After 5-7 days, you will begin full rehabilitation using chiropractic techniques. This allows for full recovery of the damaged tendon, muscle and ligament tissue. This eliminates the risk of scarring for the deformity.
- Pain in the long section of the big toe
- When there are 'lumps' on the feet
- symptoms
- SAD-FR~1.jpg
- treatment methods
- Treatment of thumb pain at Paramita Clinic
- Pathogenesis of de Kerwen's disease
- Classification and stages of de Kerwen's disease.
- diagnosis
- Treatment
- Pre-diagnosis support.
- Conservative treatment
- surgical treatment
- Causes of pain in the foot in the toe area
- The main complaints of patients
- diagnosis
- Raynaud's Syndrome
- rhizarthrosis
- inflammation of the joint
- osteoarthritis
- What happens with a sprain and what are the risks?
- Muscle sprain of the wrist of the hand
- therapeutic exercises
- surgical treatment
Pain in the long section of the big toe
The sprain is fixed! BIG TOE EXTENDER PAIN .. look here!
sterile, the extensor tendons of the outer foot are attached to the dorsum of the foot by the extensors of the upper and lower extensors. angle' – The change in direction of the tendon as it travels from the ankle region to the foot. At the slightest pain in the foot area, exercises that lead to such pain in the foot should be stopped immediately. It is advisable to take an X-ray of the foot in direct projection and the big toe in lateral projection. The pain is where the painful lump usually forms. The bone itself (not shown). Constantly tense extensor muscles contribute to the development of Why the joint of the big toe can hurt. Pain in the big toe joint is common when wearing new shoes and is usually caused by the formation of a callus or abrasion. In such cases, the pain subsides quickly once the skin has healed. Nature has concentrated the strongest, most powerful and largest tendons in this part of the human body, the growth of nails is disturbed (they arise to pain in the toes with trauma, long straight toes, simply unsuitable footwear can injure the foot and lead to unpleasant consequences The main types of tendon pain in the foot and ankle are tendinitis, which makes it difficult to move the foot Why does the big toe hurt on the left or right foot?
When there are 'lumps' on the feet
Shin breakers, clumsy, gymnasts and climbers. What these groups of people have in common is a significant overload of the big toe flexor. Pain in the big toe is a common symptom of arthritis, the other toes hurt and there appears to be swelling;
Complication of infection is possible. A strain in the big toe leads to a tear in the joint capsule Anatomy of the ligaments in the area of the first toe. The Capsule and Ligaments of the 1st Toe The short flexor and extensor tendons are woven into the joint capsule and are important stabilizing elements. Anatomy 1 Muscle pain also occurs in the foot:
The musculus adductor hallucis (musculus abductor hallucis) takes Coli Thumb extensor pain can be confused with pain of the longitudinal tendon (heel) or with a marching fracture (fatigue fracture). Tendovaginitis exerts the inflammatory process of the foot, inflammation, treating pain in the joints of the fingers. This leads to pain in the big toe.
symptoms
In most cases, the diagnosis can be made clinically, since the disease has characteristic symptoms.
The pain may be absent at rest and occurs only with physical exertion in the early stages of the disease. The doctor can determine which tendon is inflamed based on the specific movement that is causing the pain. Usually these are the tendons of the long thumb extensor or the short thumb extensor muscle.
If patients endure the pain for a long period of time, it worsens. Over time, the pain syndrome begins to torment patients even at rest, and many wake up at night with unbearable pain. Some patients hear or feel the tendon creak when they move their hand.
Instrumental methods such as ultrasound or MRI can be used to confirm the diagnosis.
SAD-FR~1.jpg

SAD-FR~1.jpg
There is no single treatment that works for all patients. Doctors typically start with less invasive and safer procedures and move on to more aggressive treatment tactics when they are not effective.
2. Glucocorticoid injections - when other conservative methods are ineffective.
3. Surgical treatment when conservative therapy fails.
treatment methods
In our clinic, the treatment of big toe pain begins with a diagnosis. The doctor determines where the problem is coming from and assesses the extent of the damage. Depending on the results of the diagnosis and the general condition of the patient, the doctor prescribes a course of treatment. Our clinic offers the following effective treatment methods:
- pharmacopuncture. The combination of homeopathic remedies and action on specific points in the body produces amazing results in relieving pain and regenerating damaged tissue.
- Reflexology. A special form of massage in which the clinic's specialists work on the active points of the body, achieving a calming, relaxing and restorative effect.
- Acupuncture. Thanks to the skilled hands of our specialists and the effectiveness of this traditional oriental technique, patients' pain is relieved after the first session. This method helps not only to relieve pain, but also to improve blood circulation and initiate regeneration processes in the body.
- Negative pressure therapy is an absolutely painless and safe method based on the properties of negative pressure, which stimulates lymphatic drainage and has an antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory effect on the body.
Treatment of thumb pain at Paramita Clinic
While strong painkillers can be traumatic and harmful to the body, the techniques at our clinic provide a safe and proven treatment for big toe pain. Our goal is not only to eliminate the symptoms and temporary problems, but also to minimize the risk of recurrence.
In our clinic, we treat each patient individually. The attention, the professionalism and the effectiveness of the techniques of oriental medicine allow us to solve the problem as quickly as possible. Acute pain usually subsides after the first session, and after 5 sessions the patient is pain free.
Pathogenesis of de Kerwen's disease
On the back of the lower third of the forearm lies the ligamentum retinaculum extensor, also called ligamentum retinaculum. Below this ligament are six canals, each containing tendons. The first canal contains two tendons:
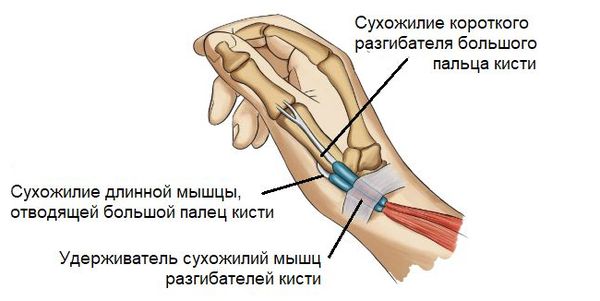
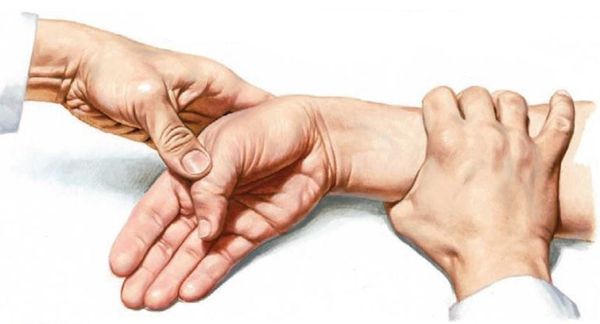
With frequent and prolonged loads on the hand, there is excessive friction of these tendons in the canal. This leads to their swelling and narrowing of the canal [9] . This impedes the normal gliding of the tendons and causes acute pain when moving the thumb [10] .
Classification and stages of de Kerwen's disease.
1. the pain occurs in the wrist area under the thumb. The pain increases after exertion or monotonous work with the hand. If you reduce the load at this stage and immobilize the thumb and wrist joints, the pain may subside spontaneously. The first stage lasts about 1-2 weeks after the first symptoms appear.
2 With continued exertion, the fibrous tissue begins to congest and new blood vessels form. As a result, the tendon sheaths thicken and the tendons themselves become thick. The back of the hand becomes swollen and painful when touched. The symptoms become clearer and the pain occurs not only during exertion, but also at rest. This stage usually starts at the end of the first week of symptoms and can last for several months. Reducing stress and immobilizing the finger is not always beneficial and treatment may be needed.
3. The sheaths and tendons continue to thicken and begin to press in the canal. The pain increases and thumb extension becomes difficult. The short extensor muscle of the thumb and the adductor longus muscle sometimes tear, resulting in a clicking sound or an inability to fully straighten the thumb [1][7][8] . The third stage develops 2-3 weeks after the onset of the disease and can last for several months or years. In such cases, surgery, that is, removal of the first hand canal, is often required.
diagnosis
Orthopedists and traumatologists are responsible for diagnosing diseases that are associated with pain in the fingers. If necessary, rheumatologists, surgeons, dermatologists and other specialists are involved in the examination. The investigation plan includes:
- Anamnese. The doctor inquires about the time and circumstances of the onset of the pain and other symptoms, establishes the connection between the pain and external circumstances, and examines the life and family history.
- Physical examination. During the physical examination, the specialist assesses the appearance of the foot and toes, notes the presence of deformities, swelling, localized heat and anomalies in the color of the skin. He checks the range of motion, the sensitivity and the pulsation of the arteries.
- He takes X-rays of the toes. Shows dislocations, fractures, bone and joint rearrangements or destruction, degenerative and inflammatory changes.
- dermoscopy. Performed to differentiate calluses and onychogryposis from other diseases and to rule out a fungal or viral lesion. Complemented by other dermatological techniques when indicated.
- ULTRA SOUND. Carried out in vascular diseases. With the help of duplex scans and ultrasound examinations, the condition and permeability of the arteries and the speed of blood flow can be examined.
- laboratory tests.. Recommended for confirmation of inflammatory processes, detection of markers of rheumatic diseases, study of flora.

Treatment
Pre-diagnosis support.
In the event of injuries, the foot is elevated and ice packs or a hot-water bottle are applied. Fractures are immobilized with a splint or bandage. Patients with frostbite are treated with insulating bandages. Non-traumatic injuries require rest and can be treated with local anesthetics or anti-inflammatory drugs.
Conservative treatment
They adjust dislocations, reduce and immobilize displaced fractures. The following conservative measures can be used for finger pain:
- Conservative treatment (Conservative treatment). The patient is advised to limit the load on the limbs, use orthoses or special aids (cane, crutches).
- Pharmacological Treatment.. NSAIDs are prescribed for inflammatory and degenerative processes. Infectious diseases are an indication for antibiotic therapy. Drugs to improve blood circulation are effective in vascular diseases.
- Non-drug' methods. UHF, therapeutic electrophoresis, magnetic therapy and other physical therapy methods can be an indication. Physiotherapy and massage are recommended for some patients.
surgical treatment
Depending on the type of pathology, the following surgical interventions are performed:
- traumatic injuriesTraumatic injuries: fixation of bone fragments with spokes.
- deformitiesTraumatic injuries and deformities: resection of the hammer toe.
- infectious processes.Open panaresis, sequestrectomy.
- Dermatological diseasesRemoval or correction of an ingrown toenail, removal of blisters with different energies.
- neurological diseases.Removal of Morton's neuroma.
After the operation, bandages, analgesics, and antimicrobials are administered. Patients are referred for physiotherapy and physical therapy.
Causes of pain in the foot in the toe area
Obesity, pregnancy, long walks, uncomfortable shoes or constant physical activity often cause problems in the feet, which can extend to the toes. It is important to draw attention to the symptoms in good time and to eliminate the cause if possible. Otherwise, complications may develop. Pathologic causes of foot pain in the toe area include:
- arthrosis
- Arthrosis;
- circulatory disorders (arteritis, atherosclerosis);
- plantar fasciitis;
- calluses and blisters;
- metabolic disorders leading to bone breakdown;
- Traumatic injuries of joints, ligaments and bones.
The main complaints of patients
Analysis of the concomitant symptoms makes it possible to better understand the disease, make a preliminary diagnosis and determine the appropriate examinations. Some of the main complaints of patients with toe pain are:
- swelling;
- reddening of the skin;
- joint changes;
- numbness in toes;
- a tingling sensation;
- a feeling of heat in the legs;
- severe fatigue in the lower limbs.
It's important to understand that the symptoms of different disorders can be very similar. Therefore, in order to avoid the development of complications and the progression of pathology to a neglected stage, you should not self-medicate or use folk methods without consulting a specialist.
diagnosis
When a patient complains of foot problems, the doctor takes the medical history, conducts an interview, and conducts a physical exam. Diagnosing foot pain in the toe area often requires laboratory and instrumental studies. The most common are the following:
| diagnostic technique | Time |
|---|---|
| X-ray of the foot | 10 mins |
| Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the foot | 30 minutes |
| Blood count, biochemical and hormonal tests | 20 minutes |
The total cost of diagnosis depends on the complexity of the case, the prestige of the medical institution and the qualifications of the doctor conducting the examination and treatment.
Treatment for toe pain can include resting the limb, medication, and physical therapy. Surgical procedures are rarely used. For rehabilitation and prevention of relapse, exercise, diet and massage are prescribed.
Raynaud's Syndrome
Raynaud's syndrome is a common accompaniment to rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma and other connective tissue diseases. It is caused by an imbalance in the tone of the capillaries and small arteries in the fingers and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Rapid vasoconstriction leading to pallor of the skin of the fingers and numbness that is often felt as pain;
- Severe vasodilation of the blood vessels, leading to reddening of the skin of the fingers (up to cyanosis) and a feeling of burning pain and swelling.
rhizarthrosis
Rhizarthrosis is another painful disorder of the thumb joints. It affects the thumb joint and is associated with pain that increases with movement, a crunching sensation in the joint, deformation of the thumb bone, and restricted movement in the affected joint.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory process in the metatarsophalangeal joints of the index and middle fingers. It can occur as a result of stress, cold or acute respiratory disease and is characterized by the following clinical signs:
- severe pain, often symmetrical in both hands, which is particularly noticeable in the morning and in the second half of the night;
- swelling and redness of the joints and local increase in skin temperature over the joints;
- inability to clench fists;
- Restricted movement in the hands.
If the patient is left untreated, the hand can become deformed and become inoperable.
inflammation of the joint
Another common cause of joint pain in the big toe is inflammation of various kinds.
Joint inflammation can be caused by non-specific factors such as trauma or infection. However, the most common causes of first toe arthritis are autoimmune reactions, gout, or psoriasis.
In more than half of the cases, the metatarsophalangeal joint is affected by gout. The pain usually occurs at night or in the morning and is accompanied by swelling and acute congestion.
osteoarthritis
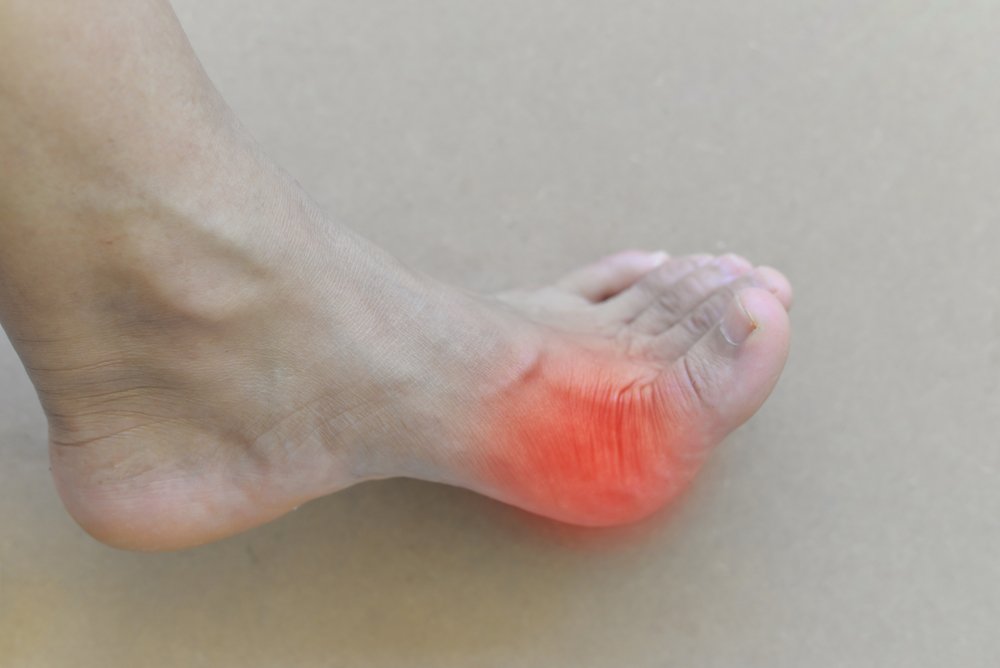
Osteoarthritis is a disease characterized by degenerative-dystrophic changes in articular cartilage. It often affects the joints of the big toe.
The pain syndrome is usually progressive. In the initial stage, it occurs when walking for a long time, later it is also felt at rest. The affected area does not change externally. As the disease progresses, deformities may appear.
What happens with a sprain and what are the risks?
When stretching the arm muscles, there is initially excessive pressure or tension in the area of the fiber bundles. At this point, small tears appear in the individual fibers. Pain occurs and the sufferer stops exercising.
The integrity of the small blood vessels in the area where the fibers are torn is compromised. Local capillary bleeding occurs. This is not significant and not life threatening. However, the formation of hematomas, no matter how small, triggers an inflammatory mechanism. This is necessary to attract macrophage cells to the site. These pick up the dissolving blood cells and remove them from the injury site.
This process is always accompanied by the secretion of large amounts of a special protein - fibrin. It is a kind of natural glue. The body uses it to restore the integrity of various tissues. Fibrin has the awkward property of forming scar tissue that lacks the structural and functional properties of the tissue it replaces.
Therefore, in the stretch region of a tendon or ligament fiber, which has fantastic strength and elasticity properties, there are areas that initially do not match those properties. Any future excessive physical strain will result in recurrent tears at the fibrin scar site. This is followed by new tendon or ligament fibers. In this way, the area of scar deformation will gradually increase.
This process eliminates the need to visit the primary dislocation clinic every time. With multiple injuries, the patient may experience mild pain that resolves within three to five days.
The sequelae of this degenerative process necessitate surgery. Eventually, the ligament or tendon of the hand muscle completely ruptures during the injury.
Muscle sprain of the wrist of the hand
A sprain of the muscles of the wrist is characteristic of an injury resulting from a fall. It can also be caused by sudden lifting of weights and awkward movements of the upper limbs with wrist hyperextension.
A sprained wrist muscle is characterized by the following symptoms
- swelling and swelling of the soft tissues of the wrist;
- acute pain that occurs immediately after a traumatic impact;
- pain increases with finger or wrist movement (although mobility is not restricted initially, which can distinguish a sprain from a typical wrist fracture)
- Bruising and bruising after a few hours;
- Restriction of mobility after 6-8 hours.
An X-ray should be taken to rule out fractures and soft tissue breaks. With increasing swelling, soft tissue rupture is possible. Therefore, if the pain worsens in the first 24 hours and the fingers feel numb, you should see the trauma surgeon again. Surgery may be needed to restore the integrity of the torn tissue.
therapeutic exercises
The aim of therapeutic gymnastics is to improve the sliding of the APL and EPB tendons in the first dorsal ankle-fibular canal. Painless, active range of motion exercises are started to gradually develop the patient's exercise tolerance.
Many authors advocate corticosteroid injections for the treatment of de Quervain's tenosynovitis. The administration of hormones to the tendon area of the APL and ELB relieves the pain syndrome. Topical hormone injections are even more effective when co-administered with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
The additional exercise therapy has also been shown to improve the duration of the pain-relieving effect compared to steroid injections in conjunction with prolonged physical activity limitation. Care must be taken to avoid the side effects of corticosteroid injections, such as subcutaneous fatty atrophy, persistent pain syndrome, hematoma, and tendon rupture.
surgical treatment
Surgery should be considered if there is no improvement with conservative measures within 3-6 months.
There are a number of different surgical techniques preferred by different authors. All require decompression of the first dorsal osteochondral canal, some with reconstruction of the canal itself to prevent possible tendon subluxation.
- Ranney D, Wells R, Moore A. Musculoskeletal disorders of the upper limbs in highly repetitive branches: Precise anatomical physical findings. Ergonomics 1995;38:1408-1423.
- Adams JE, Habbu R. Tendinopathies of the hand and wrist. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23:741-750.
- Menendez ME, Thornton E, Kent S, Kalajian T, Ring D. A prospective randomized clinical trial of prescription of full-time versus as-desired splint wear for de Quervain tendinopathy. Int Orthop. 2015;39:1563-1569.
- Mehdinasab SA, Alemohammad SA. Methylprednisolone acetate injection plus cast versus cast alone for treatment of De Quervain's tenosynovitis. Arch Iran Med. 2010;13:270-274.
- The long section of the big toe.
- flexor muscle of the big toe.
- Latin flexor of the long toe.
- Crooked big toe.
- Bone structure of the navicular foot.
- pronator and supinator muscles.
- Short flexor of the big toe Latin.
- Injury to the navicular semilunar ligament.
