Knee reconstruction after injuries that do not require complete immobilization (sprains, twists), knee pain from inflammatory and degenerative diseases (bursitis, tendinitis), cruciate ligament injuries (torn), knee instability, prevention of sports injuries
Bands and orthoses for the knee
–> Hand +30 thumb +28 torso +6 collarbone +5 spine +90 thoracic spine +34 lumbar spine +31 lumbar spine +51 lumbosacral spine +24 body +35 abdomen +18 groin +7 hip +36 legs +254 thighs +8 knees shinbone +7 ankle +47 big toe +3 foot +12
–> Breakdown 46 Attitude 59 Sports 13 stabilizers 63 walking aids 1 To block 43 Tied together 36 elastic 15
-> Ligament injuries 91 fractions 26 arthrosis 57 stretches 60 arthrosis 47 Osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis) 40 paresis 32 paralysis 19 bruises 21 bursitis 11 tendonitis 14 osteoarthritis 10 Osgood-Schlatter disease 6 valgus 1 Dislocated knee joint 1 CEREBRAL PALSIA 3 neurological disorders 13 Kneecap subluxation 7 After reconstruction of knee ligaments 12 After injuries and operations 4 Synovitis Syndrome (Runner's Knee) 2 synovitis 12 Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis 1
- Orthopedic braces and posture corrections
- cervical bandages
- posture corrections
- posture corrections
- Tugging braces
- chest and lumbar bandages
- back bandages
- Lumbar and sacral orthoses
- ankle bandages, orthoses
- thumb braces
- Laced ankle bandages
- Split ankle wraps
- Sporty bandages
- Orthoses to immobilize the ankle
- ankle bandages
- Orthotics for ankle sprains
- Orthoses for heel bone fractures
- Orthoses for lateral stabilization
- Ankle orthosis with splint
- Flexible ankle bandage
- ankle brace
- Orthoses for metatarsal fractures
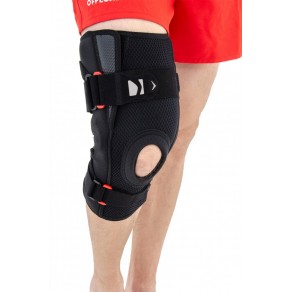
knee braces
The knee joint is a complex and important part of the human musculoskeletal system. Throughout life, it is constantly exposed to high loads, injuries and age-related changes. Athletes, overweight people and the elderly are particularly susceptible.
Knee braces are a group of orthopedic products used to treat and prevent knee problems and injuries. Most of them are easy to use, easy to put on and take off by yourself, fit snugly on the leg, and will not fall off or cause discomfort. Given the high level of responsibility in which orthoses move, manufacturers are paying more attention to the reliability of materials and production, as well as sorting out defects, which has a very positive effect on the final quality of the product.
The product is designed as a flexible orthopedic pad with strong Velcro straps for attachment. It is designed to redistribute the load on the injured part of the knee to the healthy muscles at the point of contact with the leg.
Construction
As a type of orthosis, the orthosis differs from a knee orthosis in several respects. Structurally, they are removable orthotics made of non-woven soft and rigid materials (neoprene, plastic, carbon fiber, metals, alloys). Design and manufacture are based on practical experience, modern medical advances, high-tech materials and innovative solutions. Many knee problems that used to be difficult to solve can now be successfully solved.
- Flexible cuffs (allow immobilisation on either side of the joint);
- polycentric locks (coordinate device and joint movement and have a sectorized range of motion from 0° to 150°);
- stoppers (used to limit or secure movement);
- straps (for attachment to the leg); and
- Snaps (to adjust the device to the size and individual parameters of the person).
The construction can be rigid, semi-rigid or soft and allow a certain range of motion through adjustments up to complete immobilization (as a body orthosis).
The height of the orthosis can vary: standard (covering at least the lower third of the thigh and the upper third of the lower leg) or short (optimal for athletes).
The manufacturers offer a specific range of sizes for children and adults, with the right-sized models fitting the leg optimally. Depending on the design, the models can be designed for men or women, for the left or right foot.
In special cases it makes sense to order a suitable orthosis according to the individual parameters and needs.
Therapeutic knee brace
Knee orthosis with lateral fixation - indications for use:
- joint instability, habitual dislocation;
- meniscus injuries, cruciate ligament sprains and cruciate ligament tears;
- Early phase of immobilization after fractures and dislocations;
- the postoperative period.
In children and adults, a ligament orthosis with articulated lateral limitation is also recommended for valgus or varus knee deformities that occur with X and O bends of the lower limbs.

Applying a knee orthosis with lateral limitation
Below you will find brief instructions on how to put on the orthosis correctly:
- Before putting the orthosis on the leg, set the flexion and extension angles specified by the doctor on the limiting mechanism.
- When you put the orthosis on the leg, first adjust the height of the lateral retaining pins. Make sure the constraining hinge mechanism is centered squarely on the outside of the hinge.
- Starting at the knee, first up the thigh and then down the shin, alternately adjust the straps and straps so that the product does not sag down the leg, but hugs it.
Do not pull the orthosis too tightly on the leg when putting it on. Impaired blood circulation impairs the regeneration process and in some cases can trigger the onset of necrosis.
note on the side. However, this type of orthosis is forbidden for people with dermatological problems and/or venous lesions of the lower limbs.
Incidentally, this type of orthosis with lateral fixation relieves the knee joint so effectively that it is also suitable for people with chronic knee joint pathology, e.g. B. in degenerative arthrosis grade III, is suitable.
rehabilitation
The principles of rehabilitation in conservative treatment are similar to those of postoperative treatment.
In general, for the ligament to recover in a neutral position, several important principles must be observed:
- Limit the influence of gravity. Advise the patient to avoid positions that cause shin laxity, such as flexing, for 6 weeks. B. Crouching against a wall. The patient may also be advised to place a pillow under the proximal part of the tibia when sleeping.
- One of the most important elements in treating an SCI injury is wearing a dynamic orthosis (orthosis). It acts like a spring and prevents excessive backward displacement of the tibia. This prevents the bone from 'collapsing'. Ideally, the orthosis should be worn around the clock for 16 weeks and only removed to shower. In 2010, a study was conducted with 21 participants. All subjects wore the orthosis for one year. According to the results of the study, the use of the orthosis contributed to a 2.3 mm reduction in posterior tibial extension. The results show that the orthosis has therapeutic properties and can be used to reduce the extent of damage. If the patient cannot afford a dynamic orthosis, a removable knee brace may be recommended as an alternative during the acute phase. Thereafter, the patient should wear an articulated bandage with a special pad over the SCA area for 12 months. Depending on the stability of the knee joint, the wearing time can be extended.
- When working on increasing the range of motion, choose exercises with the starting position lying on your stomach. This reduces the influence of gravity.
- If the injury is accompanied by intra-articular effusion or bleeding, then you should limit weight-bearing exercises.
- Isolated tendon contractions when the knee is flexed more than 15 degrees increase pressure on the VRS. For this reason, such exercises should be avoided for at least 16 weeks. Instead, exercises like the Romanian deadlift, where the squat angle is much smaller and therefore doesn't put undue stress on the shin, may be recommended.
Criteria for choosing the right orthosis
Orthoses are available in both standard and custom-made versions. The commonly used NKN 557 split orthosis has metal splints and polycentric joints to adjust knee flexion and is very comfortable to wear. In the case of individual preparation, the criteria depend on the respective diagnostic situation. However, the most important are:
- parameters and manufacturers. Same models but different brands may have slightly different parameters, which can significantly affect the wearing of the orthosis.
- Comfort. If you feel discomfort while wearing it, it means that not all parts are properly protected or there are manufacturing defects. This is often the case when you order from an online shop. Such use is not beneficial.
- No allergies, no swelling, no circulatory disorders, no abrasions, no wounds when wearing the orthosis - these are the most important indicators that the orthosis is suitable and will be of use to you in the future.
- Size. It must not be too big or too tight and must not slip off the knee.
use and care
Once you've chosen the right kneecap, you need to use and care for it properly. All orthopedists explain how to put on and take off the orthosis, when and how to adjust it and whether it needs to be adjusted. The recommended shin circumference is also given in the manufacturer's instructions, which are included with every knee orthosis. Care must be gentle and systematic. The orthosis must not be treated with chemicals. Carefully wipe off dirt and wash only after removing the metal inserts. Proper selection of knee pads and correct use of orthotics are critical to knee joint recovery.
Video
Video – knee splint
Wearing the orthosis every day will make it dirty. Therefore, the plastic parts should be cleaned regularly. If necessary, the product can be washed. It can be hand washed at a water temperature no higher than 20 degrees Celsius. The braces must not be washed in the washing machine. It must not be bleached, dry cleaned or ironed. To dry the bracelet, lay it flat and unfold it.
When choosing the detergent, it should be noted that the bracelet is usually made of the following materials:Types and models of bracelets
Every body orthosis is a complex multifunctional device. The price of the product depends on the manufacturer and quality characteristics. Regardless of the price, the orthosis must be safe, hypoallergenic, strong and light.
In most cases, the orthosis is semi-rigid or rigid.. Patients of all ages can benefit from this category of orthotics. The orthoses are divided into knee orthoses for adults and for children.
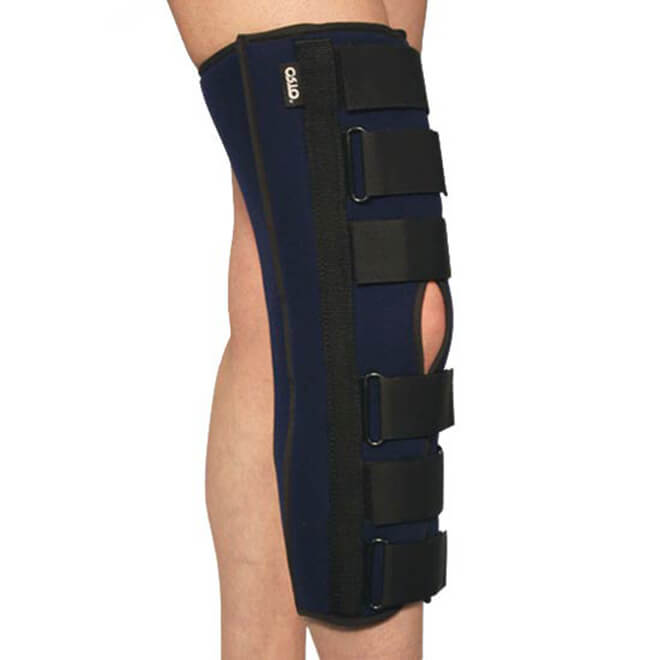
Rigid models serve to stabilize, relieve pressure and immobilize the joint. They are recommended after serious injuries and operations on the joint.
The SKN 401, which provides rigid stabilization, is commonly used. This knee orthosis has six straps arranged in parallel and a contact closure. This construction ensures that the SKN 401 is securely fixed to the aching or injured leg.
A tendon pad and an opening above the joint ensure a high level of comfort without restricting flexion. The SKN 401 is also equipped with exchangeable inserts. The insoles are on the back as well as on the outside.
The use of this orthosis ensures rigid fixation and prevents dangerous movements during rehabilitation or treatment. In contrast to a plaster bandage, the orthosis has several advantages: quick application, easy application and maintenance, and easy access to the knee.
This model is recommended for acute inflammatory and degenerative conditions of the knee. It can be used when a valgus or varus deviation of the lower limbs is diagnosed, for preventive purposes. It is indispensable as a transport splint for patients who require limb immobilization.
- What is an orthosis?.
- What is an orthosis?.
- What are knee braces?.
- What is a knee brace?.
- Overnight orthosis for plantar fasciitis heel spurs.
- Knee brace for children.
- How to wear a knee brace for osteoarthritis.
- knee brace.
