CPS block causes pain on the affected side that can radiate to the lower back, buttocks, and hamstrings. This pain is similar to the symptoms that occur with a herniated disc or ankylosing spondylitis. Your doctor will take this into account when making the diagnosis.
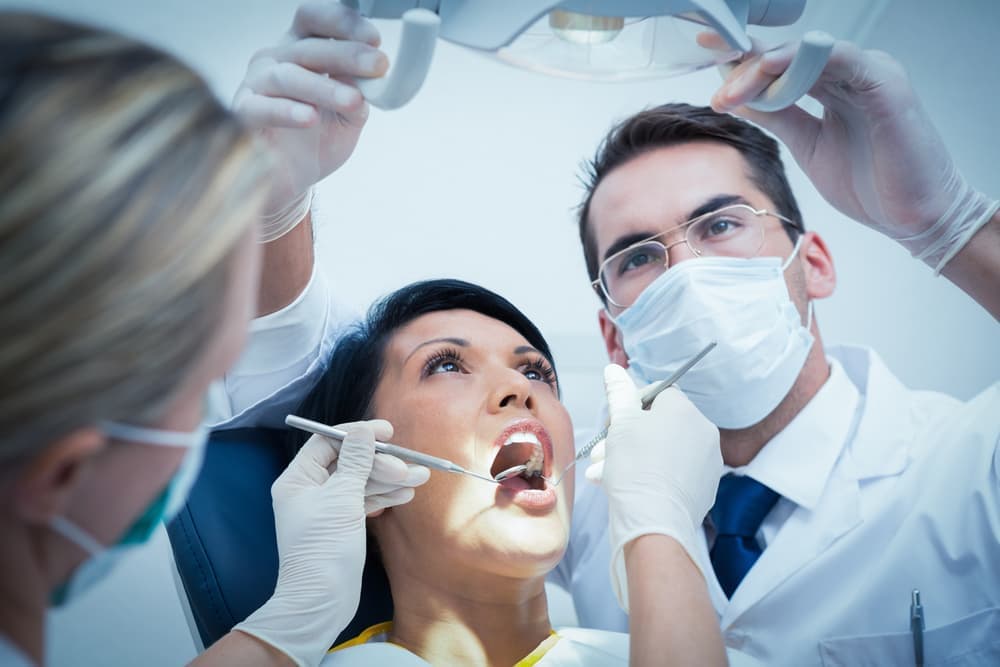

- Periodontal inflammation - symptoms and treatment
- Tooth periostitis: symptoms
- Causes of Anopic Pain Syndrome
- Symptoms of Anopic Pain Syndrome
- diagnosis of the disorder
- prevention
- Bone pain after a fracture
- treatment of bone pain
- Pain in the pelvic bones, back and lower back
- Treatment of Sinus Syndrome
- patient education
- orthopedic insoles
- Medical therapy
- Advantages of our clinic for pain therapy.
- causes of gout
- symptoms of gout
- types of tinnitus
- What you can and cannot do about an earache
- How can the pain be relieved?
- What not to do.
Periodontal inflammation - symptoms and treatment
Many people know the phenomenon as bleeding – when the cheek swells in front of their eyes next to a sore tooth and painkillers do not help with the acute pain. The periosteum of the tooth becomes inflamed, or – as doctors say – odontogenic periostitis of the jaw has developed. This disease is in itself a complication of dental problems (periodontal disease, periodontal disease), but if not treated properly, it can cause even more serious complications.
The most common of these is odontogenic periostitis of the jaw, an inflammatory process caused by diseases of the teeth or periosteal tissues. Deep caries, tooth pulpitis, periodontitis (an inflammatory process at the tip of the tooth root), periodontitis - all these diseases lead to the occurrence of inflammation if not treated in time. Another cause of inflammation can be alveolitis – inflammation of the alveolar periosteum, in some cases after tooth extraction. As a rule, periosteum inflammation after tooth extraction occurs in patients who do not immediately go to the dentist at the first signs of complications in the postoperative period.

Less common is toxic periostitis, which is caused by penetration of an infection through the blood or lymph (usually from a common infectious disease). It can also be caused by trauma to the jawbone or surrounding soft tissue.
Tooth periostitis: symptoms
Depending on the form and localization of the process, the symptoms can be as follows:
- General symptoms: pronounced pain at the site of inflammation, swelling, noticeable swelling, discoloration of the gums, mobility of the tooth unit, which caused the spread of the pathological process. Facial swelling looks different depending on the location of the infection: if the inflammation develops near the front teeth, the upper lip or middle third of the face swells; if the inflammation occurs near the chewing teeth, the cheek swells, sometimes also the lower eyelid and parotid area. To see what the different types of periodontal disease look like, see the photos.
- Acute serous periostitis of the lower or upper jaw is accompanied by severe reddening of the mucous membranes, rapid formation of nodules and increased body temperature. The general symptoms of this form of inflammation are particularly pronounced.
- Acute pus disease is characterized by severe acute pain, which decreases when it is cold and increases when it is warm. Sleep and appetite are disturbed, the temperature rises significantly, and the general condition of the patient worsens. The pain is usually radiated through the affected nerve branches. For example, acute purulent periosteum inflammation of the lower jaw can cause pain in the neck, chin, ear and jaw joint. The purulent inflammation of the periosteum of the upper jaw often causes pain in the orbit, temporal bone and ear.
- The chronic form of the disease is quite rare, with chronic mandibular periostitis being more common. The symptoms are mild, the swelling is barely noticeable and can develop gradually over a long period of time. Pain and discomfort appear from time to time (exacerbation phases).
At the initial stage of the inflammatory process, it is usually serous, and later, if left untreated, becomes purulent. If there is a large amount of pus, the abscess can rupture and drain the pus into the mouth. The swelling will go down and the pain will subside. Some patients become complacent and think that the problem is solved and do not rush to the dentist. In reality, this is only a temporary relief, because the pathological process can start again at any time.
Causes of Anopic Pain Syndrome
- pollakiuria;
- urinary incontinence;
- Chronic and recurrent diseases of the genital organs, bladder and rectum;
- visceroptosis (prolapse of internal organs);
- Cystic growths in the pelvis.
Coccygodynic pain occurs in patients with pathology of the sacral nerve plexus, periosteal and periosteal lesions in this area and the effects of trauma. Coccygodynia can be a symptom of a neoplastic process in the sacrococcygeal region. If a tumor is suspected, the admitting doctor refers the patient to an oncologist appointment at Yusupov Hospital.
Ananocopic pain syndrome can be caused by:
- limited mobility of the sciatic joint that occurs as a result of trauma
- Ischemia of the vertebral, subcostal, and prevertebral nerve plexuses resulting in intradural sympathetic plexitis, tunnel neuropathies, and reactive neuritis;
- trauma to the sacroiliac joint during delivery of a large fetus;
- Developmental anomalies or acquired defects of the pelvis and lumbar region;
- pathological processes in the pelvic organs and fibers that cause reflex musculo-tonic pain reactions or nerve irritation;
- surgical interventions in the area of the anorectum, perineum or pelvic organs.
In 30 % of the cases, doctors diagnose idiopathic coccygodynia. It is not related to trauma or organic pathology of the pelvic organs. The pain syndrome can arise from pathomorphological manifestations in the hypogastric and anterosacral nerve plexus, impaired venous drainage and a reduced pain sensitivity threshold.
Symptoms of Anopic Pain Syndrome
Patients complain of pain in the coccyx, sacrum, and periumbilical region. They are unable to accurately describe their pain. The pain is usually nagging, dull, throbbing, aching, and sometimes burning. It is limited to the tailbone or nearby areas - perineum, groin, anus, genitals, lower lumbar region, sacrum, hips. The pain disappears or diminishes when the patient stands and worsens when sitting. The pain increases when the patient lies on his back, gets up, does sports and walks, bends the trunk, during sexual intercourse and during defecation.
Patients are forced to sit on one buttock. Your movements will become fluid and cautious. Pain crises are triggered by physical factors, excessive exertion, exacerbation of chronic diseases, hypothermia, psychological stress or trauma. Intestinal disorders, peripheral vasospasm, vomiting, sweating, and pollakiuria are not uncommon in an exacerbation. Functional disorders of the pelvic and abdominal organs occur.
Over time, sitting ability asymmetry and scoliosis develop. In the early stages of the disease, patients develop depressive and asthenic reactions:
The patients develop fears of an incurable disease. In some cases, the pain syndrome is so severe that the patient is unable to sit up, bend their legs, or move their hips. His gait becomes unnatural, and he walks in small steps in an involuntarily half-stooped posture. Because the patient is in pain and unable to defecate, constipation may occur. Post-traumatic perianal pain syndrome resolves within 24 hours of injury and returns weeks or months later.
diagnosis of the disorder
A general blood test is usually not needed to diagnose the condition. If chronic low back pain occurs before the age of 45, doctors may draw blood for laboratory tests to rule out signs of spondylosis.
In addition to X-rays, computed tomography (CT) can reveal possible vertebral fractures or dislocations.
The doctor must correctly differentiate SPSS from other diseases with a similar clinical picture. This includes:
- tumors (e.g. spinal cancer);
- fractures or deformities of the bones;
- infections;
- Disc prolapse;
- ankylosing spondylitis;
- Diseases of the hip joint (e.g. arthrosis of the hip).
In the absence of absolute contraindications, doctors prescribe diclofenac or ibuprofen for short-term relief of acute pain. It is strictly forbidden to take NSAIDs for more than a week without consulting a doctor. Serious side effects, such as gastrointestinal bleeding, can occur if the drug is taken for a long time.
Other conservative treatments compensate for improper pelvic tension. The doctor recommends that the patient be given special shoe inserts or knee pads. In addition, various custom orthopedic bandages can be used to improve limb mobility. A number of pain relievers can be injected directly into the joint over a period of time until the symptoms completely disappear. Another measure is radio frequency therapy. In most cases, this therapy is not covered by statutory health insurance.
If conservative measures are not sufficient to relieve the pain of CPS, surgical measures can be used. As a rule, doctors do not know how long a patient must be treated to achieve significant results.
prevention
The most important preventive measure is to increase weekly physical activity and maintain optimal body weight. It is important to compensate for existing tension in the hip, knee or ankle area. It's important to take short breaks when exercising while seated. Some exercises can be performed to improve pelvic mobility.
Tip: It's important to see your doctor as soon as you have symptoms of acute sacroiliitis. During the acute phase (severe pain on the right or left side), painkillers should be taken. Depending on the degree of inflammation and the X-ray findings, the doctor will prescribe an appropriate anti-inflammatory treatment. Self-medication with untested medications is discouraged as it can have unpredictable effects.
Low back pain is the leading cause of physical activity limitations in people of working age. Among these symptoms, the sacroiliac joint (SJP) accounts for 30-90 %.
The sacroiliac joint (CJA) is the largest joint. The range of motion of the sacroiliac joint is limited and its primary function is support. The CPS supports the upper body and reduces the strain when walking. The joint is strengthened by the ligaments that limit its mobility: the anterior and posterior sacroiliac ligaments, the trochlear sacroiliac ligament, and the intercondylar ligament. The CPS interacts with muscles and fascia, including the thoracolumbar fascia, the gluteus medius, the gluteus medius, and the latissimus dorsi. According to W. King et al. (2015) it is more accurate to refer to the sacroiliac complex than to the CPS, which includes the joint itself and its supporting ligaments, any of which can be a source of pain.
The terms used in the literature to describe pain arising from CPPS are 'CPPS dysfunction', 'CPPS pain syndrome' (perhaps simply 'CPPS syndrome') and 'CPPS block'. The term 'CPPS pain syndrome' is used for pain originating directly from the structures of the joint itself, while the term 'CPPS dysfunction' is used for pain originating from both intra- and extra-articular structures. The term 'locked joint' is more commonly used when there is significant restriction of movement in the joint.
Bone pain after a fracture
Ossalgia is quite common in people after fractures. In most cases, they appear after excessive physical exertion. In addition, old fractures can be caused by blood diseases (lymphogranulomatosis, leukemia), disorders of collagen synthesis, autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases and severe allergic reactions. If a bone is painful on pressure after a fracture, it is advisable to see a specialist who, after examination and further tests, will recommend treatment. Vitamin and mineral supplements as well as calcium supplements can be useful as a prophylactic measure.
Diagnosis requires a comprehensive examination, including a comprehensive blood test and biochemistry, as well as device tests, such as B.
- Doppler ultrasound examination (USG)
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- electrospondylography; arthroscopy;
- X-ray examination;
- contrast-enhanced discography.
The choice of examination method is made individually, taking into account the patient's complaints.
treatment of bone pain
After carefully examining the patient and examining the results of the examination, the doctor prescribes a course of treatment. In addition to treating the underlying disease, painkillers and drugs to improve bone nutrition are prescribed. As the latter, chondroprotectors, vitamin and mineral complexes and dietary supplements can be recommended. Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are warranted for bone and joint pain with fever. Other methods include physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy and diet. With pain in the lower limbs, doctors often recommend the use of braces, special orthoses and knee pads to relieve the pressure on the joints and alleviate the patient's condition.
You will receive further information during the consultation hour. Your doctor will tell you what to do if your leg bones hurt when you walk and will prescribe a series of tests to determine the cause of your discomfort. You can make an appointment online and by calling the numbers above.
Pain in the pelvic bones, back and lower back
When pain in the lower back radiates to the pelvic bones, the first suspicion is lumbosacral osteochondrosis. It can occur in isolation, in combination with spondyloarthritis and vertebral instability, or complicated by a bulging or herniated disc. To make an accurate diagnosis, an examination by a specialist is required. It is also important to take x-rays in time to determine the location of the problem.
Persistent pain in the pelvic bones and lower back always leads to a destructive process. Pain is the body's signal that something is wrong on one side of the body or the other. In the early stages, lumbosacral osteochondrosis causes little pain and can be treated quickly and easily, but in the later stages, the person literally collapses in pain and needs long-term treatment.
If you have back and hip pain, it is advisable to see an experienced doctor as soon as possible for an accurate diagnosis. Chiropractic techniques can then be used to restore the health of your spine and hip joints. In our chiropractic clinic we use the following therapeutic techniques:
- Traction of the spine helps to eliminate compression of the radial and sciatic nerves in lumbosacral osteochondrosis;
- Osteopathy and massage can restore blood and lymph circulation and improve microcirculation in the affected area;
- Exercise therapy and kinesitherapy strengthen the muscular skeleton of the back and muscles of the lower limbs, which helps to quickly eliminate the negative symptoms and avoid the risk of future relapses;
- Reflex therapy to stimulate tissue regeneration by tapping into the body's hidden internal reserves;
- Laser therapy and other physiotherapeutic treatments.
Treatment of Sinus Syndrome
Each patient is treated individually, depending on the severity of the carpal tunnel syndrome and its cause. Mild neurological deficits are treated conservatively, while surgical treatment is indicated in more severe cases.
Conservative treatment is comprehensive and includes:
- instructing the patient in the prevention and treatment of ulnar nerve compression;
- orthoses;
- pharmacological treatment;
- physical therapy
patient education
In cubital tunnel syndrome, it is important to avoid positions and movements that could compress the ulnar nerve from surrounding anatomical structures. It is therefore advisable to avoid the habit of resting your elbows on hard surfaces, keeping your arms bent for long periods of time, such as B. on the phone, or sleeping with your arms bent under your head. Repeated bending and stretching movements of the upper limbs should also be avoided.
If the nature of the work does not allow you to avoid monotonous arm movements, more frequent breaks are recommended. It is advisable for office workers to put something soft under their elbows. However, it should also be ensured that the elbows do not hang down from the desk or rest on the edge of the desk.
orthopedic insoles
Using special bandages is an effective and safe way to prevent compression of the ulnar nerve. Patients are advised to wear orthotics to prevent them from fully flexing the elbow joint, especially at night.

Medical therapy
Pharmacotherapy is selected strictly individually, taking into account the nature of the existing concomitant diseases and the reasons for the development of ulnar canal syndrome. If necessary, patients receive symptomatic treatment to improve nerve conduction, improve nerve supply and reduce pain. This may include:
Advantages of our clinic for pain therapy.
Unique and proven methods of pain management: blockades, anesthetics, microinfusion pumps, RFD, port systems for long-term pain management
Own clinical diagnostics laboratory, X-ray diagnostics, rehabilitation center and multidisciplinary hospital - you get all diagnostics and treatment in one place.
A team of specialists (algologist - pain specialist, anesthetist, neurologist, traumatologist, rehabilitation specialist, psychotherapist, etc.) will take care of your pain immediately.
We apply western standards of treatment, and all doctors at the clinic have completed training in Israel.
We accurately diagnose the cause and relieve any type of pain, including chronic pain
convenient transportation to the clinic and fast pain relief
a personal manager will accompany you throughout your treatment
We host free seminars and webinars for our patients
comfortable rooms, operating theaters specially equipped for pain patients, no waiting times
causes of gout
All organic foods contain purines, which are the building blocks of RNA and DNA. Purine bases in food are broken down, producing uric acid. This is normal operation. Uric acid is present in body tissues and blood plasma. The blood carries uric acid to the kidneys, where it is filtered and excreted in the urine. Part of the uric acid (1/3) is excreted through the intestines. When this normal metabolism is disrupted, uric acid begins to build up in excessive amounts.
Disorders of purine metabolism can be caused by:
- genetic enzymopathy. Gout develops when the production of enzymes responsible for converting purine bases into uric acid and excreting it from the body deviates from the norm (deficiency of some enzymes is crucial, overactivity of others). This anomaly is largely due to DNA damage. The site responsible for these enzymes is on the X chromosome. Males have one X chromosome, females have two. As a result, gout is more common in men (women have a 'spare copy' of the appropriate genes, so to speak);
- an increased intake of purine bases.. In ancient times, gout was called the 'disease of kings'. Kings had the best diet of all, they could freely eat the meat of young animals, sausages and cream cakes (and these foods are leaders in purine content. Oily fish, meat and fish broth and legumes are also high in purines). Excess purines in the diet alone are not dangerous because the kidneys can normally handle all the uric acid they absorb. However, if there are genetic abnormalities or kidney problems, the likelihood of gout is very high;
- disturbed excretion of uric acid from the body. Kidney disease can decrease uric acid filtration. Less uric acid is excreted and the concentration in the blood increases;
- increased breakdown of endogenous purine compounds.. Man is part of the biological world and our body is built according to general laws. RNA and DNA are present in our bodies - in every cell - which means they have their own purine bases. Increased cellular breakdown (ie, catabolism - the breakdown of complex compounds into simpler ones) leads to the same rise in blood uric acid as when we ingest excessive amounts of external purines. Increased breakdown of endogenous purine compounds can be caused by radiotherapy or chemotherapy, taking certain medications or hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells in severe infections or blood formation disorders).
symptoms of gout
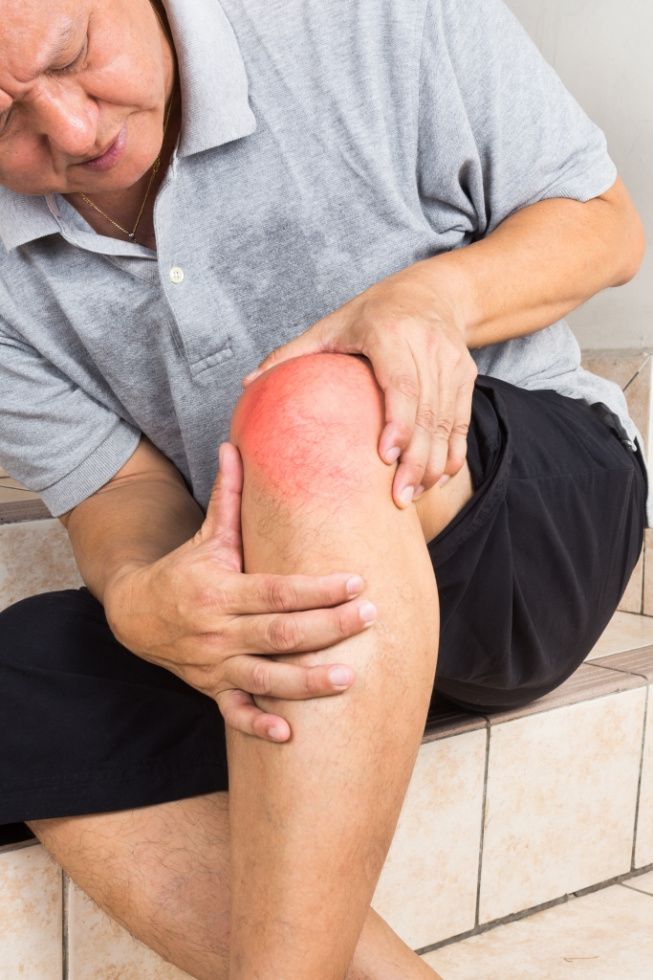
The first stage of gout is called hyperuricemia (high levels of uric acid in the blood). Hyperuricemia is detected by biochemical blood tests. In most cases, there are no other symptoms of the disease. Occasionally, there may be general weakness, sweating, itchy skin, and constipation.
Gout itself should be considered from the onset of an acute gout attack. Gouty arthritis can trigger an attack:
The joint of the big toe (big toe joint) is usually affected first. Usually only one joint of the foot is affected. Other small joints, such as the wrist or the metatarsophalangeal joints, are also often affected. Later, the gout attacks can also affect other joints. In women, the disease can initially affect several joints at the same time.
As a rule, a gout attack lasts no longer than 5-7 days, after which there is complete remission (all symptoms disappear) - until the next attack. This is called the intermittent ('interval-like') stage of gout. The disease can then progress to a chronic stage.
A gout attack is characterized by a sharp pain in a joint. The area around the joint becomes swollen and red quite quickly. The skin over the joint may turn blue. The patient feels chills and has a fever that can rise to 38°C or more. Any touching of the joint increases the pain, and the joint loses all mobility. The pain can be very severe and cannot be relieved with painkillers.
Most seizures occur at night and usually subside in the morning. In severe cases, however, the severe pain can last up to three days, after which the intensity slowly decreases.
types of tinnitus
Tinnitus pain can manifest itself in different ways. The specific nature of the pain is a guide to identifying the pathology.
- sudden pain It is accompanied by an acute sensation of pain and can be caused by trauma or a foreign body;
- progressive pain. Occurs against the background of pathology with moderate progression. May indicate a wax clog or an infection in the ear canal;
- Severe earache accompanied by throbbing. Characteristic of boils, SIA, trauma;
- It's piercing and sharp. The pain occurs intermittently and brings with it discomfort. The main cause is neuralgia;
- Dull pain. Occurs against the background of disseminated otitis media, may indicate the presence of a cerumen plug, in the chronic form - inflammation of the middle ear;
- itchy pain Refers to the cases where the lesion is external. May be due to otitis media, damage to the ear canal, or eczema;
- Intermittently. This type of sensation is characteristic of Irrigation Pain;
- Swallow. The causes include RSI, malignant growths in the mouth and throat, pharyngitis, tonsillitis.
What you can and cannot do about an earache
If your child has an earache, it's an emergency that requires a doctor's visit. If an appointment with an ENT doctor is necessary, you can make an appointment at our clinic.
How can the pain be relieved?
- ammonia and camphor. These solutions are mixed together. The gauze is dipped in the solution and placed in the ear for a few minutes to relieve pain;
- Onion-based decoction. Another way to ease the pain. The ear and the auditory canal are rubbed with the warm brew. This has a disinfecting effect and relieves pain.
Alternatively, a painkiller can be taken. In some cases, vasoconstrictive drops can also be used.

What not to do.
- heating of the ear. This measure can spread the infection;
- Treatment with antibiotics. This method is ineffective and can damage nerve endings;
- Using medication 'by prescription'. The use of drops is prescribed only by a doctor based on examinations and tests. Only the doctor can decide on the best treatment for the child and the adult, taking into account the specific clinical picture.
- 'Folk' methods of a radical nature.
Only experienced doctors with a high level of education work in our medical center in Geraci. We have precise equipment: a high-end ultrasound machine and our own laboratory for examinations.
You can view the cost of all Medical Center services under the 'Prices' section or by calling our 24-hour helpline at +7 (863) 333-20-11.
Read more:- Pain in short fibula when walking.
- Pain in the heel bone of the foot.
- pain in the tarsus.
- Why do feet hurt after running?.
- Which muscles hurt after running?.
- Pain in the periosteum of the tibia.
- Pain in the long extensor of the big toe.
- Pain in the crook of the foot.
