the fastest and most effective way of healing and prevents possible complications. Conservative treatment - skeletal traction or cast - is highly fatal and extremely difficult in elderly patients.
Surgical treatment involves an endoprosthesis, in which the damaged bone is replaced with an implant. Osteosynthesis – fixing broken bone fragments in the right position – is usually performed on younger patients.
After the operation, the elderly person needs to be cared for at home. Recovery time is different for everyone. With proper care, it is possible to return to a normal lifestyle within a year. In some cases, permanent recovery is not possible.
fracture of the hand
Fractures of the radial bone of the hand are the most common at any age. This is because the person affected instinctively leans on their hand when they fall. As a rule, there is no severe pain, the hand is not swollen, and pain occurs when trying to move the hand and fingers.
This injury is the least dangerous for the aging body. The hand receives a plaster cast for 6 to 8 weeks. Already on the third day after putting on the plaster, it is advisable to slowly move your fingers and work on the wrist after removing the plaster.
Warm baths or alcohol compresses relieve the pain, which can persist for several months even after the cast is removed, and painkillers are taken at night.
Effectiveness of taping in ankle fractures
Kinesio tape is an elastic tape with an adhesive layer that has the ability to stretch and contract, just like the skin and muscles of the human body. The patches are firmly attached to the body and allow it to breathe. The use of tape for an ankle fracture offers several advantages at once:
- The skin under the patch is lifted, which normalizes the flow of lymph and blood to the muscles. The swelling is relieved and the inflammation goes down;
- Gentle immobilisation of the joint. Elastic bands provide effective support. Does not limit the biomechanics of movement;
- Enables therapeutic exercises. The taping ensures even distribution and stress reduction. Eliminates the risk of re-injury and pain;
- Prevents the development of abnormal movement patterns. Wearing taping ensures an anatomically correct position of the ankle, avoiding gait disturbances;
- prevention of injuries. Wearing taping prevents re-injury.
Taping of the ankle after a fracture
The effectiveness of the taping treatment depends on the correct application of the elastic band. The location of the lymph nodes, muscles and ligaments should be considered when applying. Incorrect application of the taping can lead to aggravation of ankle symptoms after an injury.
The choice of taping should be made by a specialist. The tape is most commonly applied as follows:
- The skin of the lower leg at the site of the injury is prepared. The hair is removed, the skin is cleaned and degreased with medicinal alcohol;
- Prepare 2 I-shaped ribbons 5 cm wide. The length of the first band should correspond to the distance between the middle and bottom third of the shin as it passes through the heel and a similar area on the other side. The length of the second strap should correspond to the distance from the inside to the outside of the heel bone. The ends of the ribbon should be rounded;
- The patient lies on his back and bends the leg at the knee. The foot should be positioned at a 90° angle;
- The first tape is applied from the middle over the sole area and the heel bone. One side of the band goes on the outside of the ankle, the other on the inside. The bands are applied without tension;
- Starting from the middle, the second tape is applied diagonally with slight tension from the flexion line to the joint gap. The ends of the band should be close to the heel bone. They are applied without tension.
The application can last up to 5 days. After removal, at least 2 hours should elapse before a new bandage is applied. The duration of the treatment is determined by the specialist.
Causes and treatment of fractures of the ankle
The causes of fractures are obvious: thrown punches, unfortunate falls and landings, bruises, jumps, risky sports.
Therapy for the treatment of the ankle is divided into clinical and surgical treatment. Depending on the type of fracture, the complications present and the duration of the treatment, the necessary treatment is selected.

Clinical treatment of open fractures with displacement consists of repositioning of the bone by a trauma surgeon under general or local anesthesia, followed by suturing of the wound and application of a cast.
If it is a closed, uncomplicated joint fracture, medical treatment is limited to applying a plaster cast.
The surgical route is chosen by the doctor when the bone fragments cannot be reassembled or when there is a tear in the meniscus or blood vessels. Special tools such as implants and mechanical components are then required. During the operation, the damaged bones are repaired or replaced with suitable implants. This also removes dying tissue.
With complicated fractures of the ankle, the patient has to wear a plaster cast for a long time.
Therefore, attention should be paid to the condition of the affected limb. Especially if sensations like:

If this is the case, the doctor should be informed of this condition immediately as it may be the beginning of tissue necrosis.
It will likely be necessary to cut open the bandage and take steps to prevent cell death.
Rehabilitation in the post-traumatic period
The most important principles of rehabilitation after injury are consistency and graduality. Physiotherapy, physical therapy and massage are the main methods. Mobility aids (crutches) are also recommended during the rehabilitation period to avoid overloading the joint.
Physiotherapy is of great importance in rehabilitation, especially in the postoperative period. The exercises, appropriately selected by the instructor, improve muscle and vascular tone, increase their strength, increase the ability to nourish the joint and allow the gradual recovery of the lost function of the ankle.

A standard set of recovery exercises includes:
- Movements first with the toes and then with the ankle in a seated position.
- Cross-legged ('scissors') movements.
- Roll a ball with your feet.
- Crouch on toes and walk on heels.
Regular massages can sensitize the injured area, normalize blood and lymphatic circulation and relieve muscle tension.
Peculiarities of thigh fractures
The number of people who have suffered a hip fracture has increased significantly over the past decade. In Russia they make up 6 % of the population. Such injuries are very dangerous for the whole body because they cause complications: there are muscles, blood vessels and nerves near the bone, which are also damaged. There is a branch of the main artery near the hip, so an injury can provoke profuse bleeding, which is dangerous to health and even life.
After hip surgery, especially after a displaced fracture, the patient needs comprehensive treatment to minimize the unpleasant consequences of this serious injury. Reconstructive treatments should be carried out in the first few days after the operation.

As a result of a thigh fracture, the following irreversible consequences can occur: reduced mobility of the limbs, impaired muscle function, significant weight loss. The injured person can even become disabled. In order to avoid health problems in the future, it is important to follow all the treatment and rehabilitation recommendations given by doctors.
There are many causes of a hip fracture:
- Pressure on the femur that occurs when jumping, falling, traffic accidents, athletes or workers in various industries.
- Decreased bone mineral content in the elderly. People who take long-term corticosteroid medications and women who suffer from hormonal imbalances are also at risk.
- Indirect injuries caused by sudden movements, bending or twisting of the limbs.
People who have suffered this complex injury notice severe pain at the point of fracture. The hip and knee joints are stiff and they can no longer move independently. When the patient presses the injured area with his fingers, he feels severe pain and incredible mobility of bone fragments. Pain also occurs with axial loading of the leg.
Rehabilitation after surgical treatment
The hip fracture patient must lie in a special functional bed after the insertion of a skeletal splint. Standing up on one's own is strictly forbidden, but one can stand up and sit on the bed by holding on to a belt or handrails, which can be found on special furniture in the trauma departments of the clinics. Breathing training is just as important to the patient's recovery as the healing of bone and muscle tissue.
It is useful to train the breathing apparatus with simple exercises such as blowing up rubber balls or exhaling into a hose with one end placed in a bowl of water.
The patient is on strict bed rest for three days. After this time, the patient can do physical exercises, but is not yet allowed to get up. The exercises are individual for each patient and can only be selected by the rehabilitation therapist. The trainer monitors compliance and regularity with the exercises by the patient.
A fracture of any severity always results in a ridge fracture of the bone. In order for these to heal better, the patient must perform exercises that relax the thigh muscles. A major inconvenience that patients experience when lying down for long periods of time is bed sores. In order to avoid this unpleasant phenomenon, patients are advised to perform a few simple exercises: raising the elbow and repeating this exercise 10 times. The bedridden patient should wear an elastic band under the body parts that come in contact with the bed (heels, buttocks and lower back). A more modern version of these anti-decubitus devices are special orthopedic mattresses.

After some time, patients are allowed to perform more advanced exercises: bending and reversing the legs in the knee and ankle areas. The next step is a circular motion with the hands, similar to stretching an invisible rubber band that the patient imagines. A support trainer helps develop the movements of the affected leg.
Treatment at the Energy Health Clinic
Energy Health Clinic doctors are always ready to treat patients of any age. We conduct a thorough examination, determine the possible causes of encephalopathy and take all measures to eliminate them:
- We prescribe the most appropriate therapy and describe the course of treatment and the frequency of disease recurrence;
- We perform all the necessary manipulations (infusions, intravenous and intramuscular injections) in a comfortable lounge and manipulation room;
- Complement your therapy with modern physiotherapeutic treatments;
- Massages and prescription of physiotherapy treatments for maximum effectiveness.
Our neurologists will monitor the patient's condition and adjust treatment if necessary. Treating encephalopathy is a long and complex process, but we are ready to tackle it.
Benefits of the clinic
If you need a thorough examination and quality treatment, we welcome you to Health Energy Clinic. The following awaits you in our clinic
- experienced medical specialists who undergo regular training to keep abreast of all new trends in the world of medicine;
- modern diagnostic equipment;
- all the necessary equipment for physiotherapy, massage and physical therapy;
- an in-house day clinic for the slow administration of drip medication;
- Affordable prices for all services.
If you or a loved one experience symptoms of encephalopathy, you should not hesitate to contact your doctor. The earlier treatment begins, the better the results will be. Make an appointment at the Energy Health Clinic and let our doctors determine the best treatment for you.
Read more:- Photograph of a person's leg with a description.
- How do you tell if it's an ankle fracture or a dislocation?.
- Photo of the ankle.
- Damaged ligaments of the ankle photo.
- How to distinguish a fracture from an ankle sprain.
- Photo of the ligatures.
- Treatment of torn ligaments in the ankle.
- Photo: Outer malleolus fracture.
